IEC 61850-7-3:2003
(Main)Communication networks and systems in substations - Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment - Common data classes
Communication networks and systems in substations - Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment - Common data classes
Specifies common attribute types and common data classes related to substation applications. Specifies particularly: common data classes for status information, for measured information, for controllable status information, for controllable analogue set point information, for status settings, for analogue settings and attribute types used in these common data classes. Is applicable to the description of device models and functions of substations and feeder equipment.
This publication is of core relevance for Smart Grid.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 11-May-2003
- Technical Committee
- TC 57 - Power systems management and associated information exchange
- Drafting Committee
- WG 10 - TC 57/WG 10
- Current Stage
- DELPUB - Deleted Publication
- Start Date
- 16-Dec-2010
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
Overview
IEC 61850-7-3:2003 defines the common data classes and attribute types used in substation and feeder equipment models. It is part of the IEC 61850 family for communication networks and systems in substations and is of core relevance to Smart Grid deployments. The standard specifies the semantic building blocks - status, measured, controllable and setting data classes - that vendors and utilities use to describe device models and functions consistently for protection, control, metering and automation.
Key Topics and Requirements
- Common data classes for status information (single/double point, integer status, protection activation, counters) and for measured values (analogue, complex, sampled, sequence and harmonic values).
- Controllable data classes for commandable status (SPC, DPC, INC) and analogue set points (APC), including models for step positions and pulses.
- Settings classes for status and analogue settings (SPG, ING, ASG, CURVE) and descriptive classes (device and logical node nameplate).
- Attribute types and semantics: standardized attributes such as quality flags, validity, source, test, originator, units, vectors and ranges. These ensure uniform interpretation of values across devices.
- Quality and state handling: definitions for detailed quality indicators, validity/substitution logic, client–server quality relations, and operator/blocked/test flags.
- Data attribute semantics: explicit semantics for each attribute to support unambiguous data modeling in substation IEDs and system software.
- Applicability: intended for describing device models and functions of substations and feeder equipment to enable interoperable data exchange.
Applications and Practical Value
- Enables consistent data modeling for Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs), relays, and substation controllers.
- Supports interoperability between vendors by standardizing attribute names, units and quality semantics.
- Used in designing and implementing substation automation, protection schemes, metering, and SCADA interfaces in Smart Grid environments.
- Useful for system integrators and test engineers when configuring, validating and commissioning IEC 61850-based systems.
- Facilitates software development for asset management, condition monitoring and analytics by providing clear data semantics.
Who Uses This Standard
- Utility engineers and protection & control teams
- IED and relay manufacturers
- System integrators and substation automation vendors
- Test and commissioning specialists
- Smart Grid architects and solution providers
Related Standards
- Part of the IEC 61850 family (other parts cover data models, services, communication mappings and sampled values). Implementers typically reference related IEC 61850 documents to complete protocol/service mappings and network integration.
Keywords: IEC 61850-7-3, common data classes, substation automation, Smart Grid, communication networks, feeder equipment, measured values, controllable status, data modeling, IED interoperability.
Buy Documents
iec61850-7-3{ed1.0}en - IEC 61850-7-3:2003 - Communication networks and systems in substations - Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment - Common data classes Released:5/12/2003 Isbn:2831869110
iec61850-7-Browsable-Models - IEC 61850-7-3:2003 - Communication networks and systems in substations - Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment - Common data classes Released:5/12/2003 Isbn:2831869110
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

TL 9000 QuEST Forum
Telecommunications quality management system.

ANCE
Mexican certification and testing association.

Intertek Slovenia
Intertek testing, inspection, and certification services in Slovenia.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
IEC 61850-7-3:2003 is a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its full title is "Communication networks and systems in substations - Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment - Common data classes". This standard covers: Specifies common attribute types and common data classes related to substation applications. Specifies particularly: common data classes for status information, for measured information, for controllable status information, for controllable analogue set point information, for status settings, for analogue settings and attribute types used in these common data classes. Is applicable to the description of device models and functions of substations and feeder equipment. This publication is of core relevance for Smart Grid.
Specifies common attribute types and common data classes related to substation applications. Specifies particularly: common data classes for status information, for measured information, for controllable status information, for controllable analogue set point information, for status settings, for analogue settings and attribute types used in these common data classes. Is applicable to the description of device models and functions of substations and feeder equipment. This publication is of core relevance for Smart Grid.
IEC 61850-7-3:2003 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 33.200 - Telecontrol. Telemetering. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
IEC 61850-7-3:2003 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to IEC 61850-7-3:2010. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
IEC 61850-7-3:2003 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL IEC
STANDARD
61850-7-3
First edition
2003-05
Communication networks and
systems in substations –
Part 7-3:
Basic communication structure
for substation and feeder equipment –
Common data classes
Reference number
Publication numbering
As from 1 January 1997 all IEC publications are issued with a designation in the
60000 series. For example, IEC 34-1 is now referred to as IEC 60034-1.
Consolidated editions
The IEC is now publishing consolidated versions of its publications. For example,
edition numbers 1.0, 1.1 and 1.2 refer, respectively, to the base publication, the
base publication incorporating amendment 1 and the base publication incorporating
amendments 1 and 2.
Further information on IEC publications
The technical content of IEC publications is kept under constant review by the IEC,
thus ensuring that the content reflects current technology. Information relating to
this publication, including its validity, is available in the IEC Catalogue of
publications (see below) in addition to new editions, amendments and corrigenda.
Information on the subjects under consideration and work in progress undertaken
by the technical committee which has prepared this publication, as well as the list
of publications issued, is also available from the following:
• IEC Web Site (www.iec.ch)
• Catalogue of IEC publications
The on-line catalogue on the IEC web site (http://www.iec.ch/searchpub/cur_fut.htm)
enables you to search by a variety of criteria including text searches, technical
committees and date of publication. On-line information is also available on
recently issued publications, withdrawn and replaced publications, as well as
corrigenda.
• IEC Just Published
This summary of recently issued publications (http://www.iec.ch/online_news/
justpub/jp_entry.htm) is also available by email. Please contact the Customer
Service Centre (see below) for further information.
• Customer Service Centre
If you have any questions regarding this publication or need further assistance,
please contact the Customer Service Centre:
Email: custserv@iec.ch
Tel: +41 22 919 02 11
Fax: +41 22 919 03 00
INTERNATIONAL IEC
STANDARD
61850-7-3
First edition
2003-05
Communication networks and
systems in substations –
Part 7-3:
Basic communication structure
for substation and feeder equipment –
Common data classes
IEC 2003 Copyright - all rights reserved
No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Electrotechnical Commission, 3, rue de Varembé, PO Box 131, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland
Telephone: +41 22 919 02 11 Telefax: +41 22 919 03 00 E-mail: inmail@iec.ch Web: www.iec.ch
PRICE CODE
Commission Electrotechnique Internationale
XB
International Electrotechnical Commission
Международная Электротехническая Комиссия
For price, see current catalogue
– 2 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
CONTENTS
FOREWORD . 6
INTRODUCTION .8
1 Scope . 9
2 Normative references. 9
3 Terms and definitions .10
4 Abbreviated terms.10
5 Conditions for attribute inclusion.10
6 Common data attribute types .11
6.1 General .11
6.2 Quality.11
6.2.1 Overview.11
6.2.2 Validity.12
6.2.3 Detail quality.12
6.2.4 Source .13
6.2.5 Test .14
6.2.6 Blocked by operator.14
6.2.7 Quality in the client server context .14
6.2.8 Relation between quality identifiers.15
6.3 Analogue value.17
6.4 Configuration of analogue value .17
6.5 Range configuration.18
6.6 Step position with transient indication .18
6.7 Pulse configuration .19
6.8 Originator .19
6.9 Unit definition .20
6.10 Vector definition.20
6.11 Point definition.21
6.12 CtlModels definition .21
6.13 SboClasses definition .21
7 Common data class specifications .21
7.1 General .21
7.2 Name spaces.21
7.3 Common data class specifications for status information .22
7.3.1 Basic status information template .22
7.3.2 Single point status (SPS) .22
7.3.3 Double point status (DPS).23
7.3.4 Integer status (INS).24
7.3.5 Protection activation information (ACT).24
7.3.6 Directional protection activation information (ACD) .25
7.3.7 Security violation counting (SEC).25
7.3.8 Binary counter reading (BCR) .26
7.4 Common data class specifications for measurand information .27
7.4.1 Basic measurand information template.27
7.4.2 Measured value (MV).28
7.4.3 Complex measured value (CMV).29
7.4.4 Sampled value (SAV).30
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 3 –
7.4.5 Phase to ground related measured values of a three phase system (WYE) 31
7.4.6 Phase to phase related measured values of a three phase system (DEL).32
7.4.7 Sequence (SEQ).33
7.4.8 Harmonic Value (HMV) .34
7.4.9 Harmonic value for WYE (HWYE) .35
7.4.10 Harmonic value for DEL (HDEL).36
7.5 Common data class specifications for controllable status information .37
7.5.1 Application of services .37
7.5.2 Controllable single point (SPC) .38
7.5.3 Controllable double point (DPC).39
7.5.4 Controllable integer status (INC).40
7.5.5 Binary controlled step position information (BSC) .41
7.5.6 Integer controlled step position information (ISC).42
7.6 Common data class specifications for controllable analogue information .43
7.6.1 Application of services .43
7.6.2 Controllable analogue set point information (APC) .44
7.7 Common data class specifications for status settings.45
7.7.1 Application of services .45
7.7.2 Single point setting (SPG).45
7.7.3 Integer status setting (ING).46
7.8 Common data class specifications for analogue settings.47
7.8.1 Application of services .47
7.8.2 Analogue setting (ASG) .47
7.8.3 Setting curve (CURVE) .48
7.9 Common data class specifications for description information.49
