ASTM D2672-96a(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Joints for IPS PVC Pipe Using Solvent Cement
Standard Specification for Joints for IPS PVC Pipe Using Solvent Cement
ABSTRACT
This specification covers requirements, testing, and performance characteristics of joints for IPS PVC pipe using solvent cement. Testing requirements for both pressure and non-pressure pipe shall include socket dimensions, burst pressure, and joint tightness tests. PVC plastics, solvent cements, primer materials, workmanship, sampling, conditioning, marking, and quality shall conform to the requirements of this specification.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the socket produced for solvent cement joints on both pressure and non-pressure IPS pipe. It also covers the testing of the joints on both pressure and non-pressure pipe, and includes requirements for socket dimensions, burst pressure, and joint tightness tests of the solvent cemented joints. The tests described are not intended for routine quality control, but rather to evaluate the performance characteristics of the joint.
Note 1—On dual marked Schedule 40 DWV and potable water pipe, the socket bells must conform to the dimensional and physical requirements for pressure socket bells.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
Note 2—Changes in ground, water, or air temperature will produce expansion or contraction forces in PVC piping, and these will result in longitudinal shear stresses in the solvent cement joints. These stresses must be considered in the design and operation of the system.
Note 3—See Practice D 618 for information relating to this specification.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 10, of this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2672 −96a(Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Joints for IPS PVC Pipe Using Solvent Cement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2672; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers the socket produced for sol- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
vent cement joints on both pressure and non-pressure IPS pipe. D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
It also covers the testing of the joints on both pressure and D1599 Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydraulic
non-pressure pipe, and includes requirements for socket Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
dimensions, burst pressure, and joint tightness tests of the D1600 Terminology forAbbreviatedTerms Relating to Plas-
solvent cemented joints. The tests described are not intended tics
for routine quality control, but rather to evaluate the perfor- D1785 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic
Pipe, Schedules 40, 80, and 120
mance characteristics of the joint.
D2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Ther-
NOTE 1—On dual marked Schedule 40 DWV and potable water pipe,
moplastic Pipe and Fittings
the socket bells must conform to the dimensional and physical require-
D2241 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC)
ments for pressure socket bells.
Pressure-Rated Pipe (SDR Series)
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
D2565 Practice for Xenon-Arc Exposure of Plastics In-
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
tended for Outdoor Applications
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
D2665 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings
D2855 Practice for Making Solvent-Cemented Joints with
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Fittings
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
F512 Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride)
and are not considered standard.
(PVC) Conduit and Fittings for Underground Installation
NOTE 2—Changes in ground, water, or air temperature will produce
F656 Specification for Primers for Use in Solvent Cement
expansion or contraction forces in PVC piping, and these will result in
Joints of Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe and
longitudinal shear stresses in the solvent cement joints. These stresses
Fittings
must be considered in the design and operation of the system.
2.2 NSF Standard:
NOTE 3—See Practice D618 for information relating to this specifica-
tion.
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related
Materials
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
test method portion, Section 10, of this specification. This
3. Terminology
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Termi-
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
nology F412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Termi-
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
nology D1600, unless otherwise specified.
tions prior to use.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2009. Published September 2009. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D2672 – 96a(2003). Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd.,Ann
DOI: 10.1520/D2672-96AR09. Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D2672−96a (2009)
4. Materials considered satisfactory when formed from pipe which meets
the minimum wall thickness requirements of the applicable
4.1 General—PVCplasticsusedtomakethepipe,whichare
ASTM specification when measured in accordance with Test
belled under this specification, are designated in PVC product
Method D2122.
standards referencing this standard.
4.2 Solvent cements must conform to the requirements of
5.2 Joint Tests:
Specification D2565.
5.2.1 Burst Pressure—The minimum burst pressures for
4.3 Primers must conform to the requirements of Specifica- pipe and (bell) socket on pressure pipe shall be as given for
tion F656. pressure pipe in the applicable ASTM specification when
determined in accordance with 10.3.
