ASTM D2488-00
(Practice)Standard Practice for Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)
Standard Practice for Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers procedures for the description of soils for engineering purposes.
1.2 This practice also describes a procedure for identifying soils, at the option of the user, based on the classification system described in Test Method D 2487. The identification is based on visual examination and manual tests. It must be clearly stated in reporting an identification that it is based on visual-manual procedures.
1.2.1 When precise classification of soils for engineering purposes is required, the procedures prescribed in Test Method D 2487 shall be used.
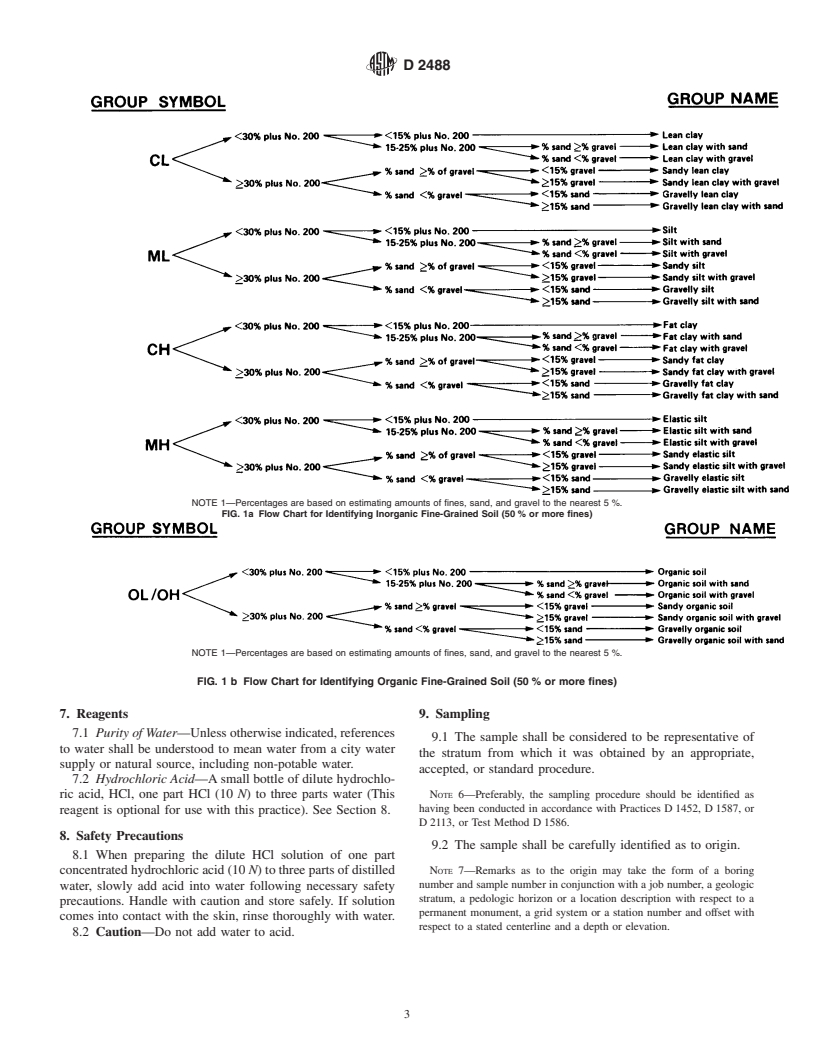
1.2.2 In this practice, the identification portion assigning a group symbol and name is limited to soil particles smaller than 3 in. (75 mm).
1.2.3 The identification portion of this practice is limited to naturally occurring soils (disturbed and undisturbed).
Note 1—This practice may be used as a descriptive system applied to such materials as shale, claystone, shells, crushed rock, etc. (see Appendix X2).
1.3 The descriptive information in this practice may be used with other soil classification systems or for materials other than naturally occurring soils.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific precautionary statements see Section 8.
1.6 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace education or experience and should be used in conjunction with professional judgment. Not all aspects of this practice may be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor should this document be applied without consideration of a project's many unique aspects. The word "Standard" in the title of this document means only that the document has been approved through the ASTM consensus process.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 2488 – 00
Standard Practice for
Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual
1
Procedure)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope * be applicable in all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not
intended to represent or replace the standard of care by which
1.1 This practice covers procedures for the description of
the adequacy of a given professional service must be judged,
soils for engineering purposes.
nor should this document be applied without consideration of
1.2 This practice also describes a procedure for identifying
a project’s many unique aspects. The word “Standard” in the
soils, at the option of the user, based on the classification
title of this document means only that the document has been
system described in Test Method D 2487. The identification is
approved through the ASTM consensus process.
based on visual examination and manual tests. It must be
clearly stated in reporting an identification that it is based on
2. Referenced Documents
visual-manual procedures.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2.1 When precise classification of soils for engineering
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
purposes is required, the procedures prescribed in Test Method
2
Fluids
D 2487 shall be used.
D 1452 Practice for Soil Investigation and Sampling by
1.2.2 In this practice, the identification portion assigning a
2
Auger Borings
group symbol and name is limited to soil particles smaller than
D 1586 Test Method for Penetration Test and Split-Barrel
3 in. (75 mm).
2
Sampling of Soils
1.2.3 The identification portion of this practice is limited to
2
D 1587 Practice for Thin-Walled Tube Sampling of Soils
naturally occurring soils (disturbed and undisturbed).
D 2113 Practice for Diamond Core Drilling for Site Inves-
2
NOTE 1—This practice may be used as a descriptive system applied to
tigation
such materials as shale, claystone, shells, crushed rock, etc. (seeAppendix
D 2487 Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes
X2).
2
(Unified Soil Classification System)
1.3 The descriptive information in this practice may be used
D 3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
withothersoilclassificationsystemsorformaterialsotherthan
Engaged in the Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and rock
3
naturally occurring soils.
as Used in Engineering Design and Construction
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
D 4083 Practice for Description of Frozen Soils (Visual-
2
as the standard.
Manual Procedure)
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3. Terminology
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1 Definitions—Except as listed below, all definitions are
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
in accordance with Terminology D 653.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
NOTE 2—For particles retained on a 3-in. (75-mm) US standard sieve,
precautionary statements see Section 8.
the following definitions are suggested:
1.6 This practice offers a set of instructions for performing
Cobbles—particles of rock that will pass a 12-in. (300-mm) square
one or more specific operations. This document cannot replace
opening and be retained on a 3-in. (75-mm) sieve, and
education or experience and should be used in conjunction
Boulders—particles of rock that will not pass a 12-in. (300-mm) square
opening.
withprofessionaljudgment.Notallaspectsofthispracticemay
3.1.1 clay—soilpassingaNo.200(75-µm)sievethatcanbe
made to exhibit plasticity (putty-like properties) within a range
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-18 on Soil and
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.07 on Identification and
Classification of Soils.
2
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 2000. Published May 2000. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.08.
e1 3
published as D 2488 – 66 T. Last previous edition D 2488 – 93 . Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.09.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 2488
with Test Method D 2487 where two symbols are required. Two symbols
of water contents, and that exhibits considerable strength when
arerequiredwhenthesoilhasbetween5and12
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.