ASTM D7518-10
(Specification)Standard Specification for 1,3 Propanediol (PDO) Base Engine Coolant for Automobile and Light-Duty Service
Standard Specification for 1,3 Propanediol (PDO) Base Engine Coolant for Automobile and Light-Duty Service
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for 1,3 propanediol base engine coolants used in automobiles or other light-duty service cooling systems. When concentrates are used at 40 to 70 % concentration by volume in water, or when prediluted glycol base engine coolants (50 volume % minimum) are used without further dilution, they will function effectively to provide protection against freezing, boiling, and corrosion.
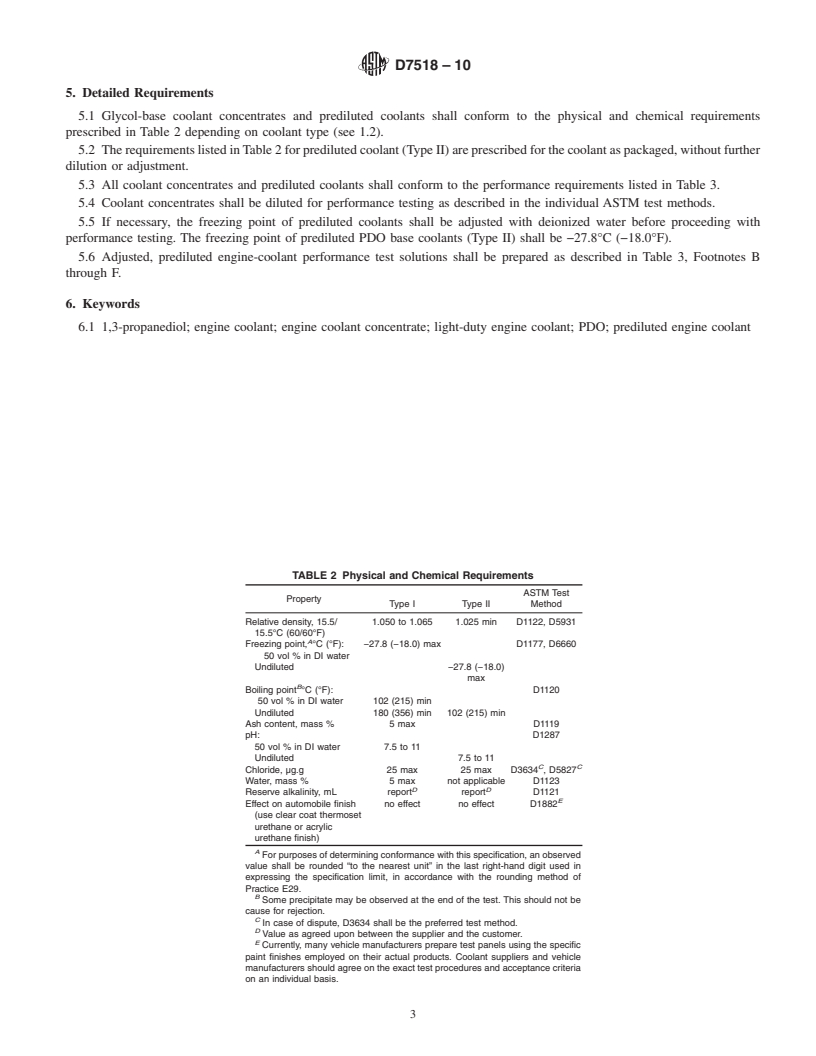
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D7518 −10
StandardSpecification for
1,3 Propanediol (PDO) Base Engine Coolant for Automobile
1
and Light-Duty Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7518; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D516Test Method for Sulfate Ion in Water
D1119Test Method for Percent Ash Content of Engine
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for 1,3 pro-
Coolants
panediol base engine coolants used in automobiles or other
D1120Test Method for Boiling Point of Engine Coolants
light-dutyservicecoolingsystems.Whenconcentratesareused
D1121Test Method for ReserveAlkalinity of Engine Cool-
at 40 to 70 % concentration by volume in water, or when
ants and Antirusts
prediluted glycol base engine coolants (50 volume % mini-
D1122Test Method for Density or Relative Density of
mum) are used without further dilution, they will function
EngineCoolantConcentratesandEngineCoolantsByThe
effectively to provide protection against freezing, boiling, and
Hydrometer
corrosion.
D1123Test Methods for Water in Engine Coolant Concen-
1.2 The coolants governed by this specification are catego-
trate by the Karl Fischer Reagent Method
rized as follows:
D1126Test Method for Hardness in Water
Coolant Type Description
D1177Test Method for Freezing Point of Aqueous Engine
I 1,3 Propanediol base concentrate Coolants
II 1,3 Propanediol predilute (50 vol
D1287TestMethodforpHofEngineCoolantsandAntirusts
%)
D1293Test Methods for pH of Water
NOTE 1—This specification is based on the knowledge of the perfor-
D1384Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants
mance of engine coolants prepared from new or virgin ingredients.
in Glassware
NOTE 2—This specification applies to automobiles and light-duty
D1881Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine
service. A specification for heavy-duty engine service is under develop-
ment.
