IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999
(Amendment)Amendment 2 - Primary batteries - Part 1: General
Amendment 2 - Primary batteries - Part 1: General
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 18-Mar-1999
- Technical Committee
- TC 35 - Primary cells and batteries
- Current Stage
- DELPUB - Deleted Publication
- Start Date
- 20-Nov-2000
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
Overview
IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 is an important amendment to the international standard for primary batteries, specifically Part 1 which covers general requirements. Issued by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), this amendment focuses on defining and standardizing key aspects such as battery voltage interchangeability and the concept of standard discharge voltage. These updates enhance safety, consistency, and reliability of primary batteries used worldwide in various electronic devices.
This document is highly relevant for manufacturers, quality assurance professionals, and researchers involved in battery design and testing. It provides clear protocols on how to measure and categorize batteries according to their electrochemical characteristics.
Key Topics
Battery Voltage Interchangeability
The amendment establishes a formula to assess interchangeability of primary battery voltages based on their standard discharge voltage. Two primary voltage ranges are defined:- Voltage Range 1: Reference voltage 1.4 V, covering nominal 1.5 V batteries (systems A, F, G, L, P, S).
- Voltage Range 2: Reference voltage 3.2 V, covering nominal 3 V batteries (systems B, C, E).
Physical design differences are mandated to prevent interchangeability between these voltage ranges, ensuring safety by avoiding improper use.
Standard Discharge Voltage (SDV)
SDV is defined as a unique voltage characteristic of a battery's electrochemical system, independent of size or construction. Its determination is through a standardized method involving discharge capacity, time, and resistor values, detailed in annex C. This approach provides an experimentally verifiable and reproducible voltage metric critical for battery classification and compatibility checks.Safe Design and Operational Guidelines
The amendment warns of safety risks such as fire, leakage, and device damage if these voltage interchangeability requirements are not met. It stresses the importance of conformity to the standard to protect users and ensure proper device function.Measurement Methodology
Annex C describes the mathematical definitions and experimental protocols for determining the standard discharge voltage using the C/R-plot technique. This includes:- Discharge capacity versus resistance analysis
- Determination of the standard discharge resistor for 98% capacity realization
- Calculation of average discharge current and discharge time under defined cutoff voltages
Applications
Battery Manufacturing and Quality Control
Manufacturers can apply these standardized voltage definitions and testing methods to ensure battery compatibility and regulatory compliance. This supports market acceptance and interoperability of primary batteries.Device Design and Safety Testing
Electronic device designers can rely on these standards to select batteries that meet voltage interchangeability requirements, reducing the risk of device malfunction or safety hazards.Research and Development
Researchers developing new electrochemical systems can use the defined procedures for measuring and reporting standard discharge voltage, facilitating comparison and standardization of innovative battery technologies.Regulatory and Certification Bodies
Testing laboratories and certification agencies benefit from the clear guidance on voltage ranges and verification processes to assess battery conformity and user safety.
Related Standards
IEC 60086-2: Primary Batteries – Part 2: Physical and Electrical Specifications
Defines cutoff voltages referenced in this amendment and provides complementary testing protocols.IEC 60086 Series
The full series covers primary battery general requirements, electrical and mechanical details, safety, and environmental considerations.Battery Safety Standards (e.g., UL 2054, IEC 62133)
Address broader battery safety including rechargeable cells, complementing the primary battery specifications in IEC 60086-1.
By adhering to the IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 amendment, stakeholders ensure safer, more reliable primary batteries with harmonized voltage standards that support global interoperability and enhanced user protection.
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Intertek Testing Services NA Inc.
Intertek certification services in North America.

UL Solutions
Global safety science company with testing, inspection and certification.

