ASTM D2639/D2639M-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Plastic Properties of Coal by the Constant-Torque Gieseler Plastometer
Standard Test Method for Plastic Properties of Coal by the Constant-Torque Gieseler Plastometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Reliable values of the plastic properties of coals are used to predict or explain the behavior of a coal or blends during carbonization or in other processes such as gasification, liquefaction, and combustion.
SCOPE
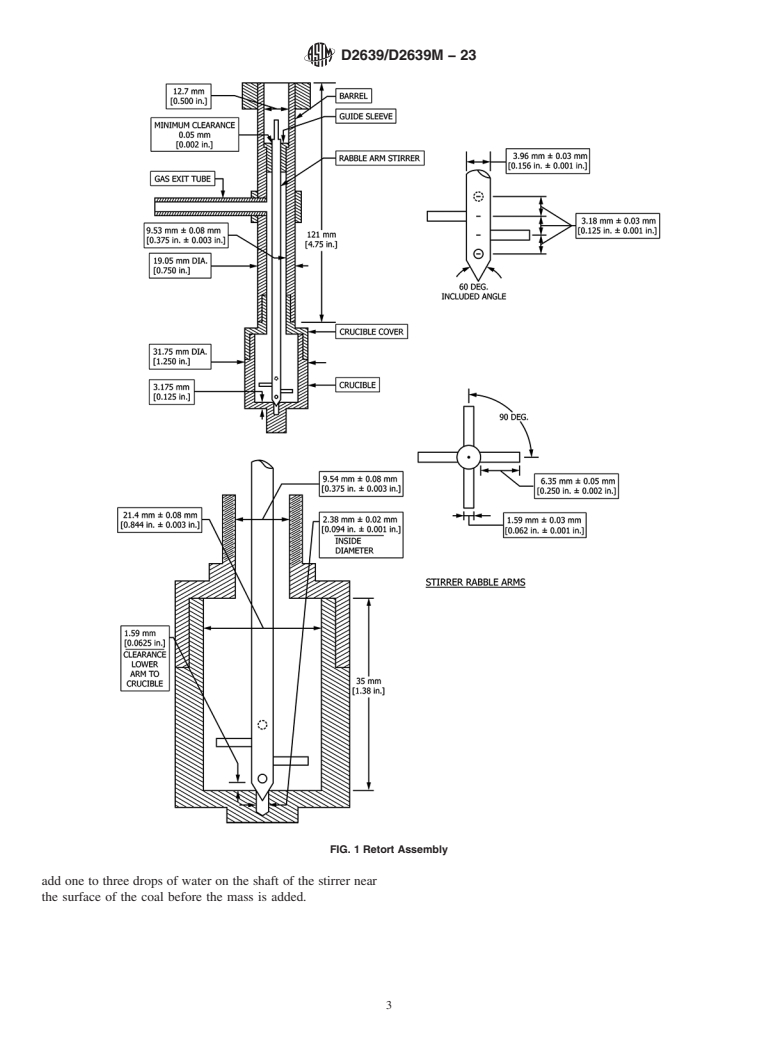
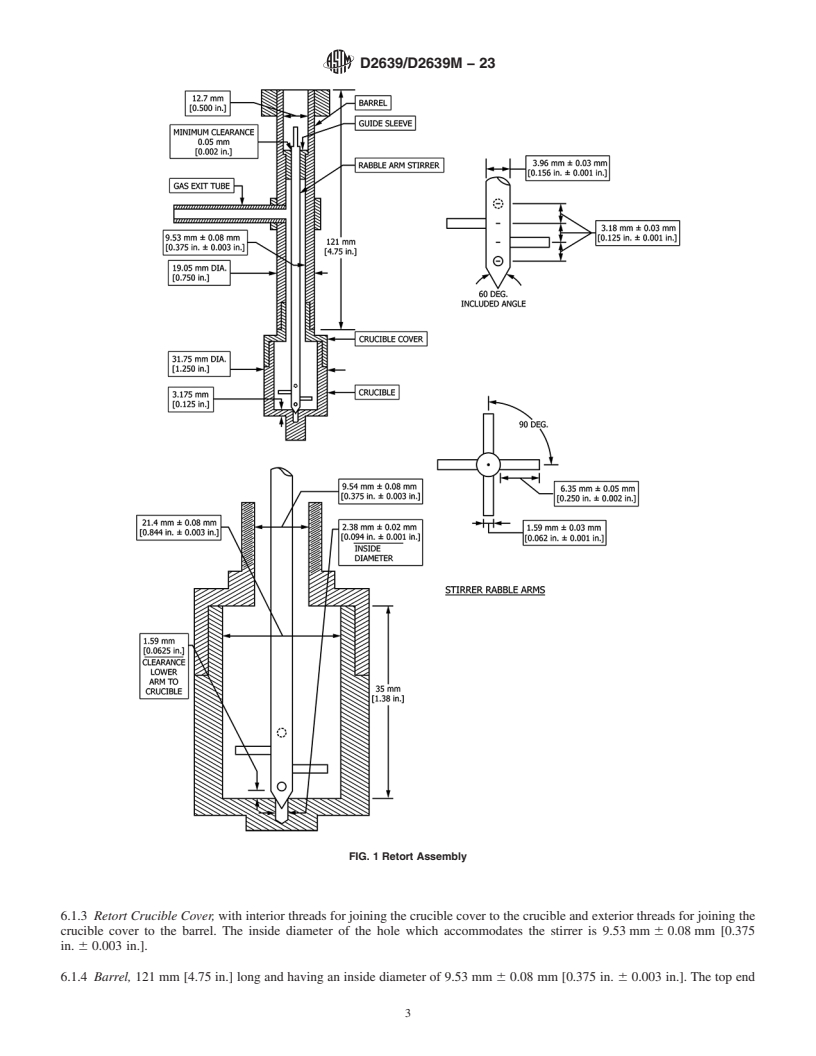
1.1 This test method covers a relative measure of the plastic behavior of coal when heated under prescribed conditions. This test method may be used to obtain semiquantitative values of the plastic properties of coals and blends used in carbonization and in other situations where determination of plastic behavior of coals is of practical importance.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.3 In this test method, the term “mass” applies to measurements expressed with both SI units (for example, kg) and inch-pound units (for example, lb).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D2639/D2639M − 23
Standard Test Method for
Plastic Properties of Coal by the Constant-Torque Gieseler
1
Plastometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2639/D2639M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D2234/D2234M Practice for Collection of a Gross Sample
of Coal
1.1 This test method covers a relative measure of the plastic
behavior of coal when heated under prescribed conditions. This
3. Terminology
test method may be used to obtain semiquantitative values of
3.1 Definitions:
the plastic properties of coals and blends used in carbonization
3.1.1 breaking, v—free spinning behavior of coal, either by
and in other situations where determination of plastic behavior
an abrupt change to rotating at maximum motor speed or by
of coals is of practical importance.
abrupt changes in rotation, which occurs as a result of a molten
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-
ball of coal forming around the base of the stirrer, and which
pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The
makes reporting of the true maximum fluidity of the coal
values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equiva-
difficult.
lents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each
3.1.2 dial division per minute, (DDPM), n—as used in this
system shall be used independently of the other, and values
test method, the stirrer rotation rate as measured by the
from the two systems shall not be combined.
accumulated rotations (full or partial) of the stirrer recorded
1.3 In this test method, the term “mass” applies to measure-
over sequential 1 min periods based upon 100 dial divisions for
ments expressed with both SI units (for example, kg) and
each complete 360° rotation of the stirrer.
inch-pound units (for example, lb).
