ISO 9269:1988
(Main)Implants for surgery — Metal bone plates — Holes and slots corresponding to screws with conical under-surface
Implants for surgery — Metal bone plates — Holes and slots corresponding to screws with conical under-surface
Specification of dimensions and tolerances of the holes and slots in bone plates used as surgical implants so as to facilitate correct fixing using screws complying with ISO 9268. This standard does not deal with the shape and dimensions of plates or with the spacing of the holes and slots. The different forms are illustrated. The informative annex A shows the interrelationship of International Standards dealing with bone screws, bone plates and relevant tools.
Implants chirurgicaux — Plaques métalliques pour os — Chambrages et alésages pour vis à embase conique
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions et les tolérances des chambrages et alésages des plaques pour os utilisées comme implants chirurgicaux afin de faciliter leur mise en place correcte à l'aide de vis conformes à l'ISO 9268. NOTES 1 La présente Norme internationale ne traite ni de la forme ni des dimensions des plaques ni de l'entraxe des chambrages et alésages. 2 Pour la relation entre les Normes internationales traitant des vis et des plaques pour os ainsi que des instruments correspondants, voir l'annexe A.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 07-Dec-1988
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 28-Aug-2023
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 9269:1988 is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that specifies the dimensions and tolerances of holes and slots in metal bone plates used as surgical implants. These holes and slots are designed to accommodate screws with a conical under-surface, ensuring secure fixation of bone plates during surgical procedures. The standard facilitates compatibility with screws complying with ISO 9268, which covers metal bone screws with conical under-surfaces.
This standard focuses specifically on the dimensional accuracy and countersink depths required for the holes and slots, promoting consistent and reliable implant performance. It does not cover the shape, overall dimensions, or hole spacing of bone plates but provides detailed information on the configuration related to screw fixation.
Key Topics
- Hole and Slot Dimensions: Specifies the precise measurements and tolerances for holes and slots in bone plates intended for screws with nominal diameters of 2.9 mm, 3.5 mm, 3.9 mm, 4.2 mm, 4.0 mm, and 4.5 mm as defined in ISO 9268.
- Countersink Depths: Defines the countersink depth for flat and curved bone plates to ensure the screw head fits correctly without protrusion, preserving biomechanical stability.
- Compatibility with Screws: Designed for use with ISO 9268-compliant screws, enabling proper conical seating between screw heads and bone plates to enhance fixation strength.
- Material Thickness Considerations: Details variation in countersink depths based on bone plate thickness, ranging from 1.4 mm up to 2.8 mm or greater, to accommodate different surgical bone plates.
- Illustrations and Tables: Includes figures and dimensional tables demonstrating hole and slot forms for different screw sizes, aiding manufacturers and healthcare professionals in compliance.
- Informative Annexes: Annex A describes the interrelationship between various international standards for bone screws, plates, and related surgical tools, ensuring a holistic approach to implant design.
Applications
ISO 9269:1988 serves a critical role in the design and manufacturing of metal bone plates for surgical implant applications, ensuring standardized compatibility with conical under-surface screws. This leads to:
- Improved Surgical Outcomes: Accurate hole and slot dimensions reduce the risk of screw loosening or poor fixation, enhancing patient recovery and implant longevity.
- Interoperability: Promotes use of standardized screws and plates across manufacturers, simplifying implantation procedures and inventory management in hospitals.
- Quality Control: Provides surgeons and biomedical engineers with clear criteria to assess surgical implants, maintain high standards, and minimize complications.
- Customization Guidance: Assists implant designers in modifying plate thickness and countersink depth without compromising screw engagement, important for patient-specific implants.
- Regulatory Compliance: Supports manufacturers in meeting global medical device requirements, facilitating market approval and international trade.
Related Standards
ISO 9269 works closely with other ISO standards to provide a comprehensive framework for surgical implants and orthopedic tools:
- ISO 9268: Specifies dimensions for metal bone screws with conical under-surfaces, integral for compatibility with ISO 9269-compliant bone plates.
