IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
(Main)Intrepretation sheet 3 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"
Intrepretation sheet 3 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"
Feuille d'intreprétation 3 - Atmosphères explosives - Partie 11: Protection de l'équipement par sécurité intrinsèque "i"
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 20-Jul-2016
- Technical Committee
- SC 31G - Intrinsically-safe apparatus
- Current Stage
- DELPUB - Deleted Publication
- Start Date
- 13-Jan-2023
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Revised
IEC 60079-11:2011 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i" - Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Revised
IEC 60079-11:2023 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i" - Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Intertek Testing Services NA Inc.
Intertek certification services in North America.

UL Solutions
Global safety science company with testing, inspection and certification.

ANCE
Mexican certification and testing association.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016 is a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its full title is "Intrepretation sheet 3 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"". This standard covers: Intrepretation sheet 3 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"
Intrepretation sheet 3 - Explosive atmospheres - Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"
IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 29.260.20 - Electrical apparatus for explosive atmospheres. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to IEC 60079-11:2011, IEC 60079-11:2023. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IEC 2016
INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION
____________
IEC 60079-11
Edition 6.0 2011-06
EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERES –
Part 11: Equipment protection by intrinsic safety "i"
INTERPRETATION SHEET 3
This interpretation sheet has been prepared by subcommittee 31G: Intrinsically-safe
apparatus, of IEC technical committee 31: Equipment for explosive atmospheres.
The text of this interpretation sheet is based on the following documents:
ISH Report on voting
31G/253/ISH 31G/255/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this interpretation sheet can be found in the
report on voting indicated in the above table.
___________
Question
Regarding IEC 60079-11:2011 Edition 6.0 (2011-06), some clauses specifically indicate
whether or not the requirement is applicable or not applicable to level of protection “ic”.
However, many other clauses include no indication one way or the other, resulting in potential
inconsistencies when applied. In the interest of improving consistency, what are the
requirements in IEC 60079-11:2011 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) that are applicable to level of
protection “ic”?
Answer
In answering this question, the following considerations were taken:
1) Requirements in IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) indicating that the requirements are
applicable to level of protection “ic” are considered “Applicable”;
2) Requirements in IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) indicating that the requirements are
not applicable to level of protection “ic” are considered “Not applicable”;
3) Regarding requirements in IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) other than those
referenced in 1) and 2) above:
• determine if the intent of these requirements for levels of protection "ia" and "ib" is to
address fault (abnormal) conditions; and
ICS 29.260.20
IEC 60079-11:2011-06/ISH3:2016-07(en-fr)
– 2 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
• if the intent is to address fault (abnormal) conditions, then the requirements are
considered not applicable for level of protection "ic".
Based on the above considerations, the following informative table (similar in concept to
Annex B of IEC 60079-0:2011 on Ex Components) provides guidance regarding which
requirements in IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) are applicable to level of protection “ic”.
Additional background
As additional background details, the following seven key issues of principle were taken into
account when developing the above answer:
1) Objective of the original transfer of type of protection “nL” to “ic”: The objective of the
original transfer of type of protection “nL” to “ic” (as first included in IEC 60079-11 Fifth
Edition) was not to substantially revise the applicable requirements, except where
the maintenance team MT 60079-11 made specific reference to level of protection “ic” in a
given clause. Examples of this include 7.1, which simplifies the rating requirements for
level of protection “ic” protective components from “nL” requirements; and 6.2.1, which
increases the separation distances for level of protection “ic” terminals (to align with
IEC 60079-14) from “nL” requirements. This objective approach is consistent with how the
transfer of other IEC 60079-15 types of protection have been handled, and are still being
handled in other IEC 60079 series standards.
2) Common applications of a level of protection “ic” circuit that protects an arcing part: The
following are common applications of a level of protection “ic” circuit that protects an
arcing part:
• The circuit does not exit the device.
• The circuit exits one device and is interconnected via a wiring method to another
device, with both devices and the interconnecting wiring method being part of a
system.
• The circuit exits a device via a receptacle, with entity parameters provided for field
connection to the receptacle.
• The circuit exits a device via a terminal block, with entity parameters provided for field
connection to the terminal block.
