ASTM D5230-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Carbon Black-Automated Individual Pellet Hardness
Standard Test Method for Carbon Black-Automated Individual Pellet Hardness
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Individual pellet hardness is related to several carbon black characteristics. Among these are mass strength and attrition. The subsequent level of dispersion obtained in some mixed compounds containing the carbon black may be affected by pellet hardness. Acceptable pellet hardness must be agreed to by the user and the producer.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring individual pellet hardness of carbon black by the automated pellet hardness tester.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Frequently Asked Questions
ASTM D5230-21 is a standard published by ASTM International. Its full title is "Standard Test Method for Carbon Black-Automated Individual Pellet Hardness". This standard covers: SIGNIFICANCE AND USE 4.1 Individual pellet hardness is related to several carbon black characteristics. Among these are mass strength and attrition. The subsequent level of dispersion obtained in some mixed compounds containing the carbon black may be affected by pellet hardness. Acceptable pellet hardness must be agreed to by the user and the producer. SCOPE 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring individual pellet hardness of carbon black by the automated pellet hardness tester. 1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only. 1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE 4.1 Individual pellet hardness is related to several carbon black characteristics. Among these are mass strength and attrition. The subsequent level of dispersion obtained in some mixed compounds containing the carbon black may be affected by pellet hardness. Acceptable pellet hardness must be agreed to by the user and the producer. SCOPE 1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring individual pellet hardness of carbon black by the automated pellet hardness tester. 1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only. 1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ASTM D5230-21 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 83.040.20 - Rubber compounding ingredients. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ASTM D5230-21 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ASTM D3313-12e1, ASTM D1900-06(2015), ASTM D1799-03a(2014), ASTM E11-13, ASTM D1511-12, ASTM D1900-06(2011), ASTM D1511-10, ASTM E11-09e1, ASTM D1799-03a(2008), ASTM D1900-06, ASTM D1511-00(2006), ASTM E11-04, ASTM D1799-03a, ASTM D1799-03, ASTM D1799-02. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
You can purchase ASTM D5230-21 directly from iTeh Standards. The document is available in PDF format and is delivered instantly after payment. Add the standard to your cart and complete the secure checkout process. iTeh Standards is an authorized distributor of ASTM standards.
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5230 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Black—Automated Individual Pellet Hardness
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5230; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A sample of carbon black is passed through two sieves
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring
to isolate a fraction of uniform size.An appropriate amount of
individual pellet hardness of carbon black by the automated
pellets from this portion is selected and placed into the tester.
pellet hardness tester.
The individual pellets are pressed against a platen with a load
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
cell for measuring force. As pressure is applied the pellet will
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
either break with a rapid force reduction or the pellet will
simply compress. The individual pellet hardness is the maxi-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mum force prior to a force reduction of at least 3 cN or the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
maximum force required to compress the pellet to 90 %,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
whichever comes first.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Significance and Use
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.1 Individual pellet hardness is related to several carbon
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
black characteristics. Among these are mass strength and
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
attrition. The subsequent level of dispersion obtained in some
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mixedcompoundscontainingthecarbonblackmaybeaffected
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
by pellet hardness. Acceptable pellet hardness must be agreed
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
to by the user and the producer.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents
2 5.1 Automated Pellet Hardness Tester, capable of achieving
2.1 ASTM Standards:
an absolute measuring accuracy of 62 cN (2 gf) for the force
D1511Test Method for Carbon Black—Pellet Size Distri-
measurement and 60.1 mm for the diameter measurement and
bution
a relative accuracy of 60.5 cN (0.5 gf) for the force measure-
D1799 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Packaged
ment and 0.02 mm for the diameter measurement and consist-
Shipments
ing of the following major components and characteristics.