ANCE
Mexican certification and testing association.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 is a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its full title is "Amendment 2 - Primary batteries - Part 1: General". This standard covers: Amendment 2 - Primary batteries - Part 1: General
Amendment 2 - Primary batteries - Part 1: General
IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 29.220.10 - Primary cells and batteries. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to IEC 60086-1:2000. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
IEC 60086-1:1996/AMD2:1999 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL IEC
STANDARD
60086-1
AMENDMENT 2
1999-03
Amendment 2
Primary batteries –
Part 1: General
Amendement 2
Piles électriques –
Partie 1: Généralités
IEC 1999 Copyright - all rights reserved
International Electrotechnical Commission 3, rue de Varembé Geneva, Switzerland
Telefax: +41 22 919 0300 e-mail: inmail@iec.ch IEC web site http://www.iec.ch
Commission Electrotechnique Internationale
PRICE CODE
F
International Electrotechnical Commission
For price, see current catalogue
– 2 – 60086-1 amend. 2 © IEC:1999(E)
FOREWORD
This amendment has been prepared by IEC technical committee 35: Primary cells and
batteries.
The text of this amendment is based on the following documents:
FDIS Report on voting
35/1090/FDIS 35/1097/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this amendment can be found in the report on
voting indicated in the above table.
A bilingual version of this amendment may be issued at a later date.
___________
Page 55
7.5 Off-load voltage limits
Add, after this subclause, the following new subclause 7.6:
7.6 Interchangeability: Battery voltage
Primary batteries as presently standardized in IEC 60086 can be categorized by their standard
1)
discharge voltage U . For a new battery system, its interchangeability by voltage is assessed
s
for compliance with the following formula:
n × (U – 15 %) < m × U < n × (U + 15 %)
r s r
where
n is the number of cells connected in series, based on reference voltage U
r;
m is the number of cells connected in series, based on standard discharge voltage U .
s
Currently two voltage ranges that conform to the above formula have been identified. They are
identified by reference voltage U , which is the midpoint of the relevant voltage range.
r
Voltage range 1, U = 1,4 (V): Batteries having a standard discharge voltage m × U equal to or
r s
within the range of n × 1,19 (V) to n × 1,61 (V)
Voltage range 2, U = 3,2 (V): Batteries having a standard discharge voltage m × U equal to or
r s
within the range of n × 2,72 (V) to n × 3,68 (V)
The term standard discharge voltage and related quantities, as well as the methods of their
determination, are given in annex C.
NOTE – For single-cell batteries and for multi-cell batteries assembled with cells of the same voltage range, m and
n will be identical; m and n will be different for multi-cell batteries if assembled with cells from a different voltage
range than those of an already standardized battery.
___________
1)
The standard discharge voltage U was introduced to comply with the principle of experimental verifiability.
s
Neither the nominal voltage nor the maximum off-load voltage complies with this requirement.
60086-1 Amend. 2 © IEC:1999(E) – 3 –
Voltage range 1 encompasses all presently standardized batteries with a nominal voltage of
about 1,5 (V), i.e. “no-letter” system, systems A, F, G, L, P and S.
Voltage range 2 encompasses all presently standardized batteries with a nominal voltage of
about 3 (V), i.e. systems B, C and E.
Because batteries from voltage range 1 and voltage range 2 show significantly different
discharge voltages, they shall be designed physically non-interchangeable. Before standard-
izing a new electrochemical system, its standard discharge voltage shall be determined in
accordance with the procedure given in annex C to resolve its interchangeability by voltage.
WARNING
Failure to comply with this requirement can present safety hazards to the user, such as
fire, explosion, leakage and/or device damage.
This requirement is necessary for safety and operational reasons.