- ISO 5836: Details metal bone plates with holes corresponding to screws with spherical under-surfaces, providing alternative screw-plate designs.
- ISO 6475: Defines mechanical requirements and test methods for bone screws, including torque and strength properties.
- ISO 8319 Parts 1 & 2: Cover orthopedic instrument drive connections like screwdrivers and keys matching various screw head types.
- ISO 9585: Provides testing methods for bending strength and stiffness of bone plates.
- ISO 9714-1: Specifies requirements for drilling instruments used with bone screws and plates, such as drill bits and countersink cutters.
By referencing ISO 9269 alongside these standards, manufacturers and healthcare providers ensure compatibility, safety, and performance of surgical implants, strengthening the reliability of orthopedic fixation techniques worldwide.
Keywords: ISO 9269, metal bone plates, surgical implants, screw holes, slots, dimensional tolerances, conical under-surface screws, ISO 9268, orthopedic surgery, implant compatibility, surgical bone plates, countersink depth, bone screw fixation, implant manufacturing standards.
ISO 9269:1988 - Implants for surgery -- Metal bone plates -- Holes and slots corresponding to screws with conical under-surface
ISO 9269:1988 - Implants chirurgicaux -- Plaques métalliques pour os -- Chambrages et alésages pour vis a embase conique
ISO 9269:1988 - Implants chirurgicaux -- Plaques métalliques pour os -- Chambrages et alésages pour vis a embase conique
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

BSI Group
BSI (British Standards Institution) is the business standards company that helps organizations make excellence a habit.

TÜV Rheinland
TÜV Rheinland is a leading international provider of technical services.

TÜV SÜD
TÜV SÜD is a trusted partner of choice for safety, security and sustainability solutions.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 9269:1988 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Implants for surgery — Metal bone plates — Holes and slots corresponding to screws with conical under-surface". This standard covers: Specification of dimensions and tolerances of the holes and slots in bone plates used as surgical implants so as to facilitate correct fixing using screws complying with ISO 9268. This standard does not deal with the shape and dimensions of plates or with the spacing of the holes and slots. The different forms are illustrated. The informative annex A shows the interrelationship of International Standards dealing with bone screws, bone plates and relevant tools.
Specification of dimensions and tolerances of the holes and slots in bone plates used as surgical implants so as to facilitate correct fixing using screws complying with ISO 9268. This standard does not deal with the shape and dimensions of plates or with the spacing of the holes and slots. The different forms are illustrated. The informative annex A shows the interrelationship of International Standards dealing with bone screws, bone plates and relevant tools.
ISO 9269:1988 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 11.040.40 - Implants for surgery, prosthetics and orthotics. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 9269:1988 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 5836-4:1984. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 9269:1988 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IS0
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
First edition
1988-12-01
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXJJYHAPOAHAfl OPI-AHM3A~MR i-l0 CTAHflAPTMSAL/MM
Implants for surgery - Metal bone plates - Holes
and slots corresponding to screws with conical
under-surface
Implants chirufgicaux - Plaques m&alliques pour 0s - Chambrages et al&ages pour vis A
embase conique
Reference number
IS0 9269 : 1988 (El
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. IS0
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all
matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council. They are approved in accordance with IS0 procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard IS0 9269 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 150,
lmplan ts for surgery.
This first edition of IS0 9269 cancels and replaces the first edition of IS0 5836-4 : 1984,
of which it constitutes a minor revision.
Annexes A and B of this International Standard are for information only.
@ International Organization for Standardization, 1988 l
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IS0 9269 : 1988 (E)
Implants for surgery - Metal bone plates - Holes
and slots corresponding to screws with conical
under-surface
1 Scope The depth of the countersink for holes or slots in flat plates hav-
ing a thickness of I,6 mm or I,4 mm shall be such as just to
accommodate the countersunk surface of the screw head.
This International Standard specifies the dimensions and
tolerances of holes and slots in bone plates used as surgical im-
For bone plates having a c rved surface, the depth of the
plants so as to facilitate correct fixing using screws complying
countersink for holes or slots shall be such that the land of the
with IS0 9268.
