ASTM D2281-68(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Wetting Agents by the Skein Test
Standard Test Method for Evaluation of Wetting Agents by the Skein Test
ABSTRACT
This test method covers the determination of the efficiency of ordinary commercial wetting agents using the skein test. It is applicable under limited and controlled conditions, but does not necessarily yield information correlating with specific end uses. The apparatus is comprised of a hook of standard weight depending on the concentration of the wetting agents and an anchor which shall be a flat, cylindrical, lead slug of specific dimensions. The reagents shall consist of water, acid and base test solutions, and wetting agent. The average of at least four determinations of the sinking time for each concentration of wetting agent shall be obtained and presented in plots with logarithmic coordinates. Standard deviation based on six replicate determinations shall also be calculated for precision.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method2,3 covers the determination of the efficiency of ordinary commercial wetting agents as defined in Terminology D 459. This test method is applicable under limited and controlled conditions, but does not necessarily yield information correlating with specific end uses.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2281–68 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Evaluation of Wetting Agents by the Skein Test
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2281; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
,
2 3
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the
efficiency of ordinary commercial wetting agents as defined in
Terminology D459. This test method is applicable under
limited and controlled conditions, but does not necessarily
yield information correlating with specific end uses.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
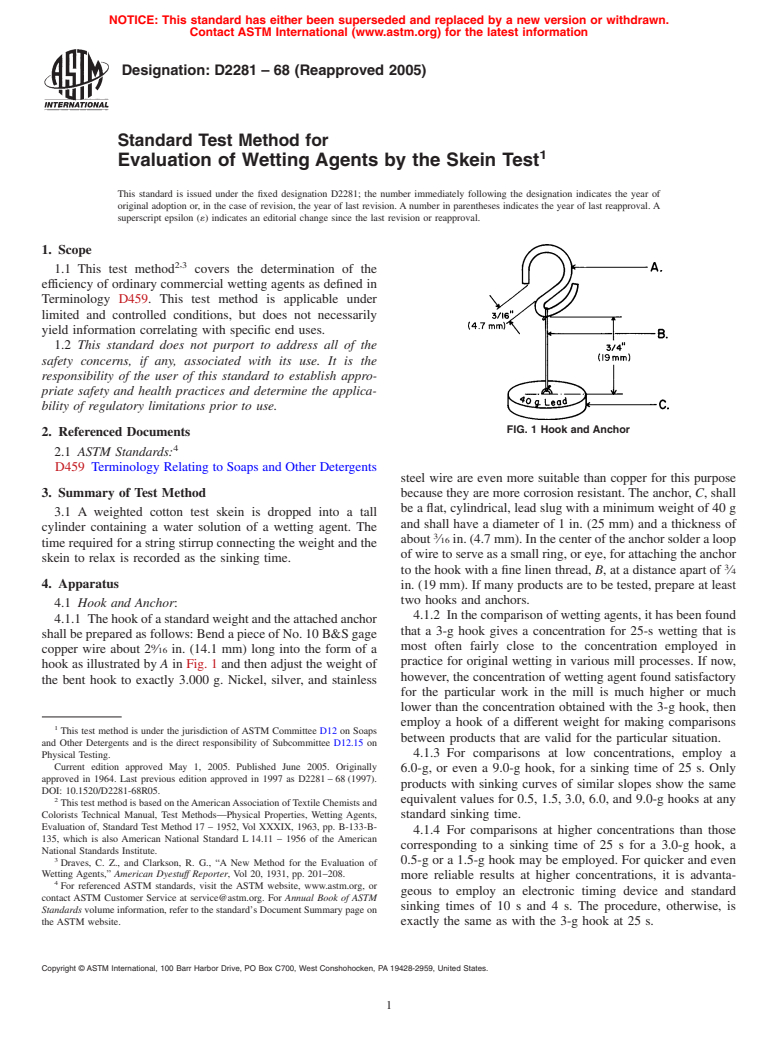
FIG. 1 Hook and Anchor
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D459 Terminology Relating to Soaps and Other Detergents
steel wire are even more suitable than copper for this purpose
3. Summary of Test Method because they are more corrosion resistant. The anchor, C, shall
be a flat, cylindrical, lead slug with a minimum weight of 40 g
3.1 A weighted cotton test skein is dropped into a tall
and shall have a diameter of 1 in. (25 mm) and a thickness of
cylinder containing a water solution of a wetting agent. The
about ⁄16in.(4.7mm).Inthecenteroftheanchorsolderaloop
time required for a string stirrup connecting the weight and the
of wire to serve as a small ring, or eye, for attaching the anchor
skein to relax is recorded as the sinking time.
