ASTM F1575/F1575M-24
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails, Spikes, and Dowel-type Threaded Fasteners
Standard Test Method for Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails, Spikes, and Dowel-type Threaded Fasteners
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Nails, spikes, and dowel-type threaded fasteners are common mechanical fasteners in wood structures. Engineering design procedures used to determine the capacities of laterally-loaded connections with these types of fasteners rely on a yield theory to establish the nominal resistance. In order to develop the nominal resistance for laterally-loaded connections, the fastener bending yield strength, length, and diameter must be known.
SCOPE
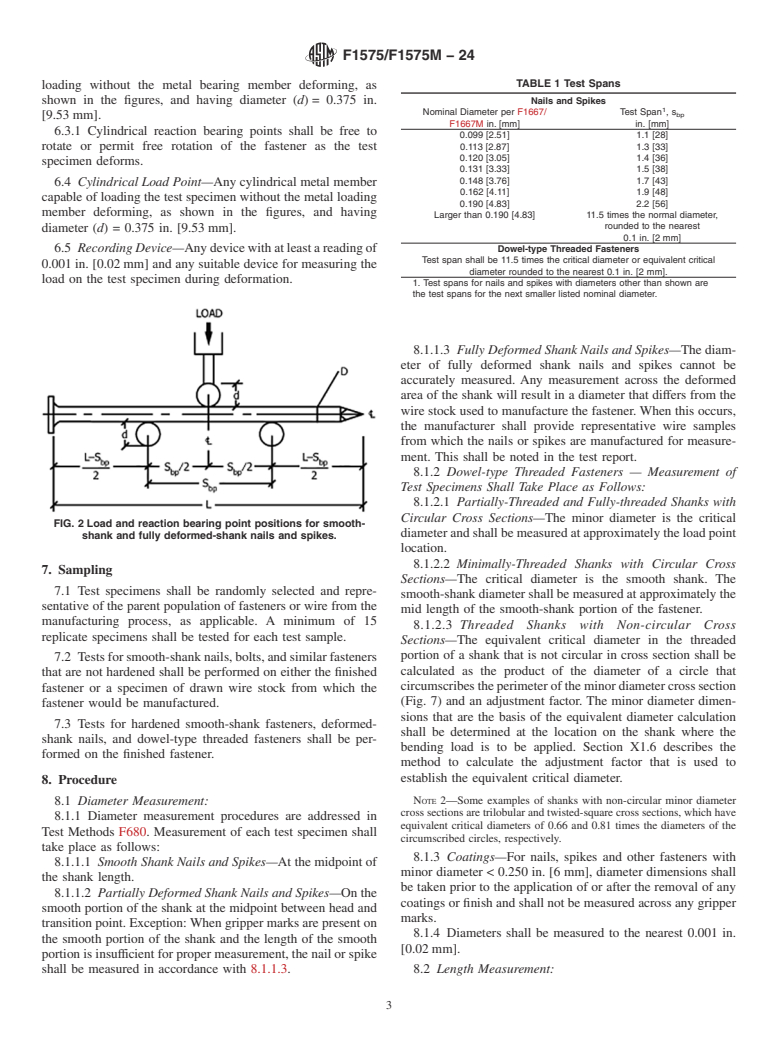
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining the bending yield moment and calculation of bending yield strength (Fyb) of nails, spikes, and dowel-type threaded fasteners (referred to collectively as fasteners) when subjected to static loading. Bending yield strength is used in engineered connection applications, in which a required connection capacity is specified by the designer.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
Note 1: This test method is applicable in either inch-pounds F1575 or SI Units [F1575M]. Values stated in SI are a mathematical conversion of two significant digits and are shown in brackets [ ].
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1575/F1575M − 24
Standard Test Method for
Determining Bending Yield Moment of Nails, Spikes, and
1
Dowel-type Threaded Fasteners
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1575/F1575M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E2309/E2309M Practices for Verification of Displacement
Measuring Systems and Devices Used in Material Testing
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining the
Machines
bending yield moment and calculation of bending yield
F680 Test Methods for Nails
strength (F ) of nails, spikes, and dowel-type threaded fasten-
yb
F1667/F1667M Specification for Driven Fasteners: Nails,
ers (referred to collectively as fasteners) when subjected to
Spikes, and Staples
static loading. Bending yield strength is used in engineered
3
2.2 ASME Standards:
connection applications, in which a required connection capac-
B18.2.1 Square, Hex, Heavy Hex, and Askew Head Bolts,
ity is specified by the designer.
and Hex, Heavy Hex, Hex Flange, Lobed Head, and Lag
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
Screws (inch Series). 2012. The American Society of
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York,
each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to
NY.
ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
B18.6.1 Wood Screws. 1981 (R2008). The American Society
used independently of the other, and values from the two
of Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York,
systems shall not be combined.
NY.
NOTE 1—This test method is applicable in either inch-pounds F1575 or
SI Units [F1575M]. Values stated in SI are a mathematical conversion of
3. Terminology
two significant digits and are shown in brackets [ ].