HC2,9 screw lies between the upper and lower countersunk
surfaces of the plates.
NOTES
1 This International Standard does not deal with the shape and
3.2 Holes and slots in bone plates for use with screws
dimensions of the plates or with the spacing (centre-to-centre
of 35 mm, 3,9 mm and 4,2 mm nominal diameters
distance) of the holes and slots.
(HC3,5, HC3,9 and HC4,2 screws in accordance with
2 The interrelationship of International Standards dealing with bone
IS0 9268)
screws, bone plates and relevant tools is shown in annex A.
Holes and slots in plates for HC3,5, HC3,9 and HC4,2 screws
shall be in accordance with figures 1 and 2 and table 1.
2 Normative reference
The depth of the countersink for holes or slots in flat plates hav-
The following standard contains provisions which, through ing a thickness of 2,8 mm or greater shall be such that at least
reference in this text, constitute provisions of this International
half of the parallel depth of the head of the HC4,2 screw shall
Standard. At the time of publication, the edition indicated was be below the external surface of the plate.
valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to
agreements based on this International Standard are encour-
aged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent
Dimension in millimetres
edition of the standard indicated below. Members of IEC and
IS0 maintain registers of currently valid International
80°5 20
Standards.
IS0 9268 : - 11, lmplan ts for surgery - Metal bone screws with
conical under-surface of head - Dimensions.
3 Dimensions and tolerances
3.1 Holes and slots in bone plates for use with screws
of 2,9 mm nominal diameter (HC2,9 screw in accordance
with IS0 9268)
Holes and slots in plates for HC2,9 screws shall be in accord-
ance with figures I and 2 and table 1.
d
The depth of the countersink for holes or slots in flat plates hav-
ing a thickness of 2 mm or greater shall be such that at least
half of the parallel depth of the head of the HC2,9 screw shall
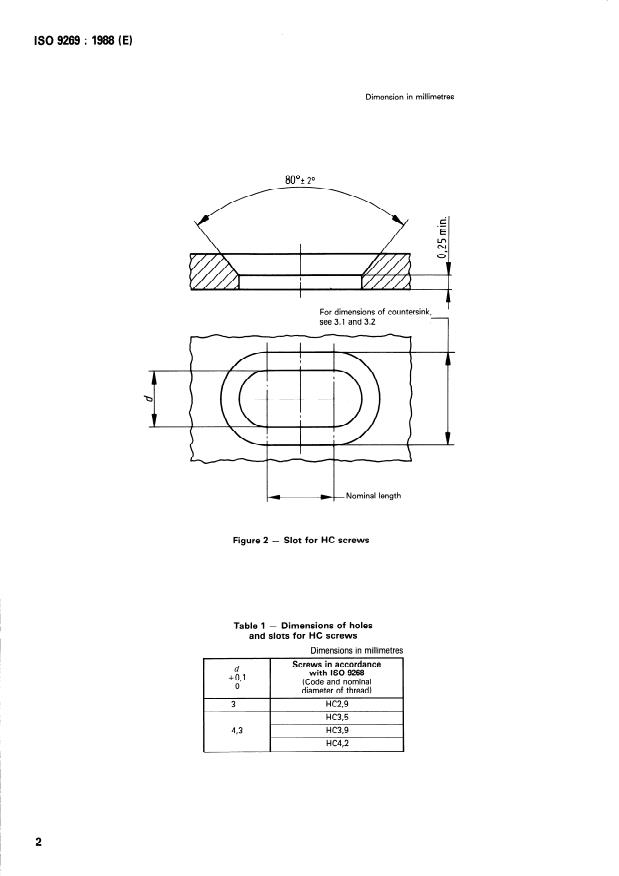
Figure 1 - Hole for HC screws
be below the superficial surface of the plate.
1) To be published; will cancel and replace ISO/DIS 5835-3 and IS0 5835-4 : 1983.
