ISO 8319-2:1986
(Main)Orthopaedic instruments — Drive connections — Part 2: Screwdrivers for single slot head screws, screws with cruciate slot and cross-recessed head screws
Orthopaedic instruments — Drive connections — Part 2: Screwdrivers for single slot head screws, screws with cruciate slot and cross-recessed head screws
The purpose is to ensure that the essential requirements of all screw keys are achieved without imposing undue restriction on design features. This standard specifies the requirements for screwdrivers used in orthopaedic surgery for inserting and removing bone screws. Screw keys with the working end specified are suitable for use with screws which conform to ISO 9268.
Instruments orthopédiques — Raccords d'entraînement — Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue, à empreinte en croix et à empreinte cruciforme
La présente partie de l'ISO 8319 spécifie les exigences requises pour les tournevis utilisés en chirurgie orthopédique, pour insérer et enlever des vis pour os à tête fendue, à empreinte en croix et à empreinte cruciforme. Les tournevis définis dans la présente partie de l'ISO 8319 sont prévus pour être utilisés avec des vis conformes à l'ISO 9268.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 08-Oct-1986
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 28-Aug-2023
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 8319-2:1986 specifies requirements for screwdrivers used in orthopaedic surgery to insert and remove bone screws with single-slot heads, cruciate slots and cross-recessed (modified Phillips) heads. The standard focuses on drive connections and screwdriver bits - defining shapes, dimensions, materials, mechanical performance and marking - while avoiding undue restrictions on design. Screwdrivers covered are intended for use with bone screws that conform to ISO 9268.
Key topics and technical requirements
- Design and dimensions
- Defines bit geometries for hand and power-driven screwdrivers for single-slot, cruciate and cross-recessed heads.
- Includes dimension tables and figures for bit shapes, flutes and recess profiles (see Table 1 and figures in the standard).
- Materials and hardness
- Blade materials specified include martensitic stainless steel (e.g., grades from ISO 683/13) and cold-worked cobalt‑chromium‑tungsten‑nickel alloys (ISO 5832/5).
- Rockwell hardness ranges are given (e.g., stainless steel ~48–54 HRC; cobalt‑chromium alloys ~48–50 HRC).
- Mechanical performance and testing
- Torque and torsion testing procedures for blades, bits and complete screwdrivers are defined (including use of torque-testing dies).
- The blade-to-handle connection must withstand specified test torques without loosening, fracture or permanent deformation (the text includes a test torque example of 9.7 N·m).
- Slot/drive test discs and dimensional tolerances are specified in relation to ISO 2380 and related test methods.
- Marking
- Required permanent markings include intended screw size (code and thread diameter per ISO 9263), manufacturer name/trademark, ISO 8319 part number (if space) and material (if space).
Applications and users
- Who uses ISO 8319-2
- Medical device manufacturers that design and produce orthopaedic screwdrivers and driving tools.
- Surgical instrument designers and quality engineers responsible for acceptance testing and compliance.
- Hospitals, procurement and sterile services teams specifying compliant instruments for orthopaedic procedures.
- Test laboratories that validate mechanical and material properties of surgical screwdrivers.
- Practical value
- Ensures interchangeability and reliable engagement between drive tools and bone screws.
- Reduces risk of tool failure during surgery by specifying materials, hardness and torque resistance.
- Supports regulatory compliance and consistent manufacturing quality.
Related standards
- ISO 9268 (metal bone screws - dimensions)
- ISO 2380 (screwdriver blades for slotted head screws)
- ISO 683/13 (heat-treated and wrought stainless steels)
- ISO 5832/5 (wrought cobalt‑chromium‑tungsten‑nickel alloy)
- ISO 6508 / ISO 6568 (hardness and test methods)
- ISO 9263 (screw size coding and marking)
Keywords: ISO 8319-2, orthopaedic instruments, drive connections, screwdrivers, bone screws, single-slot, cruciate, cross-recessed, surgical instruments, torque test, medical device standards.
ISO 8319-2:1986 - Orthopaedic instruments -- Drive connections
ISO 8319-2:1986 - Instruments orthopédiques -- Raccords d'entraînement
ISO 8319-2:1986 - Instruments orthopédiques -- Raccords d'entraînement
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

BSI Group
BSI (British Standards Institution) is the business standards company that helps organizations make excellence a habit.