For all the above applications, the level of protection "ic" circuit does not begin until
after the last protective component that establishes the necessary voltage and current
limitation. For other circuitry in the device, another type of protection, such as “nA” or
“ec”, is applied. It is also possible for an entire apparatus to be only ”Ex ic”.
3) Remarks in the draft I-SH: In the draft I-SH, the intent is for all Remarks to only be for
issues specific to level of protection “ic”. The few exceptions to this are for Remarks
highlighting requirements that, while applicable to all types of protection “i”, represent a
significant change in requirements from type of protection “nL” to “ic”.
4) Transient effects on level of protection “ic” circuits: For level of protection “ic” circuits, the
effects of transients are only addressed for diode safety barriers. This is because
connection of such barriers is to unspecified equipment. For other level of protection “ic”
circuit applications, no additional evaluation is required regarding the effects of transients
based on the following considerations:
• the presence of an explosive atmosphere is only under abnormal conditions; and
• the circuit complies with the applicable safety requirements of the relevant industrial
standards.
5) Separation distances for level of protection “ic” circuits: Separation distances are only
applicable to the level of protection “ic” circuit and to the protective components that
establish the level of protection “ic” circuit. Where separation distances are required,
separations that do not comply with the values of Table 5 or Annex F are to be shorted as
part of the evaluation, if the shorting may impair intrinsic safety.
IEC 2016
6) Protective components for level of protection “ic” circuits: Voltage and current limiting
protective components comply with the applicable requirements for components on which
intrinsic safety depends (e.g. 7.1).
7) IEC/TC 31 MT 60079-15 support: The MT 60079-15 convener has been involved in the
development of the content of this I-SH, and supports it based on the current
IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) text.
– 4 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
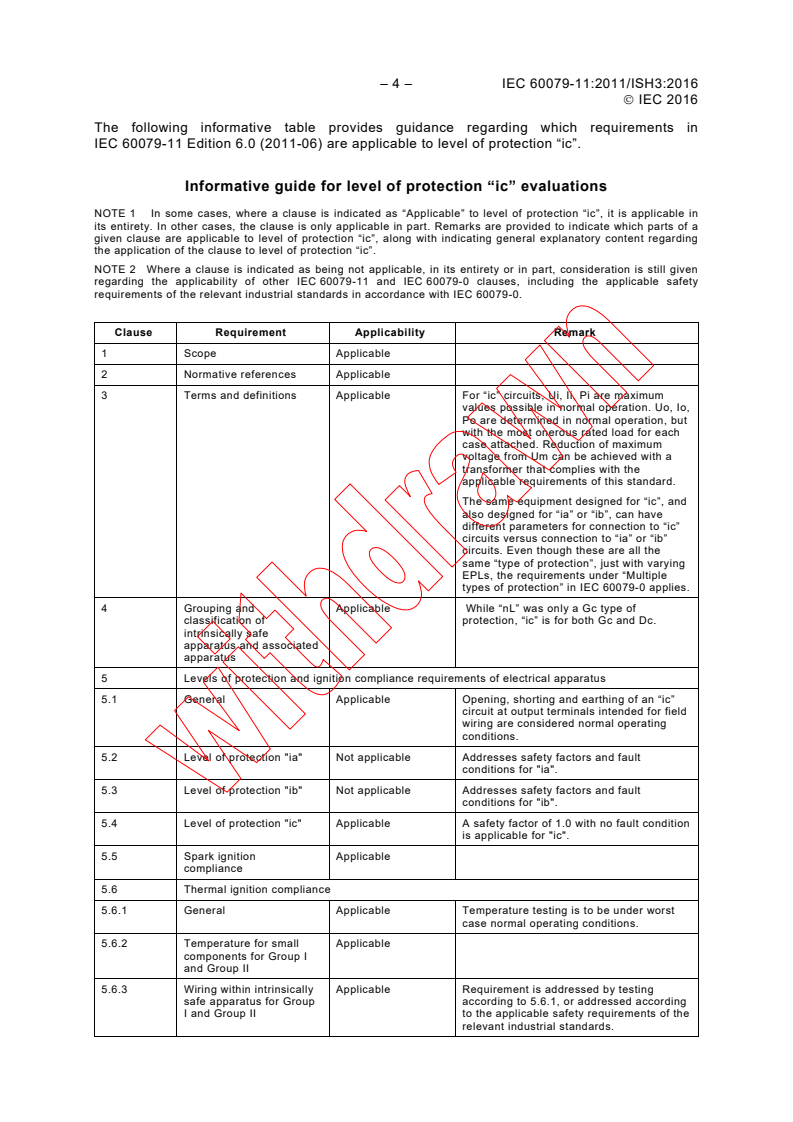
The following informative table provides guidance regarding which requirements in
IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) are applicable to level of protection “ic”.
