ASTM D6111-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Bulk Density and Specific Gravity of Plastic Lumber and Shapes by Displacement
Standard Test Method for Bulk Density and Specific Gravity of Plastic Lumber and Shapes by Displacement
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The specific gravity or density of a solid is a property that can be measured conveniently to follow physical changes in a sample, to indicate degree of uniformity among different sampling units or specimens, or to indicate the average density of a large item.
It is possible that variations in density of a particular plastic lumber or shapes specimen will be due to changes in crystallinity, loss of plasticizer/solvent content, differences in degree of foaming, or to other causes. It is possible that portions of a sample will differ in density because of difference in crystallinity, thermal history, porosity, and composition (types or proportions of resin, plasticizer, pigment, or filler).
Note 2—Reference is made to Test Method D 1622.
Density is useful for calculating strength to weight and cost to weight ratios.
If the cross-sectional area of the specimen is required for future testing on a particular sample, it is acceptable to determine it from a specific gravity measurement, see Eq 5.
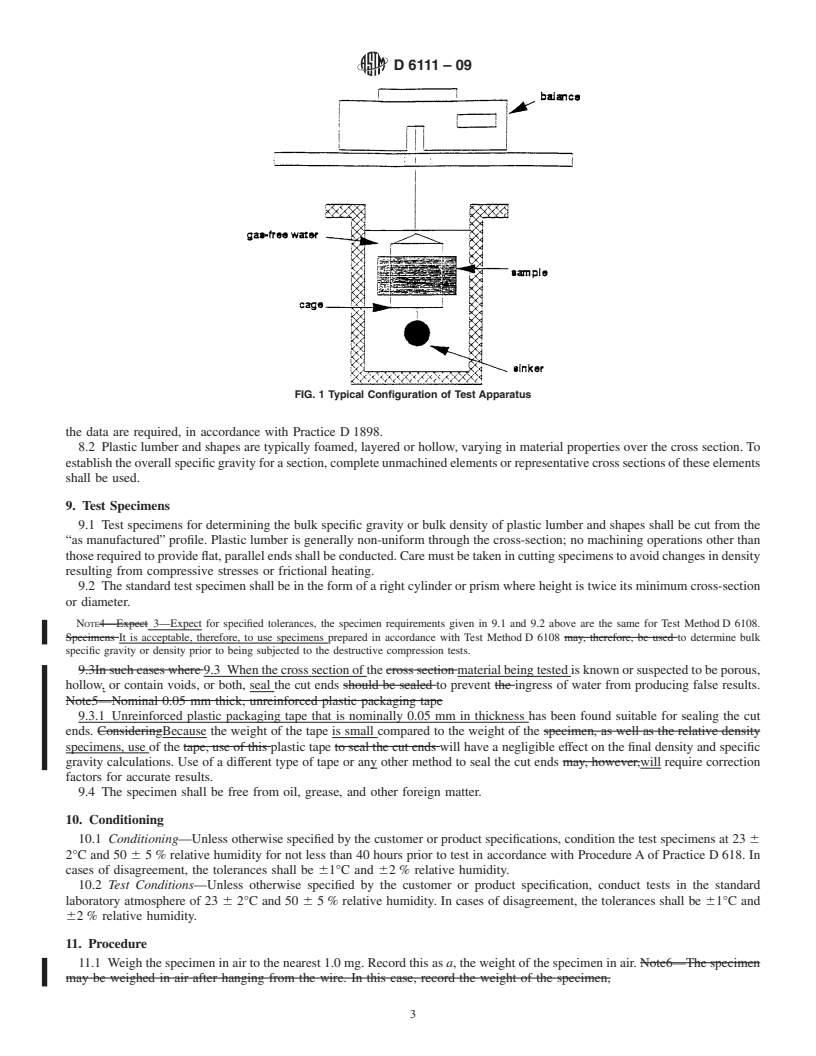
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the bulk density and specific gravity of plastic lumber and shapes in their “as manufactured” form. As such, this is a test method for evaluating the properties of plastic lumber or shapes as a product and not a material property test method.
1.2 This test method is suitable for determining the bulk specific gravity or bulk density by immersion of the entire item or a representative cross section in water. This test method involves the weighing of a one piece specimen in water, using a sinker with plastics that are lighter than water. This test method is suitable for products that are wet by, but otherwise not affected by water for the duration of the test.
1.3 Plastic lumber and plastic shapes are currently made predominately from recycled plastics. However, this test method would also be applicable to similar manufactured plastic products made from virgin resins where the product is non-homogeneous in the cross-section.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6111 −09
StandardTest Method for
Bulk Density And Specific Gravity of Plastic Lumber and
1
Shapes by Displacement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6111; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1622 Test Method for Apparent Density of Rigid Cellular
Plastics
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the bulk
3
D1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics (Withdrawn 1998)
density and specific gravity of plastic lumber and shapes in
D5033 GuideforDevelopmentofASTMStandardsRelating
their “as manufactured” form.As such, this is a test method for
to Recycling and Use of Recycled Plastics (Withdrawn
evaluating the properties of plastic lumber or shapes as a
3
2007)
product and not a material property test method.
