ISO 5838-3:1993
(Main)Implants for surgery — Skeletal pins and wires — Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires
Implants for surgery — Skeletal pins and wires — Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires
Specifies the characteristics (dimensions, ends, marking and packaging) of Kirschner wires. Material and mechanical requirements are covered by ISO 5838-1.
Implants chirurgicaux — Fils et broches pour os — Partie 3: Fils pour os de type Kirschner
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 15-Sep-1993
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 150/SC 5 - Osteosynthesis and spinal devices
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 28-Aug-2023
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Overview
ISO 5838-3:1993 - Implants for surgery - Skeletal pins and wires - Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires specifies the dimensional and product-characteristic requirements for Kirschner (K‑) wires used as surgical skeletal implants. The standard covers wire dimensions, tip/end shapes, marking and packaging. Material and mechanical property requirements are handled separately in ISO 5838‑1.
Key topics
- Scope: Defines characteristics for Kirschner skeletal wires (K‑wires) - not material/mechanical properties.
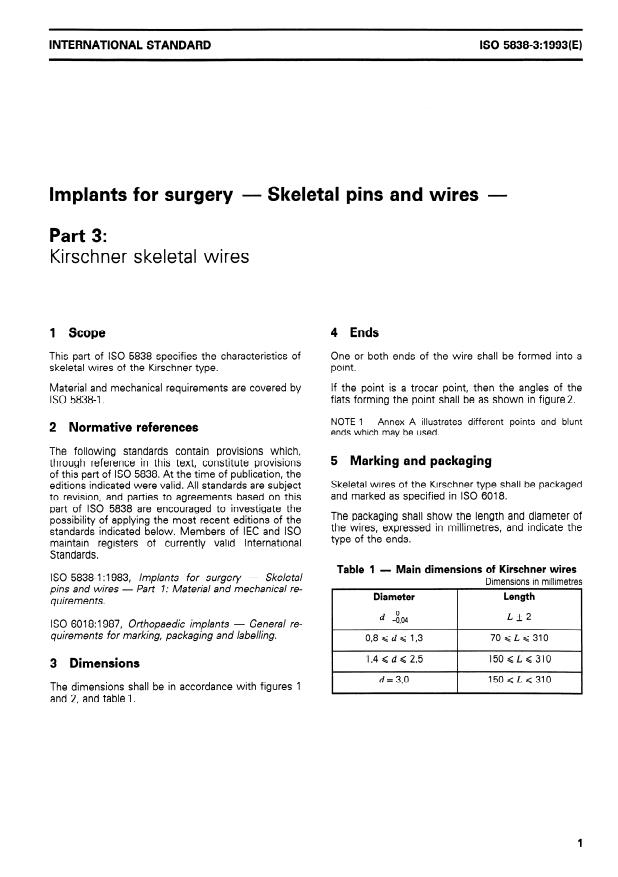
- Dimensions: Prescribes wire diameter and length ranges. Examples from the standard:
- 0.8 mm < d < 1.3 mm → 70 mm < L < 310 mm
- 1.4 mm < d < 2.5 mm → 150 mm < L < 310 mm
- d = 3.0 mm → 150 mm < L < 310 mm
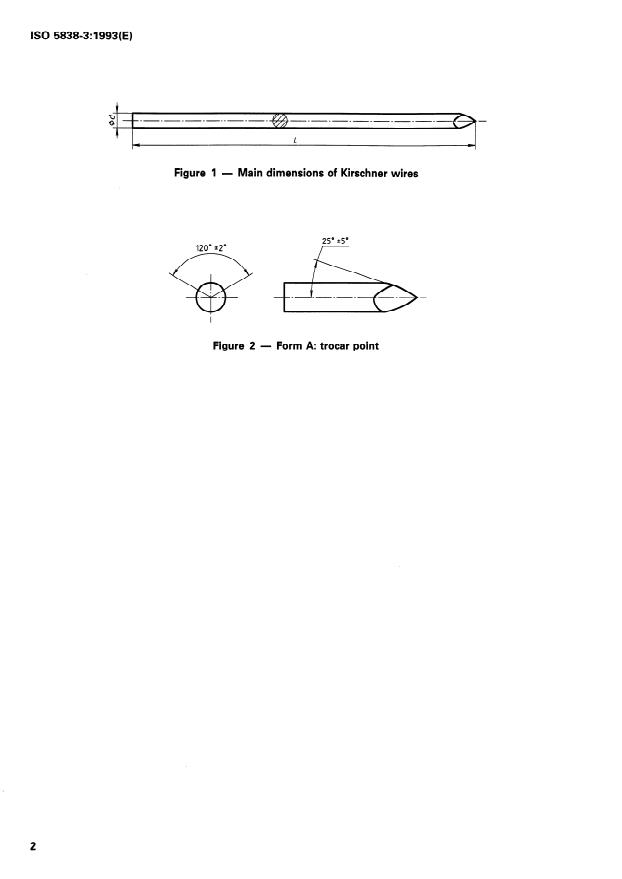
- Tip and end forms: One or both ends may be pointed; trocart-type points have specific angular requirements (illustrated in the standard). Annex A (informative) shows common tip/end variations (e.g., trocart, bayonet, Crowe, drill, Bechtol, Haynes) and notes on hooked or threaded ends.
- Marking and packaging: Packaging and marking must comply with ISO 6018 and include length and diameter in millimetres plus the tip type.
- Informative notes: Allowable options include smooth or threaded hooking ends, manufacturer-specified point/helix angles, and optional designs such as double-pointed wires or a point with a suture hole.
Applications
ISO 5838-3 is intended for practical use where consistent physical specifications for Kirschner wires are required:
- Manufacturers - to design, produce and document K‑wires that meet international dimensional and labeling conventions.
- Quality and regulatory teams - to verify conformity of products during inspection and to support technical files for medical device approvals.
- Procurement and clinical engineering - to specify and purchase K‑wires with clear dimensional and packaging information.
- Testing laboratories - to ensure samples are measured and identified consistently during acceptance or comparative testing.