Informative guide for level of protection “ic” evaluations
NOTE 1 In some cases, where a clause is indicated as “Applicable” to level of protection “ic”, it is applicable in
its entirety. In other cases, the clause is only applicable in part. Remarks are provided to indicate which parts of a
given clause are applicable to level of protection “ic”, along with indicating general explanatory content regarding
the application of the clause to level of protection “ic”.
NOTE 2 Where a clause is indicated as being not applicable, in its entirety or in part, consideration is still given
regarding the applicability of other IEC 60079-11 and IEC 60079-0 clauses, including the applicable safety
requirements of the relevant industrial standards in accordance with IEC 60079-0.
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
1 Scope Applicable
2 Normative references Applicable
3 Terms and definitions Applicable For “ic” circuits, Ui, Ii, Pi are maximum
values possible in normal operation. Uo, Io,
Po are determined in normal operation, but
with the most onerous rated load for each
case attached. Reduction of maximum
voltage from Um can be achieved with a
transformer that complies with the
applicable requirements of this standard.
The same equipment designed for “ic”, and
also designed for “ia” or “ib”, can have
different parameters for connection to “ic”
circuits versus connection to “ia” or “ib”
circuits. Even though these are all the
same “type of protection”, just with varying
EPLs, the requirements under “Multiple
types of protection” in IEC 60079-0 applies.
4 Grouping and Applicable While “nL” was only a Gc type of
classification of protection, “ic” is for both Gc and Dc.
intrinsically safe
apparatus and associated
apparatus
5 Levels of protection and ignition compliance requirements of electrical apparatus
5.1 General Applicable Opening, shorting and earthing of an “ic”
circuit at output terminals intended for field
wiring are considered normal operating
conditions.
5.2 Level of protection "ia" Not applicable Addresses safety factors and fault
conditions for "ia".
5.3 Level of protection "ib" Not applicable Addresses safety factors and fault
conditions for "ib".
5.4 Level of protection "ic" Applicable A safety factor of 1.0 with no fault condition
is applicable for "ic".
5.5 Spark ignition Applicable
compliance
5.6 Thermal ignition compliance
5.6.1 General Applicable Temperature testing is to be under worst
case normal operating conditions.
5.6.2 Temperature for small Applicable
components for Group I
and Group II
5.6.3 Wiring within intrinsically Applicable Requirement is addressed by testing
safe apparatus for Group according to 5.6.1, or addressed according
I and Group II to the applicable safety requirements of the
relevant industrial standards.
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
5.6.4 Tracks on printed circuit Applicable Requirement is addressed by testing
boards for Group I and according to 5.6.1, or addressed according
Group II to the applicable safety requirements of the
relevant industrial standards.
5.6.5 Intrinsically safe Applicable Temperature classification to be based on
apparatus and component the temperature of the surface exposed to
temperature for Group III dust.
5.7 Simple apparatus Applicable
6 Apparatus construction
6.1 Enclosures Applicable
6.2 Facilities for connection of external circuits
6.2.1 Terminals Applicable NOTE As with “ia” and “ib”, due to
IEC 60079-14 installation requirements,
circuits that exit a piece of equipment via a
terminal block, with entity parameters
provided for field connection to the terminal
block, maintain the following:
‒ at least 50 mm separation distance
between terminals for “ic” circuits and
terminals for non-intrinsically safe
circuits.
‒ at least 6 mm separation distance
between terminals for separate
intrinsically safe circuits.
