ISO 3158:1976
(Main)Timekeeping instruments — Symbolization of control positions
Timekeeping instruments — Symbolization of control positions
Lays down the definition and designations (as a symbol or by words) of test position for any timekeeping instrument, irrespective of its type, design or dimensions.
Instruments horaires — Symbolisation des positions de contrôle
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 31-Jan-1976
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 114 - Horology
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 114 - Horology
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 04-Jun-2024
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
Overview
ISO 3158:1976, titled Timekeeping Instruments - Symbolization of Control Positions, is an international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). It defines the symbols and designations used to represent and describe control or test positions for any timekeeping instrument regardless of its type, design, or size. The standard establishes a consistent framework for specifying the orientation and positioning of timekeeping devices during testing and calibration procedures.
First issued in 1976 by ISO technical committee ISO/TC 114 on horology, ISO 3158 applies universally to all kinds of clocks, watches, and movements, ensuring clear communication and uniformity in the horological industry. It addresses rotations and orientations by defining angular measurements and symbolic representations essential for quality control and technical documentation.
Key Topics
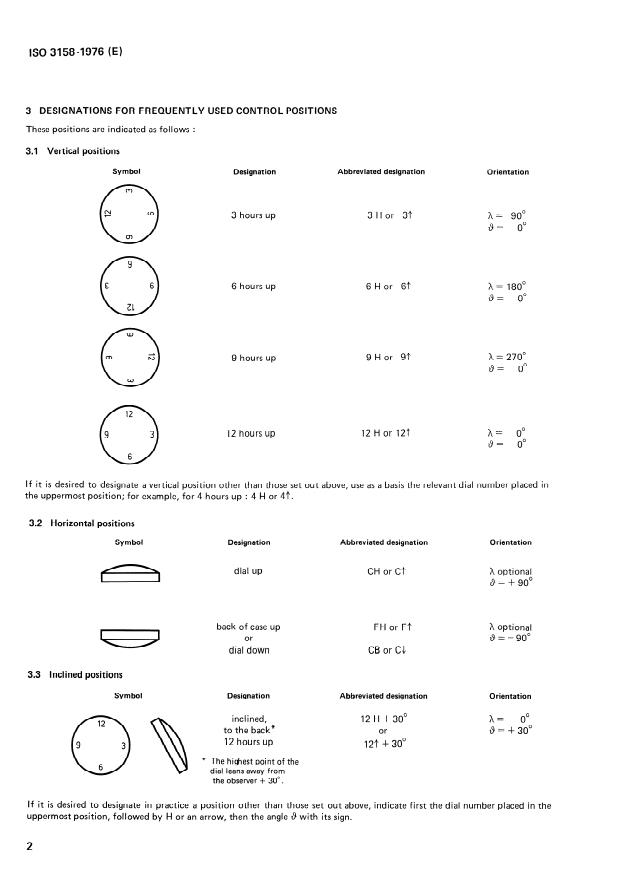
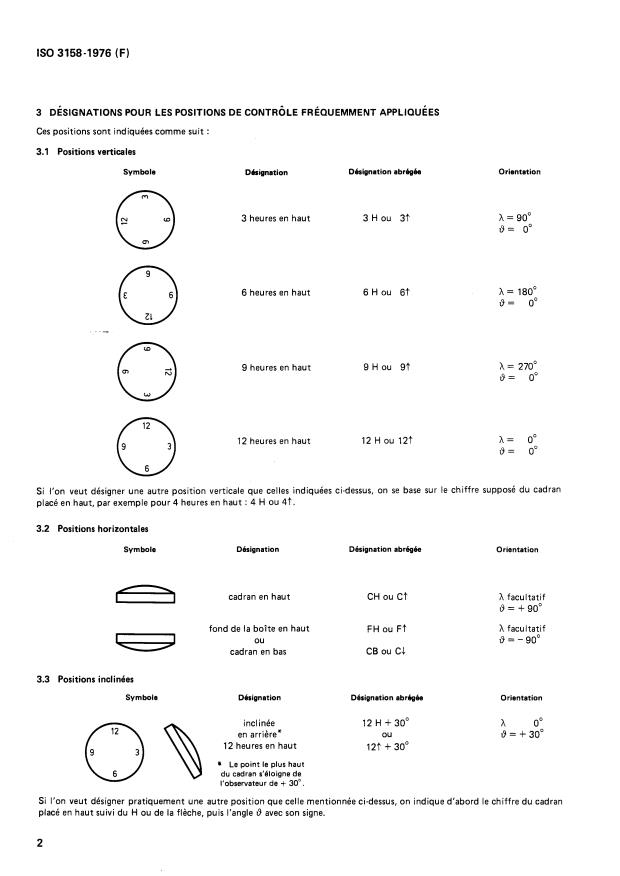
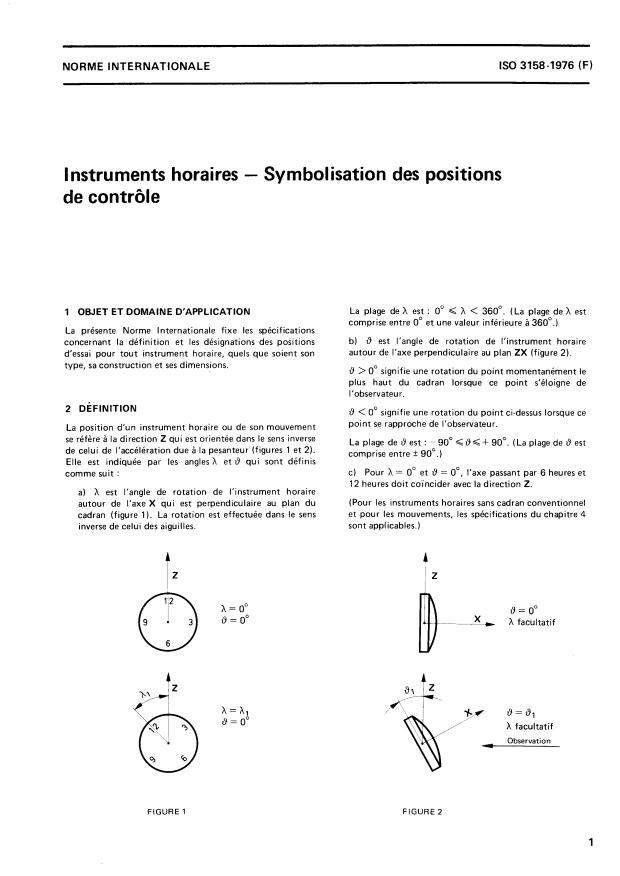
Control Positions Definition: ISO 3158 specifies the positions for testing timekeeping instruments based on two angular parameters:
- h: Rotation angle around the X-axis perpendicular to the dial plane, ranging from greater than 0° up to but not including 360°.
- θ (theta): Rotation angle describing inclination around an axis with limits from -90° to +90°, indicating tilt relative to the vertical plane.
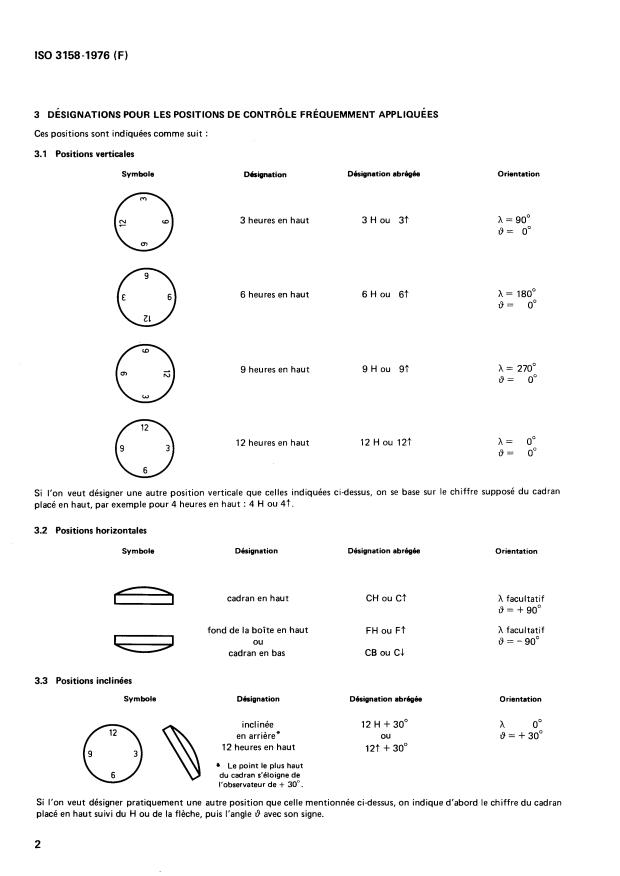
Symbolization System: The standard provides a method to symbolize test positions either through abbreviations or words. For example:
- "12 H" or "12f" represents the 12 o'clock position facing up.
- "3 H" indicates 3 o'clock in the upward position.
- Horizontal positions use symbols like "CH" (dial up) and "FH" (case back up).
- Inclined positions add angle specifications, such as "12 H + 30°," indicating the dial is tilted 30 degrees away from the observer.
