ASTM D4871-06
(Guide)Standard Guide for Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
Standard Guide for Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This standard describes an apparatus that provides the versatility required to conduct oxidation or thermal stability tests on liquids using a wide variety of test conditions. It is sufficiently flexible so that new test conditions can be chosen in response to the changing demands of the marketplace.
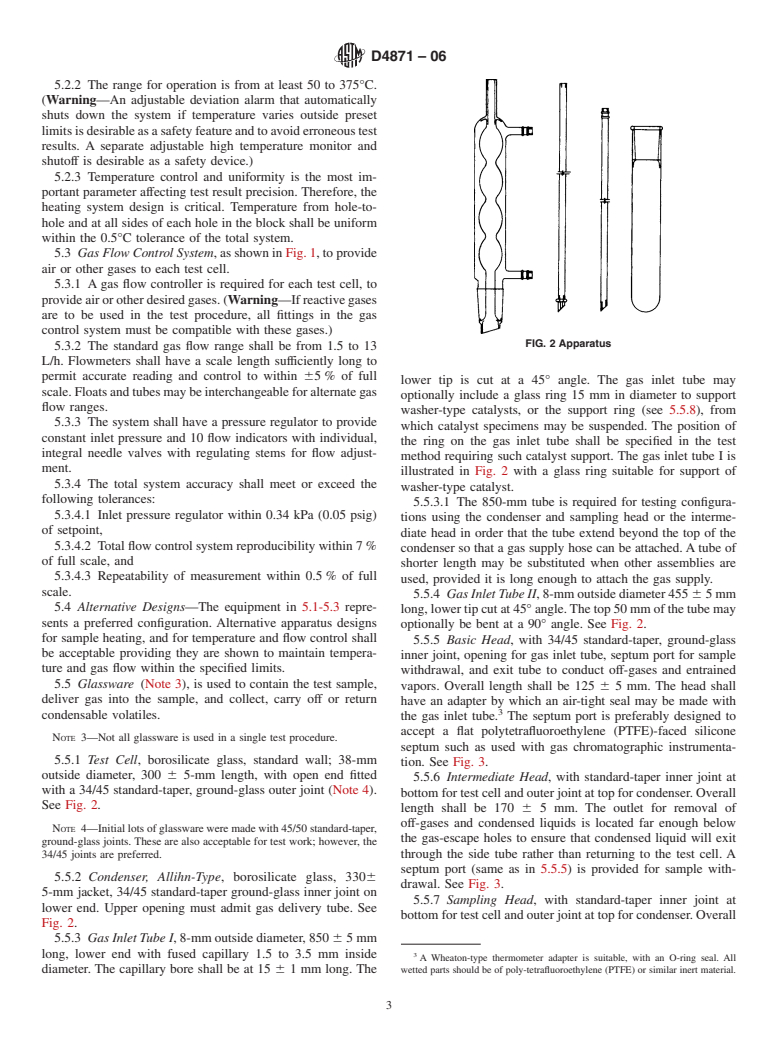
Procedures using this apparatus are described in the following ASTM standard test methods: D 5763, D 5846, and D 6514. Other procedures may be in use, but they have not been developed as ASTM standard test methods.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers an apparatus used to measure the oxidation or thermal stability of liquids by subjecting them to temperatures in the range from 50 to 375°C in the presence of air, oxygen, nitrogen, or other gases at flow rates of 1.5 to 13 L/h, or in the absence of gas flow. Stability may be measured in the presence or absence of water or soluble or insoluble catalysts. Gases evolved may be allowed to escape, condensed and collected, or condensed and returned to the test cell.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4871–06
Standard Guide for
1
Universal Oxidation/Thermal Stability Test Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4871; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D1500 TestMethodforASTMColorofPetroleumProducts
(ASTM Color Scale)
1.1 This guide covers an apparatus used to measure the
D3339 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Prod-
oxidation or thermal stability of liquids by subjecting them to
ucts by Semi-Micro Color Indicator Titration
temperatures in the range from 50 to 375°C in the presence of
D5763 Test Method for Oxidation and Thermal Stability
air, oxygen, nitrogen, or other gases at flow rates of 1.5 to
Characteristics of Gear Oils Using Universal Glassware
13 L/h, or in the absence of gas flow. Stability may be
D5770 Test Method for Semiquantitative Micro Determina-
measured in the presence or absence of water or soluble or
tion ofAcid Number of Lubricating Oils During Oxidation
insoluble catalysts. Gases evolved may be allowed to escape,
Testing
condensed and collected, or condensed and returned to the test
D5846 Test Method for Universal Oxidation Test for Hy-
cell.
draulic and Turbine Oils Using the Universal Oxidation
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Test Apparatus
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D6514 Test Method for High Temperature Universal Oxi-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
dation Test for Turbine Oils
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Summary of Guide
2. Referenced Documents 3.1 An apparatus is described in which a sample of test
2
fluid, typically from 100 ml or 100 g, is subjected to thermal or
2.1 ASTM Standards:
oxidative degradation or both. Insoluble or soluble catalyst
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
may be added. Gas may be bubbled through the liquid to
Oils
provide agitation or to promote oxidation or both. Water or
D156 Test Method for Saybolt Color of Petroleum Products
water vapor may be added.At the end of the test or at intervals
(Saybolt Chromometer Method)
throughout the test, the liquid is monitored for change in
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
neutralization number, viscosity, weight loss, formation of
and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
sludge, or for other parameters. The corrosivity of the fluid
ity)
toward any catalyst metals can be determined from the
D664 Test Method forAcid Number of Petroleum Products
appearance and weight change of the metal test specimens, if
by Potentiometric Titration
present, or by monitoring the oil and any sludge or water for
D974 Test Method for Acid and Base Number by Color-
metal content. The test is terminated after a fixed time period
Indicator Titration
or when a selected parameter reaches a condemning value.
NOTE 1—The volume of liquid at test temperature should be sufficient
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum
to cover the catalysts and should not extend beyond the heated portion of
Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.09 on
the bath.
Oxidation.
Current edition approved May 1, 2006. Published May 2006. Originally
4. Significance and Use
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D4871–00. DOI:
10.1520/D4871-06.
4.1 This standard describes an apparatus that provides the
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
versatility required to conduct oxidation or thermal stability
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on tests on liquids using a wide variety of test conditions. It is
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4871–06
FIG. 1 Universal Oxidation Test Apparatus
sufficientlyflexiblesothatnewtestconditionscanbechosenin 5.1.3 The heating system shall be geometrically and ther-
response to the changing demands of the marketplace. mally balanced. For thermal balance, sizes and locations of the
4.2 Procedures using this apparatus are described in the heaters are proportioned against heat losses.
following ASTM standard test methods: D5763, D5846, and
5.1.4 The block is cylindrical and constructed fr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.