‒ at least 3 mm separation distance
between terminals for intrinsically safe
circuits and earthed parts, if connection
to earth has not been considered in the
safety analysis.
This separation distance requirement is
different from previous Ex “nL”
requirements.
6.2.2 Plugs and sockets Applicable
6.2.3 Determination of Applicable
maximum external
inductance to resistance
ratio (L /R ) for
o o
resistance limited power
source
6.2.4 Permanently connected Applicable
cable
6.2.5 Requirements for Applicable Applicable except regarding protective
connections and circuitry for functions such as charging in
accessories for IS the non-hazardous area.
apparatus when located in
As there is no application of faults, the
the non-hazardous area
ratings of components may be ensured
without additional protection.
6.3 Separation distances
6.3.1 General Applicable Applicable to “ic” circuit and protective
components only. Where separation
distances are less than required, they are
to be shorted if the shorting may impair
intrinsic safety.
NOTE For example, an "ic" circuit is the
circuit after the last protective component
that establishes the necessary voltage and
current limitation.
– 6 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
6.3.2 Separation of conductive Applicable Applicable to "ic" circuit and protective
parts components only.
Any use of an interposing insulating
partition or earthed metallic partition is only
required to comply with the safety
requirements of the relevant industrial
standard.
6.3.2.1 Distances according to Applicable Regarding transformers, only applicable
Table 5 between external connections. Remaining
construction features of transformers are
only required to comply with the applicable
safety requirements of the relevant
industrial standards.
6.3.2.2 Distances according to Applicable Regarding transformers, only applicable
Annex F between external connections.
NOTE Remaining construction features of
transformers are only required to comply
with the applicable safety requirements of
the relevant industrial standard. Through
solid insulation of conductors are required
to comply with Table 5.
6.3.3 Voltage between Applicable For “ic”, the effects of transients are only
conductive parts addressed for diode safety barriers
because connection is to unspecified
equipment. For other “ic” applications, no
additional evaluation is required regarding
the effects of transients based on the
following considerations:
• The presence of an explosive
atmosphere is not likely to occur in
normal operation.
• The circuit complies with the applicable
safety requirements of the relevant
industrial standards.
Where separation of conductive parts is
required, separations that do not comply
with the values of Table 5 or Annex F may
be shorted as part of the evaluation if it
may impair intrinsic safety.
6.3.4 Clearance Not Applicable Any use of an interposing insulating
partition or earthed metallic partition is only
required to comply with the safety
requirements of the relevant industrial
standard. See 6.3.2.
6.3.5 Separation distances Applicable
through casting
compound
6.3.6 Separation distances Applicable
through solid insulation
6.3.7 Composite separations Applicable Applicable, except regarding the 1/3
restriction for composite separations, as
this restriction is based on fault
considerations.
6.3.8 Creepage distance Applicable Applicable, except regarding the 1/3
restriction for composite separations, and
the partition restrictions above 1,575 V.
Any use of an interposing insulating
partition or earthed metallic partition shall
comply with the safety requirements of the
relevant industrial standard. See 6.3.2.
6.3.9 Distance under coating Applicable
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
6.3.10 Requirements for Applicable Applicable, except for consideration of the
assembled printed circuit body of a component as being an
boards uninsulated live part. For example, a
component mounted over or adjacent to
tracks as defined in c) is not considered as
connected to the track.
6.3.11 Separation by earthed Applicable Where separation distances to the earthed
screens screen do not comply with the required
separation distances to earth, the screen is
to be capable of carrying the maximum
possible current to which it could be
continuously subjected (such as a short to
earth).
6.3.12 Internal wiring Applicable
6.3.13 Dielectric strength Applicable Applicable, except for the additional
rd
requirement dielectric strength testing in the 3
nd
paragraph. Regarding the 2 paragraph,
only applicable to insulation or insulating
components. Additional dielectric testing is
not required between level of protection "ic"
and other circuits, or between separate
level of protection "ic" circuits. This aligns
with previous level of protection "nL"
requirements.
NOTE Dielectric test requirements of
other applicable standards may still apply
(such as the relevant industrial standards).
6.3.14 Relays Applicable Applicable only regarding requirement for
relay to be used within its rating.
