ASTM D3527-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Life Performance of Automotive Wheel Bearing Grease
Standard Test Method for Life Performance of Automotive Wheel Bearing Grease
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method differentiates among wheel bearing greases having distinctly different high-temperature characteristics. It is not the equivalent of longtime service tests, nor is it intended to distinguish between the products having similar high-temperature performance properties.
This test method has proven to be helpful in screening greases with respect to life performance for automotive wheel bearing applications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for evaluating the high-temperature life performance of wheel bearing greases when tested under prescribed conditions.
Note 1—Changes to this test method in the 1985 revision increased test severity. Results will not be comparable with data from earlier procedures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—Apparatus dimensions in inches are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 8.1-8.4.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3527 − 11
StandardTest Method for
1
Life Performance of Automotive Wheel Bearing Grease
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3527; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.1.3.1 Discussion—The solid thickener can be fibers (such
as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for
non-soap thickeners) which are insoluble or, at the most, only
evaluating the high-temperature life performance of wheel
very slightly soluble in the liquid lubricant. The general
bearing greases when tested under prescribed conditions.
requirements are that the solid particles be extremely small,
NOTE1—Changestothistestmethodinthe1985revisionincreasedtest
uniformlydispersed,andcapableofformingarelativelystable,
severity.Resultswillnotbecomparablewithdatafromearlierprocedures.
gel-like structure with the liquid lubricant.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.2.1 automotive wheel bearing grease, n—a lubricating
standard.
grease specifically formulated to lubricate automotive wheel
1.2.1 Exception—Apparatus dimensions in inches are to be
bearings at relatively high grease temperatures and bearing
regarded as the standard.
speeds.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2.2 grease life, n— of wheel bearing grease, amount of
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
time operated under prescribed conditions of load, speed, and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
temperature until preset torque limit is exceeded.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.2.1 Discussion—The off-time, which is part of the 20 h
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
and 4 h off-cycle, is not recorded and is not included as part of
warning statements, see 8.1 – 8.4.
grease life.
2. Referenced Documents
4. Summary of Test Method
2.1 AFBMA Standard:
2 4.1 The test grease is distributed in the bearings of a
AFBMA Standard 19, 1974 (ANSI B. 3.19-1975)
modified, automobile front wheel hub-spindle-bearings assem-
3. Terminology bly. While the bearings are thrust-loaded to 111 N, the hub is
rotated at 1000 rpm and the spindle temperature maintained at
3.1 Definitions:
160°C for 20 h,4hoff operating cycle. The test is terminated
3.1.1 lubricant, n—any material interposed between two
when grease deterioration causes the drive motor torque to
surfaces that reduces the friction or wear between them.
exceed a calculated motor cut off value. Grease life is ex-
3.1.2 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of
pressed as the accumulated on-cycle hours.
a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—The dispersion of the thickener forms a
5. Significance and Use
two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by
5.1 This test method differentiates among wheel bearing
surface tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are
greases having distinctly different high-temperature character-
commonly included to impart special properties.
istics. It is not the equivalent of longtime service tests, nor is it
3.1.3 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance com-
intended to distinguish between the products having similar
posed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid lubricant
high-temperature performance properties.
to form the product’s structure.
5.2 This test method has proven to be helpful in screening
greases with respect to life performance for automotive wheel
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
bearing applications.
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.G0.05 on Functional Tests - Temperature.
