ISO 6704:1982
(Main)Automatic steam traps — Classification
Automatic steam traps — Classification
Establishes a simple classification of the main types according to the mode of actuation of their obturation device and disregarding their details of conception and construction. Three categories of steam traps can be distinguished: mechanical traps, actuated by the level of condensate; thermostatic traps, actuated by the temperature of the condensate; thermodynamic traps, actuated by fluid dynamics.
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d'eau — Classification
La présente Norme internationale établit une classification simple des principaux types de purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d'eau, en fonction du mode de commande de leur dispositif d'obturation, quels que soient leurs détails de conception et de construction.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 31-Dec-1981
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 153 - Valves
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 153 - Valves
- Current Stage
- 9092 - International Standard to be revised
- Start Date
- 28-Feb-2025
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 6704:1982 is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that defines a clear classification system for automatic steam traps. These mechanical devices are critical in steam systems for discharging condensate and non-condensable gases while minimizing steam loss. The standard categorizes steam traps based solely on the mode of actuation of their obturation (valve closing) device, regardless of design or construction details. This classification enhances equipment selection, maintenance, and communication across industries using steam technology.
Key Topics
- Purpose: Establishes a straightforward classification scheme for automatic steam traps.
- Scope: Focuses on actuation modes of obturation devices, excluding detailed design aspects.
- Classification Categories:
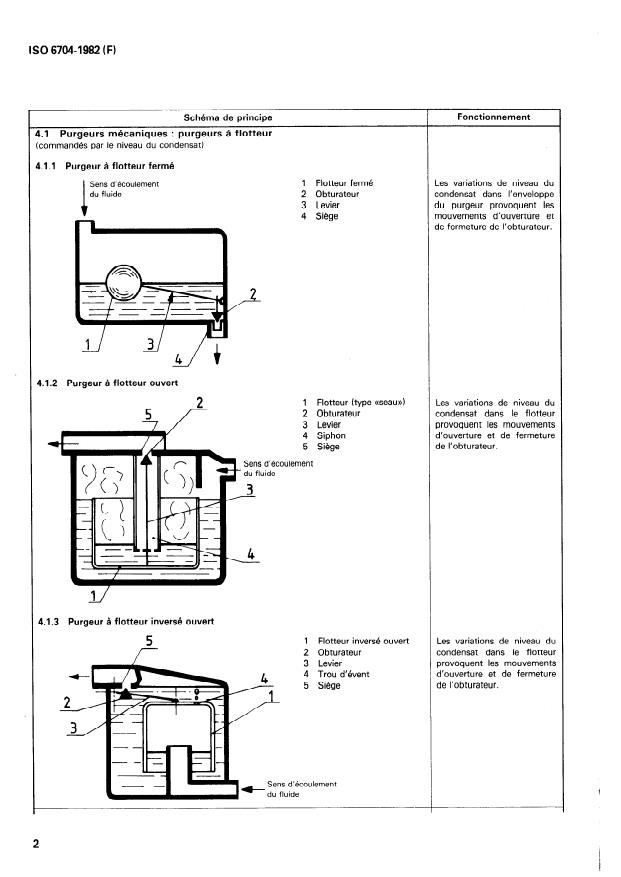
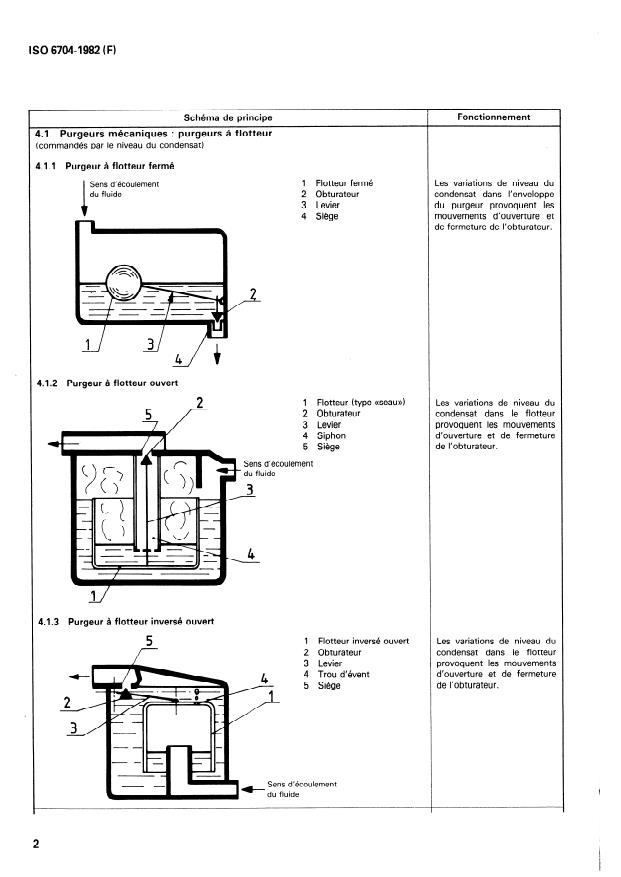
- Mechanical Traps: Operate by the level of condensate inside the trap using floats or similar mechanisms.