D1900Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Bulk Ship-
5.1.1 A means for automatic loading of a pellet on the
ments
transport platen for transporting the pellet so as to contact the
D4483Practice for Evaluating Precision for Test Method
second platen with a minimum force. Typically one platen
StandardsintheRubberandCarbonBlackManufacturing
containsaforcemeasuringdevice.Therequiredforcetodetect
Industries
the contact shall not exceed 2 cN (2 gf),
E11Specification forWovenWireTest Sieve Cloth andTest
5.1.2 A means for applying the force while moving at a
Sieves
constant speed,
5.1.3 Ameans for transporting the pellet so to minimize its
movement during the application of force.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D24 on Carbon
5.1.4 Ameans for measuring the diameter of the individual
Black and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.51 on Carbon Black
pellet under test as measured along the axis of the application
Pellet Properties.
of force.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2021. Originally
5.1.5 A control device for directing the instrument through
approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 2019 as D5230–19. DOI:
10.1520/D5230-21.
the test cycle that includes crushing the pellet under controlled
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
conditions, measuring and storing the results of the initial
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
diameter and crush force determinations, cleaning the frag-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ments from the platen surfaces, and starting the next cycle.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5230 − 21
5.1.6 An algorithm for determining the individual test end bottom sieve. The sample size required for testing depends on
point (determination) as the maximum observed force prior to the apparatus that is used.
the first occurrence of either a specified reduction in diameter
8.3 Conduct the test following the instructions in the equip-
or a specified reduction in force from the maximum force
ment operation manual.
observed,
5.1.7 A program for calculating for a specified number of 9. Report
pellets the data as requested in Section 9, and
9.1 Report the following information:
5.1.8 Ameansforidentifying,viewing,printing,andstoring
9.1.1 Proper identification of the sample,
the data in an ASCII file.
9.1.2 Average value in centinewtons (gram force) rounded
5.2 Mechanical Sieve Shaker, conforming to Test Method to the nearest millinewton (nearest 0.1 g force),
D1511.
9.1.3 Maximum value in centinewtons (gram force)
rounded to a whole number
5.3 Sieves, U.S. Standard No. 12 (1700 µm) and No. 14
9.1.4 Number of pellets tested, and
(1400 µm) conforming to Specification E11 shall be used to
9.1.5 Size of sieves used to prepare the sample.
test grades of black that can be segregated in a −12/+14
fraction.Forgradesofblackthataretoosmalltoberetainedon
10. Precision and Bias
a No. 14 sieve, i.e., acetylene and thermal blacks, it is
10.1 These precision statements have been prepared in
acceptable to test with U.S. Standard No. 16 (1180 µm) and
accordance with Practice D4483. Refer to this practice for
No. 18 (1000 µm) sieves.
terminology and other statistical details.
5.4 Bottom-Receiver Pan and Top-Sieve Cover.
10.2 The precision results in this precision and bias section
give an estimate of the precision of this test method with the
6. Sampling
materials used in the particular interlaboratory program de-
6.1 Take samples in accordance with Practice D1799 or
scribedbelow.Theprecisionparametersshouldnotbeusedfor
Practice D1900.
acceptance or rejection testing of any group of materials
without documentation that they are applicable to those par-
7. Calibration
ticular materials and the specific testing protocols of the test
7.1 Calibrateforceanddiametermeasurementfollowingthe
method.
manufacturer’s instructions.
10.3 A type 1 inter-laboratory precision program was con-
7.2 Instrument Parameters:
ducted as detailed in Tables 1-4. Both repeatability and
7.2.1 Crush diameter, 0.90. A reduction of the pellet diam-
reproducibility represent short term (daily) testing conditions.
eter to 90% of the original value is one of two end point
The testing was performed using two operators in each
criteria.
laboratory performing the test once on each of two days (total
7.2.2 Force drop. A decrease of 3 cN (3gf) from the
of four tests). The pellet hardness average test result is the
maximum force observed is one of two end point criteria.
average of all the individual pellet hardness values obtained in
7.2.3 Rate of piston movement during crush, 0.125 mm/s.
a single determination. The pellet hardness maximum test
7.2.4 Number of pellets tested; normal applications, 20
result is the highest individual value of all the individual pellet
pellets,criticalapplications,50pellets.Criticalapplicationsare
hardness values obtained in a single determination. Other
determined by agreement between customer and supplier.
techniquesforobtainingamaximumvalue,suchastheaverage
7.2.5 The following ranges of acceptable pellet diameters
of x number of the highest individual values or the average of
were established to minimize the number of pellets rejected
the highest individual values that represent y percent of the
due to instrument variation and non-spherical pellets.
total number of pellets tested are not included in these
7.2.5.1 For a −12/+14 fraction, 1.31–1.93 mm.
precision calculations. Acceptable difference values were not
7.2.5.2 For a −16/+18 fraction, 0.80–1.44 mm.
measured. The between operator component of variation is
included in the calculated values for r, (r), R, and (R).