6. Apparatus
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2011. Published December 2011. Originally
ε1
approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D3527–07 . DOI:
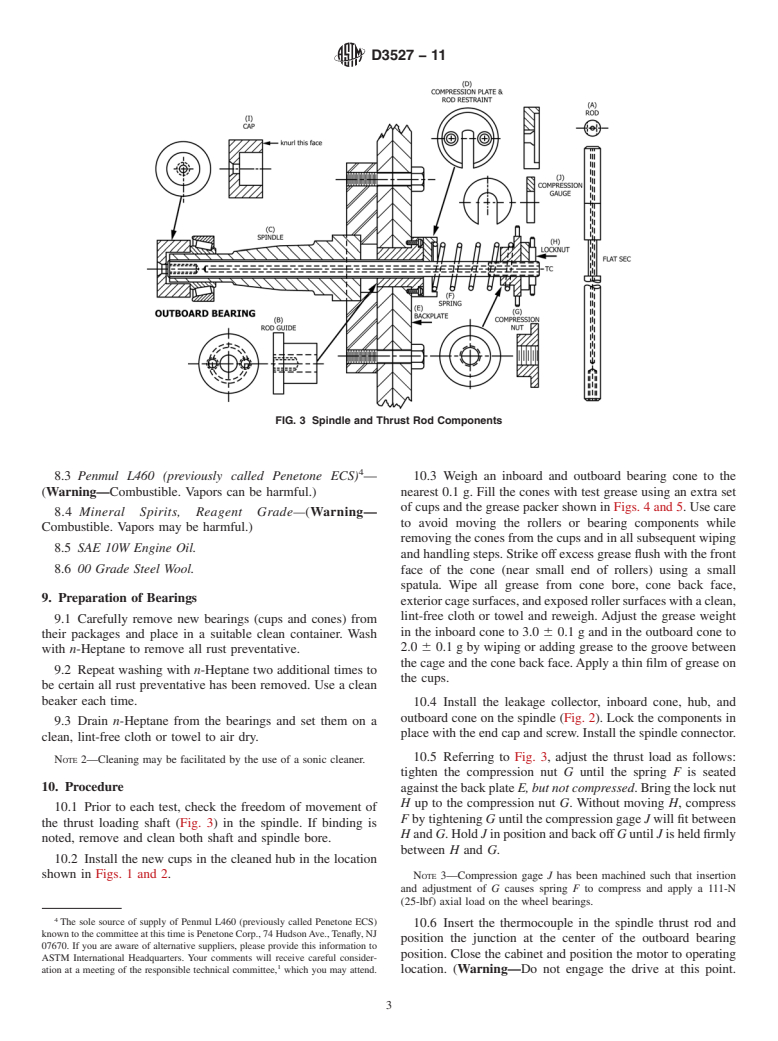
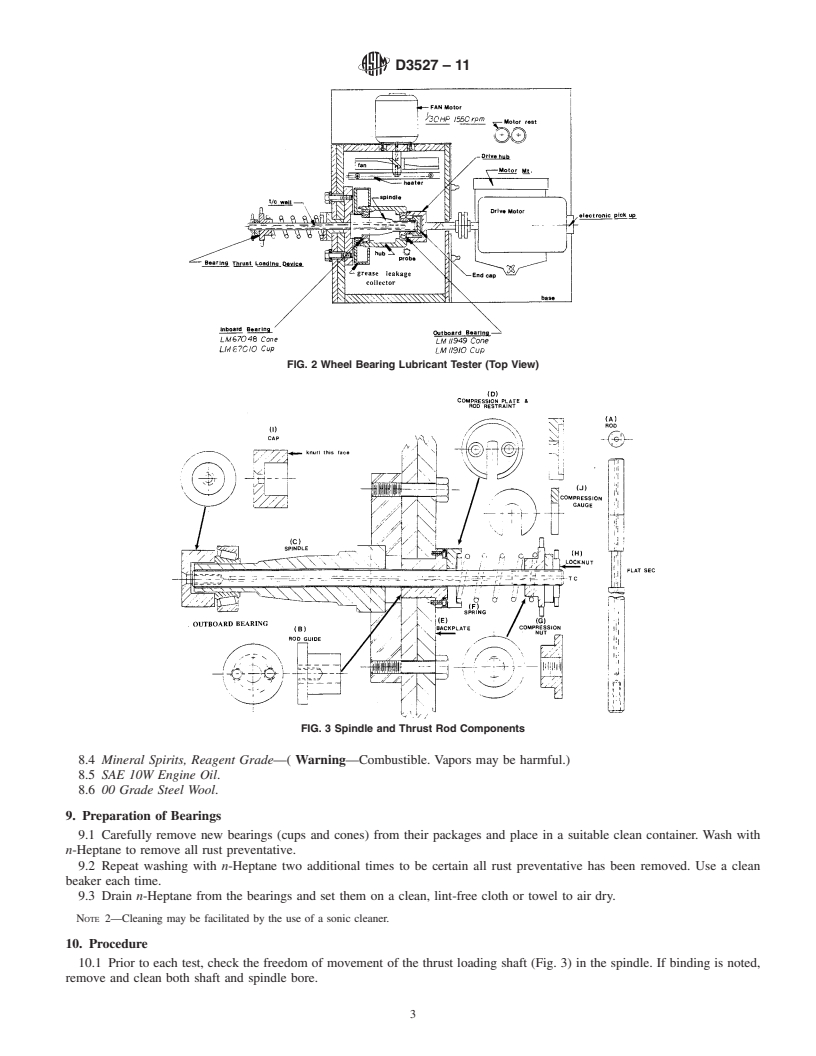
6.1 Test Assembly (see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2).
10.1520/D3527-11.
2 6.1.1 Custom-made Wheel Hub-Spindle-Bearing Assembly
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org. (Fig. 3).
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3527 − 11
NOTE
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation:D3527–07 Designation:D3527–11
Standard Test Method for
1
Life Performance of Automotive Wheel Bearing Grease
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3527; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Added Note 5 editorially in January 2009.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure for evaluating the high-temperature life performance of wheel bearing
greases when tested under prescribed conditions.
NOTE 1—Changes to this test method in the 1985 revision increased test severity. Results will not be comparable with data from earlier procedures.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—Apparatus dimensions in inches are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 8.1-8.4.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 AFBMA Standard:
2
AFBMA Standard 19, 1974 (ANSI B. 3.19-1975)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 lubricant, n—any material interposed between two surfaces that reduces the friction or wear between them.
3.1.2 lubricating grease, n—a semi-fluid to solid product of a dispersion of a thickener in a liquid lubricant.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—The dispersion of the thickener forms a two-phase system and immobilizes the liquid lubricant by surface
tension and other physical forces. Other ingredients are commonly included to impart special properties.
3.1.3 thickener, n—in lubricating grease, a substance composed of finely-divided particles dispersed in a liquid lubricant to