- Thermostatic Traps: Function based on temperature differences of the condensate, using elements like bimetallic strips or volatile liquids.
- Thermodynamic Traps: Actuated by fluid dynamics, including pressure variations causing valve movement.
- Examples of Trap Types:
- Mechanical: Closed float, open bucket float, inverted float traps.
- Thermostatic: Vapor pressure, bimetallic, liquid or solid expansion traps.
- Thermodynamic: Obturator traps, impulse (piston valve) traps, labyrinth orifice traps.
Applications
ISO 6704:1982 is essential for industries that rely on steam for heating, power generation, and processing tasks. The standard aids engineers, maintenance professionals, and equipment manufacturers in:
- Selecting appropriate steam traps consistent with operating conditions and steam system requirements.
- Improving energy efficiency by reducing steam loss through correct trap identification and classification.
- Facilitating maintenance and troubleshooting by understanding the fundamental working principle of the trap in use.
- Enhancing communication across international projects with standardized terminology and trap classification.
- Supporting steam system design optimization by categorizing traps according to functional actuation modes.
Common usage sectors include:
- Power plants
- Chemical and petrochemical industries
- Food and beverage processing
- HVAC systems
- Textile manufacturing
Related Standards
ISO 6704:1982 complements several related standards governing steam traps and valves to ensure comprehensive steam system management:
- ISO 6552 – Automatic steam traps: Terminology
- ISO 6553 – Automatic steam traps: Marking requirements
- ISO 6554 – Flanged automatic steam traps: Face-to-face dimensions
Together, these standards provide a full framework for the identification, classification, and installation of automatic steam traps to achieve reliable, safe, and energy-efficient steam operations.
Keywords: ISO 6704, automatic steam traps, steam trap classification, mechanical steam traps, thermostatic steam traps, thermodynamic steam traps, condensate removal, steam system efficiency, industrial valves, steam trap standards, steam equipment selection
Buy Documents
ISO 6704:1982 - Automatic steam traps -- Classification
ISO 6704:1982 - Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d'eau -- Classification
ISO 6704:1982 - Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d'eau -- Classification
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Institut za varilstvo d.o.o. (Welding Institute)
Slovenia's leading welding institute since 1952. ISO 3834, EN 1090, pressure equipment certification, NDT personnel, welder qualification. Only IIW Au
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 6704:1982 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Automatic steam traps — Classification". This standard covers: Establishes a simple classification of the main types according to the mode of actuation of their obturation device and disregarding their details of conception and construction. Three categories of steam traps can be distinguished: mechanical traps, actuated by the level of condensate; thermostatic traps, actuated by the temperature of the condensate; thermodynamic traps, actuated by fluid dynamics.
Establishes a simple classification of the main types according to the mode of actuation of their obturation device and disregarding their details of conception and construction. Three categories of steam traps can be distinguished: mechanical traps, actuated by the level of condensate; thermostatic traps, actuated by the temperature of the condensate; thermodynamic traps, actuated by fluid dynamics.
ISO 6704:1982 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 23.060.01 - Valves in general. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 6704:1982 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.ME~KAYHAPO~HAR OWAHMSAUMR fl0 CTAWW ’T~3Al&IWORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Automatic steam traps - Classification
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d ’eau - Classifica tion
First edition - 1982-01-15
Corrected and reprinted - 1983-01-15
UDC 621.186.6
Ref. No. ISO 67044982 (E)
w
-
Descriptors : industrial valves, traps, steam, classifications.
Price based on 4 pages
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national Standards institutes (ISO member bodies). The work of developing Inter-
national Standards is carried out through ISO technical committees. Every member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been set up has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the ISO Council.
International Standard ISO 6704 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 153,
Valves, and was circulated to the member bodies in February 1980.
lt has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries :
Australia Finland Poland
Austria France Romania
South Africa, Rep. of
Belgium Germany, F. R.
Brazil India Sweden
Canada Italy Switzerland
China Korea, Rep. of United Kingdom
Czechoslovakia Netherlands USA
Norway USSR
Denmark
No member body expressed disapproval of the document.
0 international Organkation for Standardkation, 1982
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 6704-1982 (E)
Automatic steam traps - Classification
enclosure whilst remaining tight to live steam or, if necessary,
1 Scope and field of application
allowing steam to flow at a predetermined rate.
The purpose of this International Standard is to establish a
simple classification of the main types of automatic steam traps
according to the mode of actuation of their obturation device
and disregarding their details of conception and construction.
4 Classification
2 References The types of traps defined hereunder are classified according to
their mode of actuation; other traps, combining these different
types (or of a new design) may be developed, but these traps
ISO 6552, Automatic steam traps - Terminology.
shall not be regarded as a characteristic type of automatic
steam traps in the sense of this International Standard.
ISO 6553, Automatic steam traps - Marking.