7.9.1 Basic description information template.49
7.9.2 Device name plate (DPL) .49
7.9.3 Logical node name plate (LPL) .50
7.9.4 Curve shape description (CSD).50
8 Data attribute semantic.51
Annex A (normative) Value range for units and multiplier .60
Annex B (informative) Functional constraints.63
Figure 1 – Quality identifiers in a single client – server relationship.14
Figure 2 – Quality identifiers in a multiple client – server relationship.15
Figure 3 – Interaction of substitution and validity.16
Figure 4 – Configuration of command output pulse.19
Table 1 – Quality.11
Table 2 – Analogue value.17
Table 3 – Configuration of analogue value .17
Table 4 – Range configuration .18
Table 5 – Step position with transient indication.18
Table 6 – Pulse configuration.19
Table 7 – Originator .19
Table 8 – Values for orCat .20
– 4 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
Table 9 – Unit .20
Table 10 – Vector.20
Table 11 – Point.21
Table 12 – Name space attributes .22
Table 13 – Basic status information template .22
Table 14 – Single point status common data class definition .23
Table 15 – Double point status common data class specification.23
Table 16 – Integer status common data class specification .24
Table 17 – Protection activation information common data class specification.24
Table 18 – Directional protection activation information common data class specification .25
Table 19 – Security violation counting common data class specification.25
Table 20 – Binary counter reading common data class specification .26
Table 21 – Basic measurand information template .27
Table 22 – Measured value .28
Table 23 – Complex measured value.29
Table 24 – Sampled value.30
Table 25 – WYE .31
Table 26 – Delta.32
Table 27 – Sequence .33
Table 28 – Harmonic value.34
Table 29 – Harmonic values for WYE .35
Table 30 – Harmonic values for delta .36
Table 31 – Basic controllable status information template .37
Table 32 – Controllable single point .38
Table 33 – Controllable double point .39
Table 34 – Controllable integer status .40
Table 35 – Binary controlled step position information.41
Table 36 – Integer controlled step position information.42
Table 37 – Basic controllable analogue information template .43
Table 38– Controllable analogue set point information .44
Table 39 – Basic status setting template .45
Table 40 – Single point setting .45
Table 41 – Integer status setting .46
Table 42 – Basic analogue setting template .47
Table 43 – Analogue setting.47
Table 44 – Setting curve .48
Table 45 – Basic description information template.49
Table 46 – Device name plate common data class specification.49
Table 47 – Logical node name plate common data class specification.50
Table 48 – Curve shape description common data class specification .50
Table 49 – Semantics of data attributes .51
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 5 –
Table A.1 – SI units: base units.60
Table A.2 – SI units: derived units.60
Table A.3 – SI units: extended units .61
Table A.4 – SI units: industry specific units .61
Table A.5 – Multiplier .62
Table B.1 – Functional constraints .63
– 6 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION
____________
COMMUNICATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS IN SUBSTATIONS –
Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation
and feeder equipment – Common data classes
FOREWORD
1) The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is a worldwide organisation for standardisation comprising
all national electrotechnical committees (IEC National Committees). The object of the IEC is to promote
international co-operation on all questions concerning standardisation in the electrical and electronic fields. To
this end and in addition to other activities, the IEC publishes International Standards. Their preparation is
entrusted to technical committees; any IEC National Committee interested in the subject dealt with may
participate in this preparatory work. International, governmental and non-governmental organisations liaising
with the IEC also participate in this preparation. The IEC collaborates closely with the International
Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) in accordance with conditions determined by agreement between the
two organisations.
2) The formal decisions or agreements of the IEC on technical matters express, as nearly as possible, an
international consensus of opinion on the relevant subjects since each technical committee has representation
from all interested National Committees.
3) The documents produced have the form of recommendations for international use and are published in the form
of standards, technical specifications, technical reports or guides and they are accepted by the National
Committees in that sense.
4) In order to promote international unification, IEC National Committees undertake to apply IEC International
Standards transparently to the maximum extent possible in their national and regional standards. Any
divergence between the IEC Standard and the corresponding national or regional standard shall be clearly
indicated in the latter.
5) The IEC provides no marking procedure to indicate its approval and cannot be rendered responsible for any
equipment declared to be in conformity with one of its standards.
6) Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this International Standard may be the subject
of patent rights. The IEC shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
International Standard IEC 61850-7-3 has been prepared by IEC technical committee 57:
Power system control and associated communications.
The text of this standard is based on the following documents:
FDIS Report on voting
57/618/FDIS 57/635/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this standard can be found in the report on
voting indicated in the above table.
This publication has been drafted in accordance with the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 7 –
IEC 61850 consists of the following parts, under the general title Communication networks
and systems in substations.
Part 1: Introduction and overview
Part 2: Glossary
Part 3: General requirements
Part 4: System and project management
Part 5: Communication requirements for functions and device models
Part 6: Configuration description language for communication in electrical substations
related to IEDs
Part 7-1: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Principles
and models
Part 7-2: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Abstract
communication service interface (ACSI)
Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Common
data classes
Part 7-4: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Compatible
logical node classes and data classes
Part 8-1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Mappings to MMS (ISO/IEC
9506-1 and ISO/IEC 9506-2) and to ISO/IEC 8802-3
Part 9-1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Sampled values over serial
unidirectional multidrop point to point link
Part 9-2: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Sampled values over
ISO/IEC 8802-3
Part 10: Conformance testing
The content of this part of IEC 61850 is based on existing or emerging standards and
applications. In particular the definitions are based upon:
• the specific data types defined in IEC 60870-5-101 and IEC 60870-5-103;
• the common class definitions from the Utility Communication Architecture 2.0: Generic
Object Models for Substation & Feeder Equipment (GOMSFE) (IEEE TR 1550).
The committee has decided that the contents of this publication will remain unchanged until 2005.
At this date, the publication will be
• reconfirmed;
• withdrawn;
• replaced by a revised edition, or
• amended.
A bilingual version of this standard may be issued at a later date.
———————
Under consideration.
To be published.
– 8 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
INTRODUCTION
This document is part of a set of specifications, which details layered substation com-
munication architecture. This architecture has been chosen to provide abstract definitions of
classes and services such that the specifications are independent of specific protocol stacks
and objects. The mapping of these abstract classes and services to communication stacks is
outside the scope of IEC 61850-7-x and may be found in IEC 61850-8-x (station bus) and
IEC 61850-9-x (process bus).
IEC 61850-7-1 gives an overview of this communication architecture. This part of IEC 61850
defines common attribute types and common data classes related to substation applications.
These common data classes are used in IEC 61850-7-4. To define compatible data
classes, the attributes of the instances of data shall be accessed using services defined
in IEC 61850-7-2.
This part is used to specify the abstract common data class definitions. These abstract
definitions shall be mapped into concrete object definitions that are to be used for a particular
protocol (for example MMS, ISO 9506).
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 9 –
COMMUNICATION NETWORKS AND SYSTEMS IN SUBSTATIONS –
Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation
and feeder equipment – Common data classes
1 Scope
This part of IEC 61850 specifies common attribute types and common data classes related to
substation applications. In particular it specifies:
• common data classes for status information,
• common data classes for measured information,
• common data classes for controllable status information,
• common data classes for controllable analogue set point information,
• common data classes for status settings,
• common data classes for analogue settings and
• attribute types used in these common data classes.
This international standard is applicable to the description of device models and functions of
substations and feeder equipment.
This international standard may also be applied, for example, to describe device models and
functions for:
• substation to substation information exchange,
• substation to control centre information exchange,
• power plant to control centre information exchange,
• information exchange for distributed generation, or
• information exchange for metering.
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition
of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
IEC 61850-2, Communication networks and systems in substations – Part 2: Glossary
IEC 61850-7-1, Communication networks and systems in substations – Part 7-1: Basic
communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Principles and models
IEC 61850-7-2, Communication networks and systems in substations – Part 7-2: Basic
communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Abstract communication
service interface (ACSI)
IEC 61850-7-4, Communication networks and systems in substations – Part 7-4: Basic
communication structure for substation and feeder equipment – Compatible logical node
classes and data classes
ISO 1000, SI units and recommendations for the use of their multiples and of certain other units
———————
Under consideration.
– 10 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
3 Terms and definitions
Fur the purposes of this International Standard, the terms and definitions given in
IEC 61850-2 and 61850-7-2 apply.
4 Abbreviated terms
CDC Common Data Class
dchg Trigger option for data-change
dupd Trigger option for data-update
FC Functional Constraint
qchg Trigger option for quality-change
TrgOp trigger option
NOTE Abbreviations used for the identification of the common data classes and as names of the attributes are
specified in the specific Clauses of this document and are not repeated here.
5 Conditions for attribute inclusion
This Clause lists general conditions that specify the presence of an attribute.
Abbreviation Condition
M Attribute is mandatory.
O Attribute is optional.
PICS_SUBST Attribute is mandatory, if substitution is supported (for substitution, see IEC 61850-7-2).
GC_1 At least one of the attributes shall be present for a given instance of DATA.
GC_2 (n) All or none of the data attributes belonging to the same group (n) shall be present for a given
instance of DATA.
