ASTM D3852-99
(Practice)Standard Practice for Sampling and Handling Phenol, Cresols, and Cresylic Acid
Standard Practice for Sampling and Handling Phenol, Cresols, and Cresylic Acid
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is provided to ensure that phenol and cresylic acid are properly sampled to provide representative specimens for quality assurance analyses and that they are handled in a safe manner. In general, this practice also applies to cresols, xylenols, and some other alkylated phenolic materials; however, specific information regarding these materials should be sought and used if available.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections 5 to 8 and Notes 1 and 2.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D3852–99
Standard Practice for
Sampling and Handling Phenol, Cresols, and Cresylic Acid
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3852; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Description of Products (See Tables 1 and 2)
1.1 This practice is provided to ensure that phenol and 4.1 Phenol is a colorless to light pink crystalline material
cresylic acid are properly sampled to provide representative which melts at 40 to 41°C (104 to 106°F). Technical and USP
specimens for quality assurance analyses and that they are grades melt at lower temperatures.
handled in a safe manner. In general, this practice also applies 4.2 Phenol is both extremely hygroscopic and sensitive to
to cresols, xylenols, and some other alkylated phenolic mate- discoloration. Therefore, it cannot be overemphasized that
rials; however, specific information regarding these materials proper precautions must be undertaken when unloading or
should be sought and used if available. sampling the product. Moisture must be excluded. The use of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the sampling devices that contain metals that may catalyze discol-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the oration (iron, copper) must also be avoided.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.3 Cresylic acid is a common chemical name applied to
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- mixtures of alkyl-substituted phenols. Included are mixtures of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard cresols, xylenols, and higher alkylated phenols. Many cresylic
statements, see Sections 5-8 and Note 1 and Note 2. acid mixtures contain measurable amounts of phenol.
4.4 Most cresylic acid mixtures are liquids at ambient
2. Referenced Documents
temperatures.However,atlowtemperatures(<0°C)theysome-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
timesbecomeveryviscousanddifficulttopour.Somemixtures
E 300 Practice for Handling Industrial Chemicals containing high concentrations of high melting isomers may
2.2 Other Documents:
form thick slurries or become solids at low temperatures.
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR, paragraphs 1910.1000 and 4.5 While phenol or cresylic acid is highly dangerous when
1910.1200
handled improperly, particularly at the elevated temperatures
U.S. DOT Regulations, 49 CFR Transportation, Subchapter
sometimesrequiredtounloadtankcarsortanktrucks,handling
C, Parts 171 – 180 and sampling need not be hazardous provided the dangers are
NFPA No. 704-1996
recognized. Proper precautionary measures must be provided
and scrupulously adhered to.
3. Significance and Use
4.6 Department of Transportation (DOT) Hazardous Mate-
3.1 This practice is issued to provide information useful in
rials Regulations regarding the shipment of this chemical are
establishing sampling and handling procedures. It is expected
specified in 49 CFR.
that this information will only be utilized in conjunction with
5. Hazards
an existing health and safety program. The information pro-
vided cannot be used as a substitute for expert safety and
5.1 For information on toxicity see Toxic Substances List,
medical advice, but rather as a supplement to such advice. Appendix I, 1975.
5.2 Consult current OSHA regulations suppliers’ material
safety data sheets (MSDSs), and local regulations for all
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on Aromatic
materials utilized in this practice.
Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
5.3 Health—Phenol is very corrosive to the skin and pro-
mittee D16.08 on Handling and Sampling Aromatic and Cyclic Hydrocarbons.
duces painful and dangerous burns in a very short time. Since
Current edition approved June 10, 1999. Published August 1999. Originally
phenol is a skin anesthetic, the first reaction is not pain, but a
published as D 3852 – 79. Last previous edition D 3852 – 96b.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05.
whitening of the exposed area. It is readily absorbed through
Available from Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
the skin and mucous membranes or lungs, and severe expo-
Office, Washington, DC 20402.