TÜV Rheinland
TÜV Rheinland is a leading international provider of technical services.

TÜV SÜD
TÜV SÜD is a trusted partner of choice for safety, security and sustainability solutions.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 8319-2:1986 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Orthopaedic instruments — Drive connections — Part 2: Screwdrivers for single slot head screws, screws with cruciate slot and cross-recessed head screws". This standard covers: The purpose is to ensure that the essential requirements of all screw keys are achieved without imposing undue restriction on design features. This standard specifies the requirements for screwdrivers used in orthopaedic surgery for inserting and removing bone screws. Screw keys with the working end specified are suitable for use with screws which conform to ISO 9268.
The purpose is to ensure that the essential requirements of all screw keys are achieved without imposing undue restriction on design features. This standard specifies the requirements for screwdrivers used in orthopaedic surgery for inserting and removing bone screws. Screw keys with the working end specified are suitable for use with screws which conform to ISO 9268.
ISO 8319-2:1986 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 11.040.40 - Implants for surgery, prosthetics and orthotics. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 8319-2:1986 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standar
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEIKAYHAPO~HAR OPl-AHkl3AL&lR fl0 CTAHAAPTM3A~l4kl*ORGANISATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATlON
Orthopaedic instruments - Drive connections -
Part 2: Screwdrivers for Single slot head screws, screws
with cruciate slot and Cross-recessed head screws
Instruments orthopediques - Ratcords d’en tralnemen t - Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis 5 t&e fendue, A empreinte en croix et 2
emprein te cruciforme
First edition - 1986-10-15
UDC 621.883.7 : 615.465 Ref. No. ISO 8319/2-1986 (E)
Descriptors : medical equipment, surgical implants, screwed connections, slotted head screws, cross recessed screws, surgical equipment,
screwdrivers, specifications, dimensions, dimensional tolerantes, tests, torsion tests, test equipment, marking .
Price based on 8 pages
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International
’
Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Esch member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in Iiaison with ISO, also take patt in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the ISO Council. They are approved in accordance with ISO procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard ISO 8319/2 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 150,
lmplan ts for surgery.
Users should note that all International Standards undergo revision from time to time
and that any reference made herein to any other International Standard implies its
latest edition, unless otherwise stated.
0 International Organkation for Standardization, 1986
Printed in Switzerland
ISO 8319/2-1986 (E)
INTERNATIONALSTANDARD
Orthopaedic instruments - Drive connections -
Part 2: Screwdrivers for Single slot head screws, screws
with cruciate slot and Cross-recessed head screws
0 Introduction screws with Single slot heads, with cruciate slot or cross-
recessed heads.
Essential requirements for all varieties of screwdrivers are the
following : Screwdrivers specified in this part of ISO 8319 are suitable for
use with screws which conform to ISO 9268.
-
the Point should accurately engage the head of the
screw ;
2 References
-
the materials used for the manufacture of the blade
should be satisfactory from all clinical aspects;
ISO 683/13, Heat-treated steels, alloy steels and free-cutting
-
s teels - Part 73: Wrought stainless steels.
the screwdriver should have adequate strength.
ISO 2380, Screwdriver blades for slotted head screws. 1)
The purpose of this part of ISO 8319 is to ensure that this is
achieved without imposing undue restriction on design
ISO 583215, lmplan ts for surgery - Metallic materials -
features.
Part 5: Wrought Cobalt-chromium- tungsten-nicke1 alloy.
ISO 6508, Metallic materials - Hardness test - Rockwell test
1 Scope and field of application
(scales A - 6 - C - D - E - F - G - H - Kl. 2)
This part of ISO 8319 specifies requirements for screwdrivers
ISO 9268, lmplants for surgery - Metal bone screws - Dimen-
used in orthopaedic surgery for inserting and removing bone
sions - Screws with conical under-surfaces. 3)
1) At present at the Stage of draft. (Revision of ISO 2380-1979.)
2) At present at the Stage of draft. (Revision of ISO/R 80-1968 and ISO 2713-1973.)
3) At present at the Stage of draft. (Revision of ISO/DIS 5835/3 and ISO 5835/4-1983.) See the annex for information on the interrelationship be-
tween International Standards dealing with bone screws, bone plates and relevant tools.