GC_CON A configuration data attribute shall only be present, if the (optional) specific data attributes to
which this configuration relates, is also present.
AC_LN0_M
The attribute shall be present if the data NamPlt belongs to LLN0; otherwise it may be optional.
AC_LN0_EX
The attribute shall be present only if the data NamPlt belongs to LLN0 (applies to ldNs in CDC
LPL only).
AC_DLD_M
The attribute shall be present, if LN name space of this LN deviates from the LN name space
referenced by ldNs of the logical device in which this LN is contained (applies to lnNs in CDC
LPL only).
AC_DLN_M
The attribute shall be present, if data name space of this data deviates from the data name
space referenced by either lnNs of the logical node in which the data is contained or ldNs of the
logical device in which the data is contained (applies to dataNs in all CDCs only).
AC_DLNDA_M
The attribute shall be present, if CDC name space of this data deviates from the CDC name
space referenced by either the dataNs of the data, the lnNs of the logical node in which the
data is defined or ldNs of the logical device in which the data is contained (applies to cdcNs
and cdcName in all CDCs only).
AC_SCAV The presence of the configuration data attribute depends on the presence of i and f of the
Analog Value of the data attribute to which this configuration attribute relates. For a given data
object, that attribute
1) shall be present, if both i and f are present,
2) shall be optional if only i is present and
3) is not required if only f is present
NOTE If only i is present in a device without floating point capabilities, the configuration
parameter may be exchanged offline.
———————
Under consideration.
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 11 –
Abbreviation Condition
AC_ST The attribute is mandatory, if the controllable status class supports status information.
AC_CO_M If the controllable status class supports control, this attribute is available and a mandatory
attribute.
AC_CO_O If the controllable status class supports control, this attribute is available and an optional
attribute.
AC_SG_M The attribute is mandatory, if setting group is supported.
AC_SG_O The attribute is optional, if setting group is supported.
AC_NSG_M The attribute is mandatory, if setting group is not supported.
AC_NSG_O The attribute is optional, if setting group is not supported.
AC_RMS_M The attribute is mandatory when the harmonics reference type is rms.
6 Common data attribute types
6.1 General
Common data attribute types are defined for the use in common data classes (CDC) in Clause 7.
IEC 61850-7-1 provides an overview of all IEC 61850-7 documents (IEC 61850-7-2, IEC
61850-7-3, and IEC 61850-7-4). IEC 61850-7-1 also describes the basic notation used in
IEC 61850-7-3 and the description of the relations between the IEC 61850-7 documents.
NOTE The common data attribute type "TimeStamp" is specified in IEC 61850-7-2.
6.2 Quality
6.2.1 Overview
Quality type shall be as defined in Table 1.
Table 1 – Quality
Quality Type Definition
Attribute Name Attribute Type Value/Value Range M/O/C
PACKED LIST
validity CODED ENUM good | invalid | reserved | questionable M
detailQual PACKED LIST M
overflow BOOLEAN M
outOfRange BOOLEAN M
badReference BOOLEAN M
oscillatory BOOLEAN M
failure BOOLEAN M
oldData BOOLEAN M
inconsistent BOOLEAN M
inaccurate BOOLEAN M
source CODED ENUM process | substituted M
DEFAULT process
test BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE M
operatorBlocked BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE M
The DEFAULT value shall be applied, if the functionality of the related attribute is not
supported. The mapping may specify to exclude the attribute from the message, if it is not
supported or if the DEFAULT value applies.
– 12 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
Quality shall be an attribute that contains information on the quality of the information from
the server. The different quality identifiers are not independent. Basically, there are the
following quality identifiers:
• validity;
• detail quality;
• source;
• test;
• blocked by operator.
NOTE The quality, as used within the scope of 61850, is related to the quality of the information from the server.
There may be a requirement that the client uses additional quality information within its local database. This is a
local issue and not part of the scope of IEC 61850. However, the quality of a client may have an impact on the
quality supplied by a server of a client – server relationship at a higher level (see Figure 3).
6.2.2 Validity
Validity shall be good, questionable or invalid.
good: The value shall be marked good if no abnormal condition of the acquisition function or
the information source is detected.
invalid: The value shall be marked invalid when an abnormal condition of the acquisition
function or the information source (missing or non-operating updating devices) is detected.
The value shall not be defined under this condition. The mark invalid shall be used to indicate
to the client that the value may be incorrect and shall not be used.
EXAMPLE If an input unit detects an oscillation of one input it will mark the related information as invalid.
questionable: The value shall be marked questionable if a supervision function detects an
abnormal behaviour, however the value could still be valid. The client shall be responsible for
determining whether or not values marked "questionable" should be used.
6.2.3 Detail quality
The reason for an invalid or questionable value of an attribute may be specified in more detail
with further quality identifiers. If one of these identifiers is set then validity shall be set to
invalid or questionable. The following Table shows the relation of the detailed quality
identifiers with invalid or questionable quality.
DetailQual Invalid Questionable
Overflow X
Out of Range X X
Bad Reference X X
Oscillatory X X
Failure X
Old data X
Inconsistent X
Inaccurate X
overflow: this identifier shall indicate a quality issue that the value of the attribute to which
the quality has been associated is beyond the capability of being represented properly (used
for measurand information only).
EXAMPLE A measured value may exceed the range that may be represented by the selected data type, for
example the data type is a 16-bit unsigned integer and the value exceeds 65535.
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 13 –
outOfRange: this identifier shall indicate a quality issue that the attribute to which the quality
has been associated is beyond a predefined range of values. The server shall decide if
validity shall be set to invalid or questionable (used for measurand information only).
EXAMPLE A measured value may exceed a predefined range, however the selected data type can still represent
the value, for example the data type is a 16-bit unsigned integer, the predefined range is 0 to 40 000, if the value is
between 40001 and 65535 it is considered to be out of range.
badReference: this identifier shall indicate that the value may not be a correct value due to a
reference being out of calibration. The server shall decide if validity shall be set to invalid or
questionable (used for measurand information and binary counter information only).
oscillatory: to prevent overloading of event driven communication channels, it is desirable to
detect and suppress oscillating (fast changing) binary inputs. If a signal changes in a defined
time (t ) twice in the same direction (from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0) then it shall be defined as an
osc
oscillation and the detail quality identifier “oscillatory” shall be set. If a configured numbers of
transient changes is detected, they shall be suppressed. In this time, the validity status
"questionable” shall be set. If the signal is still in the oscillating state after the defined number
of changes, the value shall be left in the state it was in when the oscillatory flag was set. In
this case, the validity status "questionable” shall be reset and “invalid” shall be set as long as
the signal is oscillating. If the configuration is such that all transient changes should be
suppressed, the validity status “invalid” shall be set immediately in addition to the detail
quality identifier “oscillatory” (used for status information only).
failure: this identifier shall indicate that a supervision function has detected an internal or
external failure.
oldData: a value shall be oldData if an update is not made during a specific time interval. The
value may be an old value that may have changed in the meantime. This specific time interval
may be defined by an allowed-age attribute.
NOTE "Fail silent" errors, where the equipment stops sending data will cause a oldData condition. In this case,
the last received information was correct.
inconsistent: this identifier shall indicate that an evaluation function has detected an
inconsistency.
inaccurate: this identifier shall indicate that the value does not meet the stated accuracy of
the source.
EXAMPLE The measured value of power factor may be noisy (inaccurate) when the current is very small.
6.2.4 Source
Source shall give information related to the origin of a value. The value may be acquired from
the process or be a substituted value.
process: the value is provided by an input function from the process I/O or is calculated from
some application function.
substituted: the value is provided by input of an operator or by an automatic source.
NOTE 1 Substitution may be done locally or via the communication services. In the second case, specific
attributes with a FC SV are used.
NOTE 2 There are various means to clear a substitution. As an example, a substitution that was done following an
invalid condition may be cleared automatically if the invalid condition is cleared. However, this is a local issue and
therefore not in the scope of this standard.
– 14 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
6.2.5 Test
Test shall be an additional identifier that may be used to classify a value being a test value
and not to be used for operational purposes. The processing of the test quality in the client
shall be a local issue. The bit shall be completely independent from the other bits within the
quality descriptor.
The test identifier should normally be propagated through all hierarchical levels.
6.2.6 Blocked by operator
operatorBlocked: this identifier shall be set if further update of the value has been blocked
by an operator. The value shall be the information that was acquired before blocking. If this
identifier is set then the identifier oldData of detailQual shall also be set.
NOTE Both an operator as well as an automatic function may block communication updating as well as input
updating. In both cases, detailQual.oldData will be set. If the blocking is done by an operator, then the identifier
operatorBlocked is set additionally. In that case, an operator activity is required to clear the condition.
EXAMPLE An operator may block the update of an input, to save the old value, if the auxiliary supply is switched
off.
6.2.7 Quality in the client server context
Information
source
Server Input
unit
Client
Communication
network
Invalid /
questionable
overFlow
Substituted outOfRange
badReference
oscillatory
failure
Questionable
oldData
IEC 808/03
Figure 1 – Quality identifiers in a single client – server relationship
The quality identifier shall reflect the quality of the information in the server, as it is supplied
to the client. Figure 1 shows potential sources that may influence the quality in a single client
– server relationship. "Information Source" is the (hardwired) connection of the process
information to the system. The information may be invalid or questionable as indicated in
Figure 1. Further abnormal behaviour of the information source may be detected by the input
unit. In that case, the input unit may keep the old data and flag it accordingly.