IS0 9269 : 1988 (El
Dimension in millimetres
80’2 20
For dimensions of countersink,
see 3.1 and 3.2
‘1
> Nominal length
Slot for HC screws
Figure 2 -
Table 1 - Dimensions of holes
and slots for HC screws
Dimensions in millimetres
Screws in accordance
d
with IS0 9268
+O,l
(Code and nominal
diamete
...
+
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Première édition
1988-12-01
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOfiHAfl OPTAHM3A~MR fl0 CTAH~APiM3A~MM
lmplants chirurgicaux - Plaques métalliques
- Chambrages et alésages pour vis à embase
pour os
conique
Holes and slots corresponding to screws with
lmplants for surgery - Metal bone plates -
conical under-surface
Numéro de référence
ISO 9269 : 1988 (F)
SO 9269 : 1988 (FI
I
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 9269 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 150,
lmplan ts chirurgicaux.
Cette première édition annule et remplace la première édition de I’ISO 5836-4 : 1984,
dont elle constitue une révision mineure.
Les annexes A et B de la présente Norme internationale sont données uniquement à
titre d’information.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 l
imprimé en Suisse
ISO 9269 : 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Implants chirurgicaux - Plaques métalliques
pour os - Chambrages et alésages pour vis à embase
conique
’ 1 Domaine d’application Pour les plaques planes ayant une profondeur de 1,6 mm ou
1,4 mm, la profondeur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de I’alé-
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions et les tolé-
sage doit être telle qu’elle corresponde juste à la surface fraisée
rances des chambrages et alésages des plaques pour os utili-
de la tête de vis.
sées comme implants chirurgicaux afin de faciliter leur mise en
Pour les plaques pour os à surface courbe, la profondeur de la
place correcte à l’aide de vis conformes à I’ISO 9268.
fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être telle que la base
NOTES de la vis HC2,9 se situe entre la partie haute et la partie basse de
la surface fraisée de la plaque.
1 La présente Norme internationale ne traite ni de la forme ni des
dimensions des plaques ni de I’entraxe des chambrages et alésages.
3.2 Chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour os à
2 Pour la relation entre les Normes internationales traitant des vis et
utiliser avec des vis de diamètre nominal 3,5 mm, 3,9 mm
des plaques pour os ainsi que des instruments correspondants, voir
et 4,2 mm (vis HC3,5, HC3,9 et HC4,2 conformément à
l’annexe A.
I’ISO 9268)
Les chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour vis HC3,5,
2 Référence normative
HC3,9 et HC4,2 doivent être conformes aux spécifications des
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par suite de la figures 1 et 2 et du tableau 1.
référence qui en est faite, constituent des dispositions valables
Pour les plaques planes de 2,8 mm d’épaisseur ou plus, la pro-
pour la présente Norme internationale. Au moment de la publi-
fondeur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être
cation de la présente Norme internationale, l’édition indiquée
telle qu’au moins la moitié de la partie cylindrique de la tête de
était en vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties
vis HC4,2 soit noyée dans la plaque.
prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente Norme internatio-
nale sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition
la plus récente de la norme indiquée ci-après. Les membres de
Dimension en millimétres
la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des normes internationa-
les en vigueur à un moment donné.
8Ook 20
ISO 9268 : - 11, lmplants chirurgicaux - Vis métalliques à
embase conique pour os - Dimensions.
/ Pour les dimensions
I I
Ire,
3.2
3 Dimensions et tolérances
3.1 Chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour os à
utiliser avec des vis de diamètre nominal 2,9 mm (vis
HC2,9 conformément à I’ISO 9268)
Les chambrages et alésages des plaques pour vis HC2,9 doi-
vent être conformes aux spécifications des figures 1 et 2 et du
tableau 1.
Pour les plaques planes de 2 mm d’épaisseur ou plus, la profon-
deur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être telle
qu’au moins la moitié de la partie cylindrique de la tête de vis
HC2,9 soit noyée dans la plaque.