Coolants in Glassware
D1882Test Method for Effect of Cooling System Chemical
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Solutions on Organic Finishes for Automotive Vehicles
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
D2570TestMethodforSimulatedServiceCorrosionTesting
only.
of Engine Coolants
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D2809Test Method for Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Corrosion Characteristics of Aluminum Pumps With En-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
gine Coolants
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D3321Test Method for Use of the Refractometer for Field
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Test Determination of the Freezing Point of Aqueous
Engine Coolants
2. Referenced Documents
2 D3634Test Method for Trace Chloride Ion in Engine Cool-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ants
D512Test Methods for Chloride Ion In Water
D4327Test Method forAnions in Water by Suppressed Ion
Chromatography
1
D4340TestMethodforCorrosionofCastAluminumAlloys
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD15onEngine
Coolants and Related Fluids and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
in Engine Coolants Under Heat-Rejecting Conditions
D15.07 on Specifications.
D4725Terminology for Engine Coolants
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
D5827Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D7518–09. DOI:
10.1520/D7518-10.
Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
D5931Test Method for Density and Relative Density of
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Engine Coolant Concentrates and Aqueous Engine Cool-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ants by Digital Density Meter
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7518−10
NOTE 3—Prediluted coolants are intended for direct addition to an
D6130Test Method for Determination of Silicon and Other
engine-coolingsystemwithnofurtherdilution.However,ifcircumstances
Elements in Engine Coolant by Inductively Coupled
requireadditionandpredilutedaqueousenginecoolantisnoavailable,use
Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
the appropriate engine-coolant concentrate (Type I) diluted to 50 volume
D6660Test MethodforFreezingPo
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately,ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D7518–09 Designation: D7518 – 10
Standard Specification for
1,3 Propanediol (PDO) Base Engine Coolant for Automobile
1
and Light-Duty Service
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7518; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for 1,3 propanediol base engine coolants used in automobiles or other light-duty
service cooling systems. When concentrates are used at 40 to 70 % concentration by volume in water, or when prediluted glycol
baseenginecoolants(50volume%minimum)areusedwithoutfurtherdilution,theywillfunctioneffectivelytoprovideprotection
against freezing, boiling, and corrosion.
1.2 The coolants governed by this specification are categorized as follows:
Coolant Type Description
I 1,3 Propanediol base concentrate
II 1,3 Propanediol predilute (50 vol %)
NOTE 1—This specification is based on the knowledge of the performance of engine coolants prepared from new or virgin ingredients.
NOTE 2—This specification applies to automobiles and light-duty service. A specification for heavy-duty engine service is under development.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D512 Test Methods for Chloride Ion In Water
D516 Test Method for Sulfate Ion in Water
D1119 Test Method for Percent Ash Content of Engine Coolants
D1120 Test Method for Boiling Point of Engine Coolants
D1121 Test Method for Reserve Alkalinity of Engine Coolants and Antirusts
D1122 Test Method for Density or Relative Density of Engine Coolant Concentrates and Engine Coolants ByThe Hydrometer
D1123 Test Methods for Water in Engine Coolant Concentrate by the Karl Fischer Reagent Method
D1126 Test Method for Hardness in Water
D1177 Test Method for Freezing Point of Aqueous Engine Coolants
D1287 Test Method for pH of Engine Coolants and Antirusts
D1293 Test Methods for pH of Water
D1384 Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants in Glassware
D1881 Test Method for Foaming Tendencies of Engine Coolants in Glassware
D1882 Test Method for Effect of Cooling System Chemical Solutions on Organic Finishes for Automotive Vehicles
D1888Methods of Test for Particulate and Dissolved Matter in Water
D2570 Test Method for Simulated Service Corrosion Testing of Engine Coolants
D2809 TestMethodforCavitationCorrosionandErosion-CorrosionCharacteristicsofAluminumPumpsWithEngineCoolants
D3321 Test Method for Use of the Refractometer for Field Test Determination of the Freezing Point of Aqueous Engine
Coolants
D3634 Test Method for Trace Chloride Ion in Engine Coolants
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D15 on Engine Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.07 on Specifications.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published May 2009. DOI: 10.1520/D7518-09.
CurrenteditionapprovedApril1,2010.PublishedMay2010.Originallyapprovedin2009.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2009asD7518–09.DOI:10.1520/D7518-10.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7518 – 10
D4327 Test Method for Anions in Water by Chemically Suppressed Ion Chromatography
D4340 Test Method for Corrosion of Cast Aluminum Alloys in Engine Coolants Under Heat-Rejecting Conditions
D4725 Terminology for Engine Coolants
D5827 Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
D5931 TestMethodforDensityandRelativeDensityofEngineCoolantConcentratesandAqueousEngineCoolantsbyDigital
Density Meter
D6130 Test Method for Determination o
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.