D6108 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Plastic
1.2 This test method is suitable for determining the bulk
Lumber and Shapes
specific gravity or bulk density by immersion of the entire item
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
or a representative cross section in water. This test method
E12 Terminology Relating to Density and Specific Gravity
involves the weighing of a one piece specimen in water, using 3
of Solids, Liquids, and Gases (Withdrawn 1996)
a sinker with plastics that are lighter than water. This test
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
method is suitable for products that are wet by, but otherwise
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
not affected by water for the duration of the test.
3. Terminology
1.3 Plastic lumber and plastic shapes are currently made
predominately from recycled plastics. However, this test
3.1 Definitions:
method would also be applicable to similar manufactured
3.1.1 density, bulk—theweightperunitvolumeofamaterial
plastic products made from virgin resins where the product is
including voids inherent in material as tested. (See Terminol-
non-homogeneous in the cross-section.
ogy D883.)
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as 3.1.1.1 Discussion—Specific gravity at 23/23°C can be
3
standard. converted to density 23°C, g/cm , as follows:
23C 3
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D , g/cm 5 sp gr 23/23°C 30.9976 (1)
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.2 plastic lumber, n—a manufactured product composed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of more than 50 weight percent resin, and in which the product
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
generally is rectangular in cross-section and typically supplied
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
in board and dimensional lumber sizes, may be filled or
unfilled, and may be composed of single or multiple resin
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
blends.
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.3 plastic shape, n—a manufactured product composed
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of more than 50 weight percent resin, and in which the product
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing generally is not rectangular in cross-section, may be filled or
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
unfilled, and may be composed of single or multiple resin
blends.
3.1.4 resin, n—a solid or pseudosolid organic material often
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
of high molecular weight, which exhibits a tendency to flow
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.20 on Plastic Lumber (Section
D20.20.01).
when subjected to stress, usually has a softening or melting
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. Originally
range, and usually fractures conchoidally. (See Terminology
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D6111 - 03. DOI:
D883.)
10.1520/D6111-09.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6111−09
3.1.4.1 Discussion—In a broad sense, the term is used to 6.2 Immersion Cage:
designate any polymer that is a basic material for plastics. 6.2.1 Wire—A corrosion-resistant wire for suspending the
cage.
3.1.5 spe
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D6111–03 Designation: D 6111 – 09
Standard Test Method for
Bulk Density And Specific Gravity of Plastic Lumber and
1
Shapes by Displacement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6111; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope *
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the bulk density and specific gravity of plastic lumber and shapes in their “as
manufactured” form. As such, this is a test method for evaluating the properties of plastic lumber or shapes as a product and not
a material property test method.
1.2 This test method is suitable for determining the bulk specific gravity or bulk density by immersion of the entire item or a
representative cross section in water. This test method involves the weighing of a one piece specimen in water, using a sinker with
plastics that are lighter than water. This test method is suitable for products that are wet by, but otherwise not affected by water
for the duration of the test.
1.3 Plasticlumberandplasticshapesarecurrentlymadepredominatelyfromrecycledplastics.However,thistestmethodwould
also be applicable to similar manufactured plastic products made from virgin resins where the product is non-homogeneous in the
cross-section.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard. 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D 1622 Test Method for Apparent Density of Rigid Cellular Plastics
3
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
D 5033 Guide for the Development of ASTM Standards Relating to the ProperRecycling and Use of Recycled Plastics
D 6108 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Plastic Lumber and Shapes
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
0
E12 Terminology Relating to Density and Specific Gravity of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 density, bulk—the weight per unit volume of a material including voids inherent in material as tested. (See Terminology
D 883.)
3
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Specific gravity at 23/23°C can be converted to density 23°C, g/cm , as follows:
23C 3
D , g/cm 5 sp gr 23/23°C 3 0.9976 (1)
3.1.2 plastic lumber, n—a manufactured product composed of more than 50 weight percent resin, and in which the product
generally is rectangular in cross-section and typically supplied in board and dimensional lumber sizes, may be filled or unfilled,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.20 on Plastic Products (Section
D20.20.01).
Current edition approved March 10, 2003. Published April 2003. Originally approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 1997 as D6111-97
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. Originally approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 6111 - 03.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6111–09
and may be composed of single or multiple resin blends.
3.1.3 plastic shape, n—a manufactured product composed of more than 50 weight percent resin, and in which the product
generally is not rectangular in cross-section, may be filled or unfilled, and may be composed of single or multiple resin blends.
3.1.4 resin, n—a solid or pseudosolid organic material often of high molecula
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.