ASTM D3705-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Misting Properties of Lubricating Fluids
Standard Test Method for Misting Properties of Lubricating Fluids
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test provides a guide for evaluating the misting characteristics of oils for use in industrial mist lubrication systems. The degree of correlation between this test and service performance has not been fully determined.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the misting characteristics of lubricating fluids.
Note 1: This test method should not be used to evaluate fluids containing solid additives such as graphite.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
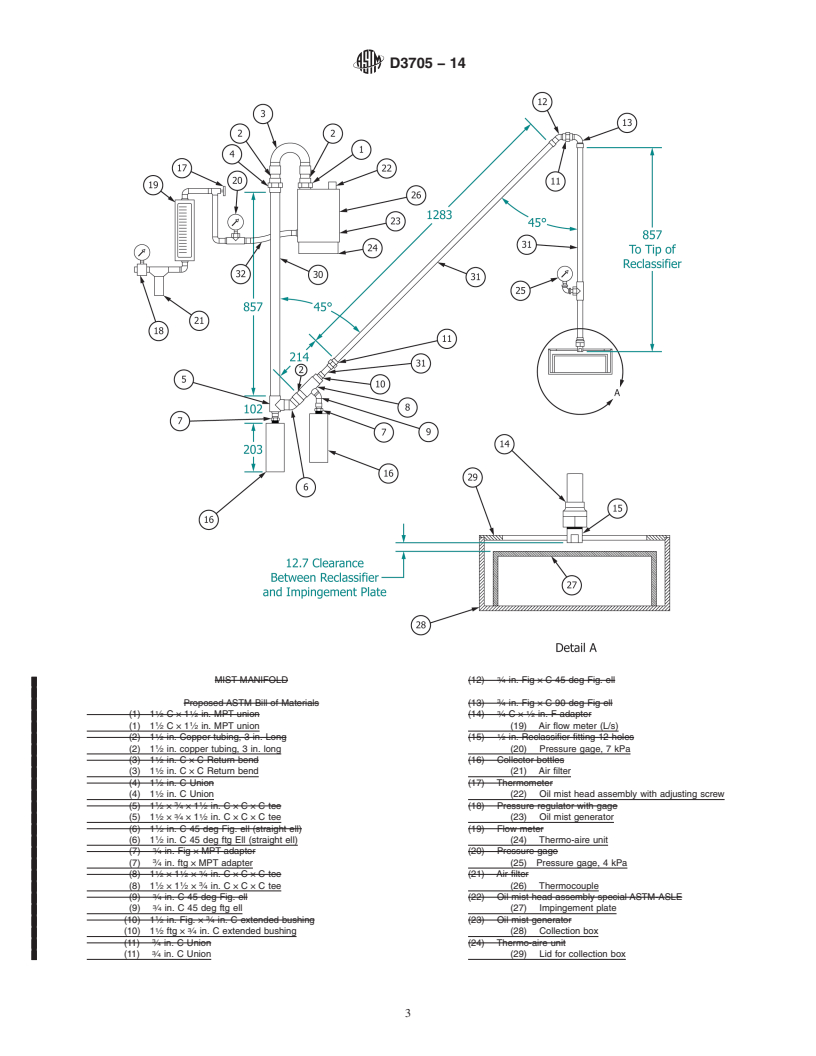
1.2.1 Inch-pound units are used to describe the various tube fittings shown in Fig. 1.
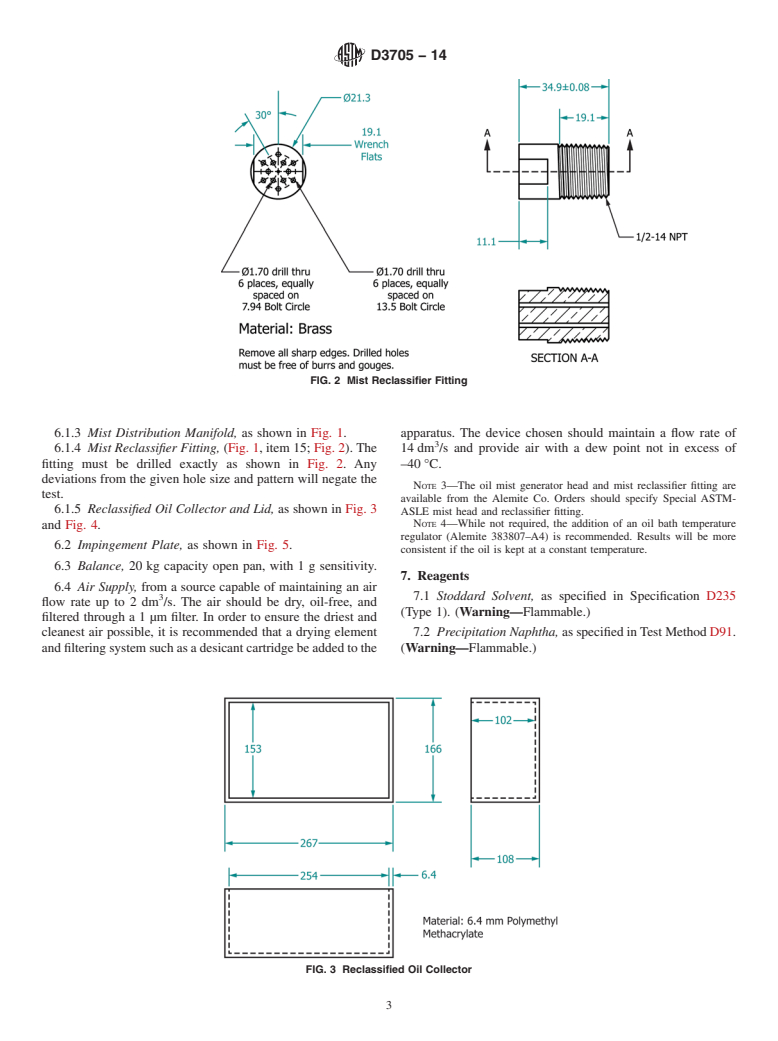
1.2.2 Inch-pound thread is shown in Fig. 2.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Sections 7 and 8.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3705 − 14
Standard Test Method for
1
Misting Properties of Lubricating Fluids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3705; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.2.2 reclassified oil, n—in a mist lubrication system, lubri-
cant that has coalesced into larger droplets at the points of
1.1 Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofthemisting
required lubrication.
characteristics of lubricating fluids.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—Mist lubrication systems are designed
NOTE 1—This test method should not be used to evaluate fluids
so that the oil mist will coalesce in the appropriate area and
containing solid additives such as graphite.
provide lubrication in the right place.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.2.1 Inch-pound units are used to describe the various tube
4.1 The mist generator is charged with oil and installed in
fittings shown in Fig. 1.
the mist system. The unit is operated for 19 h; the mist
1.2.2 Inch-pound thread is shown in Fig. 2.
generator, line condensate bottles, and reclassified oil collector
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
are weighed before and after the test. The output from the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
generator and percentages of reclassified oil, line condensate,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
and stray mist are determined from changes in weight.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
NOTE 2—Line condensate is the commonly accepted term used to
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
describe the oil that coalesces in the mist distribution lines. In this test, the
warning statements, see Sections 7 and 8.
1
oil that coalesces in the 38 mm (1 ⁄2 in.) tubing and the diagonal 19 mm
3
( ⁄4 in.) tubing is collected and weighed as line condensate. Oil that
2. Referenced Documents
3
coalesces in the vertical 19 mm ( ⁄4 in.) tubing becomes part of the
2
reclassified oil.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
5. Significance and Use
Oils
D235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) 5.1 This test provides a guide for evaluating the misting
characteristics of oils for use in industrial mist lubrication
(Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum systems.Thedegreeofcorrelationbetweenthistestandservice
performance has not been fully determined.
