ASTM E2255-03
(Practice)Standard Practice for Conducting Visual Assessments for Lead Hazards in Buildings
Standard Practice for Conducting Visual Assessments for Lead Hazards in Buildings
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes procedures for conducting visual assessments in buildings to visually identify the type and location of potential lead hazards. These potential hazards are associated with deteriorated leaded paint, lead in dust, or lead in soil.
1.2 This practices addresses visual assessment procedures for four lead-hazard activities: lead risk (hazard) assessment, clearance examination, assessment of paint condition, and re-evaluation inspection.
1.3 Because there is considerable overlap among the requirements for these four types of lead-hazard activities, this standard first describes a generic visual assessment procedure, and then defines a specific procedure for each assessment type in terms of additions to, or deletions from, the generic procedure.
1.4 This practice does not address testing needed to confirm the presence of lead hazards.
1.5 This practice contains notes, which are explanatory and are not part of the mandatory requirements of this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 2255 – 03
Standard Practice for
Conducting Visual Assessments for Lead Hazards in
Buildings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2255; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Hazards in Facilities
E 2115 Guide for Conducting Lead Hazard Assessments of
1.1 This practice describes procedures for conducting visual
Residential Housing and other Properties Frequented by
assessments in buildings to visually identify the type and
Children
location of potential lead hazards. These potential hazards are
E 2239 Practice for Record Keeping and Record Preserva-
associated with deteriorated leaded paint, lead in dust, or lead
tion for Lead Hazard Activities
in soil.
1.2 This practices addresses visual assessment procedures
3. Terminology
for four lead-hazard activities: lead risk (hazard) assessment,
3.1 For definitions of terms not presented below, refer to
clearance examination, assessment of paint condition, and
Terminology E 1605.
re-evaluation inspection.
3.2 Definitions:
1.3 Because there is considerable overlap among the re-
3.2.1 abatement, n—any set of measures designed to elimi-
quirements for these four types of lead-hazard activities, this
nate permanently lead-based paint or lead-based paint hazards.
standard first describes a generic visual assessment procedure,
3.2.1.1 Discussion—Abatement includes: (1) removal of
and then defines a specific procedure for each assessment type
paint and dust, the permanent enclosure or encapsulation of
in terms of additions to, or deletions from, the generic
lead-based paint, the replacement of painted surfaces or com-
procedure.
ponents, or the removal or permanent covering of soil, when
1.4 This practice does not address testing needed to confirm
lead-based paint hazards are present in such paint, dust or soil;
the presence of lead hazards.
and (2) preparation, cleanup, disposal, and post abatement
1.5 This practice contains notes, which are explanatory and
clearance testing activities associated with such measures.
are not part of the mandatory requirements of this standard.
3.2.2 bare soil, n—soil or sand not covered by grass, sod,
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
other live ground covers, wood chips, gravel, artificial turf or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
similar covering.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2.3 clearance examination, n—a process conducted fol-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
lowing a lead-based paint hazard reduction activity to deter-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
mine that the hazard reduction activity is complete and that no
2. Referenced Documents soil-lead hazards or dust-lead hazards exist in the work area.
3.2.4 component, n—an element of a building identified by
2.1 ASTM Standards:
form, function and location.
E 1605 Terminology Relating to Lead in Buildings
3.2.4.1 Discussion—A component of a building may in-
E 1864 Practice for Evaluating Quality Systems of Organi-
clude exterior walls, interior room (type) walls, an interior
zations Engaged in Conducting Facility and Hazard As-
windowsill in a bathroom, etc.
sessments to Determine the Presence and Extent of Lead in
3.2.5 distinct painting history, n—an application history of
Paint, Dust, Airborne Particulate, and Soil
paint and other surface coatings to a component or room in a
E 2052 Guide for Identification and Management of Lead
building, as indicated by its visual appearance or a record of
application over time.