5. Requirements
5.2.2 Joint Tightness—The (bell) socket joint on non-
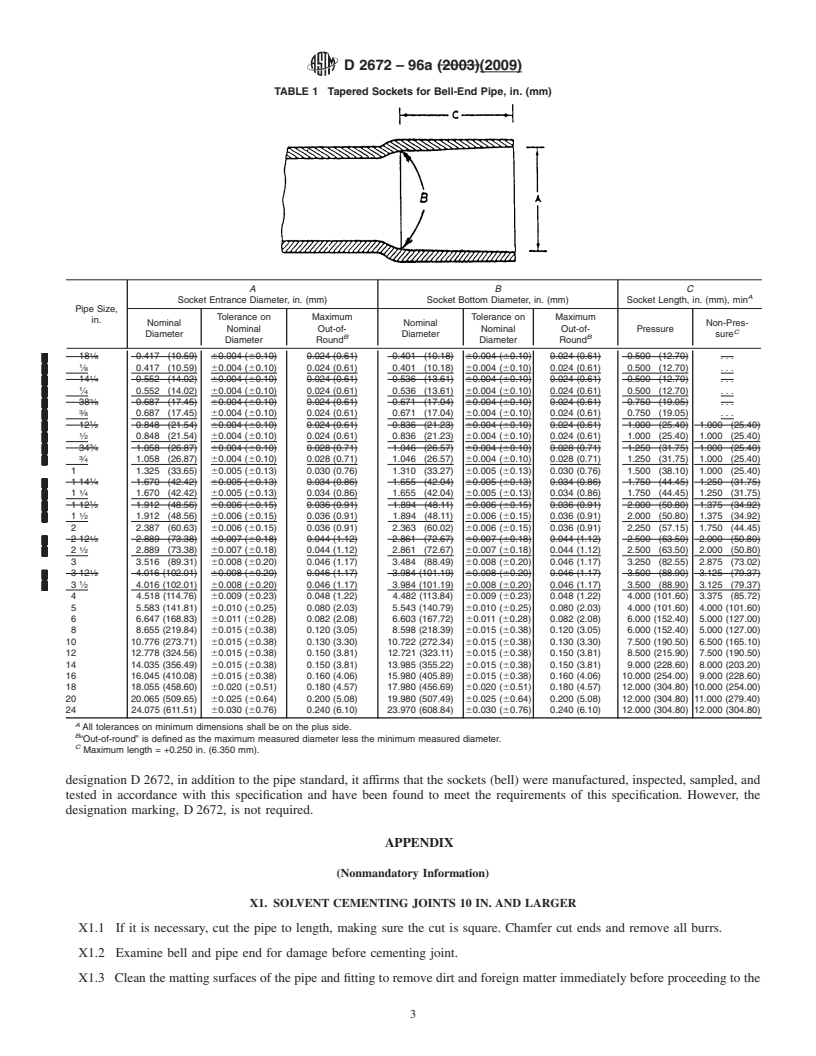
5.1 Bell Socket Dimensions and Tolerances:
pressure pipe shall not leak when tested in accordance with
5.1.1 Diameters and Length—The diameter, lengths, and
10.4.
tolerancesofthebellsocketsshallbeasshowninTable1when
measured in accordance with Test Method D2122.
6. Workmanship
5.1.2 Wall Thicknesses—The minimum wall thicknesses of
6.1 Each socket (bell) is required to be uniform in depth,
the sockets (bell) shall not be less than 90 % of the minimums
circular in cross section concentric with the pipe, and to have
shown for the pressure pipe in the applicable ASTM specifi-
cation. For non-pressure pipe, the integral socket (bell) shall be an end as square as commercially practicable.
TABLE 1 Tapered Sockets for Bell-End Pipe, in. (mm)
A B C
A
Socket Entrance Diameter, in. (mm) Socket Bottom Diameter, in. (mm) Socket Length, in. (mm), min
Pipe Size,
Tolerance on Maximum Tolerance on Maximum
in.
Nominal Nominal Non-Pres-
Nominal Out-of- Nominal Out-of- Pressure
C
Diameter Diameter sure
B B
Diameter Round Diameter Round
⁄8 0.417 (10.59) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.401 (10.18) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.500 (12.70) . . .
⁄4 0.552 (14.02) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.536 (13.61) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.500 (12.70) . . .
⁄8 0.687 (17.45) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.671 (17.04) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.750 (19.05) . . .
