ASTM D4871-00
(Guide)Standard Guide for Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
Standard Guide for Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes an apparatus used to measure the oxidation or thermal stability of liquids by subjecting them to temperatures in the range from 50 to 375°C in the presence of air, oxygen, nitrogen, or other gases at flow rates of 1.5 to 13 L/h, or in the absence of gas flow. Stability may be measured in the presence or absence of water or soluble or insoluble catalysts. Gases evolved may be allowed to escape, condensed and collected, or condensed and returned to the test cell.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D4871–00
Standard Guide for
Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4871; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Summary of Guide
1.1 This guide describes an apparatus used to measure the 3.1 An apparatus is described in which a sample of test
oxidation or thermal stability of liquids by subjecting them to fluid, typically from 100 ml or 100 g, is subjected to thermal or
temperatures in the range from 50 to 375°C in the presence of oxidative degradation or both. Insoluble or soluble catalyst
air, oxygen, nitrogen, or other gases at flow rates of 1.5 to 13 may be added. Gas may be bubbled through the liquid to
L/h, or in the absence of gas flow. Stability may be measured provide agitation or to promote oxidation or both. Water or
in the presence or absence of water or soluble or insoluble water vapor may be added.At the end of the test or at intervals
catalysts. Gases evolved may be allowed to escape, condensed throughout the test, the liquid is monitored for change in
and collected, or condensed and returned to the test cell. neutralization number, viscosity, weight loss, formation of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the sludge, or for other parameters. The corrosivity of the fluid
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the toward any catalyst metals can be determined from the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- appearance and weight change of the metal test specimens, if
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- present, or by monitoring the oil and any sludge or water for
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. metal content. The test is terminated after a fixed time period
or when a selected parameter reaches a condemning value.
2. Referenced Documents
NOTE 1—The volume of liquid at test temperature should be sufficient
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to cover the catalysts and should not extend beyond the heated portion of
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
the bath.
Oils
4. Significance and Use
D 156 Test Method for Saybolt Color of Petroleum Prod-
ucts (Saybolt Chromometer Method)
4.1 This standard describes an apparatus that provides the
D 445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
versatility required to conduct oxidation or thermal stability
and Opaque Liquids (and the Calculation of Dynamic
tests on liquids using a wide variety of test conditions. It is
Viscosity)
sufficientlyflexiblesothatnewtestconditionscanbechosenin
D 664 Test Method forAcid Number of Petroleum Products
response to the changing demands of the marketplace.
by Potentiometric Titration
5. Apparatus
D 974 Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-
Indicator Titration
5.1 Heating Block, as shown at the lower right in Fig. 1,to
D 1500 Test Method for ASTM Color of Petroleum Prod-
provide a controlled constant temperature for conducting tests.
ucts (ASTM Color Scale)
5.1.1 Test cells are maintained at constant elevated tempera-
D 3339 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Prod-
ture by means of a heated aluminum block which surrounds
ucts by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
each test cell.
D 5770 Test Method for Semi-quantitative Micro Determi-
5.1.2 Holes in the aluminum block to accommodate the test
nation ofAcid Number of Lubricating Oils During Oxida-
cells shall provide 1.0 mm max clearance for 38-mm outside
tion Testing
diameter glass tubes. The glass test cells shall fit into the block
to a depth of 225 6 5 mm.
1 NOTE 2—The original test blocks were made with spaces for ten test
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum
Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.09 on
Oxidation.
Current edition approved June 10, 2000. Published July 2000. Originally Astandardcommercialapparatushasbeenfoundsatisfactoryforthepurposeof
published as D 4871- 88. Last previous edition D 4871 - 95. thisguide.Thisapparatus,includingheatingblock,temperaturecontrolsystem,flow
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01. control system and glassware, is available from Falex Corp., 1020 Airpark Drive,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02. Sugar Grove, IL60554. Glassware for the Universal Oxidation test apparatus is also
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.03. available from W. A. Sales, Ltd., 419 Harvester Court, Wheeling, IL 60090.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D4871–00
FIG. 1 Universal Oxidation Test Apparatus
cells. Blocks with different number of holes are acceptable if other
ler shall have proportional and integral control modes, and a
requirements are met.
heater malfunction alarm.