In a multiple client - server relationship, as shown in Figure 2, information may be acquired
over a communication link (with Client B). If that communication link is broken, client B will
detect that error situation and qualify the information as questionable/old data.
61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E) – 15 –
Information
source
Server A Input
unit
Client A
Communication
network
Communication
network
Client B
Questionable
oldData
IEC 809/03
Figure 2 – Quality identifiers in a multiple client – server relationship
In the multiple client-server relationship, the quality of the data received from server A shall
reflect both the quality of the server B (acquired with client B) as well as its own quality.
Therefore, handling of prioritisation of quality from different levels may require further
specification beyond that included in this standard. For the identifier validity, the value invalid
shall dominate over the value questionable, since this is the worst case. For the identifier
source, the higher level of the multiple client – server relationship shall dominate over the
lower level.
EXAMPLE Let A be the higher level and B the lower level. The quality from server B is invalid. If now the
communication fails (questionable, oldData) between server B and client B, the quality will remain invalid and not
become questionable, since the last information was not correct. Server A therefore will report the information as
invalid.
6.2.8 Relation between quality identifiers
Validity and source have a prioritised relation. If source is in the “process” state, then validity
shall determine the quality of the origin value. If source is in the “substitute” state, then
validity shall be overruled by the definition of the substituted value. This is an important
feature, since substitution is used to replace invalid values with substituted values that may
be used by the client such as good values.
EXAMPLE 1 If both questionable and substituted are set, this means that the substituted value is questionable.
This may happen if, in a hierarchical configuration, a substitution is performed at the lowest level and the
communication fails on a higher level.
EXAMPLE 2 If an invalid value is substituted, the invalid field will be cleared and the substituted field will be set
to indicate the substitution.
The quality identifier operatorBlocked is independent of the other quality identifiers.
EXAMPLE 3 An oscillating input may cause the invalid field to be set. Due to the continuing changes in the value
many reports are generated, loading the communication network. An operator may block the update of the input. In
this case the field operatorBlocked will also be set.
An example for the interaction between the quality identifiers and the impact of multiple client
– server relation is shown in Figure 3. In this example, it is assumed that a bay level device
acts as a client of the process level server and as a server to the station level client.
NOTE This is one example of a multiple client – server relationship; other multiple client - server relationships
may exist, but the behaviour will not change.
In case A, the input is blocked, the quality of the information is marked as questionable and
oldData.
In case B, a substitution is done at process level. Now, the quality of the information to the
next higher level (the bay level) is marked as substituted (but good).
– 16 – 61850-7-3 IEC:2003(E)
In case C, the communication between process and bay level fails. Between bay level
a
...
This PDF file has been prepared by TC 57 experts and is made
available to assist the users of the IEC 61850-7 series.
Please note:
ƒ There was no IEC vote on these files, and IEC Central Office does
therefore not take any responsibility as to their contents.
ƒ Adobe Acrobat 6.0 is required to navigate through this file.
Any comments on these files are to be communicated to the following
address:
Karlheinz Schwarz
(schwarz@scc-online.de)
IEC 61850 - Communication networks and systems in substations
Informative tutorial on the object models
NOTE 1 These pdf files (html pages) are intended to provide a hypertext version of an excerpt of the main
concepts and definitions of Parts IEC 61850-7-4, IEC 61850-7-3, and IEC 61850-7-2.
NOTE 2 The content of these files is informative only. They do in no way replace the normative definitions
contained in the above referenced documents.
There are the following pages to browse and study the object models:
1. Modeling approach of logical nodes (one page - pdf)
2. IEC 61850-7-2 Overview of ACSI models
3. Logical nodes of 61850-7-4
4. Common data classes in a single window
The xml files containg the models are (not available in the pdf format):
- Logical Nodes from IEC 61850-7-4:2003 LN.xml
- DATA Semantics from IEC 61850-7-4:2003 Data-Sematic.xml
- DATA-Attributes from IEC 61850-7-3:2003 CDC.xml
- DATA-Attribute Semantics from IEC 61850-7-3:2003 DA-Semantic.xml
- Common Data Attributes from IEC 61850-7-3:2003 CDA.xml
These xml files can be used to produce any other presentation. They should not be used as normative
xml documents.
Parts of the standard
� IEC 61850-1, Part 1: Introduction and overview
� IEC 61850-2, Part 2: Glossary
� IEC 61850-3, Part 3: General requirements
� IEC 61850-4, Part 4: System and project management
� IEC 61850-5, Part 5: Communication requirements for functions and devices models
� IEC 61850-6, Part 6: Configuration description language for communication in electrical
substations related to IEDs
� IEC 61850-7-1, Part 7-1: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment -
Principles and models
� IEC 61850-7-2, Part 7-2: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment -
Abstract communication service interface (ACSI)
� IEC 61850-7-3, Part 7-3: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment -
Common data classes
� IEC 61850-7-4, Part 7-4: Basic communication structure for substation and feeder equipment -
Compatible logical node classes and data classes
� IEC 61850-8-1, Part 8-1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) - Mappings to MMS
(ISO/IEC 9506-1 and ISO/IEC 9506-2) and to ISO/IEC 8802-3
� IEC 61850-9-1, Part 9-1: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) - Sampled values
over serial unidirectional multidrop point to point link
� IEC 61850-9-2, Part 9-2: Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) - Sampled values
over ISO/IEC 8802-3
� IEC 61850-10, Part 10: Conformance testing
The web pages and the corresponding xml files have been created by
Karlheinz Schwarz, SCC. (schwarz@scc-online.de)
SCC does not take any responsibility as to the content of the files contained in the ZIP file
"IEC61850_HTML.zip" (html, xml and jpg) or the "browsable" pdf file and linked on this page
respectively.
Karlheinz Schwarz, based in Karlsruhe, Germany, is a consultant for the power systems control
industry. He is involved in several Working Groups within IEC TC 57, TC 65, and TC 88. He is a well-
known authority on the standardization and application of advanced information and communication
technologies.
© IEC 2004
Version 1.1 2004-03-22
SV
SV
SV
SV
What is a Logical Node?
By Karlheinz Schwarz, SCC, schwarz@scc-online.de
Motivation
The standard IEC 61850 „Communication networks and systems in substations“ and the
coming standard IEC 61400-25 „Communications for monitoring and control of wind power
plants“ use the concept of Logical Nodes (LN) as a key element to define the information of
a device to be communicated. This paper introduces the concept of LNs.
Modeling
A key issue are the LNs representing functions or equipment used in power systems. Each
oncept
LN provides a list of well organized and named information. The LN “XCBR5” represents
the “circuit breaker” number 5 with the data “Pos” (Position) and “Mode”. Services defined
in IEC 61850-7-2 allow the exchange of this information.
logical device (Bay)
IEC 61850-7-2
(Virtual World) virtualisation
Services
IEC 61850
models substation
equipment and func-
LN
TCP/IP
tions (focus is on
LNLN
MMS
LN
Network
protection)
IEC 61400-25 XCBR5
models components
Pos
SCSM
of wind power plants
IEC 61850-8-1
Mode
like rotor, generator,
...
Real
gear box, nacelle etc. devices in a
substation
IEC 61850-7-4 logical
(focus is on SCADA)
IEC 61850-7-4
node (circuit breaker)
data (Position)
IEC 61850-6
configuration file, XML
The substation configuration language in part 6 supports the engineering process.
Example LN
The measurement LN “MMXU” represents power, voltages, currents, and impedances in a
“MMXU”
three-phase system. The values can be communicated by various services
Logical Node „MMXU“
Read
deadbanded value
Read
TotW Total Active Power (Total P)
angle
TotVAr Total Reactive Power (Total Q)
TotVA phsA.cVTotal Appareal nt Power (Total S)
Report
Report RCB
IEC 61850-7-4 RCB
TotPF phsB.cVAverage alPower factor (Total PF)
defines some
Hz phsCFrequency.cVal
90 LNs
PPV Phase to phase voltages (VL1VL2, …)
QueryLog
QueryLog
Log
Log
500 Data PhV Phase to ground voltages (VL1ER, …)
100 Attributes A Phase currents (IL1, IL2, IL3)
10 Service models W Phase active power (P)
Configure
Configure
VAr Phase reactive power (Q)
IEC 61400-25
VA Phase apparent power (S)
Retrieve
adds some
Retrieve
PF Phase power factor
Model
Model
10 LNs
Z Phase Impedance
200 Data
IEC 61850-7-2
100 Attributes
current / voltage samples from instrument
IEC 61850-7-2
transformers represented by LN “PhsBTCTR” for
current transformer of phase B (e.g. by sampled LN PhsBTCTR LN PhsBTVTR
LN PhsBTCTR LN PhsBTVTR
Amp Vol
value exchange services of IEC 61850-7-2 SV) Amp Vol
The “MMXU” LN offers hundreds of values: measured (process) values, configuration val-
ues, description, and substitution values. These values can be communicated by various
services like read (polling), notification (publish/subscribe), logging and query.
© SCC Draft 0-2 2004-01-03
Mapping
ACSI overview and basic concepts
General
The models of the ACSI provide
� the specification of a basic model for the definition of the substation-specific information models contained
in IEC 61850-7-3 (common DATA classes) and IEC 61850-7-4 (compatible LOGICAL-NODE classes and
compatible DATA classes) and
� the specification of information exchange service models.
The information models and information exchange services are interwoven. From a descriptive point of view, the
two aspects are separated to some degree (see the excerpt shown in Figure 1). The common models (for
example, LOGICAL-NODE and DATA classes including their services) are applied in IEC 61850-7-3 and IEC
61850-7-4 to define many specialized information models - the substation automation models.