ISO 8319/2-1986 (El
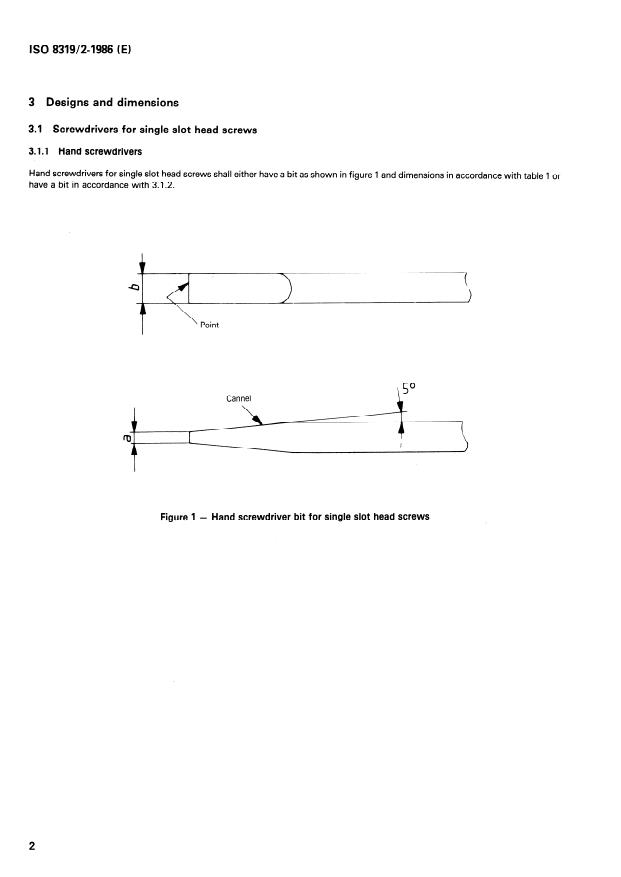
3 Designs and dimensions
3.1 Screwdrivers for Single slot head screws
3.1 .l Hand screwdrivers
Hand screwdrivers for Single slot head screws shall either have a bit as shown in figure 1 and dimensions in accordance with table 1 or
have a bit in accordance with 3.1.2.
’ Point
Cannel
Figure 1 - Hand screwdriver bit forsingle slot head screws
ISO 8319/2-1986 (El
3.1.2 Power-driven screwdrivers
Power-driven screwdrivers for Single slot head screws shall have a bit as shown in figure 2 and dimensions in accordance with table 1.
Dimensions in millimetres
0,3 x 45O
L -e
Figure 2 - Power-driven screwdriver bit for Single slot head screws
3.2 Screwdrivers for screws with cruciate slot
Screwdrivers for screws with cruciate slot shall have a bit as shown in figure 3 and dimensions in accordance with table 1.
I
I
*a
+l
Figure 3 - Screwdriver for screws with cruciate slot
Table 1 - Dimensions of screwdriver bit
Dimensions in millimetres
$=$+q
Screws in accordance with ISO 9268
+ 0,03
max.
- 0,07
HC 2,9
lt1 4,8
HC 3 5* HC 3 9; HC 4,2
“’ 1 5r6 1 HD 4: #D 4,;
IsO8319/2-1986 (EI
3.3 Screwdrivers for Cross-recessed head screws 1)
Screwdrivers for Cross-recessed head screws shall have a bit as shown in figure 4 and dimensions in accordance with figure 4.
Dimensions in millimetres
Blending of flutes
dependent on method
of manufacture
0 true form
4 flutes equispaced
+8'+l,
Figure 4 - Screwdriver bit for Cross-recessed head screw
1) These screws are also widely known as “modified Phillips scre
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.ME)I(L1YHAPO~HAR OPTAHM3AUklR Il0 CTAH~APTM3AUMM~ORGANISAilON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Instruments orthopédiques - Raccords d’entraînement -
Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue, à empreinte en
croix et à empreinte cruciforme
Orthopaedic instruments - Drive connections - Part 2: Screwdrivers for singfe slot head screws, screws with cruciate slot and
cross-recessed head screws
Première édition - 1986-1045
Eil:
Y
CDU 621.683.7 : 615.465
Réf. no : ISO 6319/2-1966 (F)
Descripteurs : matériel médical, implant chirurgical, raccord à visser, vis à tête fendue, vis à empreinte cruciforme, matériel chirurgical, tournevis,
spécification, dimension, tolérance de dimension, essai, essai de torsion, matériel d’essai, marquage.
