ASTM F1045-07(2013)
(Specification)Standard Performance Specification for Ice Hockey Helmets
Standard Performance Specification for Ice Hockey Helmets
SCOPE
1.1 This performance specification2 covers performance requirements for ice hockey helmets.
1.2 The intent of this performance specification is to reduce the risk of injury to the head without compromising the form and appeal of the game.
1.3 This performance specification covers: (1) performance tests for shock absorption properties of the complete helmet and strength and elongation of the chin strap and its attachment; and (2) requirements for area of coverage and penetration.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this performance specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1045 −07(Reapproved 2013) An American National Standard
Standard Performance Specification for
Ice Hockey Helmets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1045; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Ice hockey is a contact sport with intrinsic hazards. The use of protective equipment will not
eliminateallinjuriesbutshouldsubstantiallyreducetheseverityandfrequencyofinjury.Participation
in the sport of ice hockey by a player implies acceptance of some risk of injury. The goal is to
minimize this risk.
Thisperformancespecificationforheadprotectiveequipmenthasbeenpreparedafterconsideration
of head protection relative to the following principle risks: high-mass, low-velocity impact (various
playing situations), and fit. This performance specification may be modified as other risks are
identified.
Performance requirements were determined after consideration of state-of-the-art of helmet design
and manufacture and the demands of the sport.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This performance specification covers performance
2.1 ASTM Standards:
requirements for ice hockey helmets.
F513Specification for Eye and Face Protective Equipment
for Hockey Players
1.2 The intent of this performance specification is to reduce
F2220Specification for Headforms
the risk of injury to the head without compromising the form
and appeal of the game.
3. Terminology
1.3 This performance specification covers: (1) performance
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
tests for shock absorption properties of the complete helmet
3.1.1 retention system:
and strength and elongation of the chin strap and its attach-
3.1.1.1 chin strap—the chin strap, including a cup that
ment; and (2) requirements for area of coverage and penetra-
tion. covers the chin (see Fig. 1), is affixed to both sides of the
helmet and secures the helmet to the head when a Type I or
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Type II full face protector is not worn with the helmet.
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.1.1.2 neck strap—theneckstrapthatsecuresthehelmetto
only.
theheadisaffixedonbothsidesofthehelmetandpassesunder
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
the lower jaw in close proximity to the jaw and the neck.
test methods portion, Section 12, of this performance specifi-
Where the helmet is worn with a Type I or Type II full face
cation:This standard does not purport to address all of the
protector,theneckstrapservesastheattachmentofthehelmet
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to the head.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- NOTE 1—For a description of the Type I or Type II face protector, see
the Types of Protectors Section in Safety Specification F513.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.2 crown—apointinthemedianplanethatisequalchord
lengths from the anterior and posterior intersections of the
median and reference planes.
This performance specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee
F08 on Sports Equipment, Playing Surfaces, and Facilitiesand is the direct
responsibility of Subcommittee F08.15 on Ice Hockey.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2013. Published February 2014. Originally
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as F1045–07. DOI: For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
10.1520/F1045-07R13. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Thisperformancespecificationissubjecttorevisionasindicatedbysubsequent Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
injury statistics and subject to review at least every five years. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1045−07 (2013)
FIG. 1 Chin Strap (Includes a Chin Cup)
3.1.3 drop height—the vertical distance between the lowest
point (impact point) of the elevated helmet and the apex of the
impact surface.
3.1.4 g—the dimensionless ratio of the acceleration of the
headform during impact to the acceleration due to gravity.
3.1.4.1 g —the maximum value of g encountered during
max
impact.
3.1.5 helmet—the complete product, including the shell,
liner,chinstrap,includingthecuporneckstrap,andassociated
attachment hardware, assembled with components supplied by
the manufacturer. The helmet is intended to protect the
wearer’s head while participating in ice hockey.
3.1.6 helmet position index (HPI)—the vertical distance
from the brow of the helmet to the basic plane, when the
helmet is placed on a reference headform. The manufacturer
shallspecifythesizeoftheheadformandtheverticaldistance.