- Orthopaedic surgeons and hospitals - for clarity about the physical features (length, diameter, tip type) they select for fixation procedures.
Related standards
- ISO 5838‑1 - Implants for surgery - Materials and mechanical properties for skeletal pins and wires.
- ISO 5838‑2 - Steinmann pins - dimensions (other part of the ISO 5838 series).
- ISO 6018 - General requirements for marking, packaging and labelling of orthopaedic implants.
Keywords: ISO 5838-3:1993, Kirschner wires, K‑wires, skeletal pins and wires, implants for surgery, dimensions, marking, packaging, ISO 5838-1, ISO 6018, orthopaedic implants.
ISO 5838-3:1993 - Implants for surgery -- Skeletal pins and wires
ISO 5838-3:1993 - Implants chirurgicaux -- Fils et broches pour os
ISO 5838-3:1993 - Implants chirurgicaux -- Fils et broches pour os
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

BSI Group
BSI (British Standards Institution) is the business standards company that helps organizations make excellence a habit.

TÜV Rheinland
TÜV Rheinland is a leading international provider of technical services.

TÜV SÜD
TÜV SÜD is a trusted partner of choice for safety, security and sustainability solutions.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 5838-3:1993 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Implants for surgery — Skeletal pins and wires — Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires". This standard covers: Specifies the characteristics (dimensions, ends, marking and packaging) of Kirschner wires. Material and mechanical requirements are covered by ISO 5838-1.
Specifies the characteristics (dimensions, ends, marking and packaging) of Kirschner wires. Material and mechanical requirements are covered by ISO 5838-1.
ISO 5838-3:1993 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 11.040.40 - Implants for surgery, prosthetics and orthotics. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 5838-3:1993 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL
ISO
STANDARD
5838-3
First edition
1993-09-15
lmplants for surgery - Skeletal pins and
wires -
Part 3:
Kirschner skeletal wires
Implants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches pour OS -
Partie 3: Fils pour OS de type Kirschner
Reference number
ISO 5838-3: 1993(E)
ISO 5838-3: 1993(E)
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work
of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Esch member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be re-
presented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take patt in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(1 EC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 5838-3 was prepared by Technical Committee
ISOfTC 150, Implants for surgery, Sub-Committee SC 5, Osteosynthesis.