8. Procedure
10.4 The results of the precision calculations for this test
8.1 Prepare a sample of carbon black as follows:
method are given in Tables 1-4.
8.1.1 Stack the No. 12 above the No. 14 sieve, or to test
10.5 Repeatability—The pooled relative repeatability, (r),
smaller pellet blacks, stack the No. 16 above the No. 18 sieve
for the pellet hardness average result of this test when testing
with the receiver pan on the bottom.
20 pellets has been established as 18.6 % (see Table 1). The
NOTE 1—It is permissible to use multiples of sieve stacks to screen
pooled relative repeatability, (r), for the pellet hardness aver-
several samples simultaneously.
age result of this test when testing 50 pellets has been
8.1.2 Transfer the sample to the coarser top screen, install
established as 15.0 % (see Table 2). The pooled relative
the cover and transfer the assembly to the mechanical shaker.
repeatability,(r),forthepellethardnessmaximumresultofthis
8.1.3 Allow the sieve assembly to shake for 60 s with the
testwhentesting20pelletshasbeenestablishedas27.6%(see
hammer operating.
Table 3). The pooled relative repeatability, (r), for the pellet
8.2 Remove the assembly from the shaking device. Select a hardness maximum result of this test when testing 50 pellets
sufficiently large sample from the pellets retained on the hasbeenestablishedas19.8%(seeTable4).Thebestestimate
--------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5230 − 19 D5230 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Black—Automated Individual Pellet Hardness
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5230; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for measuring individual pellet hardness of carbon black by the automated pellet hardness
tester.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1511 Test Method for Carbon Black—Pellet Size Distribution
D1799 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Packaged Shipments
D1900 Practice for Carbon Black—Sampling Bulk Shipments
D4483 Practice for Evaluating Precision for Test Method Standards in the Rubber and Carbon Black Manufacturing Industries
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test Sieves
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A sample of carbon black is passed through two sieves to isolate a fraction of uniform size. An appropriate amount of pellets
from this portion is selected and placed into the tester. The individual pellets are pressed against a platen with a load cell for
measuring force. As pressure is applied the pellet will either break with a rapid force reduction or the pellet will simply compress.
The individual pellet hardness is the maximum force prior to a force reduction of at least 3 cN or the maximum force required to
compress the pellet to 90 %, whichever comes first.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Individual pellet hardness is related to several carbon black characteristics. Among these are mass strength and attrition. The
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D24 on Carbon Black and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D24.51 on Carbon Black Pellet
Properties.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2019Nov. 1, 2021. Published December 2019December 2021. Originally approved in 1992. Last previous edition approved in 20142019
ε1
as D5230 – 14D5230 – 19. . DOI: 10.1520/D5230-19.10.1520/D5230-21.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5230 − 21
subsequent level of dispersion obtained in some mixed compounds containing the carbon black may be affected by pellet hardness.
Acceptable pellet hardness must be agreed to by the user and the producer.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Automated Pellet Hardness Tester, capable of achieving an absolute measuring accuracy of 62 cN (2 gf) for the force
measurement and 60.1 mm for the diameter measurement and a relative accuracy of 60.5 cN (0.5 gf) for the force measurement
and 0.02 mm for the diameter measurement and consisting of the following major components and characteristics.
5.1.1 A means for automatic loading of a pellet on the transport platen for transporting the pellet so as to contact the second platen
with a minimum force. Typically one platen contains a force measuring device. The required force to detect the contact shall not
exceed 2 cN (2 gf),
5.1.2 A means for applying the force while moving at a constant speed,
5.1.3 A means for transporting the pellet so to minimize its movement during the application of force.
5.1.4 A means for measuring the diameter of the individual pellet under test as measured along the axis of the application of force.
5.1.5 A control device for directing the instrument through the test cycle that includes crushing the pellet under controlled
conditions, measuring and storing the results of the initial diameter and crush force determinations, cleaning the fragments from
the platen surfaces, and starting the next cycle.