NOTE Requirements for dielectric and
separation distances are still addressed,
along with applicable safety requirements
of the relevant industrial standards.
6.4 Protection against polarity Applicable
reversal
st
6.5 Earth conductors, Applicable
Earthing requirements in the 1 paragraph
connections and
are only applicable if earth is necessary for
terminals
"ic" circuit.
Requirements for earthing are suitably
addressed by the applicable safety
requirements of the relevant industrial
standards.
nd
Requirements in 2 paragraph only
applicable to level of protection "ia" and
level of protection "ib". A single connection
is sufficient for level of protection ‘ic’.
6.6 Encapsulation Applicable Applicable only if relying on encapsulation
to exclude the atmosphere so as to reduce
separation distances, or reduce the ignition
capability of hot components. No short
conditions are applied unless separation
distances are less than required values so
as to impair intrinsic safety (see Annex D).
7 Components on which intrinsic safety depends
7.1 Rating of components Applicable For voltage and current, this clause
simplifies the rating requirements for “ic”
protective components from “nL”
requirements.
NOTE The concept of a component
having a defined "failure mode such that
protection is maintained" as an alternative
to de-rating (as existed for "nL") does not
exist for "ic".
– 8 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
7.2 Connectors for internal Applicable Applicable except for requirement
connections, plug-in cards regarding incorrect connection of internal
st
and components
plug-in connections in the 1 paragraph,
and the open circuit failure of a connection
nd
requirement in the 2 paragraph.
While interchangeability is a concern for
external connections due to field error, it is
not considered an “ic” concern for internal
connections. Production control and proper
service expectations can address internal
applications.
Open circuit failure of a connection
requirement is not applicable because
faults are not considered for ‘ic’.
Both are not considered a normal
operations condition (see 6.5).
7.3 Fuses Applicable Where an “ic” circuit depends upon a fuse
and where the fuse is directly connected to
the mains and where the fuse is also
directly connected to a circuit that is
considered normally subject to overloading
or shorting (such as output field wiring
receptacles or terminals), the breaking
capacity of such a fuse is based upon the
prospective short circuit current of the
mains supply. A diode safety barrier would
be a common example of such an
application involving output field wring
terminals. The prospective short-circuit
current of a 250 V mains supply is
considered to not be greater than 1 500 A.”
7.4 Primary and secondary Applicable For both apparatus and associated
cells and batteries apparatus, when such involves more than
type of protection “ic” (such as ‘ic nA’
apparatus or ‘nA [ic]’ associated
apparatus), connection of cells and
batteries in parallel for ‘ic’ is only permitted
in the ‘ic’ circuit provided that intrinsic
safety is not impaired.
7.5 Semiconductors
7.5.1 Transient effects Applicable For “ic”, the effects of transients are only
addressed for diode safety barriers
because connection is to unspecified
equipment. For other “ic” applications, no
additional evaluation is required regarding
the effects of transients based on the
following considerations:
• The presence of an explosive
atmosphere not likely to occur in normal
operation.
• The circuit complies with the applicable
safety requirements of the relevant
industrial standards.
NOTE Semiconductors serving as
protective components in "ic" circuits are
required to comply with the applicable
requirements elsewhere in this standard.
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
7.5.2 Shunt voltage limiters Applicable For “ic”, the effects of transients are only
addressed for diode safety barriers
because connection is to unspecified
equipment. For other “ic” applications, no
additional evaluation is required regarding
the effects of transients based on the
following considerations:
• The presence of an explosive
atmosphere is not likely to occur in
normal operation.
• The circuit complies with the applicable
safety requirements of the relevant
industrial standards.
For level of protection ‘ic’, a single
semiconductor is sufficient.
7.5.3 Series current limiters Applicable For level of protection “ic” a single
semiconductor is sufficient.
7.6 Failure of components, Applicable Applicable except for "ia" and "ib"
nd
connections and
requirements in 2 paragraph, and
th
separations
infallible connections requirements in 5
th
and 6 paragraphs.
7.7 Piezo-electric devices Applicable Applicable only if the piezo-circuit can be
directly shorted (for example due to non-
compliant spacings or sparking
components) (see 10.7).