form the product’s structure.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—The solid thickener can be fibers (such as various metallic soaps) or plates or spheres (such as certain
non-soapthickeners)whichareinsolubleor,atthemost,onlyveryslightlysolubleintheliquidlubricant.Thegeneralrequirements
are that the solid particles be extremely small, uniformly dispersed, and capable of forming a relatively stable, gel-like structure
with the liquid lubricant.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 automotive wheel bearing grease, n—a lubricating grease specifically formulated to lubricate automotive wheel bearings
at relatively high grease temperatures and bearing speeds.
3.2.2 grease life, n— of wheel bearing grease, amount of time operated under prescribed conditions of load, speed, and
temperature until preset torque limit is exceeded.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—The off-time,whichispartofthe20hand4hoff-cycle,isnotrecordedandisnotincludedaspartofgrease
life.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The test grease is distributed in the bearings of a modified, automobile front wheel hub-spindle-bearings assembly. While
the bearings are thrust-loaded to 111 N, the hub is rotated at 1000 rpm and the spindle temperature maintained at 160°C for 20
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.G0.05
on Functional Tests - Temperature.
Current edition approved July 15, 2007. Published August 2007. Originally approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D3527–02. DOI:
10.1520/D3527-07E01.
´1
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2011. Published December 2011. Originally approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D3527–07 . DOI:
10.1520/D3527-11.
2
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3527–11
h,4hoff operating cycle. The test is terminated when grease deterioration causes the drive motor torque to exceed a calculated
motor cut off value. Grease life is expressed as the accumulated on-cycle hours.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method differentiates among wheel bearing greases having disti
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.