3.2.6 dust-lead hazard, n—surface dust in a building that
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Perfor-
contains, or is presumed to contain, a mass-per-area concen-
mance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.23 on Lead
tration of lead equal to or exceeding limits set in regulations
Hazards Associated with Buildings.
promulgated by authorities having jurisdiction.
Current edition approved May 10, 2003. Published July 2003.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.12.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E2255–03
3.2.7 friction surface, n—an interior or exterior surface that 6.4 Indelible Ink Pen or Permanent Marker.
is subject to abrasion or friction, including, but not limited to, 6.5 Flashlight, or other self powered portable light source,
certain window, floor, and stair surfaces.
as needed, for making visual observations in low light level
3.2.8 impact surface, n—an interior or exterior surface that areas.
is subject to damage by repeated sudden force, such as certain
6.6 Digital Camera (optional), with supporting equipment
parts of doorframes.
needed to create photographs that can be labeled.
3.2.9 lead-based paint hazard, n—lead-based paint on a
building surface that is deteriorated or present on chewable
7. Procedure for Conducting the Generic Visual
surfaces, friction surfaces, or impact surfaces, and that might
Assessment
result in adverse human health effects.
7.1 General Visual Assessment Requirements—The follow-
3.2.9.1 Discussion—Some regulations set by authorities
ing requirements apply to the conduct of visual assessments:
having jurisdiction include soil-lead hazards and dust-lead
7.1.1 Reporting:
hazards in their definitions of Lead-Based Paint Hazards.
7.1.1.1 Use a recording system that uniquely identifies the
3.2.10 lead-based paint inspection, n—a surface-by-surface
type and location of each hazard and each incidence of building
investigation to determine the presence of lead-based paint
component deterioration. At a minimum, the recording system
including a report explaining the results of the investigation.
must allow a reasonably educated person, when provided with
3.2.11 lead hazard activities, n—procedures, measures, and
all the records generated from a visual assessment, to deter-
actions including abatement, clearance, control, inspection,
mine what hazards and incidences of building component
maintenance, management, quality systems, reduction, and risk
deterioration were identified and where each was found. This
assessment pertaining to lead hazards in buildings.
practice provides the individual conducting the visual assess-
3.2.12 soil-lead hazard, n—bare soil on the property sur-
ment with the flexibility to use personal choices for some
rounding the building that contains or is presumed to contain
recording needs.
lead concentration equal or exceeding limits set in regulations
7.1.1.2 Examples of forms (site plans, building face
promulgated by authorities having jurisdiction.
sketches, floor plans, building component condition, paint/
dust/debris, and grounds) for recording information are shown
4. Significance and Use
in Appendix X1. An example of using these forms is presented
4.1 This practice supports lead poisoning prevention activi-
in Appendix X2.
ties by providing standardized procedures for conducting
7.1.1.3 Alternate forms are acceptable provided that they
visual assessments.
allow unique identification of all hazards and incidences of
4.2 This practice is intended to be used with other ASTM
building component deterioration.
standards, as appropriate, for conducting lead-hazard assess-
7.1.1.4 Information recorded on any particular form can be
ments. Consult Practice E 1864 for information regarding a
limited to only those areas where potential hazards are found.
quality system for field activities.
The example floor-plan shown in Appendix X2 includes detail
4.3 This practice is intended for use by individuals trained
for the living room, dining room and porch only because
to conduct visual assessments associated with lead-hazard
potential hazards were not identified in other rooms. However,
activities and in reporting their results. This practice is also
the individuals conducting visual assessments are cautioned
applicable for use by others interested in visual assessment of
against overly sparse records when no potential hazards are
properties for lead hazards, such as building code officials,
found. Lack of records may be viewed as a potential indicator
homeowners, and insurers.
that portions of the assessed area were not inspected.
7.1.1.5 Use of a camera to photographically capture the
5. Requirements for Individuals Conducting Visual
structures and grounds included within the boundaries of the
Assessments
assessment area provides a means of complementing forms.