NOTE The potential for the enclosure to
be impacted is a normal operating
condition, and therefore is applicable to
"ic".
7.8 Electrochemical cells for Applicable
the detection of gases
8 Infallible components, Not applicable According to 8.1, Clause 8, in its entirety,
infallible assemblies of does not apply for "ic" circuits.
components and infallible
connections on which
intrinsic safety depends
9 Supplementary requirements for specific apparatus
9.1 Diode safety barriers Applicable For “ic”, the effects of transients are
addressed for diode safety barriers
because connection is to unspecified
equipment.
NOTE Earthing requirements are
applicable to “ic” due to the earthing
requirements of intrinsically safe circuits in
IEC 60079-14.
9.2 FISCO apparatus Applicable
9.3 Handlights and caplights Applicable
10 Type verifications and type tests
10.1 Spark ignition test Applicable A safety factor of 1.0 with no countable or
non-countable fault conditions is applicable
for "ic".
10.2 Temperature tests Applicable Applicable except for non-linear concerns
st
in the last line of the 1 paragraph, which
would require mandatory testing of
components with non-linear aspects in the
actual rated ambient. Such an approach to
testing is not applicable for "ic" circuits,
and is only to be an option.
10.3 Dielectric strength tests Applicable See 6.3.13.
– 10 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
10.4 Determination of Applicable
parameters of loosely
specified components
10.5 Tests for cells and Applicable Applicable except short circuit testing is
batteries only to be considered at points external to
the cell or battery where the required
separation distances are not met.
Where temperature rise testing of the cells
and batteries is required, only one sample
need be subjected to the testing.
10.6 Mechanical tests
10.6.1 Casting compound Applicable Force and impact testing is applicable to
casting compounds that complete
enclosures.
As such, this is a normal operating
conditions concern, and the testing is
therefore applicable to "ic".
10.6.2 Determination of the Applicable While encapsulation of fuses for “ic” is not
acceptability of fuses generally required, the concern regarding
requiring encapsulation encapsulation flowing within the chamber
of a fuse, and preventing the element to
open, does reflect a normal operating
conditions concern, and therefore is
applicable to "ic" circuits (also see 7.3).
NOTE One example of such a concern is
for glass cartridge fuses.
10.6.3 Partitions Not applicable Any use of an interposing insulating
partition or earthed metallic partition is only
required to comply with the safety
requirements of the relevant industrial
standard.
10.7 Tests for intrinsically safe Applicable Applicable only if the piezo-circuit can be
apparatus containing directly shorted (for example due to non-
piezoelectric devices compliant spacings or sparking
components)(see 7.7).
NOTE The potential for the enclosure to
be impacted is a normal operating
condition, and therefore is applicable to
"ic".
10.8 Type tests for diode Applicable For level of protection “ic”, the effects of
safety barriers and safety transients are to be addressed for diode
shunts safety barriers because connection is to
unspecified equipment. (See 7.5.1)
10.9 Cable pull test Applicable
10.10 Transformer tests Not applicable This testing is required by 8.2.4, which is
explicitly waived for "ic" circuits.
NOTE Applicable safety requirements of
the relevant industrial standards still apply.
10.11 Optical isolators tests Not applicable This testing is required by 8.9.2, which is
explicitly waived for "ic" circuits.
NOTE Applicable safety requirements of
the relevant industrial standards still apply.
10.12 Current carrying capacity Not applicable This testing is required by 8.8, which is
of infallible printed circuit explicitly waived for "ic" circuits.
board connections
11 Routine verifications and tests
11.1 Routine tests for diode safety barriers
11.1.1 Completed barriers Applicable NOTE Removable links are not generally
needed for level of protection “ic” safety
barriers.
IEC 2016
Clause Requirement Applicability Remark
11.1.2 Diodes for 2-diode "ia" Not applicable This testing is applicable only to "ia"
barriers circuits.
11.2 Routine tests for infallible Not applicable This testing is required by 8.2.5, which is
transformers explicitly waived for "ic" circuits.
