ASTM D6940-04
(Practice)Standard Practice for Measuring Sifting Segregation Tendencies of Bulk Solids
Standard Practice for Measuring Sifting Segregation Tendencies of Bulk Solids
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers an apparatus and procedure for simulating the segregation tendencies of bulk solids by means of the sifting mechanism.
1.2 Temperature- and humidity-sensitive bulk solids may need to be tested at different temperatures and moisture contents, as would happen in an industrial environment.
1.3 The maximum particle size should be limited to 3 mm, to reduce the likelihood of binding the slide gate.
1.4 This standard is not applicable to all bulk solids and segregation mechanisms: while sifting is a common segregation mechanism experienced by many bulk solids, other segregation mechanisms not evaluated by this standard might induce segregation in practice.
1.5 The extent to which segregation will occur in an industrial situation is not only a function of the bulk solid and its tendency to segregate, but also the handling equipment (for example, bin design), process (for example, transfer rates), and environment.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D6940–04
Standard Practice for
1
Measuring Sifting Segregation Tendencies of Bulk Solids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6940; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This practice covers an apparatus and procedure for 3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms used in this test
simulating the segregation tendencies of bulk solids by means method shall be in accordance with Terminology D653.
of the sifting mechanism. 3.1.1 funnel flow pattern, n—a flow sequence in a bin or
1.2 Temperature- and humidity-sensitive bulk solids may hopper characterized by having some bulk solids moving
need to be tested at different temperatures and moisture through stagnant bulk solids. In general, there is no flow along
contents, as would happen in an industrial environment. the hopper walls.
1.3 The maximum particle size should be limited to 3 mm, 3.1.2 segregation, n—a process through which blended or
to reduce the likelihood of binding the slide gate. uniform powders or bulk solids become non-uniform, with
1.4 This standard is not applicable to all bulk solids and regions of varying composition, for example, particle size.
segregation mechanisms: while sifting is a common segrega- 3.1.3 sifting segregation, n—a mechanism in which finer
tion mechanism experienced by many bulk solids, other particles preferentially percolate into a zone within the bulk
segregation mechanisms not evaluated by this standard might solid.
induce segregation in practice. 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.5 The extent to which segregation will occur in an 3.2.1 collection cup, n—a collection cup holds a sample of
industrial situation is not only a function of the bulk solid and bulk solid once it is discharged from the apparatus.
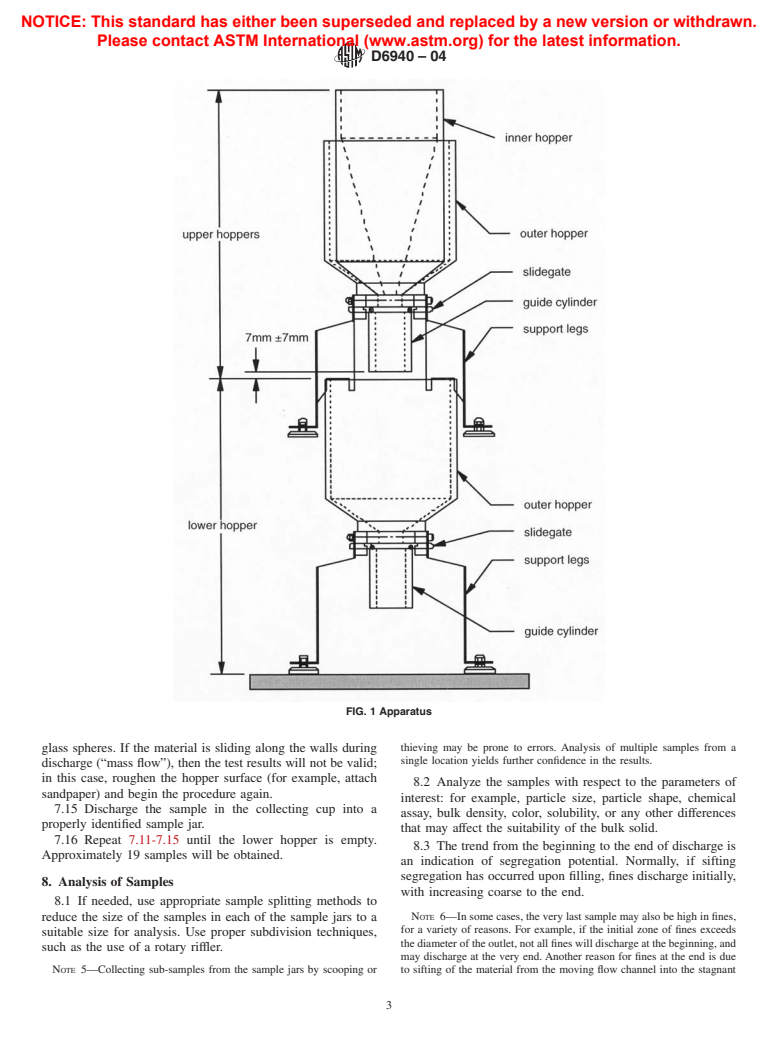
its tendency to segregate, but also the handling equipment (for 3.2.2 inner hopper, n—the inner hopper is transparent. It
example, bin design), process (for example, transfer rates), and hasasteepinnerconicalsectiondesignedtositwithintheouter
environment. hopper.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.2.3 outer hopper, n—the outer hopper consists of a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the shallow transparent hopper designed to provide funnel flow for
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- most bulk solids. It has an attached slide gate/guide cylinder
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- and support legs.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.2.4 representative sample, n—a quantity of the bulk solid
to be tested that is representative of that solid in an industrial
2. Referenced Documents
application being studied. Parameters of interest that may
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: affect whether or not a sample is representative include:
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
moisture, particle size distribution, raw material variation,
Fluids method of production, aging, chemical composition.
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
4. Summary of Practice
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
Used in Engineering Design and Construction 4.1 A representative sample of a bulk solid is placed in the
upper hopper of the apparatus.
4.2 The bulk solid is discharged to form a pile within the
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D18 on Soil and
lower hopper, allowing segregation to take place.
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.24 on Characterization
4.3 The segregated material is discharged in a funnel flow
and Handling of Powders and Bulk Solids.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2004. Published February 2004. Originally
pattern intended to recover zones of segregated material in a
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D6940–03. DOI:
known sequence. Samples are collected from the discharge
10.1520/D6940-04.
2
stream.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standardsvolume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D6940–04
solid being tested, placing this hop
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.