5.1 Persons conducting visual assessments need a range of
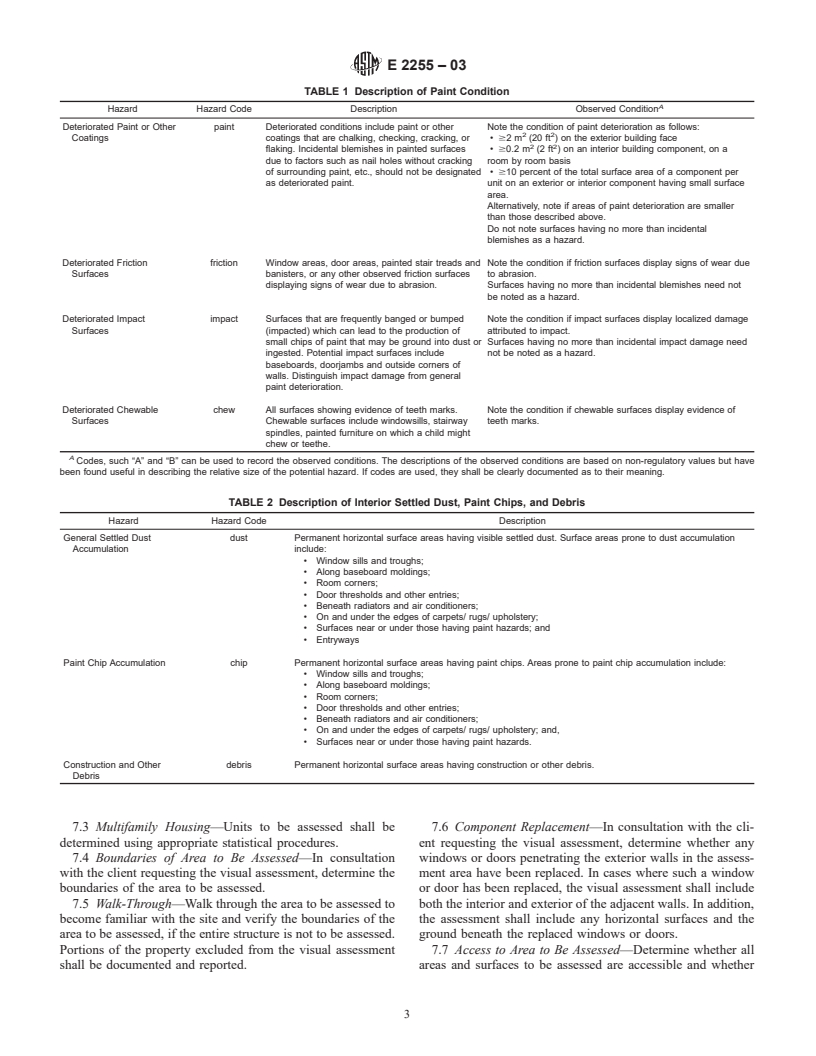
7.1.2 Symbols and Codes—Use of symbols and codes is not
expertise, including the ability to identify the type, extent, and
required but is recommended to reduce the effort needed to
cause of coating deterioration and component deterioration,
record building and grounds locations and observations of
and to determine the presence of settled dust, debris, and bare
hazards and component deterioration. The symbols and codes,
soil. Users of visual assessment services should review their
if used, shall be sufficiently defined to identify the items to
credentials and experience to determine whether they are
which they refer. The codes provided in various sections of this
qualified to conduct the work.
standard, such as in Tables 1-3, are exemplary; others may be
5.1.1 Visual assessments conducted as part of a lead-based
used depending on the needs of the person conducting the
paint activity within the scope of regulations promulgated by
visual assessment.
authorities having jurisdiction shall be conducted by appropri-
7.2 Existing Information—Review historic lead-hazard
ately certified or licensed individuals.