3.1.7 liner—the material inside the shell for the purpose of
shock absorption or comfortable fit, or both.
FIG. 3 Test Headform—Basic, Reference, and Misadgittal Planes
3.1.8 Reference Planes:
3.1.8.1 basic plane—an anatomical plane that includes the
superiorrimoftheexternalauditorymeatus(upperedgeofthe
external openings of the ear) and the inferior margin of the
3.1.8.2 coronal plane—an anatomical plane perpendicular
orbit (the lowest point of the floor of the eye socket). The
to both the basic and midsagittal planes and passing through
headforms are marked with the basic plane (see Figs. 2 and 3).
the superior rims of the right and left auditory meatuses. The
transverse plane corresponds to the coronal plane (see Figs. 2
and 3).
3.1.8.3 midsagittal plane—an anatomical plane perpendicu-
lar to the basic plane and containing the midpoint of the line
connecting the notches of the right and left inferior orbital
ridgesandthemidpointofthelineconnectingthesuperiorrims
of the right and left external auditory meatus.The longitudinal
plane corresponds to the midsagittal plane (see Figs. 2 and 3).
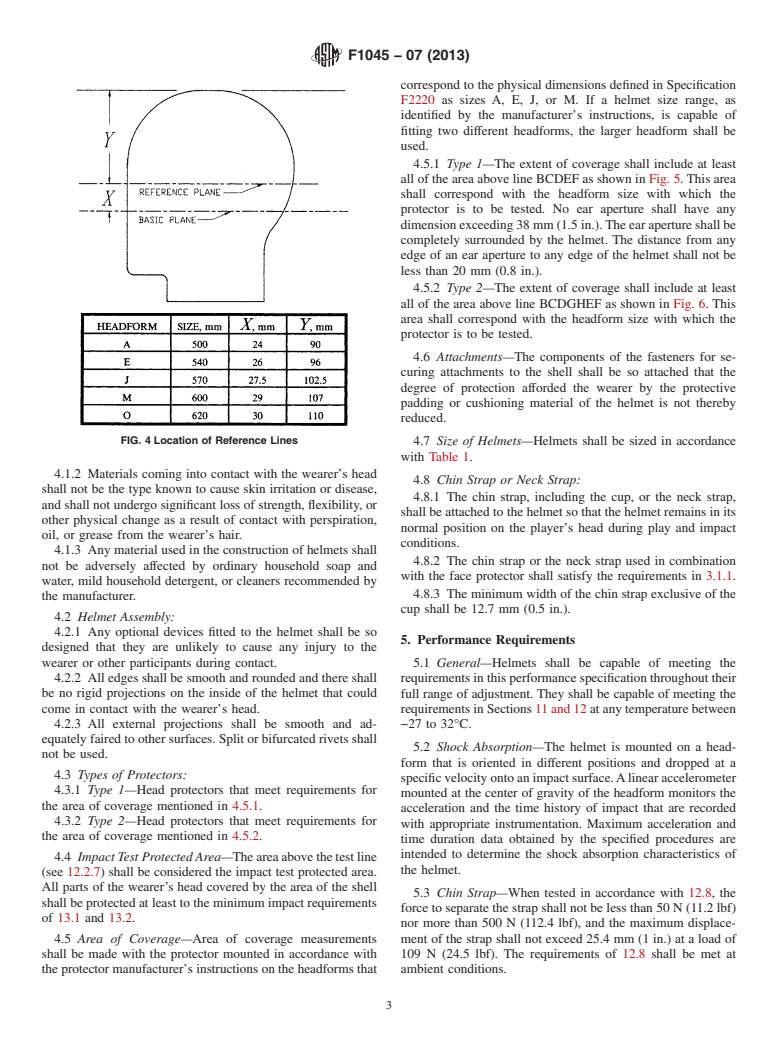
3.1.8.4 reference plane—a plane marked on the headforms
ataspecifieddistanceaboveandparalleltothebasicplane(see
Fig. 4).
3.1.9 shell—therigidoutermaterialthatgivesthehelmetits
form.
