ASTM D1785-06
(Specification)Standard Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40, 80, and 120
Standard Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40, 80, and 120
ABSTRACT
This specification covers poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) plastic pipe, schedules 40, 80, and 120 for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only. This specification also includes classification criteria, nomenclature system, test methods, requirements, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst pressure, flattening, extrusion quality, finish, appearance, and marking methods for PVC plastic pipe. PVC pipe covered are marked with one of six type/grade/design stress designation and defined by four hydrostatic design stresses. PVC plastics are categorized by short-term and long term-strength tests.
SCOPE
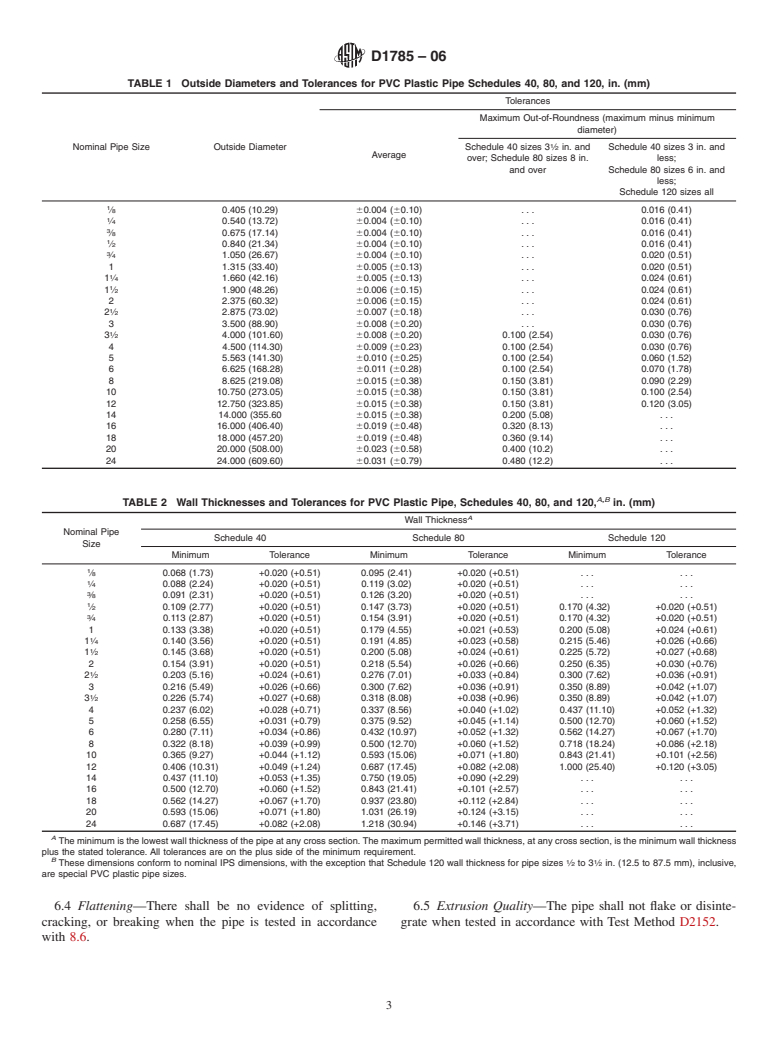
1.1 This specification covers poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) pipe made in Schedule 40, 80, and 120 sizes and pressure-rated for water (see Appendix X1). Included are criteria for classifying PVC plastic pipe materials and PVC plastic pipe, a system of nomenclature for PVC plastic pipe, and requirements and test methods for materials, workmanship, dimensions, sustained pressure, burst pressure, flattening, and extrusion quality. Methods of marking are also given.
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only, which are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Due to inherent hazards associated with testing components and systems with compressed air or other compressed gases some manufacturers do not allow pneumatic testing of their products. Consult with specific product/component manufacturers for their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.Note 1
Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases contain large amounts of stored energy which present serious saftey hazards should a system fail for any reason.Note 2
This standard specifies dimensional, performance and test requirements for plumbing and fluid handling applications, but does not address venting of combustion gases.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section , of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. A specific precautionary statement is given in Note 0. Note 4
CPVC plastic pipes, Schedules 40 and 80, which were formerly included in this specification, are now covered by Specification F 441/ F441M.Note 5
The sustained and burst pressure test requirements, and the pressure ratings in the , are calculated from stress values obtained from tests made on pipe 4 in. (100 mm) and smaller. However, tests conducted on pipe as large as 24-in. (600-mm) diameter have shown these stress values to be valid for larger diameter PVC pipe.Note 6
PVC pipe made to this specification is often belled for use as line pipe. For details of the solvent cement bell, see Specification D 2672 and for details of belled elastomeric joints, see Specifications D 3139 and D 3212.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D1785 – 06
Standard Specification for
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40, 80,
1
and 120
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1785; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
tions prior to use. A specific precautionary statement is given
1.1 This specification covers poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)
in Note 9.