⁄2 0.848 (21.54) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 0.836 (21.23) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.024 (0.61) 1.000 (25.40) 1.000 (25.40)
⁄4 1.058 (26.87) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.028 (0.71) 1.046 (26.57) ±0.004 (±0.10) 0.028 (0.71) 1.250 (31.75) 1.000 (25.40)
1 1.325 (33.65) ±0.005 (±0.13) 0.030 (0.76) 1.310 (33.27) ±0.005 (±0.13) 0.030 (0.76) 1.500 (38.10) 1.000 (25.40)
1 ⁄4 1.670 (42.42) ±0.005 (±0.13) 0.034 (0.86) 1.655 (42.04) ±0.005 (±0.13) 0.034 (0.86) 1.750 (44.45) 1.250 (31.75)
1 ⁄2 1.912 (48.56) ±0.006 (±0.15) 0.036 (0.91) 1.894 (48.11) ±0.006 (±0.15) 0.036 (0.91) 2.000 (50.80) 1.375 (34.92)
2 2.387 (60.63) ±0.006 (±0.15) 0.036 (0.91) 2.363 (60.02) ±0.006 (±0.15) 0.036 (0.91) 2.250 (57.15) 1.750 (44.45)
2 ⁄2 2.889 (73.38) ±0.007 (±0.18) 0.044 (1.12) 2.861 (72.67) ±0.007 (±0.18) 0.044 (1.12) 2.500 (63.50) 2.000 (50.80)
3 3.516 (89.31) ±0.008 (±0.20) 0.046 (1.17) 3.484 (88.49) ±0.008 (±0.20) 0.046 (1.17) 3.250 (82.55) 2.875 (73.02)
3 ⁄2 4.016 (102.01) ±0.008 (±0.20) 0.046 (1.17) 3.984 (101.19) ±0.008 (±0.20) 0.046 (1.17) 3.500 (88.90) 3.125 (79.37)
4 4.518 (114.76) ±0.009 (±0.23) 0.048 (1.22) 4.482 (113.84) ±0.009 (±0.23) 0.048 (1.22) 4.000 (101.60) 3.375 (85.72)
5 5.583 (141.81) ±0.010 (±0.25) 0.080 (2.03) 5.543 (140.79) ±0.010 (±0.25) 0.080 (2.03) 4.000 (101.60) 4.000 (101.60)
6 6.647 (168.83) ±0.011 (±0.28) 0.082 (2.08) 6.603 (167.72) ±0.011 (±0.28) 0.082 (2.08) 6.000 (152.40) 5.000 (127.00)
8 8.655 (219.84) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.120 (3.05) 8.598 (218.39) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.120 (3.05) 6.000 (152.40) 5.000 (127.00)
10 10.776 (273.71) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.130 (3.30) 10.722 (272.34) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.130 (3.30) 7.500 (190.50) 6.500 (165.10)
12 12.778 (324.56) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.150 (3.81) 12.721 (323.11) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.150 (3.81) 8.500 (215.90) 7.500 (190.50)
14 14.035 (356.49) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.150 (3.81) 13.985 (355.22) ±0.015 (±0.38) 0.1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation: D 2672 – 96a (Reapproved 2003)2009)
Standard Specification for
Joints for IPS PVC Pipe Using Solvent Cement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2672; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the socket produced for solvent cement joints on both pressure and non-pressure IPS pipe. It also
covers the testing of the joints on both pressure and non-pressure pipe, and includes requirements for socket dimensions, burst
pressure, and joint tightness tests of the solvent cemented joints. The tests described are not intended for routine quality control,
but rather to evaluate the performance characteristics of the joint.
NOTE 1—On dual marked Schedule 40 DWV and potable water pipe, the socket bells must conform to the dimensional and physical requirements for
pressure socket bells.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
NOTE 2—Changes in ground, water, or air temperature will produce expansion or contraction forces in PVC piping, and these will result in longitudinal
shear stresses in the solvent cement joints. These stresses must be considered in the design and operation of the system.
NOTE 3—See Practice D 618 for information relating to this specification.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 10, of this specification.Thisstandard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standardtoestablishappropriatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 1599 Test Method for Resistance to Short-Time Hydraulic Failure Pressure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
D 1785 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40, 80, and 120
D 2122 Test Method for Determining Dimensions of Thermoplastic Pipe and Fittings
D 2241 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pressure-Rated Pipe (SDR Series)
D2564SpecificationforSolventCementsforPoly(VinylChloride)(PVC)PlasticPipingSystems 2565 PracticeforXenon-Arc
Exposure of Plastics Intended for Outdoor Applications
D 2665 Specification for Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Drain, Waste, and Vent Pipe and Fittings
D 2855 Practice for Making Solvent-Cemented Joints with Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Pipe and Fittings
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
F 512 Specification for Smooth-Wall Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Conduit and Fittings for Underground Installation
F 656 Specification for Primers for Use in Solvent Cement Joints of Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (PVC) Plastic Pipe and Fittings
2.2 NSF Standard:
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related Materials
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2003.1, 2009. Published September 2003.2009. Originally approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 19962003 as
D 2672 – 96a(2003).
