ISO 5014:1997
(Main)Dense and insulating shaped refractory products — Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
Dense and insulating shaped refractory products — Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants — Détermination du module de rupture par flexion à température ambiante
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 25-Jun-1997
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 33 - Refractories
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 33 - Refractories
- Current Stage
- 9599 - Withdrawal of International Standard
- Start Date
- 12-Mar-2025
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2023
Overview
ISO 5014:1997 is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) focused on dense and insulating shaped refractory products. This standard specifies a precise method for determining the modulus of rupture (MOR) of these refractory materials at ambient temperature. The modulus of rupture is a critical mechanical property that measures the maximum bending stress a shaped refractory test piece can withstand before failure.
The procedure outlined in ISO 5014:1997 is primarily applicable to shaped and fired refractories. For chemically bonded or tar-bonded bricks, a preliminary heat treatment may be required prior to testing, though this treatment is outside the standard’s scope and should be agreed upon by involved parties. This standard plays a vital role in quality control, product development, and materials characterization of refractory products used in high-temperature industrial applications.
Key Topics
- Modulus of Rupture (MOR) Definition: The maximum stress in a prismatic test piece during bending using a three-point flexural test at ambient temperature.
- Test Method Principle: Application of load at a constant rate of increase of stress on test specimens until failure, using a three-point bending device.
- Test Pieces: Includes standard rectangular bricks of specified sizes, or samples cut out of bricks with consideration given to pressing direction and faces.
- Apparatus Requirements: Loading device with three bearing edges-two supports and one load application edge-with specific dimensions and curvature tolerances to ensure uniform loading and accurate stress measurement.
- Testing Procedure:
- Dry the refractory test pieces at 110°C until constant mass is achieved.
- Measure dimensions with high precision for accurate calculation.
- Apply load using the specified loading device at a controlled rate until the sample breaks.
- Record the maximum load and calculate the modulus of rupture in megapascals.
- Calculation Formula: The MOR is calculated using the breaking load, span length between supports, and cross-sectional dimensions of the test piece.
- Test Reporting: Comprehensive documentation including test conditions, sample details, results, and any pre-treatments to ensure traceability and reproducibility.
Applications
ISO 5014:1997 is essential for stakeholders in industries involving refractory materials such as:
- Steel and Metallurgical Industries: Ensuring shaped refractories used in furnaces and kilns possess adequate mechanical strength for safe operation.
- Ceramic and Glass Manufacturing: Quality control of kiln linings and insulating bricks exposed to mechanical stresses.
- Construction of High-Temperature Installations: Verification of the mechanical performance of insulating and dense refractory bricks utilized in thermal insulation and structural components.
- Research and Development: Material scientists and engineers use this standard to compare the flexural strength of new refractory formulations for improved durability.
- Quality Assurance Laboratories: Routine mechanical testing of produced refractory shapes to certify compliance with required performance criteria.
Related Standards
ISO 5014:1997 aligns with a network of standards governing refractory products and testing procedures, including:
- ISO 10064 Series: Methods for determining other mechanical and physical properties of refractory products.
- ISO 18757: Determination of thermal shock resistance of refractory shaped products.
- ASTM C133: Standard test method for cold crushing strength and modulus of rupture of refractory brick and shapes.
- EN 993-5: European standard for methods of test for dense refractories, including determination of modulus of rupture.
- ISO 5019: Determination of permanent linear changes of fired shaped refractory products after heating.
These complementary standards provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating refractory materials, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of high-temperature industrial environments.
Keywords: ISO 5014, modulus of rupture, refractory products, dense refractories, insulating refractories, bending test, three-point flexure, mechanical testing, shaped refractories, ambient temperature, quality control, refractory bricks, testing standards.
Buy Documents
ISO 5014:1997 - Dense and insulating shaped refractory products -- Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
ISO 5014:1997 - Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants -- Détermination du module de rupture par flexion a température ambiante
ISO 5014:1997 - Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants -- Détermination du module de rupture par flexion a température ambiante
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 5014:1997 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Dense and insulating shaped refractory products — Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature". This standard covers: Dense and insulating shaped refractory products — Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
Dense and insulating shaped refractory products — Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
ISO 5014:1997 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 81.080 - Refractories. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 5014:1997 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 5014:2025. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 5014:1997 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IS0
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
Second edition
1997-07-01
Dense and insulating shaped refractory
Determination of modulus
products -
of rupture at ambient temperature
Prod& Gfractaires faGonn6s denses et isolanis - D6terminaiion
du module de rupture par flexion 2 temphrature ambiante
Reference number
IS0 5014:1997(E)
IS0 5014: 1997(E)
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national
standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally
carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a
technical committee has been established has the right to be represented on that co ittee.