3.1.2.1 Discussion—Historically stirrer rotations were re-
corded on manual plastometers by a simple timed observation
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
of the total rotations at the completion of each sequential whole
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
minute interval as the furnace was ramped over the required
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
temperature range. Modern instruments have the ability to
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
record the accumulated stirrer rotations at any given point
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
during the test and as such can present the DDPM over any
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
discrete 60 s interval. For the purposes of this empirical
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
standard and in order to ensure consistency between
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
instrumentation, the recorded DDPM shall be taken at the end
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
of each sequential minute interval commencing at the start of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
the test and ending with the recorded solidification tempera-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ture. That is to say, upon regaining the initial temperature of
2. Referenced Documents
300 °C, total accumulated stirrer rotations shall be recorded at
2
times 00:01:00, 00:02:00, 00:03:00, 00:04:00, etc. until the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
solidification temperature is reached.
D2013/D2013M Practice for Preparing Coal Samples for
Analysis 3.1.3 initial softening temperature, n—as used in this test
method, the temperature at which the DDPM (see 3.1.2) first
reaches a reading of equal to or greater than 1.0.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D05 on Coal
and Coke and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D05.15 on Metallurgical 3.1.4 jamming, v—swelling up of coal into the retort tube
Properties of Coal and Coke.
during the test, which may produce lower fluidity results than
Current edition approved March 1, 2023. Published March 2023. Originally
expected and can only be noted after visual inspection of the
approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2022 as D2639/D2639M – 22.
disassembled crucible and retort at the conclusion of the test.
DOI: 10.1520/D2639_D2639M-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3.1.5 maximum fluidity, n—as used in this test method, the
contact ASTM Customer Se
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2639/D2639M − 22 D2639/D2639M − 23
Standard Test Method for
Plastic Properties of Coal by the Constant-Torque Gieseler
1
Plastometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2639/D2639M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a relative measure of the plastic behavior of coal when heated under prescribed conditions. This test
method may be used to obtain semiquantitative values of the plastic properties of coals and blends used in carbonization and in
other situations where determination of plastic behavior of coals is of practical importance.
1.2 Units—The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used
independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.3 In this test method, the term “mass” applies to measurements expressed with both SI units (for example, kg) and inch-pound
units (for example, lb).
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2013/D2013M Practice for Preparing Coal Samples for Analysis
D2234/D2234M Practice for Collection of a Gross Sample of Coal
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 breaking, v—free spinning behavior of coal, either by an abrupt change to rotating at maximum motor speed or by abrupt
changes in rotation, which occurs as a result of a molten ball of coal forming around the base of the stirrer, and which makes
reporting of the true maximum fluidity of the coal difficult.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D05 on Coal and Coke and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D05.15 on Metallurgical Properties
of Coal and Coke.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022March 1, 2023. Published December 2022March 2023. Originally approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 20212022
as D2639/D2639M – 21a.D2639/D2639M – 22. DOI: 10.1520/D2639_D2639M-22.10.1520/D2639_D2639M-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2639/D2639M − 23
3.1.2 dial division per minute, (DDPM), n—as used in this test method, the stirrer rotation rate as measured by the accumulated
rotations (full or partial) of the stirrer recorded over sequential 1 min periods based upon 100 dial divisions for each complete 360°
rotation of the stirrer.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—
Historically stirrer rotations were recorded on manual plastometers by a simple timed observation of the total rotations at the
completion of each sequential whole minute interval as the furnace was ramped over the required temperature range. Modern
instruments have the ability to record the accumulated stirrer rotations at any given point during the test and as such can present
the DDPM over any discrete 60 s interval. For the purposes of this empirical standard and in order to ensure consistency between
instrumentation, the recorded DDPM shall be taken at the end of each sequential minute interval commencing at the start of the
test and ending with the recorded solidification temperature. That is to say, upon regaining the initial temperature of 300 °C, total
accumulated stirrer rotations shall be recorded at times 00:01:00, 00:02:00, 00:03:00, 0
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.