Orientation Conventions: The standard clarifies orientation relative to the observer and gravitational force, using a reference axis for consistency. Positive and negative angle values distinguish between rotation directions away or toward the observer.
Application to All Instruments: ISO 3158 applies to any timekeeping device-even those without a conventional dial, such as digital watches or standalone movements-by assuming a virtual dial for orientation references.
Applications
Manufacturing and Testing: ISO 3158 standardizes the orientation of timekeeping instruments during functional tests, ensuring repeatable and accurate measurements of performance under specific positional stresses.
Quality Control: Watchmakers, laboratories, and quality assurance teams use the symbolization prescribed in ISO 3158 to describe test conditions unambiguously in technical reports, facilitating communication across international borders and regulatory compliance.
Technical Documentation: The symbolic language allows for clear annotation in manuals, repair guides, and scientific papers, improving understanding and reducing errors in assembly or servicing.
Calibration Procedures: When calibrating movements and full instruments, ISO 3158-defined control positions enable consistent orientation alignment, critical to precise timekeeping accuracy verification.
Instrument Design and Development: Designers use the position definitions early in product development to anticipate how orientation impacts movement and timekeeping reliability, guiding engineering decisions.
Related Standards
ISO 3157 (Horology - Testing of watches): ISO 3157 covers general procedures for watch testing, complementing ISO 3158 by outlining broader testing criteria.
ISO 1413 (Shock resistance testing for watches): Focuses on testing watch resistance under shocks, often performed at defined control positions standardized by ISO 3158.
ISO 764 (Magnetic resistance for watches): Specifies magnetic resistance test methods where specific instrument positions can be applied using ISO 3158 guidelines.
Other Horology Standards from ISO/TC 114: For comprehensive timekeeping instrument quality and testing, other ISO standards in the horology sector integrate well with ISO 3158 to ensure full coverage of product performance requirements.
Keywords: ISO 3158, timekeeping instruments, control positions, symbolization, horology standards, watch testing, timepiece orientation, calibration positions, clock movement testing, timepiece quality control, horological measurement.
ISO 3158:1976 - Timekeeping instruments -- Symbolization of control positions
ISO 3158:1976 - Instruments horaires -- Symbolisation des positions de contrôle
ISO 3158:1976 - Instruments horaires -- Symbolisation des positions de contrôle
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 3158:1976 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Timekeeping instruments — Symbolization of control positions". This standard covers: Lays down the definition and designations (as a symbol or by words) of test position for any timekeeping instrument, irrespective of its type, design or dimensions.
Lays down the definition and designations (as a symbol or by words) of test position for any timekeeping instrument, irrespective of its type, design or dimensions.
ISO 3158:1976 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 39.040.01 - Horology in general. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 3158:1976 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 2338:1997. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 3158:1976 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATIOf’J FOR STANDARDIZATION l MEXaYHAPOfiHAII OPI-AHM3ALViII I-Io CTAHAAPTM3ALWiW~ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Timekeeping instruments - Symbolkation of control
positions
Instruments horaires - Symbolisa tion des positions de con tr6le
First edition - 1976-02-01
UDC 681.11 : 658.562 Ref. No. ISO 3158-1976 (E)
Descriptors : time-measuring instruments, orientation, Symbols.
Price based on 3 pages
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation
of national Standards institutes (ISO Member Bodies). The work of developing
International Standards is carried out through ISO Technical Committees. Every
Member Body interested in a subject for which a Technical Committee has been set
up has the right to be represented on that Committee. International organizations,
governmental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the Technical Committees are circulated
to the Member Bodies for approval before their acceptance as International
Standards by the ISO Council.
International Standard ISO 3158 was drawn up by Technical Committee
ISO/TC 114, Horology, and circulated to the Member Bodies in April 1975.
lt has been approved by the Member Bodies of the following countries :
Czechoslovakia Mexico Turkey
France Portugal United Kingdom
Germany South Africa, Rep. of U.S.S. R.
I rel and Spain
Japan Switzerland
No Member Body expressed disapproval of the document.