International organizations, governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part
in the work. IS0 collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on
all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member
bodies for voting. Publication as an International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the
member bodies casting a vote.
International Standard IS0 5014 was prepared by Technical Committee ISOITC 33,
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (IS0 5014: 1986), whit
technically revised.
0 IS0 1997
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be
reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 l CH-1211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Internet central@iso.ch
x.400 c=ch; a=400net; p=iso; o=isocs; s=central
Printed in Switzerland
ii
IS0 5014: 1997(E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD o IS0
Dense and insulating shaped refractory products - Determination
of modulus of rwture
at ambient temperature
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies a method for the determination of the modulus of rupture of
dense and insulating shaped refractory products at ambient temperature, under conditions of a
constant rate of increase of stress.
The method relates primarily to shaped and fired refractories.
If it is to be applied to chemically
bonded or tar-bonded bricks, they will usually require some form of preliminary heat treatment.
This preliminary treatment, the details of which are outside the scope of this standard, is a matter of
agreement between the interested parties and is described in the test report.
2 Definition
For the purposes of this International Standard, the following definition applies:
2.1 modulus of rupture: The maximum stress that a prismatic test piece of specified dimensions
can withstand when it is bent in a three-point bending device.
3 Principle
Loading of test pieces of the product to be tested at a constant rate of increase of stress until failure
occurs.
4 Apparatus
4.1 Loading device
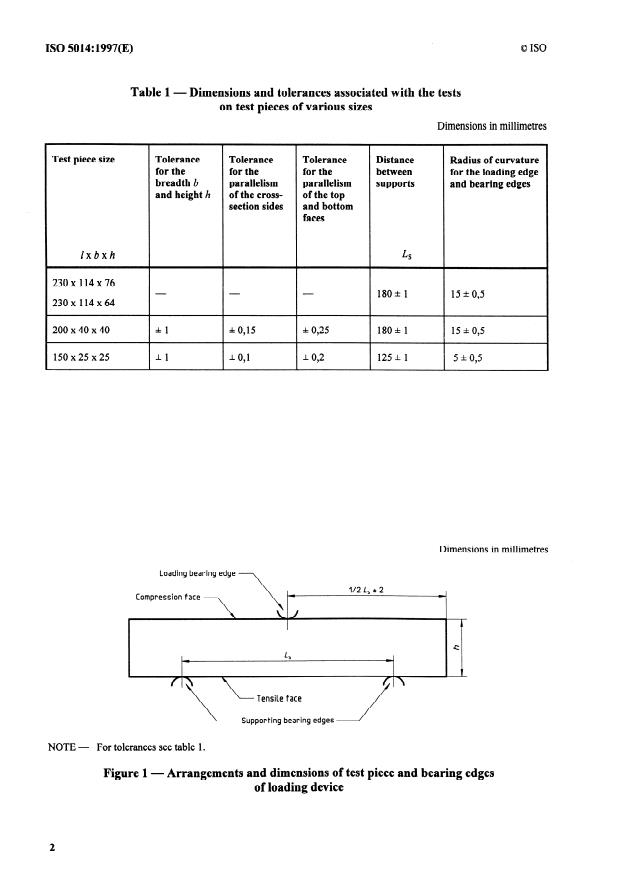
4.1.1 The loading device shall have three bearing edges, two to support the test piece and one for the
application of the load (see figure 1). The three edges shall have a radius of curvature in accordance
with the requirements given in table 1 and shall be of length not less than 5 mm greater than the
breadth (b) of the test piece (see figure 2). The contact lines of the three edges shall be parallel to
each other in a direction perpendicular to the length and the plane of the breadth of the test piece.
Two supporting edges shall rest on an intermediate bearing piece, cylindrical on its lower surface,
so that each edge may rotate independently in a vertical plane to accommodate any slight twist in
the test piece (see figure 2). Alternatively, one supporting edge may be fixed, with the other
supporting edge and the load-bearing edge being capable of rotation in a vertical plane. The
distance between the two supporting edges shall be in accordance with table 1 and the load-bearing
edge shall be positioned equidistantly, at L,/2 k 2 mm from each supporting edge.