4 sures may prove fatal unless prompt first aid and medical
Available from National Fire ProtectionAssoc., 1 Battery March Park, Quincy,
MA 02269-9101. treatmentareexercised.Sincesevereinjuryordeathmayresult
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D3852–99
TABLE 1 Cresylic Properties
safety goggles and chemically impermeable gloves, as a
Flammability minimum. Depending upon circumstances, additional personal
Boiling Flash Specific
Limits, %
protection may be advisable, including face shield, rubber
Point, °C Point, °F Gravity
Lower Higher
shoes or boots, rubber aprons or acid-proof suits, and industrial
Phenol 181 175 1.7 8.6 1.06
A
Cresylic Acid 220-250 200 1.1 . . . 1.05 gas masks or fresh air masks. Wearing full protective clothing
Cresols 181-250 175 1.1 . . . 1.05
is recommended when sampling tank cars, tank trucks, barges,
A
A mixture of phenolic materials boiling above the cresol range.
ships, drums, process lines and process vessels. Working areas
shall have immediately available deluge-type safety showers,
easily accessible, plainly marked, and controlled by quick-
from excessive exposure to vapor or mist, adequate ventilation
opening valves. In addition, there shall be at hand a water hose
of working areas is imperative. It is therefore recommended
that will deliver clean water at a moderate pressure. A small
that tank cars or tank trucks shall be unloaded in the open,
stream, such as from an eyewash fountain, is recommended for
rather than inside a closed building and workers shall wear
washing eyes (see 7.2).
appropriate protective clothing and personal protective equip-
ment.
7. First Aid
5.3.1 Qualitatively, cresylic acid is slightly less acute as a
7.1 The establishment of first aid procedures must be done
health hazard than phenol. However, contact of cresylic acid
prior to sampling and handling of phenol and cresylic acid
with the skin can produce painful and serious burns in a short
under the guidance of competent safety and medical advice.
time. It is readily absorbed through the skin and mucous
7.2 The first aid procedures established should include, but
membranes, through the gastro-intestinal tract, or through the
not be limited to, the following considerations:
lungs (either as a vapor or in droplet form), potentially
7.2.1 Speed in removing phenol or cresylic acid from the
resulting in systemic poisoning.Although no safety limits have
skin in case of accidental contact is of primary importance.
been defined for cresylic acid vapor, severe injury or death can
7.2.2 It is extremely important to immediately place under a
result from excessive exposure to high concentrations of the
physician’s care any person injured by skin contact, inhalation,
vapor or mist, or prolonged exposure to low concentrations.
or ingestion of phenol or cresylic acid.
Therefore, adequate ventilation of work areas is imperative.
5.4 Fire—Cresylic acid parallels phenol in its fire hazard
8. Precautions
properties, being somewhat less hazardous due primarily to
8.1 Any person sampling or handling these products should
lower vapor pressure at any given temperature. Phenol is
have specific first aid instructions and equipment available for
placed in Category 2 of the NFPA 704M fire hazard classifi-
use in the event of personal contact or exposure.
cation system (Note 1) while m- and p-cresols are in Category
8.2 Conduct sampling and handling operations only by
1. Phenol and cresylic acid are combustible and flammable;
carefully instructed, experienced, reliable employees, under
toxic vapor will be given off at elevated temperature should
adequate supervision.
this material become involved in a fire. Water (fog or spray),
8.3 Accomplish loading, unloading, and sampling opera-
carbon dioxide extinguishers, foam, and dry chemical extin-
tions only when adequate lighting is provided.
guishers are effective in fighting fires involving phenol and
8.4 Take extreme care to avoid spills and leaks. In case of a
cresylic acid.
spill, wash contaminated areas thoroughly with large quantities
NOTE 1—For full description of NFPA categories, see NFPA publica-
of water and collect the liquid in the local chemical waste
tion No. 704-1996. Classification runs from 0 (no hazard) to 4 (very
system. All spill-related activities should comply with appli-
hazardous).
cable EPA, OSHA, and local regulations and laws.