5.1.6 An algorithm for determining the individual test end point (determination) as the maximum observed force prior to the first
occurrence of either a specified reduction in diameter or a specified reduction in force from the maximum force observed,
5.1.7 A program for calculating for a specified number of pellets the data as requested in Section 9, and
5.1.8 A means for identifying, viewing, printing, and storing the data in an ASCII file.
5.2 Mechanical Sieve Shaker, conforming to Test Method D1511.
5.3 Sieves, U.S. Standard No. 12 (1700 μm) and No. 14 (1400 μm) conforming to Specification E11 shall be used to test grades
of black that can be segregated in a −12/+14 fraction. For grades of black that are too small to be retained on a No. 14 sieve, i.e.,
acetylene and thermal blacks, it is acceptable to test with U.S. Standard No. 16 (1180 μm) and No. 18 (1000 μm) sieves.
5.4 Bottom-Receiver Pan and Top-Sieve Cover.
6. Sampling
6.1 Take samples in accordance with Practice D1799 or Practice D1900.
7. Calibration
7.1 Calibrate force and diameter measurement following the manufacturer’s instructions.
7.2 Instrument Parameters:
7.2.1 Crush diameter, 0.90. A reduction of the pellet diameter to 90 % of the original value is one of two end point criteria.
7.2.2 Force drop. A decrease of 3 cN (3gf) from the maximum force observed is one of two end point criteria.
7.2.3 Rate of piston movement during crush, 0.125 mm/s.
7.2.4 Number of pellets tested; normal applications, 20 pellets, critical applications, 50 pellets. Critical applications are determined
by agreement between customer and supplier.
D5230 − 21
7.2.5 The following ranges of acceptable pellet diameters were established to minimize the number of pellets rejected due to
instrument variation and non-spherical pellets.
7.2.5.1 For a −12/+14 fraction, 1.31–1.93 mm.
7.2.5.2 For a −16/+18 fraction, 0.80–1.44 mm.
8. Procedure
8.1 Prepare a sample of carbon black as follows:
8.1.1 Stack the No. 12 above the No. 14 sieve, or to test smaller pellet blacks, stack the No. 16 above the No. 18 sieve with the
receiver pan on the bottom.
NOTE 1—It is permissible to use multiples of sieve stacks to screen several samples simultaneously.
8.1.2 Transfer the sample to the coarser top screen, install the cover and transfer the assembly to the mechanical shaker.
8.1.3 Allow the sieve assembly to shake for 60 s with the hammer operating.
8.2 Remove the assembly from the shaking device. Select a sufficiently large sample from the pellets retained on the bottom sieve.
The sample size required for testing depends on the apparatus that is used.
8.3 Conduct the test following the instructions in the equipment operation manual.
9. Report
9.1 Report the following information:
9.1.1 Proper identification of the sample,
9.1.2 Average value in centinewtons (gram force) rounded to the nearest millinewton (nearest 0.1 g force),
9.1.3 Maximum value in centinewtons (gram force) rounded to a whole number
9.1.4 Number of pellets tested, and
9.1.5 Size of sieves used to prepare the sample.
10. Precision and Bias
10.1 These precision statements have been prepared in accordance with Practice D4483. Refer to this practice for terminology and
other statistical details.
10.2 The precision results in this precision and bias section give an estimate of the precision of this test method with the materials
used in the particular interlaboratory program described below. The precision parameters should not be used for acceptance or
rejection testing of any group of materials without documentation that they are applicable to those particular materials and the
specific testing protocols of the test method.