IS0 5014:1997(E)
Table 1 - Dimensions and tolerances associate
on test pieces of various sizes
Dimensions in millimetres
Tolerance Tolerance Distance Radius of curvature
Test piece size Tolerance
for the between
for the for the for the loading edge
breadth b parallelism parallelism supports and bearing edges
and height h of the cross- of the top
section sides and bottom
faces
lxbxh L
230x114~76
18Ok 1
15 f: 0,5
230x 114x64 -
200x40~40 =tl k 0,15 * 0,25 180-i 1 15 k 0,5
150x25~25 fl rf: 0,l * 0,2 125k 1 5 k O,5
Dimensions in millimetres
Loading bearing edge
Compression face
,
/ \ ‘l Tensile face
I‘
Supporting bearing edges
NOTE - For tolerances see table 1.
Figure 1 - Arrangements and dimensions of test piece and bearing edges
of loading device
IS0 5014: 1997(E)
Loading edge
Test piece
Intermediate bearing piece
Supporting edge
b
Diagrammatic represent
...
NORME
Iso
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxibme édition
1997-07-01
Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et
isolants - Détermination du module de
rupture par flexion à température ambiante
Dense and insuating shaped refractory products - Determination of
modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
Numéro de réfbrence
Avant-propos
LIS0 (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale d’organismes nationaux de
normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé a cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales, en
liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO collabore étroitement avec la Commission
électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis aux comités membres pour
vote. Leur publication comme Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des comités
membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 5014 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISOTTC 33, Matériaux réfractaires.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 5014:1986), dont elle constitue une révision
technique.
0 ISO 1997
Droits de reproduction reset-v&. Sauf prescription differente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut Qtre reproduite ni utilisee sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cede, electronique ou mkanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
&xit de IWteur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 l CH-1 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Internet central @ iso.ch
x.400 c=ch; a=4OOnet; p=iso; o=isocs; s=central
Imprime en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE o ISO ISO 5014: 1997(F)
Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants - Détermination
du module de rupture par flexion à température ambiante
1 Domaine d’application
La présente Norme internationale prescrit une méthode pour la détermination du module de rupture des produits
réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants à température ambiante dans des conditions d’accroissement continu de la
contrainte.
La méthode est applicable en premier lieu aux réfractaires façonnés ayant subi une cuisson. Si l’on doit soumettre à
l’essai des produits liés chimiquement ou liés au goudron, un traitement thermique préalable sera probablement
nécessaire. Les conditions de ce traitement dépassent le domaine d’application de la présente Norme internationale
et doivent faire l’objet d’un accord entre les parties intéressées; elles sont décrites dans le rapport d’essai.
2 Définition
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale, la définition suivante s’applique.
2.1 module de rupture
contrainte maximale que peut supporter une éprouvette prismatique de dimensions spécifiées lorsqu’elle est mise
en charge au moyen d’un dispositif de flexion en trois points
3 Principe
Application, aux éprouvettes du produit soumis à essai, d’une charge s’accroissant à vitesse constante jusqu’à la
rupture.
4 Appareillage
4.1 Dispositif d’application de la charge
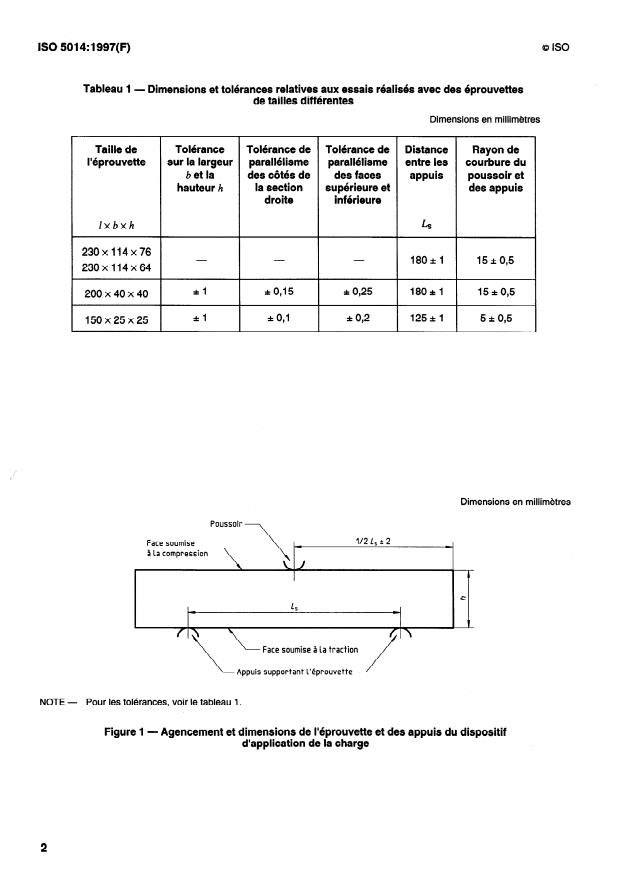
4.1.1 Le dispositif d’application de la charge doit être muni de trois « appuis », dont deux servent à supporter
l’éprouvette soumise à essai et le troisième pour l’application de la force (voir figure 1). Les trois appuis doivent
avoir un rayon de courbure conforme aux exigences du tableau 1 et une longueur au moins égale à la largeur (b) de
l’éprouvette (voir figure 2), plus 5 mm. Les lignes de contact des trois appuis doivent être parallèles l’une par rapport
à l’autre, dans une direction perpendiculaire à la longueur et au plan correspondant à la largeur de l’éprouvette. Les
deux appuis servant de support doivent reposer sur un support intermédiaire cylindrique sur sa face inférieure de
façon à ce que les appuis puissent pivoter indépendamment dans un plan vertical de façon à compenser tout
gauchissement de l’éprouvette (voir figure 2). Facultativement, un appui peut être fixe, l’autre et le poussoir
d’application de la charge étant capable de pivoter dans un plan vertical. La distance entre les deux appuis doit être
conforme au tableau 1 et le poussoir d’application de la charge doit être placé à égale distance de chaque appui, à
Ls/2 f: 2 mm.