5.5 Molten phenol or cresylic acid dissolves carbon dioxide
8.5 Follow shipper’s instructions always, and read and
and releases it on solidification. Therefore, special precautions
observe all caution markings on containers.
shall be observed if “inert gas” containing carbon dioxide is
8.6 Although the vapor given off at elevated temperatures
used to agitate or empty containers of phenol or cresylic acid
from phenol or cresylic acid will ignite, these materials can
to avoid pressure build-up (for example, leave vents open).
generally be handled with little direct danger of fire. The flash
5.6 For chemical emergency (spill, leak, fire, exposure, or
points of the liquids are higher than the temperatures at which
accident) call CHEMTREC, day or night, at 1-800-424-9300. they are normally handled. In spite of this, carefully restrict
For emergency calls outside the United States, call 703-527-
open flames and smoking in the vicinity of loading, unloading,
3887. (Collect calls are accepted and all calls are recorded.) and storage operations.
8.7 Do not permit any person ever to enter an empty phenol
6. Protective Equipment
or cresylic acid tank, tank car, or tank truck until it has been
6.1 No personal protection equipment is an adequate sub- thoroughly washed out with warm water, followed by a
stitute for safe working conditions and intelligent conduct on thorough steaming. Ensure that oxygen content is acceptable
the part of employees who work with phenol or cresylic acid. and vessel is free of organic vapors. Require the approval and
Employees who work with phenol or cresylic acid should be observation by a supervisor in every case. Review Sections 6
well trained and should maintain safe working conditions. and 7 in detail.
6.2 Persons engaged in the handling of phenol or cresylic 8.8 Allow no eating or drinking in close proximity to the
acid shall use protective equipment as dictated by the extent of phenol or cresylic acid handling or sampling operation.
their exposure. The worker shall always wear chemical-type 8.9 Employees shall:
D3852–99
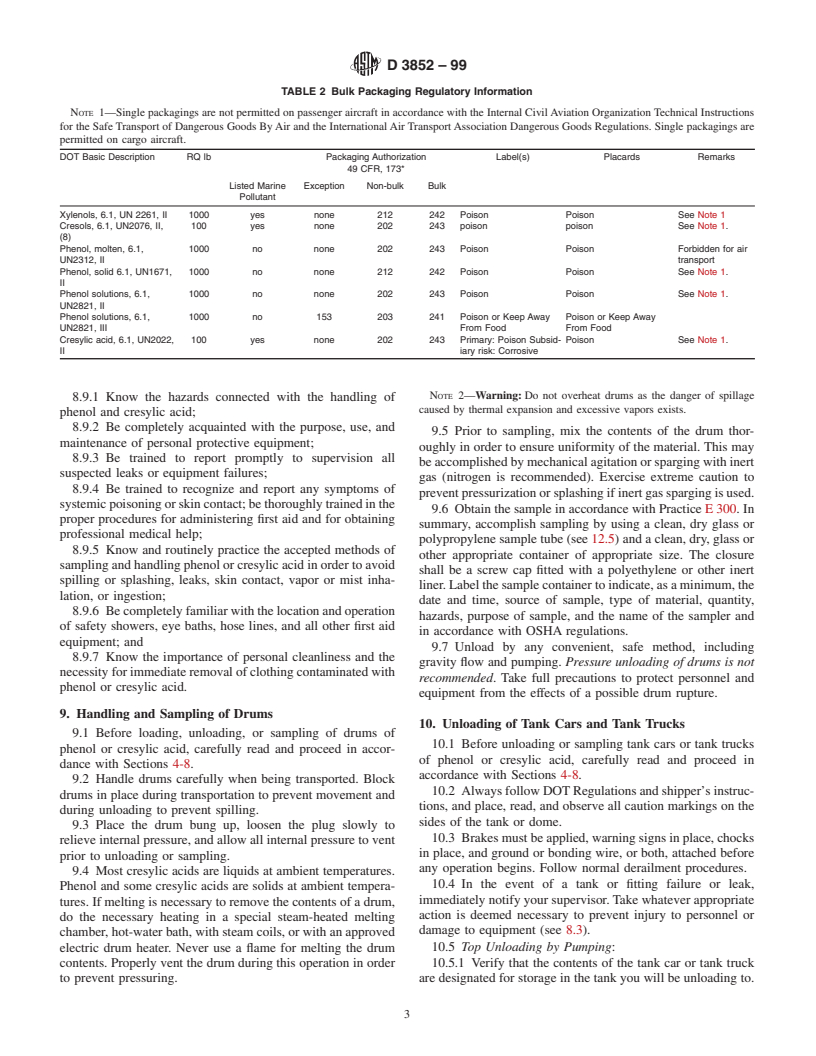
TABLE 2 Bulk Packaging Regulatory Information
NOTE 1—Single packagings are not permitted on passenger aircraft in accordance with the Internal CivilAviation Organization Technical Instructions
for the Safe Transport of Dangerous Goods ByAir and the InternationalAir TransportAssociation Dangerous Goods Regulations. Single packagings are
permitted on cargo aircraft.