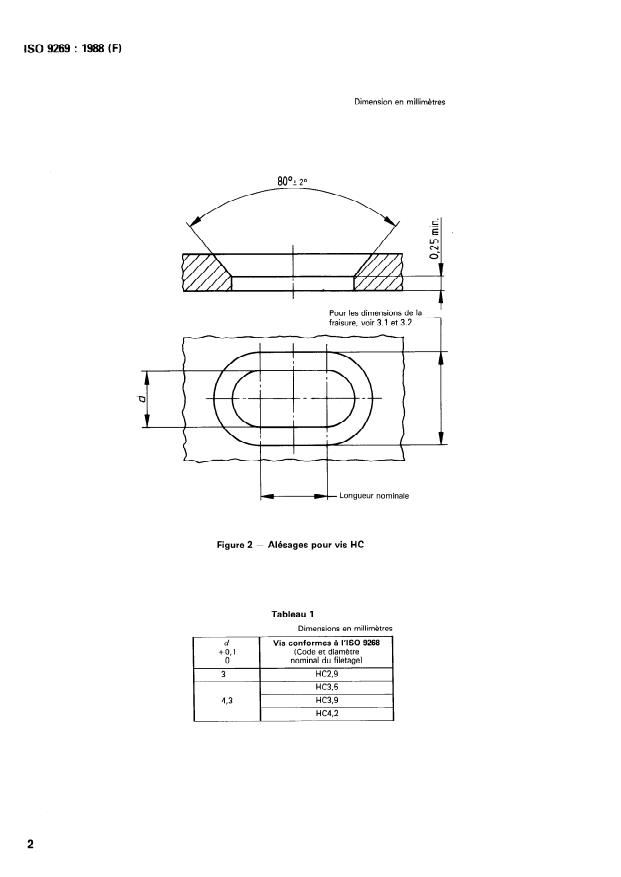
Figure 1 - Trous pour vis HC
1) À publier. Annulera et remplacera I’ISO/DIS 5835-3 et I’ISO 5835-4 : 1983.
ISO 9269 : 1988 (FI
Dimension en millimètres
80°2 20
Pour les dimensions de la
fraisure, voir 3.1 et 3.2
w- Longueur nominale
Figure 2 - Alésages pour
...
+
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Première édition
1988-12-01
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOfiHAfl OPTAHM3A~MR fl0 CTAH~APiM3A~MM
lmplants chirurgicaux - Plaques métalliques
- Chambrages et alésages pour vis à embase
pour os
conique
Holes and slots corresponding to screws with
lmplants for surgery - Metal bone plates -
conical under-surface
Numéro de référence
ISO 9269 : 1988 (F)
SO 9269 : 1988 (FI
I
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 9269 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 150,
lmplan ts chirurgicaux.
Cette première édition annule et remplace la première édition de I’ISO 5836-4 : 1984,
dont elle constitue une révision mineure.
Les annexes A et B de la présente Norme internationale sont données uniquement à
titre d’information.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 l
imprimé en Suisse
ISO 9269 : 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Implants chirurgicaux - Plaques métalliques
pour os - Chambrages et alésages pour vis à embase
conique
’ 1 Domaine d’application Pour les plaques planes ayant une profondeur de 1,6 mm ou
1,4 mm, la profondeur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de I’alé-
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions et les tolé-
sage doit être telle qu’elle corresponde juste à la surface fraisée
rances des chambrages et alésages des plaques pour os utili-
de la tête de vis.
sées comme implants chirurgicaux afin de faciliter leur mise en
Pour les plaques pour os à surface courbe, la profondeur de la
place correcte à l’aide de vis conformes à I’ISO 9268.
fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être telle que la base
NOTES de la vis HC2,9 se situe entre la partie haute et la partie basse de
la surface fraisée de la plaque.
1 La présente Norme internationale ne traite ni de la forme ni des
dimensions des plaques ni de I’entraxe des chambrages et alésages.
3.2 Chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour os à
2 Pour la relation entre les Normes internationales traitant des vis et
utiliser avec des vis de diamètre nominal 3,5 mm, 3,9 mm
des plaques pour os ainsi que des instruments correspondants, voir
et 4,2 mm (vis HC3,5, HC3,9 et HC4,2 conformément à
l’annexe A.