Page 95
Add, after annex B, the new annex C as follows:
Annex C
(informative)
Standard discharge voltage – definition and method of determination
C.1 Definition
The standard discharge voltage U is typical for a given electrochemical system. It is a unique
s
voltage in that it is independent of both the size and the internal construction of the battery. It
only depends on its charge-transfer reaction. The standard discharge voltage U is defined by
s
the formula in (1):
C
s
=×
U R (1)
s s
t
s
where
U is the standard discharge voltage;
s
C is the standard discharge capacity;
s
t is the standard discharge time;
s
R is the standard discharge resistor.
s
– 4 – 60086-1 amend. 2 © IEC:1999(E)
C.2 Determination
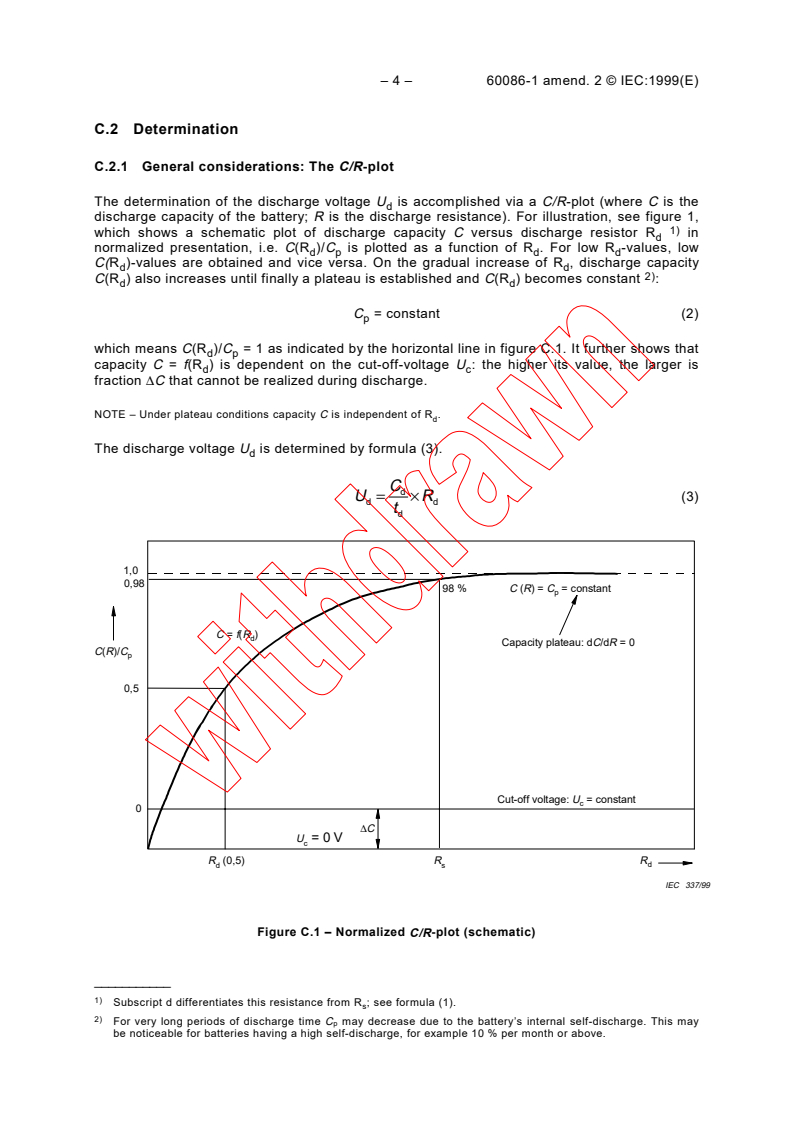
C/R
C.2.1 General considerations: The -plot
The determination of the discharge voltage U is accomplished via a C/R-plot (where C is the
d
discharge capacity of the battery; R is the discharge resistance). For illustration, see figure 1,
1)
which shows a schematic plot of discharge capacity C versus discharge resistor R in
d
normalized presentation, i.e. C(R )/C is plotted as a function of R . For low R -values, low
d p d d
C(R )-values are obtained and vice versa. On the gradual increase of R , discharge capacity
d d
2)
C(R ) also increases until finally a plateau is established and C(R ) becomes constant :
d d
C = constant (2)
p
which means C(R )/C = 1 as indicated by the horizontal line in figure C.1. It further shows that
d p
capacity C = f(R ) is dependent on the cut-off-voltage U : the higher its value, the larger is
d c
fraction ΔC that cannot
...



Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...