DOT Basic Description RQ lb Packaging Authorization Label(s) Placards Remarks
49 CFR, 173*
Listed Marine Exception Non-bulk Bulk
Pollutant
Xylenols, 6.1, UN 2261, II 1000 yes none 212 242 Poison Poison See Note 1
Cresols, 6.1, UN2076, II, 100 yes none 202 243 poison poison See Note 1.
(8)
Phenol, molten, 6.1, 1000 no none 202 243 Poison Poison Forbidden for air
UN2312, II transport
Phenol, solid 6.1, UN1671, 1000 no none 212 242 Poison Poison See Note 1.
II
Phenol solutions, 6.1, 1000 no none 202 243 Poison Poison See Note 1.
UN2821, II
Phenol solutions, 6.1, 1000 no 153 203 241 Poison or Keep Away Poison or Keep Away
UN2821, III From Food From Food
Cresylic acid, 6.1, UN2022, 100 yes none 202 243 Primary: Poison Subsid- Poison See Note 1.
II iary risk: Corrosive
NOTE 2—Warning: Do not overheat drums as the danger of spillage
8.9.1 Know the hazards connected with the handling of
caused by thermal expansion and excessive vapors exists.
phenol and cresylic acid;
8.9.2 Be completely acquainted with the purpose, use, and
9.5 Prior to sampling, mix the contents of the drum thor-
maintenance of personal protective equipment;
oughly in order to ensure uniformity of the material. This may
8.9.3 Be trained to report promptly to supervision all
beaccomplishedbymechanicalagitationorspargingwithinert
suspected leaks or equipment failures;
gas (nitrogen is recommended). Exercise extreme caution to
8.9.4 Be trained to recognize and report any symptoms of
preventpressurizationorsplashingifinertgasspargingisused.
systemicpoisoningorskincontact;bethoroughlytrainedinthe
9.6 Obtain the sample in accordance with Practice E 300.In
proper procedures for administering first aid and for obtaining
summary, accomplish sampling by using a clean, dry glass or
professional medical help;
polypropylene sample tube (see 12.5) and a clean, dry, glass or
8.9.5 Know and routinely practice the accepted methods of
other appropriate container of appropriate size. The closure
sampling and handling phenol or cresylic acid in order to avoid
shall be a screw cap fitted with a polyethylene or other inert
spilling or splashing, leaks, skin contact, vapor or mist inha-
liner.Labelthesamplecontainertoindicate,asaminimum,the
lation, or ingestion;
date and time, source of sample, type of material, quantity,
8.9.6 Becompletelyfamiliarwiththelocationandoperation
hazards, purpose of sample, and the name of the sampler and
of safety showers, eye baths, hose lines, and all other first aid
in accordance with OSHA regulations.
equipment; and
9.7 Unload by any convenient, safe method, including
8.9.7 Know the importance of personal cleanliness and the
gravity flow and pumping. Pressure unloading of drums is not
necessityforimmediateremovalofclothingcontaminatedwith
recommended. Take full precautions to protect personnel and
phenol or cresylic acid.
equipment from the effects of a possible drum rupture.
9. Handling and Sampling of Drums
10. Unloading of Tank Cars and Tank Trucks
9.1 Before loading, unloading, or sampling of drums of
10.1 Before unloading or sampling tank cars or tank trucks
phenol or cresylic acid, carefully read and proceed in accor-
of phenol or cresylic acid, carefully read and proceed in
dance with Sections 4-8.
accordance with Sections 4-8.
9.2 Handle drums carefully when being transported. Block
10.2 AlwaysfollowDOTRegulationsandshipper’sinstruc-
dr
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.