ASTM D3343-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Estimation of Hydrogen Content of Aviation Fuels
Standard Test Method for Estimation of Hydrogen Content of Aviation Fuels
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is intended for use as a guide in cases in which an experimental determination of hydrogen content is not available. Table 1 shows a summary for the range of each variable used in developing the correlation. The mean value and its distribution about the mean, namely the standard deviation, is shown. This indicates, for example, that the mean density for all fuels used in developing the correlation was 783.5 kg/m3 and that two thirds of the samples had a density between 733.2 kg/m3 and 841.3 kg/m3, that is, plus and minus one standard deviation. The correlation is most accurate when the values of the variables to be used in the equation are within one standard deviation of the mean, but is useful up to two standard deviations of the mean. The use of this correlation may be applicable to other hydrocarbon distillates similar to aviation fuels, but only limited data on nonaviation fuels were included in the correlation.
5.2 Hydrogen content is required to correct gross heat of combustion to net heat of combustion. Net heat is used in aircraft calculation because all combustion products are in the gaseous state, but experimental methods measure gross heat.
SCOPE
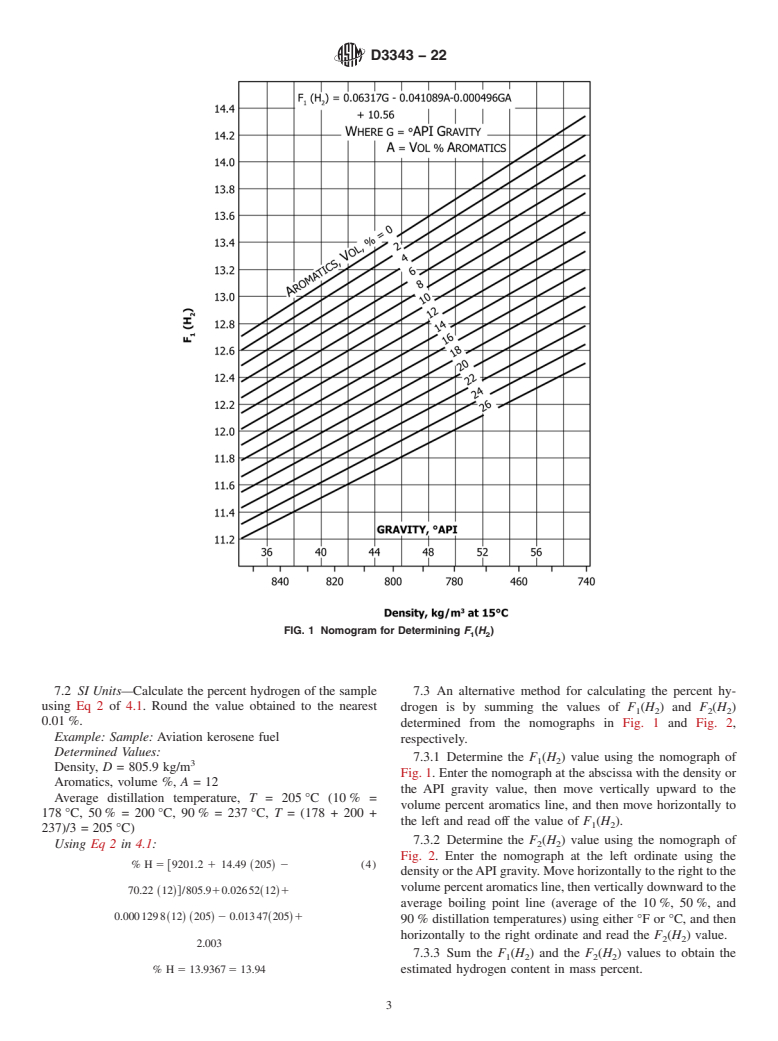
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the hydrogen content (mass percent) of aviation gasolines and aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels.
1.2 This test method is empirical and is applicable to liquid hydrocarbon fuels that conform to the requirements of specifications for aviation gasolines or aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels of types Jet A, Jet A-1, Jet B, JP-4, JP-5, JP-7, and JP-8.
Note 1: The procedure for the experimental determination of hydrogen in petroleum fractions is described in Test Methods D1018, D3701, D5291, and D7171.
Note 2: The estimation of the hydrogen content of a hydrocarbon fuel is justifiable only when the fuel belongs to a well-defined class for which a relationship among the hydrogen content and the distillation range, density, and aromatic content has been derived from accurate experimental measurements on representative samples of that class. Even in this case, the possibility that the estimates may be in error by large amounts for individual fuels should be recognized. The fuels used to establish the correlation presented in this test method are defined by the following specifications:
Fuel
Specification
Aviation gasolines
D910
Aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels
JP-4 and JP-5
MIL-DTL-5624
JP-7
MIL-DTL-38219
JP-8
MIL-DTL-83133
Jet A and Jet A-1
D1655
Miscellaneous hydrocarbons
No. 2 Diesel fuel
Kerosene distillates (similar to Jet A)
Miscellaneous (includes thinners, gasoline fractions, and unidentified blends)
Special production fuels (commercial products of nearly pure hydrocarbons
and special high-temperature fuels (HTF) produced for Air Force tests.