pipemadeinSchedule40,80,and120sizesandpressure-rated
for water (see Appendix X1). Included are criteria for classi-
NOTE 3—CPVC plastic pipes, Schedules 40 and 80, which were
fying PVC plastic pipe materials and PVC plastic pipe, a formerly included in this specification, are now covered by Specification
F441/F441M.
systemofnomenclatureforPVCplasticpipe,andrequirements
NOTE 4—The sustained and burst pressure test requirements, and the
and test methods for materials, workmanship, dimensions,
pressure ratings in the Appendix X1, are calculated from stress values
sustained pressure, burst pressure, flattening, and extrusion
obtained from tests made on pipe 4 in. (100 mm) and smaller. However,
quality. Methods of marking are also given.
tests conducted on pipe as large as 24-in. (600-mm) diameter have shown
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended
these stress values to be valid for larger diameter PVC pipe.
for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only, which
NOTE 5—PVC pipe made to this specification is often belled for use as
are chemically compatible with the piping materials. Due to line pipe. For details of the solvent cement bell, see Specification D2672
and for details of belled elastomeric joints, see Specifications D3139 and
inherent hazards associated with testing components and sys-
D3212.
tems with compressed air or other compressed gases some
manufacturersdonotallowpneumatictestingoftheirproducts.
2. Referenced Documents
Consult with specific product/component manufacturers for
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
NOTE 1—Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases
D1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
contain large amounts of stored energy which present serious saftey
Under Constant Internal Pressure
hazards should a system fail for any reason.
D1599 TestMethodforResistancetoShort-TimeHydraulic
NOTE 2—This standard specifies dimensional, performance and test
Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
requirements for plumbing and fluid handling applications, but does not
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
address venting of combustion gases.
Plastics
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
(CPVC) Compounds
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
D2152 Test Method for Adequacy of Fusion of Extruded
information only.
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Molded Fittings by
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
Acetone Immersion
test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This
D2672 Specification for Joints for IPS PVC Pipe Using
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Solvent Cement
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
D2837 TestMethodforObtainingHydrostaticDesignBasis
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
forThermoplastic Pipe Materials or Pressure Design Basis
for Thermoplastic Pipe Products
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl
2
Based Pipe.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2006. Published May 2006. Originally
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D1785 – 05. DOI:
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D1785-0
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:D 1785–05 Designation: D1785 – 06
Standard Specification for
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40, 80,
1
and 120
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1785; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC) pipe made in Schedule 40, 80, and 120 sizes and pressure-rated for
water (see Appendix X1). Included are criteria for classifying PVC plastic pipe materials and PVC plastic pipe, a system of
nomenclatureforPVCplasticpipe,andrequirementsandtestmethodsformaterials,workmanship,dimensions,sustainedpressure,
burst pressure, flattening, and extrusion quality. Methods of marking are also given.
1.2 The products covered by this specification are intended for use with the distribution of pressurized liquids only, which are
chemically compatible with the piping materials. Due to inherent hazards associated with testing components and systems with
compressed air or other compressed gases some manufacturers do not allow pneumatic testing of their products. Consult with
specific product/component manufacturers for their specific testing procedures prior to pneumatic testing.
NOTE 1—Pressurized (compressed) air or other compressed gases contain large amounts of stored energy which present serious saftey hazards should
a system fail for any reason.
NOTE 2—This standard specifies dimensional, performance and test requirements for plumbing and fluid handling applications, but does not address
venting of combustion gases.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.5 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 8, of this specification: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
A specific precautionary statement is given in Note 9.
NOTE 3—CPVC plastic pipes, Schedules 40 and 80, which were formerly included in this specification, are now covered by Specification F 441F
441F441/F441M.
NOTE 4—The sustained and burst pressure test requirements, and the pressure ratings in the Appendix X1, are calculated from stress values obtained
from tests made on pipe 4 in. (100 mm) and smaller. However, tests conducted on pipe as large as 24-in. (600-mm) diameter have shown these stress
values to be valid for larger diameter PVC pipe.
NOTE 5—PVC pipe made to this specification is often belled for use as line pipe. For details of the solvent cement bell, see Specification D 2672D2672
and for details of belled elastomeric joints, see Specifications D 3139 and D 3212D3139 and D3212.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe Under Constant Internal Pressure
D1599 Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydraulic Failure Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D1784 Specification for Rigid Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Compounds and Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC)
Compounds
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.25 on Vinyl Based
Pipe.
Current edition approved August 1, 2005. Published August 2005. Originally approved in 1960. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D 1785–04a.
CurrenteditionapprovedMay1,2006.PublishedMay2006.Originallyapprovedin1960.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2005asD1785 – 05.DOI:10.1520/D1785-06.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
v
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.