ASTM D3466-76(1998)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ignition Temperature of Granular Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Ignition Temperature of Granular Activated Carbon
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of reference ignition temperature of granular activated carbon in flowing air. This test method provides a basis for comparing the ignition characteristics of different carbons, or the change in ignition characteristics of the same carbon after a period of service.
1.2 The ignition temperature as determined by this test method cannot be interpreted as the probable ignition temperature of the same carbon under the operating conditions of a specific application unless those conditions are essentially the same as those in this test method. If it is desired to determine the ignition temperature of the carbon under a specific set of operating conditions, the test may be modified to simulate such conditions, taking into consideration the following variables: (1) air flow rate; (2) moisture content of the carbon; (3) bed depth; (4) relative humidity of the air stream; (5) heating rate; (6) contaminants (for example, hydrocarbons, etc.) in the air stream; and (7) contaminants that may have been adsorbed by the carbon under prior service conditions.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D 3466–76 (Reapproved 1998)
Standard Test Method for
Ignition Temperature of Granular Activated Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3466; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E 220 Method for Calibration of Thermocouples by Com-
parison Techniques
1.1 This test method covers the determination of reference
E 300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
ignition temperature of granular activated carbon in flowing
air. This test method provides a basis for comparing the
3. Terminology
ignition characteristics of different carbons, or the change in
3.1 Definitions—Terms relating to this test method are
ignition characteristics of the same carbon after a period of
defined in Terminology D 2652.
service.
1.2 The ignition temperature as determined by this test
4. Summary of Test Method
method cannot be interpreted as the probable ignition tempera-
4.1 Asampleofcarbonisexposedtoaheatedairstream,the
ture of the same carbon under the operating conditions of a
temperature of which is slowly increased until the carbon
specific application unless those conditions are essentially the
ignites. The temperature of the carbon bed and of the air
same as those in this test method. If it is desired to determine
entering the bed are recorded, and ignition is defined as the
the ignition temperature of the carbon under a specific set of
point at which the carbon temperature suddenly rises above the
operating conditions, the test may be modified to simulate such
temperature of the air entering the bed.
conditions, taking into consideration the following variables:
(1) air flow rate; (2) moisture content of the carbon; (3) bed
5. Significance and Use
depth; (4) relative humidity of the air stream; (5) heating rate;
5.1 Activated carbons used in gas-phase adsorption may be
(6) contaminants (for example, hydrocarbons, etc.) in the air
subjected to heating, either from heat applied externally to the
stream; and (7) contaminants that may have been adsorbed by
carbon bed, or heat generated by radioactive contaminants, or
the carbon under prior service conditions.
by the adsorption process itself. If the application of heat is
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sudden, or if no ample means to conduct the heat from the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
carbon bed exists, the carbon bed may ignite. This test method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
provides a controlled laboratory test to determine the tempera-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
tures at which such ignition occurs. As stated in 1.2, this does
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
not necessarily give the temperature at which ignition will
tionary statements are given in Section 7.
occur under a specific bed operating condition. This test
method does, however, allow some ranking of carbons with
2. Referenced Documents
regard to ignition temperature, and is a useful quality-control
2.1 ASTM Standards:
method for unused carbons.
D 2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
D 2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated
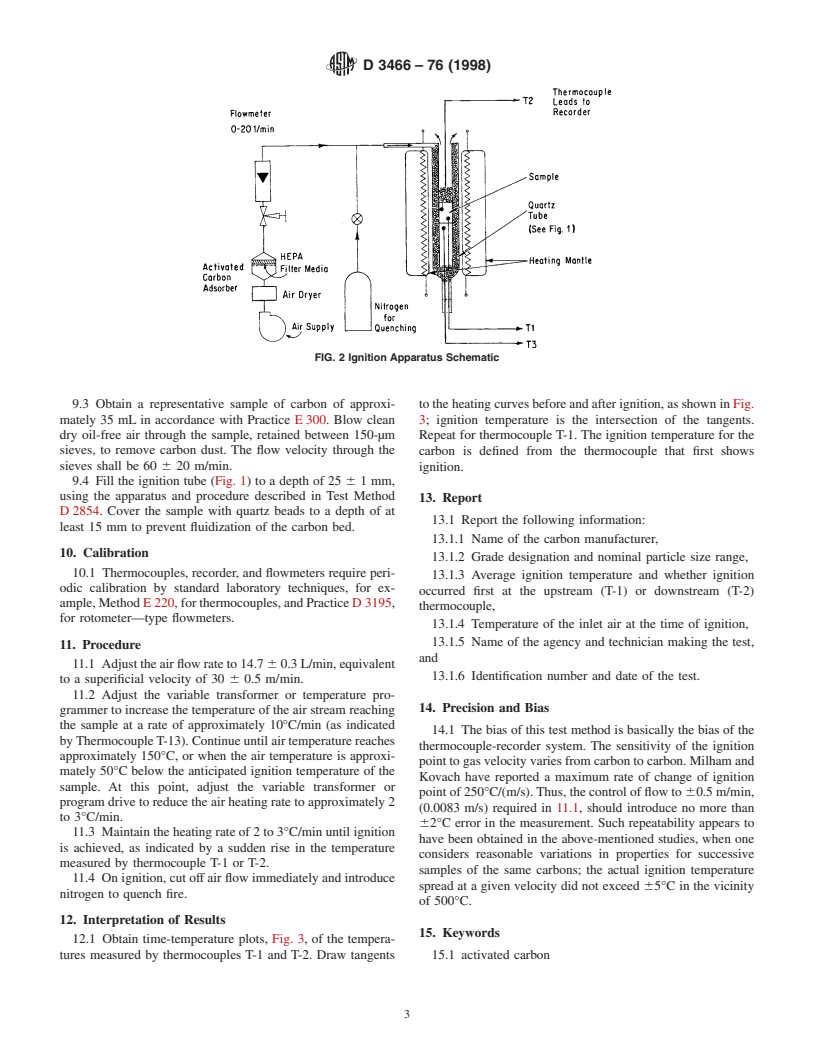
6. Apparatus
Carbon
6.1 Quartz Ignition Tube and Sample Holder, as shown in
D 3195 Practice for Rotameter Calibration
Fig. 1.
E11 Specification for Wire-Cloth Sieves for Testing Pur-
6.2 Thermocouples, Chromel-Alumel with Inconel sheath,
poses
0.635-mm diameter, three required.
6.3 Supply of Clean, Dry, Oil-Free Air—The air must be
passed through a HEPA filter and a bed of activated carbon
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-28 on
Activated Carbon, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D 28.04 on Gas
Evaluation Tests.
Current edition approved June 25, 1976. Published October 1976. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
2 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.05.
3 7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.03. Milham and Kovoch, “Treatment of Airborne Radioactive Wastes,” Interna-
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. tional Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1968. (Paper SM-110/49).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 3466–76 (1998)
FIG. 1 Ignition Tube and Sample Assembly
containing at least 300 mLof carbon per litre per minute of air 7. Hazards
flow. Relative humidity of the air must be less than 5 % at
7.1 The temperature rise in a carbon bed is quite sudden at
25°C.
ignition. An adequate supply of nitrogen and an operator must
6.4 Flowmeter, capable of metering air flow rates to 20
be present to quench the fire when this rise occurs. Do not stop
L/min.
nitrogen flow until all thermocouples indicate temperatures
6.5 Heating Mantle, tape, or oven to surround the ignition
substantially below ignition.
tube; at least 50 W.
7.2 Combustion products of carbon or carbon impreg-nants
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.