4. General Requirements
4.1 Materials:
4.1.1 All materials used in the fabrication of helmets shall
be known to be suitable for the intended application. For
example, shell materials shall remain strong, semirigid, and
firm,andshallnotpermanentlydistortduringanexposureofat
least4htoanytemperatureintherangefrom−27to32°C,nor
shall the material be significantly affected by exposure to
ultraviolet radiation, water, dirt, or vibration. All materials
shall be rot-resistant. In addition, paints, glues, and finishes
used in manufacture shall be compatible with the helmet shell
FIG. 2 Anatomical Planes and shock absorption system materials.
F1045−07 (2013)
correspond to the physical dimensions defined in Specification
F2220 as sizes A, E, J, or M. If a helmet size range, as
identified by the manufacturer’s instructions, is capable of
fitting two different headforms, the larger headform shall be
used.
4.5.1 Type 1—The extent of coverage shall include at least
alloftheareaabovelineBCDEFasshowninFig.5.Thisarea
shall correspond with the headform size with which the
protector is to be tested. No ear aperture shall have any
dimensionexceeding38mm(1.5in.).Theearapertureshallbe
completely surrounded by the helmet. The distance from any
edge of an ear aperture to any edge of the helmet shall not be
less than 20 mm (0.8 in.).
4.5.2 Type 2—The extent of coverage shall include at least
all of the area above line BCDGHEF as shown in Fig. 6. This
area shall correspond with the headform size with which the
protector is to be tested.
4.6 Attachments—The components of the fasteners for se-
curing attachments to the shell shall be so attached that the
degree of protection afforded the wearer by the protective
padding or cushioning material of the helmet is not thereby
reduced.
FIG. 4Location of Reference Lines
4.7 Size of Helmets—Helmets shall be sized in accordance
with Table 1.
4.1.2 Materials coming into contact with the wearer’s head
4.8 Chin Strap or Neck Strap:
shall not be the type known to cause skin irritation or disease,
4.8.1 The chin strap, including the cup, or the neck strap,
and shall not undergo significant loss of strength, flexibility, or
shallbeattachedtothehelmetsothatthehelmetremainsinits
other physical change as a result of contact with perspiration,
normal position on the player’s head during play and impact
oil, or grease from the wearer’s hair.
conditions.
4.1.3 Any material used in the construction of helmets shall
4.8.2 The chin strap or the neck strap used in combination
not be adversely affected by ordinary household soap and
with the face protector shall satisfy the requirements in 3.1.1.
water, mild household detergent, or cleaners recommended by
4.8.3 The minimum width of the chin strap exclusive of the
the manufacturer.
cup shall be 12.7 mm (0.5 in.).
4.2 Helmet Assembly:
4.2.1 Any optional devices fitted to the helmet shall be so
5. Performance Requirements
designed that they are unlikely to cause any injury to the
wearer or other participants during contact. 5.1 General—Helmets shall be capable of meeting the
4.2.2 All edges shall be smooth and rounded and there shall requirementsinthisperformancespecificationthroughouttheir
be no rigid projections on the inside of the helmet that could full range of adjustment. They shall be capable of meeting the
come in contact with the wearer’s head. requirementsinSections11and12atanytemperaturebetween
4.2.3 All external projections shall be smooth and ad- −27 to 32°C.
equatelyfairedtoothersurfaces.Splitorbifurcatedrivetsshall
5.2 Shock Absorption—The helmet is mounted on a head-
not be used.
form that is oriented in different positions and dropped at a
4.3 Types of Protectors:
specificvelocityontoanimpactsurface.Alinearaccelerometer
4.3.1 Type 1—Head protectors that meet requirements for
mounted at the center of gravity of the headform monitors the
the area of coverage mentioned in 4.5.1.
acceleration and the time history of impact that are recorded
4.3.2 Type 2—Head protectors that meet requirements for
with appropriate instrumentation. Maximum acceleration and
the area of coverage mentioned in 4.5.2.
time duration data obtained by the specified procedures are
intended to determine the shock absorption characteristics of
4.4 Impact Test ProtectedArea—Theareaabovethetestline
the helmet.
(see 12.2.7) shall be considered the impact test protected area.