10.3 A type 1 inter-laboratory precision program was conducted as detailed in Tables 1-4. Both repeatability and reproducibility
represent short term (daily) testing conditions. The testing was performed using two operators in each laboratory performing the
test once on each of two days (total of four tests). The pellet hardness average test result is the average of all the individual pellet
hardness values obtained in a single determination. The pellet hardness maximum test result is the highest individual value of all
the individual pellet hardness values obtained in a single determination. Other techniques for obtaining a maximum value, such
as the average of x number of the highest individual values or the average of the highest individual values that represent y percent
D5230 − 21
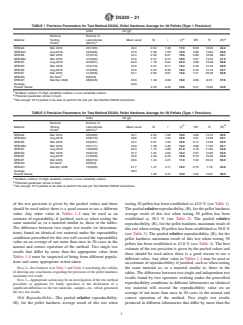
TABLE 1 Precision Parameters for Test Method D5230, Pellet Hardness Average for 20 Pellets, (Type 1 Precision)
Units cN (gf)
Nominal Number of
B
Material Testing Laboratories Mean Level Sr r (r) SR R (R)
A
Period (M/H/L)
SRB-8F Mar 2010 30(1/2/0) 19.3 1.67 4.73 24.5 3.98 11.25 58.2
SRB-8C Sep 2010 30(3/2/0) 23.9 1.55 4.38 18.4 2.10 5.95 24.9
ITRB2 Mar 2011 22(2/2/0) 24.5 2.06 5.83 23.8 2.90 8.22 33.6
N234 (Birla) Mar 2012 29(3/1/0) 25.4 2.09 5.92 23.3 2.54 7.17 28.2
SRB-8E Sep 2008 16(1/0/0) 26.4 1.80 5.11 19.3 2.81 7.96 30.1
N650 (Orion) Sep 2012 21(1/1/0) 30.1 2.08 5.88 19.5 3.13 8.87 29.5
SRB-8D Mar 2009 23(1/3/0) 35.3 2.39 6.77 19.2 7.02 19.88 56.4
SRB-8B Jun 2009 28(1/2/0) 36.2 2.35 6.66 18.4 3.98 11.27 31.2
SRB-8A Sep 2011 27(2/2/0) 36.9 1.97 5.57 15.1 4.19 11.86 32.2
SRB-8A Mar 2008 19(1/1/0) 38.4 2.35 6.65 17.3 5.21 14.75 38.4
N550 (Cabot) Sep 2013 34(2/3/0) 41.1 2.18 6.16 15.0 5.69 16.10 39.1
SRB-8A2 Mar 2013 36(3/3/0) 42.6 2.38 6.73 15.8 4.77 13.51 31.7
Average 31.7
Pooled Values 2.09 5.92 18.7 4.26 12.06 38.1
TABLE 1 Precision Parameters for Test Method D5230, Pellet Hardness Average for 20 Pellets (Type 1 Precision)
Units cN (gf)
Nominal Number of
B B
Material Testing Laboratories Mean Level Sr r (r) SR R (R)
A
Period (M/H/L)
SRB-9A Mar 2013 45(1/2/0) 43.4 2.64 7.48 17.3 6.50 18.39 42.4
SRB-9A2 Aug 2018 43(0/0/0) 37.9 2.58 7.29 19.3 4.89 13.84 36.6
SRB-9B Mar 2016 51(0/1/0) 42.4 2.93 8.31 19.6 5.86 16.58 39.1
SRB-9B2 Mar 2019 47(0/0/0) 42.0 2.37 6.72 16.0 4.67 13.22 31.5
SRB-9C Aug 2019 37(0/0/1) 22.6 1.78 5.04 22.3 4.69 13.28 58.8
SRB-9D Mar 2018 47(0/1/0) 34.6 2.37 6.71 19.4 4.40 12.45 36.0
SRB-9E Aug 2016 47(0/0/0) 34.6 2.23 6.30 18.2 5.34 15.10 43.7
SRB-9F Mar 2015 41(0/0/0) 34.1 2.00 5.67 16.6 7.21 20.40 59.8
C
SRB-9G No Data 0(0/0/0)
SRB-9H Mar/Apr 2020 48(0/2/0) 23.0 1.30 3.69 16.0 3.06 8.67 37.6
Average 34.9
Pooled Values 2.29 6.49 18.6 5.31 15.02 43.0
A
M=Mean M=Mean outliers; H=High variability outliers; L=Low variability outliers. For a 1-sided k test there are no low outliers.
B
Preferred Preferred parameter shown in bold.
C
Not enough 12/14 pellets to be able to perform the test per Test Method D5230 instructions.
of the total number of pellets tested are not included in these precision calculations. Acceptable difference values were not
measured. The between operator component of variation is included in the calculated values for r, (r), R, and (R).
10.4 The results of the precision calculations for this test method are given in Tables 1-4. The materials are arranged in ascending
“mean level” order.
10.5 Repeatability—The pooled relative repeatability, (r), for the pellet hardness average result of this test when testing 20 pellets
has been established as 18.718.6 % (see Table 1). The pooled relative repeatability, (r), for the pellet hardness average result of
this test when testing 50 pellets has been established as 16.415.0 % (see Table 2). The pooled relative repeatability, (r), for the
pellet hardness maximum result of this test when testing 20 pellets has been established as 27.127.6 % (see Table 3). The pooled
relative repeatability, (r), for the pellet
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...