4.1.2 Le dispositif d’application de la charge doit permettre d’appliquer cette charge uniformément dans l’axe
transversal de l’éprouvette avec un accroissement à vitesse constante. Il doit comporter un dispositif permettant
d’enregistrer ou d’indiquer la charge de rupture avec une exactitude de =t 2 %.
4.2 Étuve, susceptible d’être contrôlée à (110 f: 5) OC.
0 ISO
Tableau 1 - Dimensions et tolérances relatives aux essais réalises avec des éprouvettes
de tailles différentes
Dimensions en millimétres
Taille de Tolérance Tolérance de Tolérance de
Distance Rayon de
l’éprouvette sur la largeur parallélisme parallélisme
entre les courbure du
b et la des côtés de des faces
appuis poussoir et
la section supérieure et
hauteur h des appuis
droite inférieure
lxbxh
LS
230x114~76
18Od 15* 0,5
230x114~64
*l *0,15 zt 0,25 18Od 15* 0,5
200x40x40
*l * 0,l * 0,2 125d 5* 0,5
150x25~25
Dimensions en millimètres
Poussoir
112 L, A 2
Face soumise
3 la compression
,\\,-
c
Face soumise à la traction
Appuis supportant l’éprouvette
NOTE - Pour les toléran
...
NORME
Iso
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxibme édition
1997-07-01
Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et
isolants - Détermination du module de
rupture par flexion à température ambiante
Dense and insuating shaped refractory products - Determination of
modulus of rupture at ambient temperature
Numéro de réfbrence
Avant-propos
LIS0 (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale d’organismes nationaux de
normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé a cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales, en
liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO collabore étroitement avec la Commission
électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis aux comités membres pour
vote. Leur publication comme Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des comités
membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 5014 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISOTTC 33, Matériaux réfractaires.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 5014:1986), dont elle constitue une révision
technique.
0 ISO 1997
Droits de reproduction reset-v&. Sauf prescription differente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut Qtre reproduite ni utilisee sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cede, electronique ou mkanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord
&xit de IWteur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 l CH-1 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Internet central @ iso.ch
x.400 c=ch; a=4OOnet; p=iso; o=isocs; s=central
Imprime en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE o ISO ISO 5014: 1997(F)
Produits réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants - Détermination
du module de rupture par flexion à température ambiante
1 Domaine d’application
La présente Norme internationale prescrit une méthode pour la détermination du module de rupture des produits
réfractaires façonnés denses et isolants à température ambiante dans des conditions d’accroissement continu de la
contrainte.
La méthode est applicable en premier lieu aux réfractaires façonnés ayant subi une cuisson. Si l’on doit soumettre à
l’essai des produits liés chimiquement ou liés au goudron, un traitement thermique préalable sera probablement
nécessaire. Les conditions de ce traitement dépassent le domaine d’application de la présente Norme internationale
et doivent faire l’objet d’un accord entre les parties intéressées; elles sont décrites dans le rapport d’essai.
2 Définition
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale, la définition suivante s’applique.