5.2.2 Therangeforoperationisfromatleast50°Cto375°C.
5.1.3 The heating system shall be geometrically and ther-
(Warning—An adjustable deviation alarm that automatically
mally balanced. For thermal balance, sizes and locations of the
shuts down the system if temperature varies outside preset
heaters are proportioned against heat losses.
limitsisdesirableasasafetyfeatureandtoavoiderroneoustest
5.1.4 The block is cylindrical and constructed from forged
results. A separate adjustable high temperature monitor and
aluminum. The block has a minimum thickness of 38 mm of
shutoff is desirable as a safety device.)
insulation on all sides, top and bottom. An insulation of
5.2.3 Temperature control and uniformity is the most im-
thermally efficient ceramic fiber material is suggested.
portant parameter affecting test result precision. Therefore, the
5.1.5 The exterior jacket, sides and top are stainless steel or
heating system design is critical. Temperature from hole-to-
equivalent.
hole and at all sides of each hole in the block shall be uniform
5.1.6 The block is equipped with a well for a thermocouple
within the 0.5°C tolerance of the total system.
for temperature control and measurement, and a thermometer
5.3 GasFlowControlSystem,asshowninFig.1,toprovide
well for temperature calibration.
air or other gases to each test cell.
5.2 Temperature Control System, as shown at lower left in
Fig. 1, to maintain the heating block at a set temperature.
5.3.1 A gas flow controller is required for each test cell, to
5.2.1 The temperature controller shall be capable of main- provideairorotherdesiredgases.(Warning—Ifreactivegases
taining the block temperature within 60.5°C of the desired test are to be used in the test procedure, all fittings in the gas
temperature for the duration of the test. The preferred control- control system must be compatible with these gases.)
D4871–00
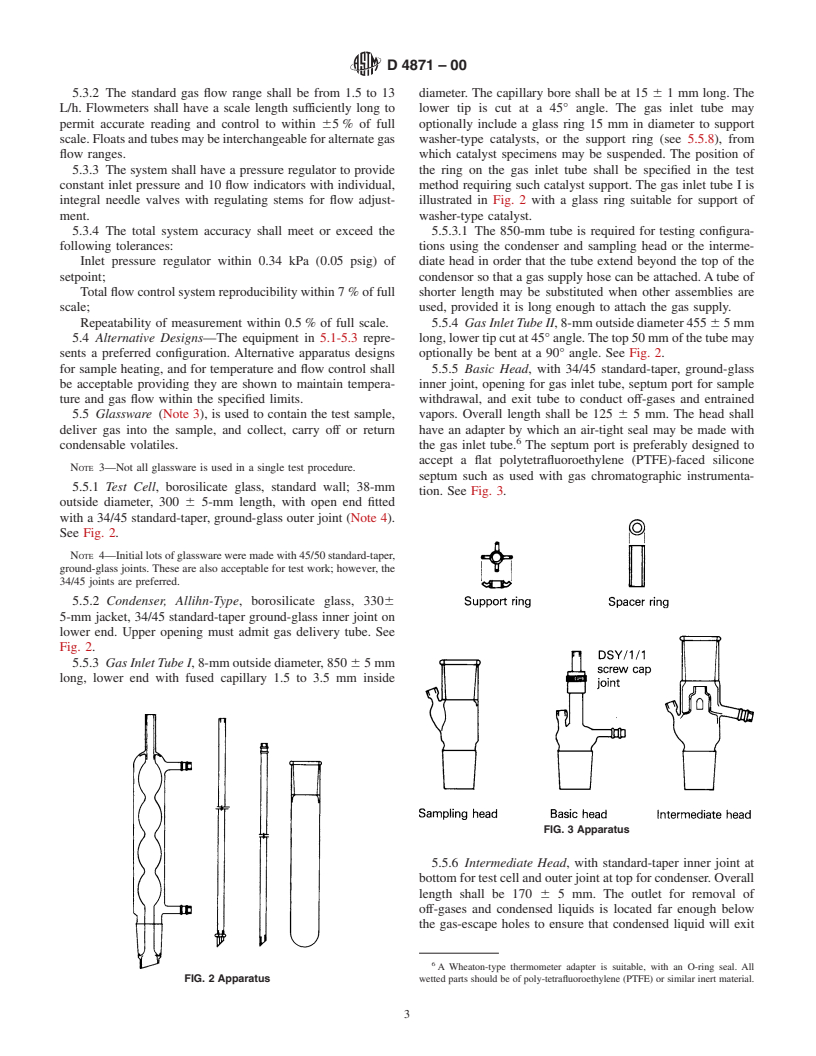
5.3.2 The standard gas flow range shall be from 1.5 to 13 diameter. The capillary bore shall be at 15 6 1 mm long. The
L/h. Flowmeters shall have a scale length sufficiently long to lower tip is cut at a 45° angle. The gas inle
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.