0 International Organkation for Standardization, 1976 l
Printed in Switzerland
ISO 31584976 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Timekeeping instruments - Symbolkation of control
positions
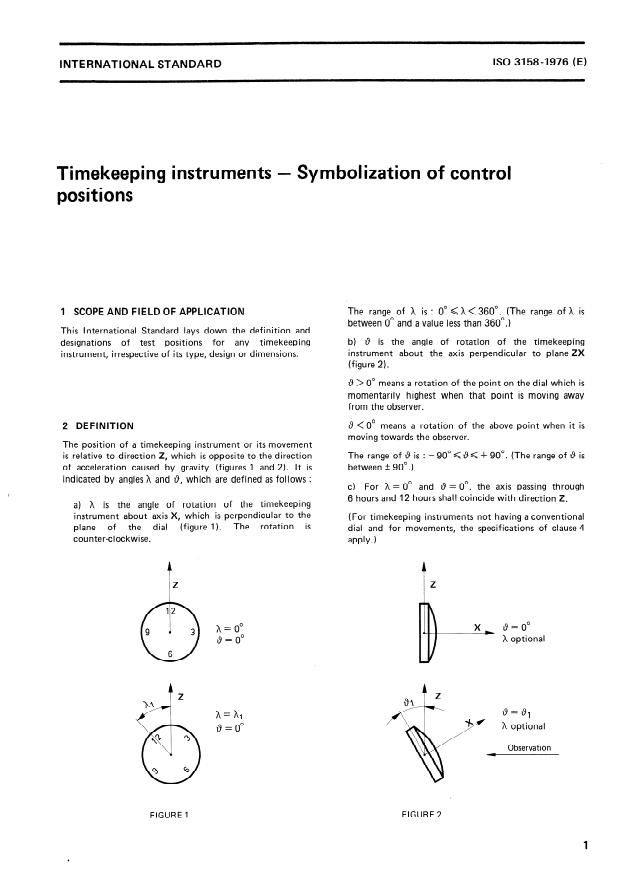
1 SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The range of X is : 0” < h < 360”. (The range of X is
between 0” and a value less than 360”.)
This International Standard lays down the definition and
of test positions for any timekeeping b) 0 is the angle of rotation of the timekeeping
designations
instrument about the axis perpendicular to plane ZX
instrument, irrespective of its type, design or dimensions.
(figure 2).
9. > 0” means a rotation of the Point on the dial which is
momentarily highest when that Point is moving away
from the observer.
8 < 0” means a rotation of the above Point when it is
2 DEFINITION
moving towards the observer.
The Position of a timekeeping instrument or its movement
is relative to direction 2, which is opposite to the direction The range of 8 is : - 90”<9f + 90”. (The range of 0 is
of acceleration caused by gravity (figures 1 and 2). lt is between + 90”.)
indicated by angles X and 0, which are defined as follows :
c) For X
...
NORME INTERNATIONALE @ 3158
‘*Xe
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION *WEXJYHAPOLlHAR OPrAHMJAUMP no CTAHJAPTM3AUMH .ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Instruments horaires - Symbolisation des positions
de contrôle
Timekeeping instruments - Symbotization of control positions
Première édition - 1976-02-01
U
-
CDU 681.11 : 658.562
Réf. no : IS0 3158-1976 (FI
U)
b
O)
c
Descripteurs : instrument de mesure du temps, orientation, symbole.
r
m
Prix base sur 3 pages
AV AN T-P R O POS
L'ISO (Organisation Internationale de Normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (Comités Membres ISO). L'élaboration de
Normes Internationales est confiée aux Comités Techniques ISO. Chaque Comité
Membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du Comité Technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementale_s, en liaison avec I'ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les Projets de Normes Internationales adoptés par les Comités Techniques sont
soumis aux Comités Membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme
Normes Internationales par le Conseil de I'ISO.
La Norme Internationale IS0 3158 a été établie par le Comité Technique
ISO/TC 114, Horlogerie, et soumise aux Comités Membres en avril 1975.
Elle a été approuvée par les Comités Membres des pays suivants :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d' Japon Tchécoslovaquie
Allemagne Mexique Tu rqu ie
Espagne Portugal U.R.S.S.
France Royaume-Uni
Irlande Suisse
Aucun Comité Membre n'a désapprouvé le document.