Figure 1 - Excerpt of conceptual model
Other service models required for substation automation systems (for example, DATA-SET and reporting provide
specific information exchange services) are also defined in this part of the standard; these models are linked to
LOGICAL-NODEs and DATA. The information exchange services are completely defined in the ACSI. The
information models defined in IEC 61850-7-4 reference the services defined in the various models of the ACSI.
Overview of basic information models
The conceptual models to build the domain-specific information models are:
� SERVER - represents the external visible behaviour of a device. All other ACSI models are part of the
server.
NOTE 1 A server has two roles: to communicate with a client (most service models in IEC 61850 provide
communication with client devices) and to send information to peer devices (for example, for sampled
values).
� LOGICAL-DEVICE (LD) - contains the information produced and consumed by a group of domain-specific
application functions; functions are defined as LOGICAL-NODEs.
� LOGICAL-NODE (LN) - contains the information produced and consumed by a domain-specific application
function, for example, overvoltage protection or circuit-breaker.
� DATA - provide means to specify typed information, for example, position of a switch with quality
information and timestamp, contained in LOGICAL-NODEs.
Each of these information models is defined as a class. The classes comprise attributes and services. The
conceptual class diagram of the ACSI is depicted in Figure 2.
NOTE 2 The classes are major building blocks that provide the framework for substation automation device
models. Additional details on the modelling and relations between IEC 61850-7-4, IEC 61850-7-3, and this part of
IEC 61850 can be found in IEC 61850-7-1.
Click on boxes to get the definitions!
Figure 2 - Basic conceptual class model of the ACSI
Click on boxes to get the definitions!
NOTE 3 The numbers in the circles indicate the respective clauses in this part of IEC 61850.
The Name class is inherited by the classes LOGICAL-DEVICE, LOGICAL-NODE, DATA, and DataAttribute.
EXAMPLE In an implementation the logical device, logical node, data, and data attribute have each an object
name (instance name) which is a unique name among classes of the same container to which they belong. In
addition, each of the four has an ObjectReference (path name) which is a concatenation of all object names from
each container. The four object names (one per column) can be concatenated.
Logical device Logical node Data Data attribute
Object name "Atlanta_HV5" "XCBR1" "Pos" "stVal"
Description
High-voltage station 5 Circuit-breaker 1 Position Status value
Overview of the other service models
In addition to the models listed above, the ACSI comprises the following models that provide services operating
on data, data attributes, and data sets.
� DATA-SET - permits the grouping of data and data attributes. Used for direct access and for reporting and
logging.
� Substitution - supports replacement of a process value by another value.
� SETTING-GROUP-CONTROL-BLOCK - defines how to switch from one set of setting values to another
one and how to edit setting groups.
� REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK and LOG-CONTROL-BLOCK - describe the conditions for generating
reports and logs based on parameters set by the client. Reports may be triggered by changes of process
data values (for example, state change or dead band) or by quality changes. Logs can be queried for later
retrieval. Reports may be sent immediately or deferred. Reports provide change-of-state and sequence-of-
events information exchange.
� control blocks for generic substation event (GSE) - supports a fast and reliable system-wide distribution of
input and output data values; peer-to-peer exchange of IED binary status information, for example, a trip
signal.
� control blocks for transmission of sampled values - fast and cyclic transfer of samples, for example, of
instrument transformers.
� control - describes the services to control, for example, devices.
� time and time synchronization - provides the time base for the device and system.
� file transfer - defines the exchange of large data blocks such as programs.
An overview of the conceptual service model of the ACSI is shown in Figure 3.
Click on boxes to get the definitions!
Figure 3 - Conceptual service model of the ACSI
Click on boxes to get the definitions!
NOTE 1 The numbers in the circles indicate the respective clauses in this part of IEC 61850.
NOTE 2 The class diagrams are conceptual. Details are defined in the respective clauses. Comprehensive
diagrams are contained in IEC 61850-7-1. The DATA class may be defined recursively. The operations for
substitution and control are restricted to the lowest level in the DATA class. The DataAttributes may be defined
recursively as well.
The logical node is one of the major building blocks that has associations to most of the other information
exchange models, for example, report control, log control, and setting control.
Any other information exchange service model, for example, report control, log control, and setting control shall
inherit the ObjectName and ObjectReference as depicted in Figure 2.
NOTE 3 The class models and services are defined using an object-oriented approach allowing for the mapping
of class models and services to different application layer and middle ware solutions.
Overview of ACSI services
The complete list of ACSI classes and their services is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 - ACSI classes
SERVER model (Clause 6) LOG-CONTROL-BLOCK model:
GetServerDirectory GetLCBValues
SetLCBValues
QueryLogByTime
ASSOCIATION model (Clause 7)
QueryLogAfter
Associate
GetLogStatusValues
Abort
Release
Generic substation event model —
GSE (Clause 15)
LOGICAL-DEVICE model (Clause 8)
GOOSE
GetLogicalDeviceDirectory
SendGOOSEMessage
GetGoReference
LOGICAL-NODE model (Clause 9)
GetGOOSEElementNumber
GetLogicalNodeDirectory
GetGoCBValues
GetAllDataValues
SetGoCBValues
GSSE
DATA model (Clause 10)
SendGSSEMessage
GetDataValues
GetGsReference
SetDataValues
GetGSSEDataOffset
GetDataDirectory
GetGsCBValues
GetDataDefinition
SetGsCBValues
DATA-SET model (Clause 11)
Transmission of sampled values model
GetDataSetValues
(Clause 16)
SetDataSetValues
MULTICAST-SAMPLE-VALUE-CONTROL-BLOCK:
CreateDataSet
SendMSVMessage
DeleteDataSet
GetMSVCBValues
GetDataSetDirectory
SetMSVCBValues
UNICAST-SAMPLE-VALUE-CONTROL-BLOCK:
Substitution model (Clause 12)
SetDataValues SendUSVMessage
GetUSVCBValues
GetDataValues
SetUSVCBValues
SETTING-GROUP-CONTROL-BLOCK model
Control model (Clause 17)
(Clause 13)
Select
SelectActiveSG
SelectWithValue
SelectEditSG
Cancel
SetSGValues
Operate
ConfirmEditSGValues
CommandTermination
GetSGValues
TimeActivatedOperate
GetSGCBValues
Time and time synchronization (Clause 18)
TimeSynchronization
REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK and LOG-
CONTROL-BLOCK model (Clause 14) FILE transfer model (Clause 20)
BUFFERED-REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK: GetFile
SetFile
Report
DeleteFile
GetBRCBValues
GetFileAttributeValues
SetBRCBValues
UNBUFFERED-REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK:
Report
GetURCBValues
SetURCBValues
5 ObjectName
The ObjectName shall specify a unique instance name among instances of a class owned by the same parent
class with a type as specified in Table 3 - ObjectName type
ObjectName type
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation Used by
ObjectName VISIBLE STRING32 Name of an instance of a class of a IEC 61850-7-4
single hierarchy level IEC 61850-7-3
IEC 61850-7-2
NOTE Clause 19 specifies constraints on the use of the type ObjectName.
5 ObjectReference
Instances of classes in the hierarchical information model (ACSI class hierarchy of logical device, logical node,
data, data attributes) shall be constructed by the concatenation of all instance names comprising the whole
path-name of an instance of a class that identifies the instance uniquely. The type of the ObjectReference shall
be as specified in Table 4.
Table 4 - ObjectReference type
ObjectReference type
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation Used by
ObjectReference VISIBLE STRING255 ObjectReference comprises the IEC 61850-7-2
whole path-name of an instance of a
class that identifies the instance
uniquely
The ObjectReference syntax shall be:
LDName/LNName[.Name[. .]]
The "/" shall separate the instance name of a logical device (LDName) from the name of an instance of a
logical node (LNName). The "." shall separate the further names in the hierarchy. The "[ ]" shall indicate an
option. The inner square bracket "[. .]" shall indicate further names of recursively nested definitions.
NOTE 1 In any case where the context of the text provides sufficient information that an instance of a class is
meant, the term "instance of" is not used.
NOTE 2 Clause 19 specifies constraints on the use of the type ObjectReference.
6 Server
The class SERVER shall represent the externally visible behaviour of a device. The SERVER shall be a
composition as defined in Table 11.
NOTE 1 For simple devices the server may comprise just one logical device with the GOOSE control model
with no other service.
Table 11 - SERVER class definition
SERVER class
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation
ServiceAccessPoint [1.n] (*) (*) Type is SCSM specific
LogicalDevice [1.n] LOGICAL-DEVICE
File [0.n] FILE
TPAppAssociation [0.n] TWO-PARTY-APPLICATION-
ASSOCIATION
MCAppAssociation [0.n] MULTICAST-APPLICATION-
ASSOCIATION
Services
GetServerDirectory
NOTE 2 The server's relationship to the underlying communication system and the concrete implementation
depend on the SCSM (specific communication service mapping, see IEC 61850-8-x and IEC 61850-9-x) used.
Network management (as part of an SCSM), device management, and system management are outside the
scope of IEC 61850-7-2.
8 Logical Device
The LOGICAL-DEVICE (LD) shall be a composition of LOGICAL-NODE as defined in Table 14.
NOTE- A LOGICAL-DEVICE can be used simply as a container of a group of LOGICAL-NODEs or as a device
that functions as a gateway or proxy. Details on the use of LOGICAL-DEVICE can be found in IEC 61850-7-1.