Pure hydrocarbons
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3343 − 22
Standard Test Method for
1
Estimation of Hydrogen Content of Aviation Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the hydrogen
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
content (mass percent) of aviation gasolines and aircraft
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
turbine and jet engine fuels.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.2 This test method is empirical and is applicable to liquid
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
hydrocarbon fuels that conform to the requirements of speci-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
ficationsforaviationgasolinesoraircraftturbineandjetengine
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
fuels of types Jet A, Jet A-1, Jet B, JP-4, JP-5, JP-7, and JP-8.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
NOTE 1—The procedure for the experimental determination of hydro-
2. Referenced Documents
gen in petroleum fractions is described in Test Methods D1018, D3701,
D5291, and D7171. 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 2—The estimation of the hydrogen content of a hydrocarbon fuel
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and
is justifiable only when the fuel belongs to a well-defined class for which
a relationship among the hydrogen content and the distillation range, Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
density, and aromatic content has been derived from accurate experimen-
D910 Specification for Leaded Aviation Gasolines
tal measurements on representative samples of that class. Even in this
D1018 Test Method for Hydrogen In Petroleum Fractions
case,thepossibilitythattheestimatesmaybeinerrorbylargeamountsfor
3
(Withdrawn 2021)
individual fuels should be recognized. The fuels used to establish the
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API
correlation presented in this test method are defined by the following
specifications: Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Prod-
ucts by Hydrometer Method
Fuel Specification
Aviation gasolines D910
D1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petro-
Aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels
leum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
JP-4 and JP-5 MIL-DTL-5624
D1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels
JP-7 MIL-DTL-38219
JP-8 MIL-DTL-83133
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Pe-
Jet A and Jet A-1 D1655
troleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
Miscellaneous hydrocarbons
D3701 Test Method for Hydrogen Content of Aviation
No. 2 Diesel fuel
Kerosene distillates (similar to Jet A)
Turbine Fuels by Low Resolution Nuclear Magnetic
Miscellaneous (includes thinners, gasoline fractions, and unidentified blends)
Resonance Spectrometry
Special production fuels (commercial products of nearly pure hydrocarbons
and special high-temperature fuels (HTF) produced for Air Force tests. D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid
Pure hydrocarbons
Fuels, and Lubricants
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
D5291 Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of
standard. Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products
1.3.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for
and Lubricants
information only. D7171 Test Method for Hydrogen Content of Middle Dis-
tillate Petroleum Products by Low-Resolution Pulsed
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee D02.04.0K on Correlative Methods. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2022. Published November 2022. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D3343 – 16. DOI: The l
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3343 − 16 D3343 − 22
Standard Test Method for
1
Estimation of Hydrogen Content of Aviation Fuels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the estimation of the hydrogen content (mass percent) of aviation gasolines and aircraft turbine and
jet engine fuels.
1.2 This test method is empirical and is applicable to liquid hydrocarbon fuels that conform to the requirements of specifications
for aviation gasolines or aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels of types Jet A, Jet A-1, Jet B, JP-4, JP-5, JP-7, and JP-8.
NOTE 1—The procedure for the experimental determination of hydrogen in petroleum fractions is described in Test Methods D1018, D3701, D5291, and
D7171.
NOTE 2—The estimation of the hydrogen content of a hydrocarbon fuel is justifiable only when the fuel belongs to a well-defined class for which a
relationship among the hydrogen content and the distillation range, density, and aromatic content has been derived from accurate experimental
measurements on representative samples of that class. Even in this case, the possibility that the estimates may be in error by large amounts for individual
fuels should be recognized. The fuels used to establish the correlation presented in this test method are defined by the following specifications:
Fuel Specification
Aviation gasolines D910
Aircraft turbine and jet engine fuels
JP-4 and JP-5 MIL-DTL-5624
JP-7 MIL-DTL-38219
JP-8 MIL-DTL-83133
Jet A and Jet A-1 D1655
Miscellaneous hydrocarbons
No. 2 Diesel fuel
Kerosene distillates (similar to Jet A)
Miscellaneous (includes thinners, gasoline fractions, and unidentified blends)
Special production fuels (commercial products of nearly pure hydrocarbons
and special high-temperature fuels (HTF) produced for Air Force tests.
Pure hydrocarbons
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3.1 Exception—The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0K on Correlative Methods.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2016Nov. 1, 2022. Published February 2016November 2022. Originally approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 20152016
as D3343 – 05 (2015).D3343 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/D3343-16.10.1520/D3343-22.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3343 − 22
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products and Liquid Fuels at Atmospheric Pressure
D910 Specification for Leaded Aviation Gasolines
3
D1018 Test Method for Hydrogen In Petroleum Fractions (Withdrawn 2021)
D1298 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, or API Gravity of Crude Petroleum and Liquid Petroleum Products by
Hydrometer Method
D1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
D1655 Specification for Aviation Turbine Fuels
D2887 Test Method for Boiling Range Distribution of Petroleum Fractions by Gas Chromatography
D3701 Test Method for Hydrogen Content of Aviation Turbine Fuels by Low Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Spectrometry
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants
D5291 Test Methods for Instrumental Det
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.