Prix basé sur 8 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requiérent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 8319/2 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 150, lmplants chirurgicaux.
L’attention des utilisateurs est attirée sur le fait que toutes les Normes internationales
sont de temps en temps soumises à révision et que toute référence faite à une autre
Norme internationale dans le présent document implique qu’il s’agit, sauf indication
contraire, de la dernière édition.
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1986
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 8319/2-1986 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Raccords d’entraînement -
Instruments orthopédiques -
Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue, à empreinte en
croix et à empreinte cruciforme
0 Introduction Les tournevis définis dans la présente partie de I’ISO 8319 sont
prévus pour être utilisés avec des vis conformes à I’ISO 9268.
Les conditions essentielles requises pour toutes les variétés de
tournevis sont les suivantes :
-
la pointe devrait s’engager à fond dans la tête de la vis;
2 Références
-
les matériaux utilisés pour la fabrication de la lame
ISO 683/ 13, Aciers pour traitement thermique, aciers allies et
devraient donner satisfaction à tous points de vue sur le
plan clinique; aciers pour décolletage - Partie 73: Aciers corroyes inoxyda-
bles.
-
le tournevis devrait présenter une résistance mécanique
suffisante.
ISO 2380, Lames de tournevis pour vis à tête fenduel).
L’objet de la présente partie de I’ISO 8319 est de permettre de
remplir ces conditions sans apporter d’entraves injustifiées à la
ISO 503215, lmplants chirurgicaux - Produits à base de
conception des outils.
métaux -
Partie 5: Alliage à forger à base de cobalt, de
chrome, de tungstene et de nickel.
1 Objet et domaine d’application
ISO 6508, Materiaux métalliques - Essai de dureté - Essai
Rockwell (échelles A - B-C-D-E-F-G-%-K).2
La présente partie de I’ISO 8319 spécifie les exigences requises
pour les tournevis utilisés en chirurgie orthopédique, pour insé-
rer et enlever des vis pour os à tête fendue, à empreinte en croix
ISO 9268, lmplants chirurgicaux - Vis métalliques pour os -
et à empreinte cruciforme.
Vis à embase conique. 3)
1) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO 2380-1979.)
2) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO/R 80-1968 et de I’ISO 2713-1973.)
3) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO/DIS 5835/3 et de I’ISO 5835/4-1983.) Pour la relation entre les Normes internationales traitant
des vis et plaques pour os ainsi que des instruments correspondants, voir l’annexe.
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
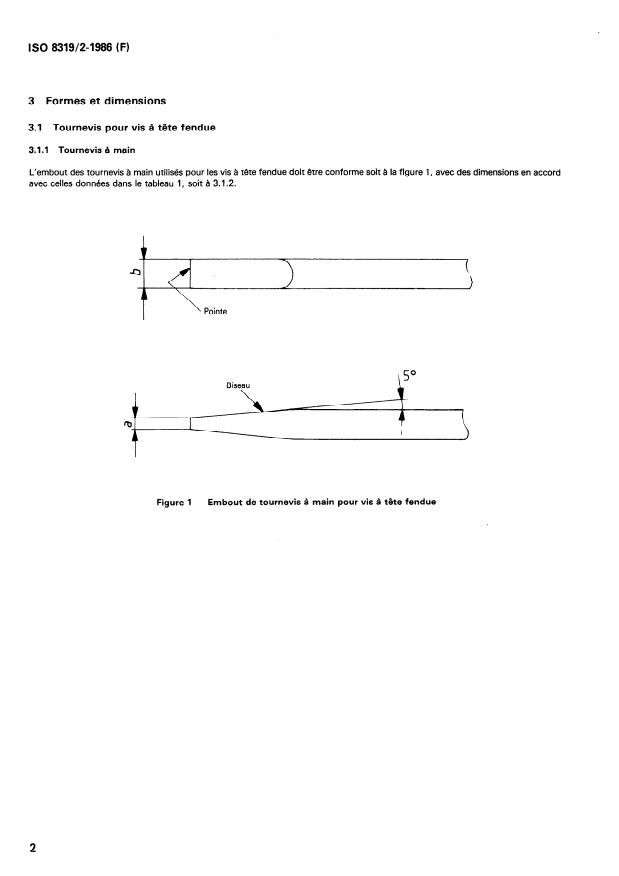
3 Formes et dimensions
3.1 Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue
3.1.1 Tournevis à main
L’embout des tournevis à main utilisés pour les vis à tête fendue doit être conforme soit à la figure 1, avec des dimensions en accord
avec celles données dans le tableau 1, soit à 3.1.2.