Table 14 - LOGICAL-DEVICE (LD) class definition
LOGICAL-DEVICE class
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation
LDName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of LOGICAL-
DEVICE
LDRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of LOGICAL-
DEVICE
LogicalNode [3.n] LOGICAL-NODE IEC 61850-7-4 specifies specialized classes
of LOGICAL-NODE
Services
GetLogicalDeviceDirectory
9 LOGICAL NODE
The LOGICAL-NODE shall be a composition of DATA, DATA-SET, BRCB, URCB, LCB, LOG, SGCB, GoCB,
GsCB, MSVCB, and USVCB as defined in Table 15.
Table 15 - LOGICAL-NODE (LN) class definition
LOGICAL-NODE class
Attribute name Attribute type Explanation
LNName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of
LOGICAL-NODE
LNRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of
LOGICAL-NODE
Data [1.n] DATA
DataSet [0.n] DATA-SET
BufferedReportControlBlock [0.n] BRCB
UnbufferedReportControlBlock [0.n] URCB
LogControlBlock [0.n] LCB
IF compatible LN class defined in IEC 61850-7-4 equals LLN0
SettingGroupControlBlock [0.1] SGCB
Log [0.1] LOG
GOOSEControlBlock [0.n] GoCB
GSSEControlBlock [0.n] GsCB
MulticastSampledValueControlBlock [0.n] MSVCB
UnicastSampledValueControlBlock [0.n] USVCB
Services
GetLogicalNodeDirectory
GetAllDataValues
NOTE 1 IEC 61850-7-4 defines specialized logical node classes - the compatible logical node classes, for
example, XCBR representing circuit-breakers.
The definition of LOGICAL-NODEs for the substation-application domain is refined by the definition of specific
DATAin IEC 61850-7-4. The definitions in IEC 61850-7-4 (and IEC 61850-7-3 for the common DATA classes)
shall be taken into account to get the comprehensive definition of substation-domain-specific LOGICAL-
NODEs.
NOTE 2 IEC 61850-7-4 defines further attributes for LOGICAL-NODEs; for example,, the mode (behaviour:
ON, BLOCKED, TEST, etc.) of the substation-specific LOGICAL-NODE is defined in IEC 61850-7-4. The state
model of a LOGICAL-NODE is modelled as a specific DATA (named Mod).
10 Data
The DATA shall have the structure defined in Table 16.
Table 16 - DATA class definition
DATA class
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation
DataName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of DATA,
for example, PhV (1st level), phsA (2nd
level)
DataRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of DATA,
for example, MMXU1.PhV or
for example, MMXU1.PhV.PhsA
Presence BOOLEAN Indicates mandatory/optional
DataAttribute [0.n] DAType For example, Vector class of IEC 61850-7-
DataAttributeTypeFunctionalConstraint FC 3
TrgOp [0.n] TriggerConditions for example, MX
for example, dchg
Specializations of DATA
CompositeCDC [0.n] DATA For example, WYE class of IEC 61850-7-3
SimpleCDC [0.n] COMMON-DATA For example, CMV class of IEC 61850-7-3
Services
GetDataValues
SetDataValues
GetDataDirectory
GetDataDefinition
An instance of a DATA class may contain zero or more instances of a CompositeCDC, SimpleCDC or a
DataAttribute. However, they cannot all be absent, so at least one of these elements shall be present.
NOTE 5 The structure of a DATA class is recursive since a CompositeCDC is also of type DATA class. The
level of recursion may be restricted by a SCSM, so the number of levels of recursion of CompositeCDCs is
normally no greater than 1.
NOTE 6 DATA or part of a DATA may be referenced in a DATA-SET. The persistent existence of DATA is
expected as long as they are referenced as members of a DATA-SET. A system has to take special measures
to ensure their existence.
10 Data Attribute Type
The DAType shall be as defined in Table 17.
Table 17 - DAType definition
DAType
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation
DATName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of DAType,
for example, cVal (1stlevel), mag (2nd level), f
(3rd level)
DATRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of DAType
for example, MMXU1.PhV.phsA.cVal
for example, MMXU1.PhV.phsA.cVal.mag or
for example, MMXU1.PhV.phsA.cVal.mag.f
Presence BOOLEAN Indicates mandatory/optional
Specializations of DAType
CompositeComponent [0.n] DAType For example, mag in Vector class of IEC 61850-
7-3
for example, f in AnalogueValue of IEC 61850-7-
PrimitiveComponent [0.1] BasicType For example, FLOAT32 class of IEC 61850-7-3
for f
NOTE 1 An instance of a DAType may contain 0 or more instances of a CompositeComponent or a
PrimitveDAT. However, they cannot both be absent, so at least one of these elements must be present.
NOTE 2 The structure of a DAType is recursive since a CompositeComponent is also of type DAType. The
level of recursion may be restricted by a SCSM, so the number of levels of recursion of
CompositeComponents is normally no greater than 2.
11 DATA-SET class syntax
The DATA-SET shall have the structure as defined in Table 21.
Table 21 - DATA-SET (DS) class definition
DATA-SET class
Attribute name Attribute type Value/value range/explanation
DSName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of DATA-SET
DSRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of DATA-SET
DSMemberRef [1.n] (*) (*) Functionally constrained data (FCD) or
functionally constrained data attribute (FCDA)
Services
GetDataSetValues
SetDataSetValues
CreateDataSet
DeleteDataSet
GetDataSetDirectory
13 SETTING-GROUP-CONTROL-BLOCK class model
The SGCB shall have the structure defined in Table 22.
Clients should use the existence of a SGCB to determine if the LOGICAL-DEVICE contains SGs.
Table 22 - SGCB class definition
SGCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
SGCBName ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of SGCB
SGCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of SGCB
NumOfSG INT8U SP - n = NumOfSG
ActSG INT8U SP dchg Allowable range: 1 . n
EditSG INT8U SP dchg Allowable range: 0 . n
CnfEdit BOOLEAN SP dchg
LActTm TimeStamp SP dchg
Services
SelectActiveSG
SelectEditSG
SetSGValues
ConfirmEditSGValues
GetSGValues
GetSGCB Values
Values of the attributes of the instances of SGCB shall be configured.
14 BUFFERED-REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK (BRCB)
The BRCB class shall have the structure defined in Table 23.
Table 23 - BRCB class definition
BRCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
BRCBName ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of BRCB
BRCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of BRCB
Specific to report handler
RptID VISIBLE STRING65 BR -
RptEna BOOLEAN BR dchg
DatSet ObjectReference BR dchg
ConfRev INT32U BR dchg
OptFlds PACKED LIST BR dchg
sequence-number BOOLEAN
report-time-stamp BOOLEAN
reason-for-inclusion BOOLEAN
data-set-name BOOLEAN
data-reference BOOLEAN
buffer-overflow BOOLEAN
entryID BOOLEAN
conf-revision BOOLEAN
BufTm INT32U BR dchg
SqNum INT16U BR -
TrgOp TriggerConditions BR dchg
IntgPd INT32U BR dchg 0. MAX; 0 implies no integrity report.
GI BOOLEAN BR -
PurgeBuf BOOLEAN BR -
EntryID EntryID BR -
TimeOfEntry EntryTime BR -
Services
Report
GetBRCBValues
SetBRCBValues
These attributes determine the service procedures of the Report service. The impact of the various values
shall be as defined in the following attribute definitions.
14 UNBUFFERED-REPORT-CONTROL-BLOCK (BRCB)
The URCB class shall have the structure defined in Table 25.
Table 25 - URCB class definition
URCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
URCBName ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of URCB
URCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of URCB
Specific to report handler
RptID VISIBLE STRING65 RP -
RptEna BOOLEAN RP dchg
Resv BOOLEAN RP -
DatSet ObjectReference RP dchg
ConfRev INT32U RP dchg
OptFlds PACKED LIST RP dchg
reserved BOOLEAN
sequence-number BOOLEAN
report-time-stamp BOOLEAN
reason-for-inclusion BOOLEAN
data-set-name BOOLEAN
data-reference BOOLEAN
reserved BOOLEAN Used for buffer-overflow in BRCB
reserved BOOLEAN Used for entryID in BRCB
conf-revision BOOLEAN
BufTm INT32U RP dchg 0 . MAX
SqNum INT8U RP -
TrgOp TriggerConditions RP dchg
IntgPd INT32U RP dchg 0. MAX
GI BOOLEAN BR -
Services
Report
GetURCBValues
SetURCBValues
Except URCBName, URCBRef, RptEna, and Resv all other attributes shall be as defined for the BRCB in
14.2.2.
14 LOG-CONTROL-BLOCK class model
The LCB shall control the procedures that are required for storing values of DataAttribute (the log entry) into a
LOG. Each enabled LCB shall associate DATA-SET with a LOG. Changes in a value of a member of a DATA-
SET shall be stored as LOG entry. Multiple LCBs allow multiple DATA-SETs to feed a LOG.
It shall be the responsibility of access control, to prevent unauthorized clients to modify an LCB.
NOTE The internal notification, local storage mechanism, internal formats, etc. for log entries are all local
issues and outside the scope of this part of IEC 61850.
The LCB shall have the structure specified in Table 26.
Table 26 - LCB class definition
LCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
LCBName ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of LCB
LCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of LCB
Specific to log handler
LogEna BOOLEAN LG dchg
DatSet ObjectReference LG dchg
OptFlds PACKED LIST LG dchg
reason-for-inclusion BOOLEAN
TrgOp TriggerConditions LG dchg Valid values for TrgOp of type
TriggerConditions shall be dchg, qchg,
dupd, and integrity.