I’ISO 9268)
Les chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour vis HC3,5,
2 Référence normative
HC3,9 et HC4,2 doivent être conformes aux spécifications des
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par suite de la figures 1 et 2 et du tableau 1.
référence qui en est faite, constituent des dispositions valables
Pour les plaques planes de 2,8 mm d’épaisseur ou plus, la pro-
pour la présente Norme internationale. Au moment de la publi-
fondeur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être
cation de la présente Norme internationale, l’édition indiquée
telle qu’au moins la moitié de la partie cylindrique de la tête de
était en vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties
vis HC4,2 soit noyée dans la plaque.
prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente Norme internatio-
nale sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition
la plus récente de la norme indiquée ci-après. Les membres de
Dimension en millimétres
la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des normes internationa-
les en vigueur à un moment donné.
8Ook 20
ISO 9268 : - 11, lmplants chirurgicaux - Vis métalliques à
embase conique pour os - Dimensions.
/ Pour les dimensions
I I
Ire,
3.2
3 Dimensions et tolérances
3.1 Chambrages et alésages dans les plaques pour os à
utiliser avec des vis de diamètre nominal 2,9 mm (vis
HC2,9 conformément à I’ISO 9268)
Les chambrages et alésages des plaques pour vis HC2,9 doi-
vent être conformes aux spécifications des figures 1 et 2 et du
tableau 1.
Pour les plaques planes de 2 mm d’épaisseur ou plus, la profon-
deur de la fraisure du chambrage ou de l’alésage doit être telle
qu’au moins la moitié de la partie cylindrique de la tête de vis
HC2,9 soit noyée dans la plaque.
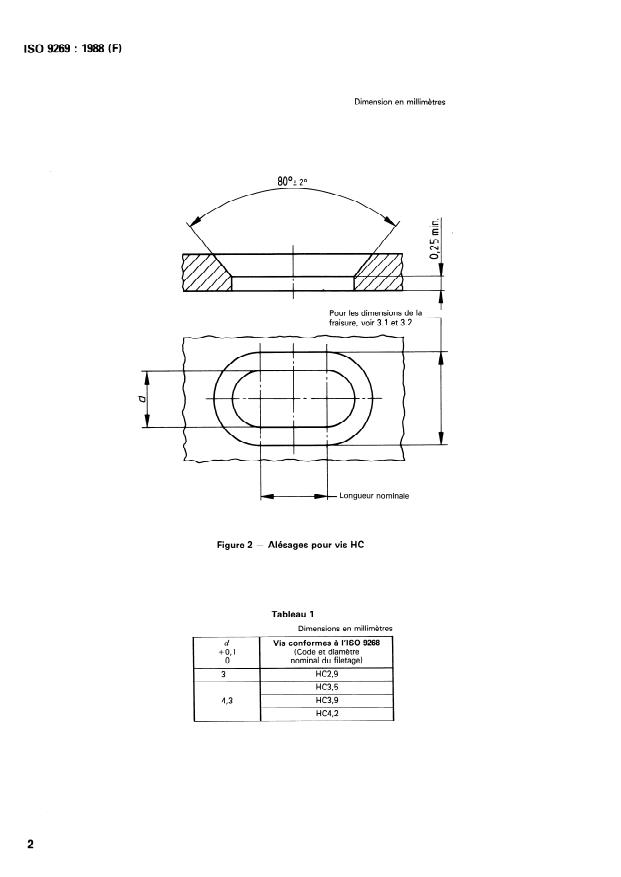
Figure 1 - Trous pour vis HC
1) À publier. Annulera et remplacera I’ISO/DIS 5835-3 et I’ISO 5835-4 : 1983.
ISO 9269 : 1988 (FI
Dimension en millimètres
80°2 20
Pour les dimensions de la
fraisure, voir 3.1 et 3.2
w- Longueur nominale
Figure 2 - Alésages pour
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...