to the hook with a fine linen thread, B, at a distance apart of ⁄4
4. Apparatus
in. (19 mm). If many products are to be tested, prepare at least
two hooks and anchors.
4.1 Hook and Anchor:
4.1.2 In the comparison of wetting agents, it has been found
4.1.1 Thehookofastandardweightandtheattachedanchor
that a 3-g hook gives a concentration for 25-s wetting that is
shall be prepared as follows: Bend a piece of No. 10 B&S gage
most often fairly close to the concentration employed in
copper wire about 2 ⁄16 in. (14.1 mm) long into the form of a
practice for original wetting in various mill processes. If now,
hook as illustrated by A in Fig. 1 and then adjust the weight of
however, the concentration of wetting agent found satisfactory
the bent hook to exactly 3.000 g. Nickel, silver, and stainless
for the particular work in the mill is much higher or much
lower than the concentration obtained with the 3-g hook, then
employ a hook of a different weight for making comparisons
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D12 on Soaps
between products that are valid for the particular situation.
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.15 on
Physical Testing. 4.1.3 For comparisons at low concentrations, employ a
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published June 2005. Originally
6.0-g, or even a 9.0-g hook, for a sinking time of 25 s. Only
approved in 1964. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D2281 – 68 (1997).
products with sinking curves of similar slopes show the same
DOI: 10.1520/D2281-68R05.
equivalent values for 0.5, 1.5, 3.0, 6.0, and 9.0-g hooks at any
This test method is based on theAmericanAssociation ofTextile Chemists and
Colorists Technical Manual, Test Methods—Physical Properties, Wetting Agents,
standard sinking time.
Evaluation of, Standard Test Method 17 – 1952, Vol XXXIX, 1963, pp. B-133-B-
4.1.4 For comparisons at higher concentrations than those
135, which is also American National Standard L 14.11 – 1956 of the American
corresponding to a sinking time of 25 s for a 3.0-g hook, a
National Standards Institute.
0.5-g or a 1.5-g hook may be employed. For quicker and even
Draves, C. Z., and Clarkson, R. G., “A New Method for the Evaluation of
Wetting Agents,” American Dyestuff Reporter, Vol 20, 1931, pp. 201–208.
more reliable results at higher concentrations, it is advanta-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
geous to employ an electronic timing device and standard
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
sinking times of 10 s and 4 s. The procedure, otherwise, is
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. exactly the same as with the 3-g hook at 25 s.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D2281–68 (2005)