12 Marking Applicable Where it is necessary to include marking
from one of the other methods of protection
listed in IEC 60079-0, the symbol “ic” shall
occur first.
13 Documentation Applicable Where “ic” live maintenance procedures
are specified by the manufacturer in the
instructions provided, the effects of this live
maintenance do not invalidate intrinsic
safety under both normal operating
conditions and under conditions that may
reasonably be considered to occur during
live maintenance.
Annex A Assessment of Applicable
(normative) intrinsically safe circuits
Annex B Spark test apparatus for Applicable
(normative) intrinsically safe circuits
Annex C Measurement of creepage distances, clearances and separation distances through casting
(informative) compound and through solid insulation
Annex D Encapsulation Applicable Applicable only if relying on encapsulation
(normative) to exclude the atmosphere so as to reduce
separation distances, or reduce the ignition
capability of hot components. No fault
conditions are applied unless separation
distances are less than required values
(see 6.6.2).
Annex E Transient energy test
(informative)
Annex F Alternative separation Applicable Regarding transformers, only applicable
(normative) distances for assembled between external connections.
printed circuit boards and
NOTE Remaining construction features of
separation of
transformers are required to only comply
components
with the applicable safety requirements of
the relevant industrial standard. Through
solid insulation of conductors are required
to comply with Table 5.
Annex G Fieldbus intrinsically safe Applicable
(normative) concept (FISCO) -
Apparatus requirements
Annex H Ignition testing of semiconductor limiting power supply circuits
(informative)
– 12 – IEC 60079-11:2011/ISH3:2016
IEC 2016
COMMISSION ÉLECTROTECHNIQUE INTERNATIONALE
____________
IEC 60079-11
Edition 6.0 2011-06
ATMOSPHÈRES EXPLOSIVES –
Partie 11: Protection de l'équipement par sécurité intrinsèque "i"
FEUILLE D'INTERPR É TA TI O N 3
Cette feuille d’interprétation a été établie par le sous-comité 31G: Matériels à sécurité
intrinsèque, du comité d'études 31 de l'IEC: Equipements pour atmosphères explosives.
Le texte de cette feuille d’interprétation est issu des documents suivants:
ISH Rapport de vote
31G/253/ISH 31G/255/RVD
Le rapport de vote indiqué dans le tableau ci-dessus donne toute information sur le vote ayant
abouti à l'approbation de cette feuille d’interprétation.
___________
Question
Certains articles de l'IEC 60079-11:2011 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) indiquent précisément si
l'exigence est applicable ou non applicable au niveau de protection “ic”. De nombreux autres
articles, cependant, ne comportent aucune indication de quelque nature que ce soit,
contribuant ainsi à des incohérences possibles lorsque cette exigence s'applique. Quelles
sont les exigences de l'IEC 60079-11:2011 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) applicables au niveau de
protection "ic" dans la perspective d'une plus grande cohérence?
Réponse
Les éléments suivants ont été pris en compte dans la réponse à cette question:
1) Les exigences définies dans l'IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) qui indiquent que les
exigences sont applicables au niveau de protection “ic” sont considérées comme
“Applicables”;
2) Les exigences définies dans l'IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) qui indiquent que les
exigences ne sont pas applicables au niveau de protection “ic” sont considérées comme
“Non applicables”;
3) Dans le cas des exigences définies dans l'IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06) autres que
celles citées en référence en 1) et 2) ci-dessus:
IEC 2016
• déterminer si ces exigences relatives aux niveaux de protection "ia" et "ib" ont pour
objectif de s'appliquer aux conditions de défaut (anormales); et
• si tel est le cas, les exigences sont alors considérées comme non applicables au
niveau de protection "ic".
Compte tenu des éléments susmentionnés, le tableau informatif suivant (dont le concept est
analogue à l'Annexe B de l'IEC 60079-0:2011 pour les composants Ex) fournit un guide
permettant de déterminer les exigences définies dans l'IEC 60079-11 Edition 6.0 (2011-06)
qui s’appliquent au niveau de protection “ic”.
Contexte complémentaire
Les sept questions de principe fondamentales suivantes (en qualité d'informations détaillées
relatives au contexte complémentaire) ont contribué à l'é
...



Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...