All parts of the wearer’s head covered by the area of the shell
5.3 Chin Strap—When tested in accordance with 12.8, the
shallbeprotectedatleasttotheminimumimpactrequirements
forcetoseparatethestrapshallnotbelessthan50N(11.2lbf)
of 13.1 and 13.2.
nor more than 500 N (112.4 lbf), and the maximum displace-
4.5 Area of Coverage—Area of coverage measurements ment of the strap shall not exceed 25.4 mm (1 in.) at a load of
shall be made with the protector mounted in accordance with 109 N (24.5 lbf). The requirements of 12.8 shall be met at
theprotectormanufacturer’sinstructionsontheheadformsthat ambient conditions.
F1045−07 (2013)
NOTE 1—A-Reference plane, B-Coronal plane
FIG. 5Type 1–Area of Coverage
5.4 Penetration Resistance Test Requirements—It shall not 6.1.2.2 System Accuracy—The impact recording system
be possible to touch the test headform with the curved end of shall be capable of measuring shocks of up to 500 g peak
the test stick blade within the required area of coverage, acceleration with an accuracy of 65%.
excluding the ear opening. 6.1.2.3 Impact Recording—The impact shall be recorded on
single- or dual-trace storage oscilloscope with 0.1-mVto 20-V
6. Apparatus
deflectionfactor,1to5-mssweepspeed-division,and500-kHz
bandwidth.
6.1 Shock Absorption Test—The apparatus for the shock
6.1.2.4 Test Headforms—Test headforms that correspond to
absorption test shall consist of the following:
thephysicaldimensionsdefinedinSpecificationF2220assizes
6.1.1 Guide Assembly—The headform shall be attached to
A,E,J,andM.Theweightofthedropassembly,includingthe
the free fall drop assembly carriage by an adjustable mounting
headform, shall be in accordance with 12.4 unless otherwise
that will allow impacts to be delivered to any prescribed point
specified in the individual performance specifications.The test
onthehelmet(seeFig.7).Thecarriageshallbefreetoslideon
headformsshallincludesurfacemarkingscorrespondingtothe
vertical guides. If wires are used, they must be placed under at
basic, coronal, midsagittal, and reference planes (see Figs. 2
least 845.2 N (190 lbf) tension (see 12.4 for guide assembly
and 3).
specifications and allowable weight of drop assembly).
6.1.2.5 Reference Headforms—Measuring headforms con-
6.1.2 Recording Equipment—Therecordingequipmentshall
toured in the same configuration as the test headforms sizesA,
meet the following criteria:
E, J, and M, as defined in Specification F2220. The reference
6.1.2.1 Acceleration Transducer—The linear accelerometer
headformsshallincludesurfacemarkingscorrespondingtothe
is mounted at the center of gravity of the combined test
basic, coronal, midsagittal, and reference planes (see Figs.
headformandcarriageassemblywiththesensitiveaxisaligned
2-4).
to within 5° of the vertical when the helmet and headform are
in the impact position. This transducer shall be capable of
withstandingashockof1000 gwithoutdamageandshallhave
Equivalent instrumentation capable of recording, displaying, and providing a
afrequencyresponse(variation 61.5%)overtherangefrom5
permanent record of the generated accelerometer shock signal will meet this
to 900 Hz. requirement.
F1045−07 (2013)
NOTE 1—A-Reference plane, B-Coronal plane
NOTE 2—Dimension Y and Z are taken and must cover between the reference and the basic plane.
NOTE 3—A-Headform does not have Type 2 coverage.
FIG. 6Type 2–Area of Coverage
TABLE 1 Hat Sizes and Head Fittings
5 Durometer ShoreAHardness impact surface. The base shall
consist of a rigid slab weighing at least 136.1 kg (300 lb). The
NOTE 1—These are U.S. and Canadian hat sizes.
top surface of this base may be used as the flat metal anvil if
Circumference of Head
Hat Size
it is faced with a steel plate with minimum thickness of 25.4
in. mm
2 2
mm (1 in.) and minimum top surface area of 0.09 m (1 ft ). If
6 19 483
1 3
a detachable flat metal anvil is used it must have a top s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.