2.1 module de rupture
contrainte maximale que peut supporter une éprouvette prismatique de dimensions spécifiées lorsqu’elle est mise
en charge au moyen d’un dispositif de flexion en trois points
3 Principe
Application, aux éprouvettes du produit soumis à essai, d’une charge s’accroissant à vitesse constante jusqu’à la
rupture.
4 Appareillage
4.1 Dispositif d’application de la charge
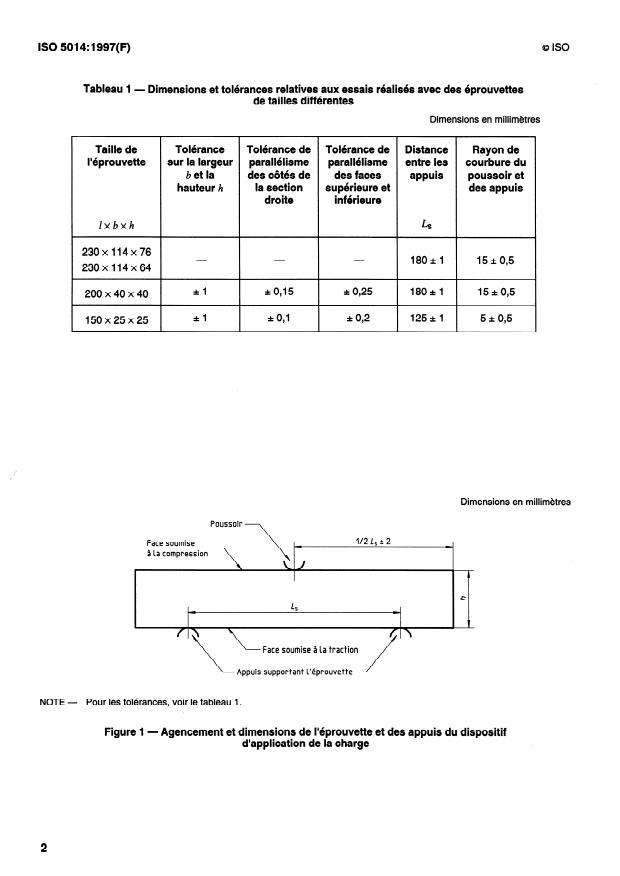
4.1.1 Le dispositif d’application de la charge doit être muni de trois « appuis », dont deux servent à supporter
l’éprouvette soumise à essai et le troisième pour l’application de la force (voir figure 1). Les trois appuis doivent
avoir un rayon de courbure conforme aux exigences du tableau 1 et une longueur au moins égale à la largeur (b) de
l’éprouvette (voir figure 2), plus 5 mm. Les lignes de contact des trois appuis doivent être parallèles l’une par rapport
à l’autre, dans une direction perpendiculaire à la longueur et au plan correspondant à la largeur de l’éprouvette. Les
deux appuis servant de support doivent reposer sur un support intermédiaire cylindrique sur sa face inférieure de
façon à ce que les appuis puissent pivoter indépendamment dans un plan vertical de façon à compenser tout
gauchissement de l’éprouvette (voir figure 2). Facultativement, un appui peut être fixe, l’autre et le poussoir
d’application de la charge étant capable de pivoter dans un plan vertical. La distance entre les deux appuis doit être
conforme au tableau 1 et le poussoir d’application de la charge doit être placé à égale distance de chaque appui, à
Ls/2 f: 2 mm.
4.1.2 Le dispositif d’application de la charge doit permettre d’appliquer cette charge uniformément dans l’axe
transversal de l’éprouvette avec un accroissement à vitesse constante. Il doit comporter un dispositif permettant
d’enregistrer ou d’indiquer la charge de rupture avec une exactitude de =t 2 %.
4.2 Étuve, susceptible d’être contrôlée à (110 f: 5) OC.
0 ISO
Tableau 1 - Dimensions et tolérances relatives aux essais réalises avec des éprouvettes
de tailles différentes
Dimensions en millimétres
Taille de Tolérance Tolérance de Tolérance de
Distance Rayon de
l’éprouvette sur la largeur parallélisme parallélisme
entre les courbure du
b et la des côtés de des faces
appuis poussoir et
la section supérieure et
hauteur h des appuis
droite inférieure
lxbxh
LS
230x114~76
18Od 15* 0,5
230x114~64
*l *0,15 zt 0,25 18Od 15* 0,5
200x40x40
*l * 0,l * 0,2 125d 5* 0,5
150x25~25
Dimensions en millimètres
Poussoir
112 L, A 2
Face soumise
3 la compression
,\\,-
c
Face soumise à la traction
Appuis supportant l’éprouvette
NOTE - Pour les toléran
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...