ISO 5838 consists of the following Parts, under the general title Implants
for surgery - Skeletal pins and wires:
- Part 1: Material and mechanical requiremen ts
- Part 2: Steinmann skeletal pins - Dimensions
- Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires
Annex A of this part of ISO 5838 is for information only.
0 ISO 1993
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or
by any means, electronie or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without per-
mission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-1 211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
ISO 5838=3:1993(E)
Implants for surgery
- Skeletal pins and wires -
Part 3:
Kirschner skeletal wires
1 Scope 4 Ends
This part of ISO 5838 specifies the characteristics of
One or both ends of the wire shall be formed into a
skeletal wires of the Kirschner type. Point.
Material and mechanical requirements are covered by
If the Point is a trocar Point, then the angles of the
ISO
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 5838-3
Première édition
1993-09-15
lmplants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches
pour os -
Partie 3:
Fils pour os de type Kirschner
- Skeletal pins and wires -
Implants for surgery
Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires
Numéro de référence
ISO 5838=3:1993(F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une féderation
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comites membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
etude a le droit de faire partie du comite technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptes par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 5838-3 a été élaborée par le comité techni-
que ISODC 150, Implan ts chirurgicaux, sous-comité SC 5,
Ost&os yn thèse.
L’ISO 5838 comprend les parties suivantes, prése ntées sous le titre gé-
1 pour
néral Implants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches os:
- Partie 1: Matériaux et propriétés mécaniques
- Partie 2: Broches de type Steinmann - Dimensions
- Partie 3: Fils pour os de type Kirschner
L’annexe A de la présente partie de I’ISO 5838 est donnée uniquement à
titre d’information.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction réservés. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit. et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 5838-3: 1993(F)
Implants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches pour os -
Partie 3:
Fils pour os de type Kirschner