IntgPd INT32U LG dchg 1.MAX; 0 implies no integrity logging.
Specific to building the log
LogRef ObjectReference LG
Services
GetLCBValues
SetLCBValues
14 LOG
The LOG shall be filled on a first-in first-out basis. When the list of log entries reaches a point where the stored
data reaches the maximal size of the log, the oldest log entry shall be overwritten. This action shall have no
impact to the further incrementing of the EntryID of the added log entries.
The LOG shall have the structure defined in Table 27.
Table 27 - LOG class definition
LOG class
Attribute name Attribute type FC Value/value range/explanation
LogName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of LOG
LogRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of LOG
OldEntrTm TimeStamp LG
NewEntrTm TimeStamp LG
OldEntr INT32U LG
NewEntr INT32U LG
Entry [1.n]
TimeOfEntry EntryTime
EntryID EntryID
EntryData [1.n]
DataRef ObjectReference
Value (*) (*) type(s) depend on the definition of common data
classes in IEC 61850-7-3
ReasonCode TriggerConditions If reason-for-inclusion (="TRUE)" in optFlds.
ReasonCode general-interrogation shall never
occur as TRUE.
Services
QueryLogByTime
QueryLogAfter
GetLogStatusValues
15 GOOSE-CONTROL-BLOCK (GoCB) class
The GoCB shall be as defined in Table 28.
Table 28 - GOOSE control block class definition
GoCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
GoCBName ObjectName GO - Instance name of an instance of GoCB
GoCBRef ObjectReference GO - Path-name of an instance of GoCB
GoEna BOOLEAN GO dchg Enabled (TRUE) | disabled (FALSE)
AppID VISIBLE STRING65 GO Attribute that allows a user to assign a
system unique identification for the
application that is issuing the GOOSE.
DEFAULT GoCBRef
DatSet ObjectReference GO dchg
ConfRev INT32U GO dchg
NdsCom BOOLEAN GO dchg
Services
SendGOOSEMessage
GetGoReference
GetGOOSEElementNumber
GetGoCBValues
SetGoCBValues
15 Generic substation state event (GSSE) control block (GsCB)
The GsCB shall be as defined in Table 30.
Table 30 - GSSE control block class definition
GsCB class
Attribute name Attribute type FC Value/value range/explanation
GsCBName ObjectName Instance name of an instance of GsCB
GsCBRef ObjectReference Path-name of an instance of GsCB
GsEna BOOLEAN GS Enabled (TRUE) | disabled (FALSE)
AppID VISIBLE STRING65 GS
DataLabel [1.n] VISIBLE STRING65 GS
LSentData [1.n] GSSEData GS Derived from GSSE message
Services
SendGSSEMessage
GetGsReference
GetGSSEDataOffset
GetGsCBValues
SetGsCBValues
16 Transmission of sampled values using multicast (MSVCB)
The transmission of sampled values using multicast (MULTICAST-SAMPLE-VALUE-CONTROL-BLOCK -
MSVCB) shall be based on configured configuration in the producer device. The data exchange shall be based
on the multicast application association. To support self-descriptive capabilities, any client may read the
attributes of the sampled value control instance. Authorized clients may modify attributes of the sampled value
control.
The MSVCB shall be as defined in Table 32.
Table 32 - MSVCB class definition
MSVCB class
Attribute Attribute type FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
name
MsvCBNam ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of MSVCB
MsvCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of MSVCB
SvEna BOOLEAN MS dchg Enabled (TRUE) | disabled (FALSE), DEFAULT
FALSE
MsvID VISIBLE STRING65 MS -
DatSet ObjectReference MS dchg
ConfRev INT32U MS dchg
SmpRate INT16U MS - (0.MAX)
OptFlds PACKED LIST MS dchg
refresh-time BOOLEAN
sample-synchronized BOOLEAN
sample-rate BOOLEAN
Services
SendMSVMessage
GetMSVCBValues
SetMSVCBValues
16 Transmission of sampled values using unicast (USVCB)
The transmission of sampled values using unicast (UNICAST-SAMPLE-VALUE-CONTROL-BLOCK - USVCB)
shall be based on two-party application associations. The subscriber shall establish the association with the
producer. The subscriber may then configure the class and enable the transmission of the sampled values with
the attribute SvEna. When the association is released, the transmission of the sampled values shall stop and
the instance of the control class shall be released.
The samples shall be sent using the two-party application association.
The USVCB shall be as defined in Table 33.
Table 33 - USVCB class definition
USVCB class
Attribute name Attribute FC TrgOp Value/value range/explanation
UsvCBNam ObjectName - - Instance name of an instance of UNICAST-
SVC
UsvCBRef ObjectReference - - Path-name of an instance of UNIICAST-
SVC
SvEna BOOLEAN US dchg Enabled (TRUE) | disabled (FALSE),
DEFAULT FALSE
Resv BOOLEAN US -
UsvID VISIBLE STRING65 US -
DatSet ObjectReference US dchg
ConfRev INT32U US dchg
SmpRate INT16U US dchg (0.MAX)
OptFlds PACKED LIST US dchg
refresh-time BOOLEAN
sample-synchronized BOOLEAN
sample-rate BOOLEAN
Services
SendUSVMessage
GetUSVCBValues
SetUSVCBValues
All LN classes defined in IEC 61850-7-4
� The first column (Summary) provides all logical nodes with data
names and explanation only.
� The second column (IEC) provides almost all information of all
logical nodes as in IEC 61850-7-4
How to view?
If you want to see one of the following logical nodes (available in HTML Format only!!)
together with the Common Data Classes (CDC) AND the Semantic of all names,
with the following three frames:
� Upper frame: logical node (LN),
� Middle frame: the common data class (CDC), and
� Bottom frame: the semantic of the names).
Then navigate through the LNs below (on this page).
Summary IEC
LPHD Summary LPHD IEC Table
CLN Summary CLN IEC Table
LLN0 Summary LLN0 IEC Table
PDIF Summary PDIF IEC Table
PDIR Summary PDIR IEC Table
PDIS Summary PDIS IEC Table
PDOP Summary PDOP IEC Table
PDUP Summary PDUP IEC Table
PFRC Summary PFRC IEC Table
PHAR Summary PHAR IEC Table
PHIZ Summary PHIZ IEC Table
PIOC Summary PIOC IEC Table
PMRI Summary PMRI IEC Table
PMSS Summary PMSS IEC Table
POPF Summary POPF IEC Table
PPAM Summary PPAM IEC Table
PSCH Summary PSCH IEC Table
PSDE Summary PSDE IEC Table
PTEF Summary PTEF IEC Table
PTOC Summary PTOC IEC Table
PTOF Summary PTOF IEC Table
PTOV Summary PTOV IEC Table
PTRC Summary PTRC IEC Table
PTTR Summary PTTR IEC Table
PTUC Summary PTUC IEC Table
PTUV Summary PTUV IEC Table
PUPF Summary PUPF IEC Table
PTUF Summary PTUF IEC Table
PVOC Summary PVOC IEC Table
PVPH Summary PVPH IEC Table
PZSU Summary PZSU IEC Table
RDRE Summary RDRE IEC Table
RADR Summary RADR IEC Table
RBDR Summary RBDR IEC Table
RDRS Summary RDRS IEC Table
RBRF Summary RBRF IEC Table
RDIR Summary RDIR IEC Table
RFLO Summary RFLO IEC Table
RPSB Summary RPSB IEC Table
RREC Summary RREC IEC Table
RSYN Summary RSYN IEC Table
CALH Summary CALH IEC Table
CCGR Summary CCGR IEC Table
CILO Summary CILO IEC Table
CPOW Summary CPOW IEC Table
CSWI Summary CSWI IEC Table
GAPC Summary GAPC IEC Table
GGIO Summary GGIO IEC Table
GSAL Summary GSAL IEC Table
IARC Summary IARC IEC Table
IHMI Summary IHMI IEC Table
ITCI Summary ITCI IEC Table
ITMI Summary ITMI IEC Table
ANCR Summary ANCR IEC Table
ARCO Summary ARCO IEC Table
ATCC Summary ATCC IEC Table
AVCO Summary AVCO IEC Table
MDIF Summary MDIF IEC Table
MHAI Summary MHAI IEC Table
MHAN Summary MHAN IEC Table
MMTR Summary MMTR IEC Table
MMXN Summary MMXN IEC Table
MMXU Summary MMXU IEC Table
MSQI Summary MSQI IEC Table
MSTA Summary MSTA IEC Table
SARC Summary SARC IEC Table
SIMG Summary SIMG IEC Table
SIML Summary SIML IEC Table
SPDC Summary SPDC IEC Table
XCBR Summary XCBR IEC Table
XSWI Summary XSWI IEC Table
TCTR Summary TCTR IEC Table
TVTR Summary TVTR IEC Table
YEFN Summary YEFN IEC Table
YLTC Summary YLTC IEC Table
YPSH Summary YPSH IEC Table
YPTR Summary YPTR IEC Table
ZAXN Summary ZAXN IEC Table
ZBAT Summary ZBAT IEC Table
ZBSH Summary ZBSH IEC Table
ZCAB Summary ZCAB IEC Table
ZCAP Summary ZCAP IEC Table
ZCON Summary ZCON IEC Table
ZGEN Summary ZGEN IEC Table
ZGIL Summary ZGIL IEC Table
ZLIN Summary ZLIN IEC Table
ZMOT Summary ZMOT IEC Table
ZREA Summary ZREA IEC Table
ZRRC Summary ZRRC IEC Table
ZSAR Summary ZSAR IEC Table
ZTCF Summary ZTCF IEC Table
ZTCR Summary ZTCR IEC Table
Logical node classes (LN) of IEC 61850-7-4
Version 2004-03-22
This web page (pdf file) is intended to provide a hypertext version of an excerpt of the main
concepts and definitions of Parts IEC 61850-7-4
NOTE The content of this web page (pdf file) is informative only. The page does in no way
replace the normative definitions contained in IEC 61850-7-4.