Figure 1 - Embout de tournevis à main pour vis à tête fendue
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
3.1.2 Tournevis à machine
L’embout des tournevis à machine utilisés pour les vis à tête fendue doit être conforme à la figure 2 et avoir des dimensions en accord
avec celles données dans le tableau 1.
Dimensions en millimètres
-F
i
Figure 2 - Embout de tournevis à machine pour vis à tête fendue
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
3.2 Tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte en croix
L’embout des tournevis utilisés pour les vis à tête à empreinte en croix doit être conforme à la figure 3 et avoir des dimensions en
accord avec celles données dans le tableau 1.
I
Q
+
I
t
I l
-4-b
Figure 3 - Embout de tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte en croix
Tableau 1 - Dimensions des embouts de tournevis
Dimensions en millimètres
Vis conformes à I’ISO 9268
HC 2,9
l,l 43
I I I
3.3 Tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciformel)
L’embout des tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciforme doit être conforme à la figure 4.
Dimensions en millimètres
4 cannelures
18"~0
espacées de 90°
ppp
--=T- Il
/I
Figure 4 - Embout de tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciforme
1) Ces vis sont également très connues sous l’appellation wis à tête à empreinte Phillips modifiée)).
----------------------
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.ME)I(L1YHAPO~HAR OPTAHM3AUklR Il0 CTAH~APTM3AUMM~ORGANISAilON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Instruments orthopédiques - Raccords d’entraînement -
Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue, à empreinte en
croix et à empreinte cruciforme
Orthopaedic instruments - Drive connections - Part 2: Screwdrivers for singfe slot head screws, screws with cruciate slot and
cross-recessed head screws
Première édition - 1986-1045
Eil:
Y
CDU 621.683.7 : 615.465
Réf. no : ISO 6319/2-1966 (F)
Descripteurs : matériel médical, implant chirurgical, raccord à visser, vis à tête fendue, vis à empreinte cruciforme, matériel chirurgical, tournevis,
spécification, dimension, tolérance de dimension, essai, essai de torsion, matériel d’essai, marquage.
Prix basé sur 8 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requiérent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 8319/2 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 150, lmplants chirurgicaux.
L’attention des utilisateurs est attirée sur le fait que toutes les Normes internationales
sont de temps en temps soumises à révision et que toute référence faite à une autre
Norme internationale dans le présent document implique qu’il s’agit, sauf indication
contraire, de la dernière édition.
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1986
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 8319/2-1986 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Raccords d’entraînement -
Instruments orthopédiques -
Partie 2: Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue, à empreinte en
croix et à empreinte cruciforme
0 Introduction Les tournevis définis dans la présente partie de I’ISO 8319 sont
prévus pour être utilisés avec des vis conformes à I’ISO 9268.
Les conditions essentielles requises pour toutes les variétés de
tournevis sont les suivantes :
-
la pointe devrait s’engager à fond dans la tête de la vis;
2 Références
-
les matériaux utilisés pour la fabrication de la lame
ISO 683/ 13, Aciers pour traitement thermique, aciers allies et
devraient donner satisfaction à tous points de vue sur le
plan clinique; aciers pour décolletage - Partie 73: Aciers corroyes inoxyda-
bles.
-
le tournevis devrait présenter une résistance mécanique
suffisante.
ISO 2380, Lames de tournevis pour vis à tête fenduel).
L’objet de la présente partie de I’ISO 8319 est de permettre de
remplir ces conditions sans apporter d’entraves injustifiées à la
ISO 503215, lmplants chirurgicaux - Produits à base de
conception des outils.
métaux -
Partie 5: Alliage à forger à base de cobalt, de
chrome, de tungstene et de nickel.