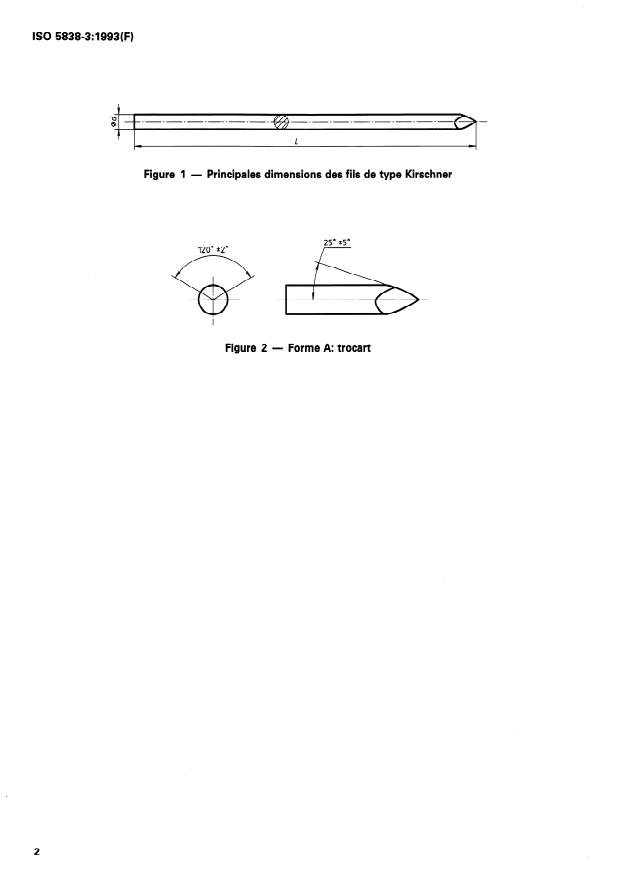
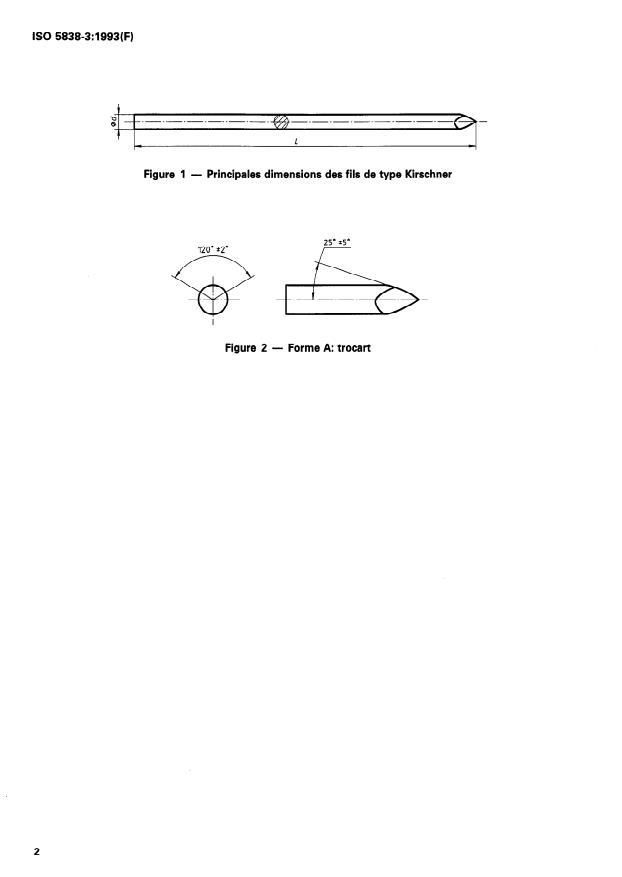
4 Extrémités
1 Domaine d’application
La présente partie de I’ISO 5838 prescrit les caracté-
Une (ou les deux) extrémité(s) du fil doit (doivent)
ristiques des fils pour os de type Kirschner.
avoir la forme d’une pointe.
Les prescriptions relatives aux matériaux et aux pro-
Si la pointe est un trocart, les angles des plans for-
priétés mécaniques font l’objet de I’ISO 5838-l.
mant la pointe doivent être tels qu’indiqués à la
figure 2.
2 Référence
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 5838-3
Première édition
1993-09-15
lmplants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches
pour os -
Partie 3:
Fils pour os de type Kirschner
- Skeletal pins and wires -
Implants for surgery
Part 3: Kirschner skeletal wires
Numéro de référence
ISO 5838=3:1993(F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une féderation
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comites membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
etude a le droit de faire partie du comite technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptes par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 5838-3 a été élaborée par le comité techni-
que ISODC 150, Implan ts chirurgicaux, sous-comité SC 5,
Ost&os yn thèse.
L’ISO 5838 comprend les parties suivantes, prése ntées sous le titre gé-
1 pour
néral Implants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches os:
- Partie 1: Matériaux et propriétés mécaniques
- Partie 2: Broches de type Steinmann - Dimensions
- Partie 3: Fils pour os de type Kirschner
L’annexe A de la présente partie de I’ISO 5838 est donnée uniquement à
titre d’information.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction réservés. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit. et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 5838-3: 1993(F)
Implants chirurgicaux - Fils et broches pour os -
Partie 3:
Fils pour os de type Kirschner
4 Extrémités
1 Domaine d’application
La présente partie de I’ISO 5838 prescrit les caracté-
Une (ou les deux) extrémité(s) du fil doit (doivent)
ristiques des fils pour os de type Kirschner.
avoir la forme d’une pointe.
Les prescriptions relatives aux matériaux et aux pro-
Si la pointe est un trocart, les angles des plans for-
priétés mécaniques font l’objet de I’ISO 5838-l.
mant la pointe doivent être tels qu’indiqués à la
figure 2.
2 Référence
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...