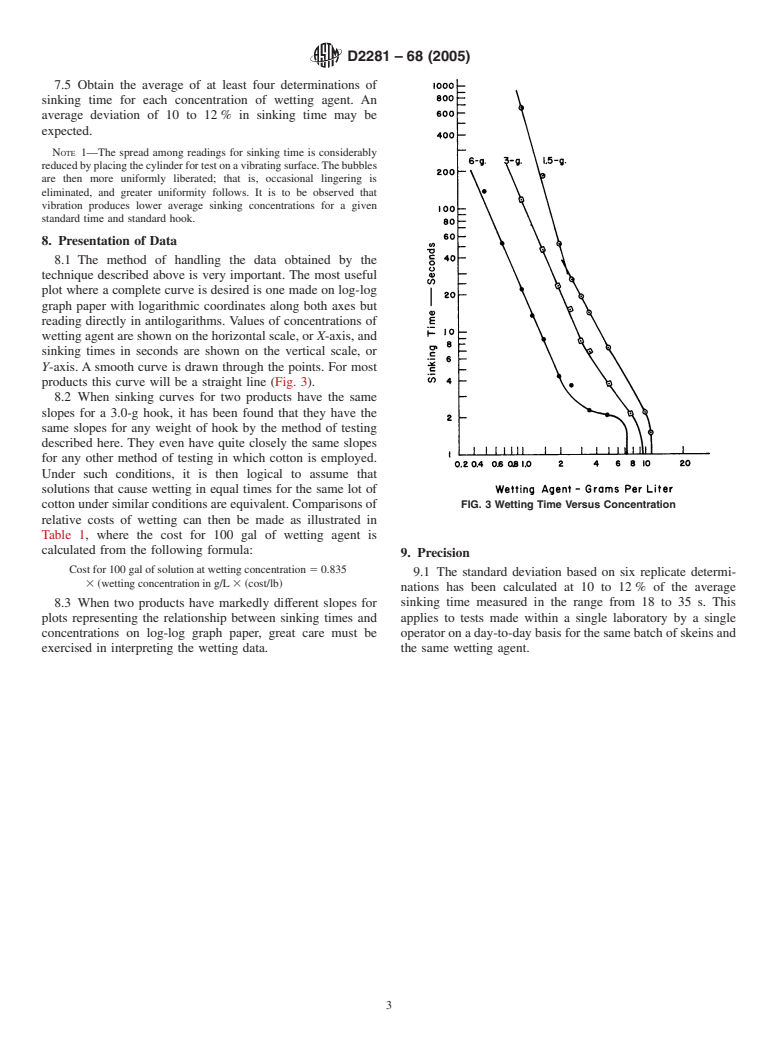
5. Test Skein wetting agent/L. This range of concentrations is sufficient for
the study of any commercial product.
5.1 40s/2 combed Peeler yarn with a lisle twist of 18 to 20
turns in. and a balanced construction is suitable. All the tubes
7. Procedure
of grey cotton yarn used for making 5-g skeins for a given
series of wetting tests shall be from the same lot of cotton. To
7.1 Pourthedilutedtestsolutionfroma1-Lvolumetricflask
average out the slight differences still remaining between
into a 1.5-Lbeaker to ensure mixing. Divide the solution in the
different tubes of the same lot and to increase the number of
beakerequallybetweentwo500-mLgraduatedcylinders.Ifthe
skeins that are closely alike in wetting properties for the series,
more dilute solutions are tested first, the mixing beaker and
it is urged that each skein be reeled simultaneously from 4 to
cylinders need not be rinsed out and dried each time.Wait after
12 tubes of yarn. In the case of purchased skeins, the weights
the cylinders have been filled until all bubbles below the
of the skeins shall be corrected individually to within 10 mg of
surface of the solution have risen to the top before making the
5 g or to within 1 grain of 77 grains.
sinking tests. Remove foam on the surface of the solution
5.2 For a determination, fold a 5.00-g (77 61-grain) skein
either with a 100-mL bulb pipet or with an aspirator. Where
of yarn enough times to form a loop 18 in. (460 mm) around.
there is little tendency for exhaustion of the wetting agent on
A36-in.(910-mm)skeinismostconvenientandcanbeformed
the test skeins, practically always true for cotton, it is permis-
into an 18-in. loop with only two folds; a 54-in. (1370-mm)
sible to use the same diluted solution over again several times
skein requires three folds; a 72-in. (1830-mm) skein, four
rather than to make a new diluted solution for each new skein.
folds; and a 90-in. (2290-mm) skein requires five folds.
In this case only one 500-mLcylinder may be filled repeatedly
from the solutions of a certain concentration.
6. Reagents
7.2 Since temperature often markedly affects wetting, stan-
6.1 Water—The quality of the water used in the testing of
dard temperatures of 77, 122, 158, and 194°F (25, 50, 70, and
wetting agents must be given careful consideration. The stock
90°C) have been chosen for testing so as to include the
solution is best prepared with distilled water. When it is not
complete commercially useful range. It is most convenient to
known under what conditions the wetting agent is to be
attain a temperature of 77°F
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.