O Organisation Internationale de Normalisation, 1976 O
Imprimé en Suisse
NORME INTERNATIONALE IS0 3158-1976 (FI
Instruments horaires - Symbolisation des positions
de contrôle
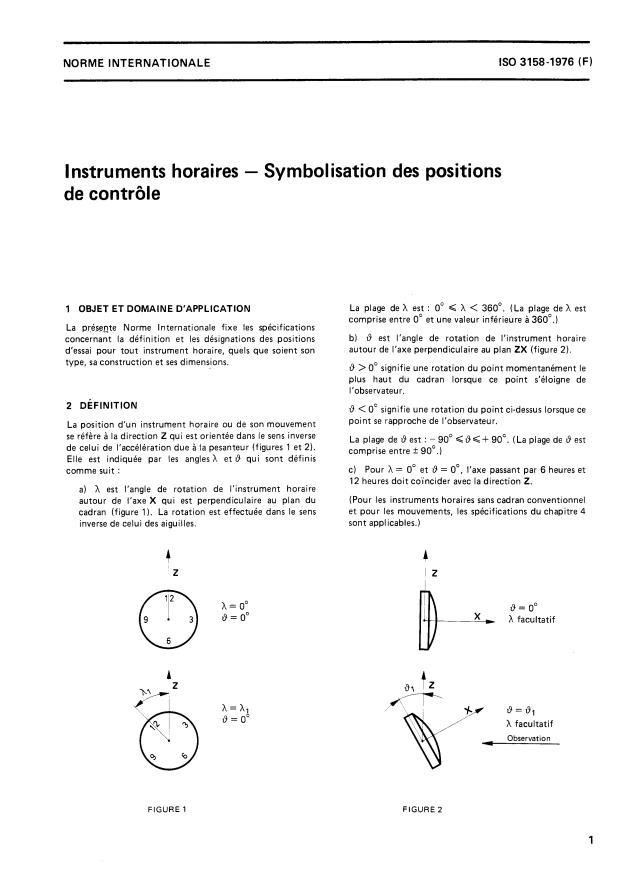
1 OBJET ET DOMAINE D'APPLICATION La plage de h est : O" < h < 360". (La plage de h est
comprise entre O" et une valeur inférieure à 360".)
La présente Norme Internationale fixe les spécifications
b) 6 est l'angle de rotation de l'instrument horaire
concernant la définition et les désignations des positions
autour de l'axe perpendiculaire au plan ZX (figure 2).
d'essai pour tout instrument horaire, quels que soient son
type, sa construction et ses dimensions.
9 >O" signifie une rotation du point momentanément le
plus haut du cadran lorsque ce point s'éloigne de
l'observateur.
2 DÉFINITION
9 < O" signifie une rotation du point ci-dessus lorsque ce
point se rapproche de l'observateur.
La position d'un instrument horaire ou de son mouvement
se réfère à la direction 2 qui est orientée dans le sens inverse
La plage de 9 est : - 90"
de ce
...
NORME INTERNATIONALE @ 3158
‘*Xe
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION *MEXJYHAPORHAR OPrAHM3AUMR no CTAHLlAPTM3AUMM.ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Instruments horaires - Symbolisation des positions
de contrôle
Timekeeping instruments - Symbotization of control positions
Première édition - 1976-02-01
-
U
-
CDU 681.11 : 658.562 Réf. no : IS0 3158-1976 (F)
(D
Descripteurs : instrument de mesure du temps, orientation, symbole.
m
(?
s
Prix base sur 3 pages
r.
AVANT-PROPOS
L'ISO (Organisation Internationale de Normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (Comités Membres ISO). L'élaboration de
Normes Internationales est confiée aux Comités Techniques ISO. Chaque Comité
Membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du Comité Technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I'ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les Projets de Normes Internationales adoptés par les Comités Techniques sont
soumis aux Comités Membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme
Normes Internationales par le Conseil de I'ISO.
La Norme Internationale IS03158 a été établie par le Comité Technique
ISO/TC 114, Horlogerie, et soumise aux Comités Membres en avril 1975.
Elle a été approuvée par les Comités Membres des pays suivants :
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d' Japon Tchécoslovaquie
Allemagne Mexique Turquie
Espagne
Portugal U.R.S.S.
France Royaume-Uni
Irlande Suisse
Aucun Comité Membre n'a désapprouvé le document.
O Organisation Internationale de Normalisation, 1976 0
Imprimé en Suisse
IS0 3158-1976 (FI
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Instruments horaires - Symbolisation des positions
de contrôle
1 OBJET ET DOMAINE D'APPLICATION La plage de h est : O" < h < 360". (La plage de h est
comprise entre O" et une valeur inférieure à 360O.)
La présente Norme Internationale fixe les spécifications
b) 9 est l'angle de rotation de l'instrument horaire
concernant la définition et les désignations des positions
autour de l'axe perpendiculaire au plan ZX (figure 2).
d'essai pour tout instrument horaire, quels que soient son
sa construction et ses dimensions.
type,
19 > O' signifie une rotation du point momentanément le
plus haut du cadran lorsque ce point s'éloigne de
l'observateur.
2 DÉFINITION
I9 < O" signifie une rotation du point ci-dessus lorsque ce
point se rapproche de l'observateur.
La position d'un instrument horaire ou de son mouvement
se réfère à la direction Z qui est orientée dans le sens inverse
La plage de I9 est : ~- 90"
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...