If one considers the mode of actuation of the obturation
ISO 6554, Flanged automatic steam traps - Face-to-face
device, three categories of automatic steam traps tan be
dimensions.
distinguished :
-
mechanical traps, actuated by the level of condensate
3 Definition
(4.1);
For this International Standard, the following definitio
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWlE~YHAPO~HAR OPrAHM3AUMR Il0 CTAHL1APTM3AUMM@ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Classification
Au toma tic s team traps - Classifïca tion
Première édition - 1982-01-15
Corrigée et réimprimée - 1983-01-l 5
CDU 621.186.6
Réf. no : ISO 67044982 (F)
Descripteurs : robinetterie industrielle, piége, vapeur d’eau sous pression, classification.
Prix basé sur 4 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 6704 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 153,
Robinetterie, et a été soumise aux comités membres en février 1980.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’ Corée, Rép. de Pologne
Allemagne, R. F. Danemark Roumanie
Royaume-Uni
Australie Finlande
Autriche France Suède
Belgique Inde Suisse
Brésil Italie Tchécoslovaquie
Canada Norvège URSS
Chine Pays- Bas USA
Aucun comité membre ne l’a désapprouvée.
Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1982
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 6704-1982 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Classification
sats se formant dans une enceinte contenant de la vapeur
1 Objet et domaine d’application
d’eau, tout en restant étanche en présence de vapeur vive ou
La présente Norme internationale établit une classification sim- en établissant si nécessaire un écoulement prédéterminé ou
ple des principaux types de purgeurs automatiques de vapeur réglé de vapeur.
d’eau, en fonction du mode de commande de leur dispositif
d’obturation, quels que soient leurs détails de conception et de
construction.
4 Classification
2 Références Les types de purgeurs définis ci-après sont classés suivant leur
mode d’ouverture; des purgeurs différents, combinant ces dif-
férents types (ou présentant une conception nouvelle) peuvent
ISO 6552, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Termino-
logie. être développés, mais ces purgeurs ne sauraient être considérés
comme un type caractéristique de purgeur automatique de
vapeur d’eau au sens de la présente Norme internationale.
ISO 6553, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Mar-
quage.
Si l’on prend en considération le mode de commande du dispo-
ISO 6554, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau à brides - sitif d’obturation, on peut distinguer trois grandes catégories de
purgeurs automatiques :
Dimensions face-à-face.
-
les purgeurs mécaniques, commandés par le niveau du
condensat (4.1. );
3 Définition
-
les purgeurs thermostatiques, commandés par la tem-
Dans le cadre de la présente Norme internationale, la définition
pérature du condensat (4.2);
suivante est applicable :
- les purgeurs thermodynamiques, commandés par la
purgeur automatique de v
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATIONWlE~YHAPO~HAR OPrAHM3AUMR Il0 CTAHL1APTM3AUMM@ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Classification
Au toma tic s team traps - Classifïca tion
Première édition - 1982-01-15
Corrigée et réimprimée - 1983-01-l 5
CDU 621.186.6
Réf. no : ISO 67044982 (F)
Descripteurs : robinetterie industrielle, piége, vapeur d’eau sous pression, classification.
Prix basé sur 4 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 6704 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 153,
Robinetterie, et a été soumise aux comités membres en février 1980.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’ Corée, Rép. de Pologne
Allemagne, R. F. Danemark Roumanie
Royaume-Uni
Australie Finlande
Autriche France Suède
Belgique Inde Suisse
Brésil Italie Tchécoslovaquie
Canada Norvège URSS
Chine Pays- Bas USA
Aucun comité membre ne l’a désapprouvée.
Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1982
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 6704-1982 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Classification
sats se formant dans une enceinte contenant de la vapeur
1 Objet et domaine d’application
d’eau, tout en restant étanche en présence de vapeur vive ou
La présente Norme internationale établit une classification sim- en établissant si nécessaire un écoulement prédéterminé ou
ple des principaux types de purgeurs automatiques de vapeur réglé de vapeur.
d’eau, en fonction du mode de commande de leur dispositif
d’obturation, quels que soient leurs détails de conception et de
construction.
4 Classification
2 Références Les types de purgeurs définis ci-après sont classés suivant leur
mode d’ouverture; des purgeurs différents, combinant ces dif-
férents types (ou présentant une conception nouvelle) peuvent
ISO 6552, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Termino-
logie. être développés, mais ces purgeurs ne sauraient être considérés
comme un type caractéristique de purgeur automatique de
vapeur d’eau au sens de la présente Norme internationale.
ISO 6553, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau - Mar-
quage.
Si l’on prend en considération le mode de commande du dispo-
ISO 6554, Purgeurs automatiques de vapeur d’eau à brides - sitif d’obturation, on peut distinguer trois grandes catégories de
purgeurs automatiques :
Dimensions face-à-face.
-
les purgeurs mécaniques, commandés par le niveau du
condensat (4.1. );
3 Définition
-
les purgeurs thermostatiques, commandés par la tem-
Dans le cadre de la présente Norme internationale, la définition
pérature du condensat (4.2);
suivante est applicable :
- les purgeurs thermodynamiques, commandés par la
purgeur automatique de v
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...