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
, Vol 08.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 2672 – 96a (2003)(2009)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412 and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology
D 1600, unless otherwise specified.
4. Materials
4.1 General—PVC plastics used to make the pipe, which are belled under this specification, are designated in PVC product
standards referencing this standard.
4.2 Solvent cements must conform to the requirements of Specification D 2564.
4.3 Primers must conform to the requirements of Specification F 656.
5. Requirements Requirements
5.1 Bell Socket Dimensions and Tolerances:
5.1.1 Diameters and Length—The diameter, lengths, and tolerances of the bell sockets shall be as shown in Table 1 when
measured in accordance with Test Method D 2122.
5.1.2 Wall Thicknesses—The minimum wall thicknesses of the sockets (bell) shall not be less than 90 % of the minimums
shown for the pressure pipe in the applicable ASTM specification. For non-pressure pipe, the integral socket (bell) shall be
considered satisfactory when formed from pipe which meets the minimum wall thickness requirements of the applicable ASTM
specification when measured in accordance with Test Method D 2122.
5.2 Joint Tests:
5.2.1 Burst Pressure—The minimum burst pressures for pipe and (bell) socket on pressure pipe shall be as given for pressure
pipe in the applicable ASTM specification when determined in accordance with 10.3.
5.2.2 Joint Tightness—The (bell) socket joint on non-pressure pipe shall not leak when tested in accordance with 10.4.
6. Workmanship
6.1 Each socket (bell) is required to be uniform in depth, circular in cross section concentric with the pipe, and to have an end
as square as commercially practicable.
7. Retest and Rejection
7.1 If the results of any test(s) do not meet the requirements of this specification, the test(s) shall be conducted again only by
agreement between the purchaser and the seller. Under such agreement, minimum requirements shall not be lowered, nor tests
omitted, substituted, changed, or modified, nor shall specification limits be changed. If upon retest, failure occurs, the quantity of
product represented by the test(s) does not meet the requirements of this specification.
8. Sampling and Test Specimens
8.1 Take at random a sample of the pipe with (bell) socket sufficient to determine conformance with this specification.
8.1.1 The test specimens for any pressure test shall have at least a part of the marking in their central sections. The central
section is that portion of pipe which is at least one pipe diameter away from an end closure.
8.1.2 DryFitofJoint—Manuallyinsertachamferedordeburredpipespigotintothesocket(bell).Theremustbeaninterference
between the spigot and bell after inserting the spigot one third to two thirds of socket (bell) depth.
9. Conditioning
9.1 Condition the test specimens at 2373.4 6 2°C (73.43.6°F (23 6 3.6°F)2°C) and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less
than 40 h prior to test in accordance with Procedure A of Practice D 618, for those tests requiring conditioning.
10. Test Methods
10.1 Test Conditions—Conduct the tests in the Standard LaboratoryAtmosphere of 2373.4 6 3.6°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 65%
relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in Practice D 618 or in this specification.
10.2 Socket Joint Assembly—Assemble the socket joint per Practice D 2855, and condition at 23°C (73.4°F)73.4°F (23°C) for
a minimum of 48 h.
10.3 Burst Pressure Test of Joint Assembly—Determine the burst pressure of one specimen in accordance with Test Method
D 1599. The assembled socket (bell) joint shall be within the middle 30 % of the overall specimen length. The time to failure of
the specimen shall be between 60 and 70 s.
10.4 Socket Joint Tightness Test—Subject the assembly to an internal pressure of 170 kPa (25 psi)25 psi (170 kPa) using water
as the test medium. Maintain this pressure for at least 1 h. There shall be no leakage.
11. Marking and Quality Assurance
11.1 When pipe, made in accordance with Specifications D 1785, D 2241, D 2665 , and F512and F 512, is marked withASTM
Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd., Ann Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
D 2672 – 96a (2003)(2009)
TABLE 1 Tapered Sockets for Bell-End Pipe, in. (mm)
A B C
A
Socket Entrance Diameter, in. (mm) Socket Bottom Diameter, in. (mm) Socket Length, in. (mm), min
Pipe Size,
Tolerance on Maximum Tolerance on Maximum
in.
Nominal Nominal Non-Pres-
Nominal Out-of- Nominal Out-of- Pressure
C
Diameter Diamete
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.