Copyright of transformation (c) 2004 by Karlheinz Schwarz, SCC
Send comment to Karlheinz
2004-03-22
Brief tables of LN classes defined in IEC 61850-7-4
(Tables provide just DATA Class Names and Explanation)
LPHD - Physical device information
This LN is introduced in this part to model common issues for physical devices.
LPHD class
DATA Class Explanation
PhyNam
Physical device name plate
PhyHealth
Physical device health
OutOv
Output communications buffer overflow
Proxy
Indicates if this LN is a proxy
InOv
Input communications buffer overflow
NumPwrUp
Number of Power ups
WrmStr
Number of Warm Starts
WacTrg
Number of watchdog device resets detected
PwrUp
Power Up detected
PwrDn
Power Down detected
PwrSupAlm
External power supply alarm
RsStat
Reset device statistics
CLN - Common Logical Node
The compatible logical node classes defined in this document are specilisations of this
Common Logical Node Class.
CLN class
DATA Class Explanation
Mandatory Logical Node Information (Shall be inherited by ALL LN but LPHD)
Mod
Mode
Beh
Behaviour
Health
Health
NamPlt
Name plate
Optional Logical Node Information
Loc
Local operation
EEHealth
External equipment health
EEName
External equipment name plate
OpCntRs
Operation counter resetable
OpCnt
Operation counter
OpTmh
Operation time
Data Sets (see IEC 61850-7-2)
LLN0 - Logical node zero
This logical node shall be used to address common issues for logical devices.
LLN0 class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
Loc
Local operation for complete logical device
OpTmh
Operation time
Controls
Diag
Run Diagnostics
LEDRs
LED reset
PDIF - Differential
See IEC 61850-5 (LNs PLDF, PNDF, PTDF, PBDF, PMDF, and PPDF). This LN shall be
used for all kind of current differential protection. Proper current samples for the dedicated
application shall be subscribed.
PDIF class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
TmASt
Active curve characteristic
Measured Values
DifAClc
Differential Current
RstA
Restraint Current
Settings
LinCapac
Line capacitance (for load currents)
LoSet
Low operate value, percentage of the nominal current
HiSet
High operate value, percentage of the nominal current
MinOpTmms
Minimum Operate Time
MaxOpTmms
Maximum Operate Time
RstMod
Restraint Mode
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
TmACrv
Operating Curve Type
PDIR - Direction comparison
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5. The operate decision is based on an
agreement of the fault direction signals from all directional fault sensors (for example
directional relays) surrounding the fault. The directional comparison for lines is made with
PSCH.
PDIR class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start (appearance of the first related fault direction)
Op
Operate (decision from all sensors that the surrounded object is faulted)
Settings
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
PDIS - Distance
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5. The phase start value and ground start value
are minimum thresholds to release the impedance measurements depending on the distance
function characteristic given by the algorithm and defined by the settings. The settings
replace the data curve as used for the characteristic on some other protection LNs.
PDIS class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
Settings
PoRch
Polar Reach is the diameter of the Mho diagram
PhStr
Phase Start Value
GndStr
Ground Start Value
DirMod
Directional Mode
PctRch
Percent Reach
Ofs
Offset
PctOfs
Percent Offset
RisLod
Resistive reach for load area
AngLod
Angle for load area
TmDlMod
Operate Time Delay Mode
OpDlTmms
Operate Time Delay
PhDlMod
Operate Time Delay Multiphase Mode
PhDlTmms
Operate Time Delay for Multiphase Faults
GndDlMod
Operate Time Delay for Single Phase Ground Mode
GndDlTmms
Operate Time Delay for single phase ground faults
X1
Positive sequence line (reach) reactance
LinAng
Line Angle
RisGndRch
Resistive Ground Reach
RisPhRch
Resistive Phase Reach
K0Fact
Residual Compensation Factor K0
K0FactAng
Residual Compensation Factor Angle
RsDlTmms
Reset Time Delay
PDOP - Directional overpower
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5 (LN PDPR). This LN shall be used for the
overpower part of PDPR. Additionally, PDOP is used to model a reverse overpower function
(IEEE device function number 32R, from IEEE 32R.2,1996) when the DirMod is set to
reverse.
PDOP class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
Settings
DirMod
Directional Mode
StrVal
Start Value
OpDlTmms
Operate Delay Time
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
PDUP - Directional underpower
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5 (LN PDPR). This LN shall be used for the
underpower part of PDPR.
PDUP class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
Settings
StrVal
Start Value
OpDlTmms
Operate Delay Time
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
DirMod
Directional Mode
PFRC - Rate of change of frequency
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5 (LN PFRQ). This LN shall be used to model the
rate of frequency change of PFRQ. One instance shall be used per stage.
PFRC class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
BlkV
Blocked because of voltage
Settings
StrVal
Start Value df/dt
BlkVal
Voltage Block Value
OpDlTmms
Operate Delay Time
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
PHAR - Harmonic restraint
This LN shall be used to represent the harmonic restraint data of the transformer differential
protection (see PDIF) in a dedicated node. There may be multiple instantiations of this LN
with different settings, especially with different data HaRst.
PHAR class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start (active when restraint is needed)
Settings
HaRst
Number of harmonic restrained
PhStr
Start Value
PhStop
Stop Value
OpDlTmms
Operate Delay Time
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
PHIZ - Ground detector
For a description of this LN, see IEC 61850-5. This LN shall be used for high-impedance
isolation faults only.
PHIZ class
DATA Class Explanation
Common Logical Node Information
LN shall inherit all Mandatory Data from Common Logical Node Class
OpCntRs
Resetable operation counter
Status Information
Str
Start
Op
Operate
Settings
AStr
Current Start Value
VStr
Voltage Start Value
HVStr
Third Harmonic Voltage Start Value
OpDlTmms
Operate Delay Time
RsDlTmms
Reset Delay Time
...







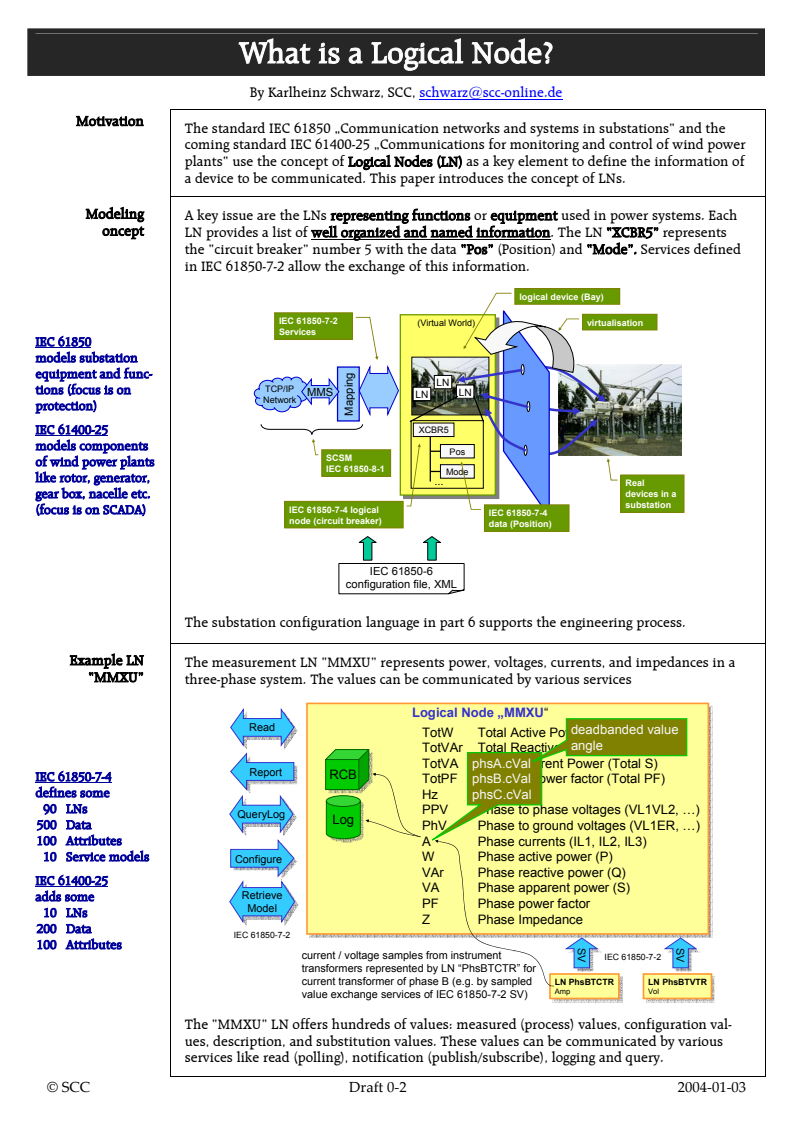
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...