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1 Definitions of Terms Related to All Fasteners of this
Standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3.1.1 bending yield moment—the moment determined from
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- the yield load point on the load-deformation curve that is
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. intermediate between the proportional limit load and maximum
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- load for the fastener.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.2 bending yield strength—the fastener strength charac-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
teristic used in yield limit equations to determine lateral
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
capacity of connection; determined from the bending yield
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
moment and dimensions of the fastener.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.1.3 certifying body—an organization that is recognized
through compliance with national standards for the purpose of
2. Referenced Documents
product evaluation.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.4 proportional limit—the load at which the load-
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
deformation curve deviates from a straight line fitted to the
ing Machines
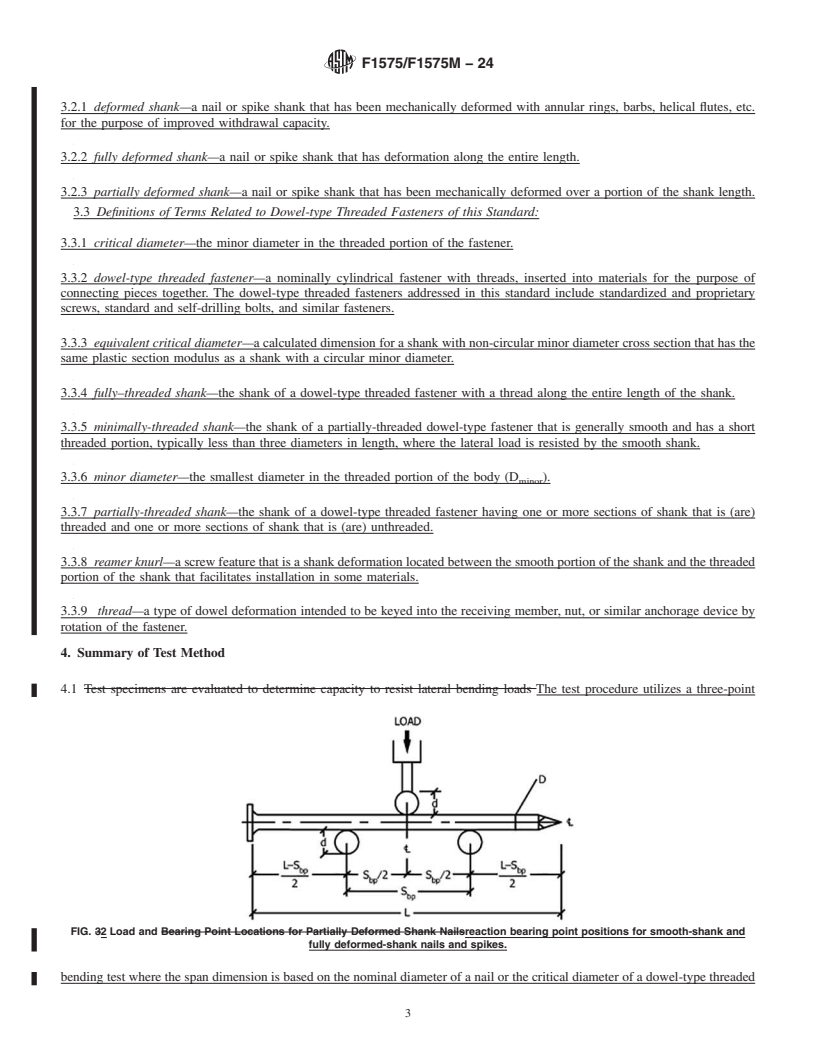
initial portion of the load-deformation curve (Fig. 1).
3.1.5 shank—a portion of the fastener below the head,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on
excluding the tip, which is embedded in the connected mate-
Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.05 on Driven and
Other Fasteners. rials and the portion of the fastener engaged in a nut or similar
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2024. Published March 2024. Originally
anchorage device, if applicable.
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2021 as F1575 – 21. DOI:
10.1520/F1575_F1575M-24.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
the ASTM website. www.asme.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
-------------------
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1575/F1575M − 21 F1575/F1575M − 24
Standard Test Method for
Determining Bending Yield Moment of NailsNails, Spikes,
1
and Dowel-type Threaded Fasteners
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1575/F1575M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This test method covers procedures for determining the bending yield moment of nails and calculation of bending yield
strength (F ) of nails, spikes, and dowel-type threaded fasteners (referred to collectively as fasteners) when subjected to static
yb
loading. It is intended only for nails Bending yield strength is used in engineered connection applications, in which a required
connection capacity is specified by the designer.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used
independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
NOTE 1—This test method is applicable in either inch-pounds F1575 or SI Units [F1575M]. Values stated in SI are a mathematical conversion of two
significant digits and are shown in brackets [ ].
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Testing Machines
E2309/E2309M Practices for Verification of Displacement Measuring Systems and Devices Used in Material Testing Machines
F680 Test Methods for Nails
F1667/F1667M Specification for Driven Fasteners: Nails, Spikes, and Staples
3
2.2 ASME Standards:
B18.2.1 Square, Hex, Heavy Hex, and Askew Head Bolts, and Hex, Heavy Hex, Hex Flange, Lobed Head, and Lag Screws (inch
Series). 2012. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York, NY.
B18.6.1 Wood Screws. 1981 (R2008). The American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Three Park Avenue, New York, NY.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F16 on Fasteners and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F16.05 on Driven and Other Fasteners.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2021Feb. 1, 2024. Published January 2022March 2024. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 20172021 as
F1575 – 17.F1575 – 21. DOI: 10.1520/F1575_F1575M-21.10.1520/F1575_F1575M-24.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.asme.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1575/F1575M − 24
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:Related to All Fasteners of this Standard:
3.1.1 bending yield moment—the moment determined from the yield load point on the load-deformation curve that is intermediate
between the proportional limit load and maximum load for the nail. It is calculated by the intersection of the load-deformation
curve with a line represented by the initial tangent modulus offset 5 % of the fastener diameter. fastener.
3.1.2 bending yield strength—the fastener strength characteristic used in yield limit equations to determine lateral capacity of
connection; determined from the bending yield moment and dimen
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.