1 Objet et domaine d’application
ISO 6508, Materiaux métalliques - Essai de dureté - Essai
Rockwell (échelles A - B-C-D-E-F-G-%-K).2
La présente partie de I’ISO 8319 spécifie les exigences requises
pour les tournevis utilisés en chirurgie orthopédique, pour insé-
rer et enlever des vis pour os à tête fendue, à empreinte en croix
ISO 9268, lmplants chirurgicaux - Vis métalliques pour os -
et à empreinte cruciforme.
Vis à embase conique. 3)
1) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO 2380-1979.)
2) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO/R 80-1968 et de I’ISO 2713-1973.)
3) Actuellement au stade de projet. (Révision de I’ISO/DIS 5835/3 et de I’ISO 5835/4-1983.) Pour la relation entre les Normes internationales traitant
des vis et plaques pour os ainsi que des instruments correspondants, voir l’annexe.
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
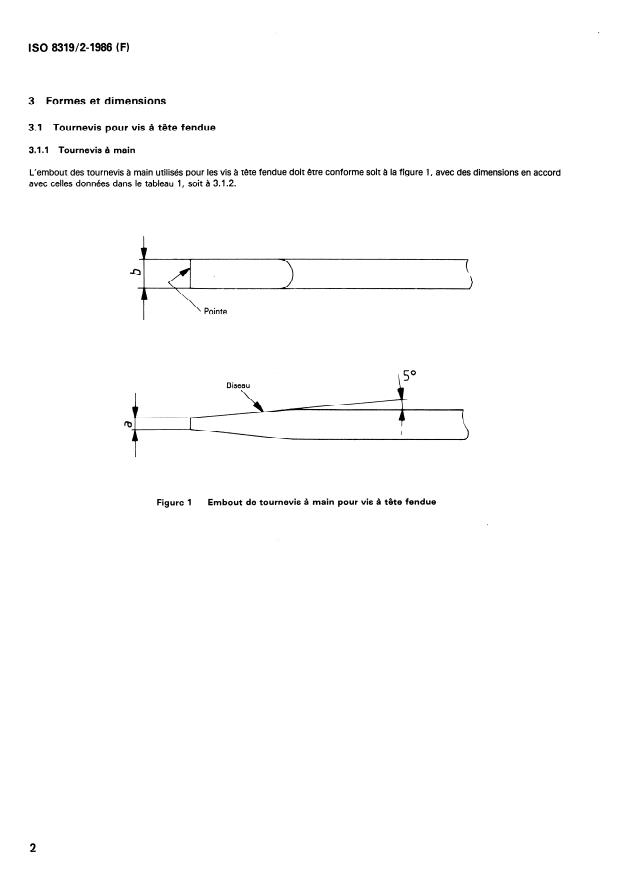
3 Formes et dimensions
3.1 Tournevis pour vis à tête fendue
3.1.1 Tournevis à main
L’embout des tournevis à main utilisés pour les vis à tête fendue doit être conforme soit à la figure 1, avec des dimensions en accord
avec celles données dans le tableau 1, soit à 3.1.2.
Figure 1 - Embout de tournevis à main pour vis à tête fendue
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
3.1.2 Tournevis à machine
L’embout des tournevis à machine utilisés pour les vis à tête fendue doit être conforme à la figure 2 et avoir des dimensions en accord
avec celles données dans le tableau 1.
Dimensions en millimètres
-F
i
Figure 2 - Embout de tournevis à machine pour vis à tête fendue
ISO 8319/2-1986 (FI
3.2 Tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte en croix
L’embout des tournevis utilisés pour les vis à tête à empreinte en croix doit être conforme à la figure 3 et avoir des dimensions en
accord avec celles données dans le tableau 1.
I
Q
+
I
t
I l
-4-b
Figure 3 - Embout de tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte en croix
Tableau 1 - Dimensions des embouts de tournevis
Dimensions en millimètres
Vis conformes à I’ISO 9268
HC 2,9
l,l 43
I I I
3.3 Tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciformel)
L’embout des tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciforme doit être conforme à la figure 4.
Dimensions en millimètres
4 cannelures
18"~0
espacées de 90°
ppp
--=T- Il
/I
Figure 4 - Embout de tournevis pour vis à tête à empreinte cruciforme
1) Ces vis sont également très connues sous l’appellation wis à tête à empreinte Phillips modifiée)).
----------------------
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...