evaluation, hazard reduction and clearance reports and other
information describing on-going maintenance activities, and
6. Materials and Supplies
relevant building operations to identify changes from previous
6.1 Copies of Forms, (see Appendix X1). conditions and locations of renovation, remodeling, construc-
6.2 Clipboard, for holding forms. tion or abatement activity. Use this review to help define the
6.3 Pencil And Sharpener. boundaries of the assessment area.
E2255–03
TABLE 1 Description of Paint Condition
A
Hazard Hazard Code Description Observed Condition
Deteriorated Paint or Other paint Deteriorated conditions include paint or other Note the condition of paint deterioration as follows:
2 2
Coatings coatings that are chalking, checking, cracking, or • $2m (20 ft ) on the exterior building face
2 2
flaking. Incidental blemishes in painted surfaces • $0.2 m (2 ft ) on an interior building component, on a
due to factors such as nail holes without cracking room by room basis
of surrounding paint, etc., should not be designated • $10 percent of the total surface area of a component per
as deteriorated paint. unit on an exterior or interior component having small surface
area.
Alternatively, note if areas of paint deterioration are smaller
than those described above.
Do not note surfaces having no more than incidental
blemishes as a hazard.
Deteriorated Friction friction Window areas, door areas, painted stair treads and Note the condition if friction surfaces display signs of wear due
Surfaces banisters, or any other observed friction surfaces to abrasion.
displaying signs of wear due to abrasion. Surfaces having no more than incidental blemishes need not
be noted as a hazard.
Deteriorated Impact impact Surfaces that are frequently banged or bumped Note the condition if impact surfaces display localized damage
Surfaces (impacted) which can lead to the production of attributed to impact.
small chips of paint that may be ground into dust or Surfaces having no more than incidental impact damage need
ingested. Potential impact surfaces include not be noted as a hazard.
baseboards, doorjambs and outside corners of
walls. Distinguish impact damage from general
paint deterioration.
Deteriorated Chewable chew All surfaces showing evidence of teeth marks. Note the condition if chewable surfaces display evidence of
Surfaces Chewable surfaces include windowsills, stairway teeth marks.
spindles, painted furniture on which a child might
chew or teethe.
A
Codes, such “A” and “B” can be used to record the observed conditions. The descriptions of the observed conditions are based on non-regulatory values but have
been found useful in describing the relative size of the potential hazard. If codes are used, they shall be clearly documented as to their meaning.
TABLE 2 Description of Interior Settled Dust, Paint Chips, and Debris
Hazard Hazard Code Description
General Settled Dust dust Permanent horizontal surface areas having visible settled dust. Surface areas prone to dust accumulation
Accumulation include:
• Window sills and troughs;
• Along baseboard moldings;
• Room corners;
• Door thresholds and other entries;
• Beneath radiators and air conditioners;
• On and under the edges of carpets/ rugs/ upholstery;
• Surfaces near or under those having paint hazards; and
• Entryways
Paint Chip Accumulation chip Permanent horizontal surface areas having paint chips. Areas prone to paint chip accumulation include:
• Window sills and troughs;
• Along baseboard moldings;
• Room corners;
• Door thresholds and other entries;
• Beneath radiators and air conditioners;
• On and under the edges of carpets/ rugs/ upholstery; and,
• Surfaces near or under those having paint hazards.
Construction and Other debris Permanent horizontal surface areas having construction or other debris.
Debris
7.3 Multifamily Housing—Units to be assessed shall be 7.6 Component Replacement—In consultation with the cli-
determined using appropriate statistical procedures. ent requesting the visual assessment, determine whether any
7.4 Boundaries of Area to Be Assessed—In consultation windows or doors penetrating the exterior walls in the assess-
with the client requesting the visual assessment, determine the ment area have been replaced. In cases where such a window
boundaries of the area to be assessed. or door has been replaced, the visual assessment shall include
7.5 Walk-Through—Walk through the area to be assessed to both the interior and exterior of the adjacent walls. In addition,
become familiar with the site and verify the boundaries of the the assessment shall include any horizontal surfaces and the
area to be assessed, if the entire structure is not to be assessed. ground beneath the replaced windows or doors.
Portions of the property e
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.