Products, and Lubricants
6. Apparatus
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to 6.1 The basic system consists of the following:
3,4
6.1.1 Oil Mist Generator,AlemiteNo.383802-B4 (Fig.1,
Terminology D4175.
item23)withspecialASTM-ASLEmisthead383803–B4(Fig.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1, item 22). The oil mist generator is attached to the manifold
3.2.1 line condensate, n—in a mist lubrication system, oil
so that it may be easily disconnected in order to determine its
mist which has coalesced in the distribution lines and is not
mass before and after the test.
available for lubrication purposes.
6.1.2 Air Temperature Regulator, Alemite thermo-aire No.
4,5
383808–A4 (Fig. 1, item 24).
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
3
Subcommittee D02.L0.01 on Metal Removal Fluids and Lubricants. The sole source of supply of known to the committee at this time is Alemite
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally Co., Stewart Warner, 1826 West Diversey Parkway, Chicago, IL 60614.
4
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as D3705 – 86 (2009). If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to
DOI: 10.1520/D3705-14. ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consider-
1
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or ation at a meeting of the responsible technical committee , which you may attend.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM The sole source of supply of Alemite thermo-aire unit No. 383808-A4 known
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on to the committee at this time is Alemite Co., Stewart Warner, 1826 West Diversey
the ASTM website. Parkway, Chicago, IL 60614.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbo
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3705 − 86 (Reapproved 2009) D3705 − 14
Standard Test Method for
1
Misting Properties of Lubricating Fluids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3705; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the misting characteristics of lubricating fluids.
NOTE 1—This test method should not be used to evaluate fluids containing solid additives such as graphite.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.2.1 Inch-pound units are used to describe the various tube fittings shown in Fig. 1.
1.2.2 Inch-pound thread is shown in Fig. 2.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see Sections 67 and 78.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating Oils
D235 Specification for Mineral Spirits (Petroleum Spirits) (Hydrocarbon Dry Cleaning Solvent)
D4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum Products, and Lubricants
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology D4175.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 line condensate, n—in a mist lubrication system, oil mist which has coalesced in the distribution lines and is not available
for lubrication purposes.
3.2.2 reclassified oil, n—in a mist lubrication system, lubricant that has coalesced into larger droplets at the points of required
lubrication.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.L0.02D02.L0.01 on Machinery Lubricants (Combined into L.01)Metal Removal Fluids and Lubricants.
Current edition approved April 15, 2009Oct. 1, 2014. Published July 2009November 2014. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20032009 as
ε1
D3705–86(2003)D3705 – 86 (2009). . DOI: 10.1520/D3705-86R09.10.1520/D3705-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—
Mist lubrication systems are designed so that the oil mist will coalesce in the appropriate area and provide lubrication in the right
place.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The mist generator is charged with oil and installed in the mist system. The unit is operated for 19 h; the mist generator,
line condensate bottles, and reclassified oil collector are weighed before and after the test. The output from the generator and
percentages of reclassified oil, line condensate, and stray mist are determined from changes in weight.
NOTE 2—Line condensate is the commonly accepted term used to describe the oil that coalesces in the mist distribution lines. In this test, the oil that
1 3
coalesces in the 38-mm 38 mm (1 ⁄2-in.) in.) tubing and the diagonal 19-mm 19 mm ( ⁄4-in.) in.) tubing is collected and weighed as line condensate. Oil
3
that coalesces in the vertical 19-mm 19 mm ( ⁄4-in.) in.) tubing becomes part of the reclassified oil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3705 − 14
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test provides a guide for evaluating the misting characteristics of oils for use in industrial mist lubrication systems. The
degree of correlation between this test and service performance has not been fully determined.
6. Apparatus
6.1 The basic system consists of the following:
, 3,4
6.1.1 Oil Mist Generator, Alemite No. 383802-B4 (Fig. 1, item 23) with special ASTM-ASLE mist head
assembly.383803–B4 (Fig. 1, item 22). The oil mist generator is attached to the manifold so that it may be easily disconnected in
order to determine its mass before and after the test.
, 4,5
6.1.2 A
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.