ASTM G101-01
(Guide)Standard Guide for Estimating the Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance of Low-Alloy Steels
Standard Guide for Estimating the Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance of Low-Alloy Steels
SCOPE
1.1 This guide presents two methods for estimating the atmospheric corrosion resistance of low-alloy weathering steels, such as those described in Specifications A242/A242M, A588/A588M, A606 Type 4, A709/A709M grades 50W, HPS 70W, and 100W, A852/A852M, and A871/A871M. One method gives an estimate of the long-term thickness loss of a steel at a specific site based on results of short-term tests. The other gives an estimate of relative corrosion resistance based on chemical composition.
General Information
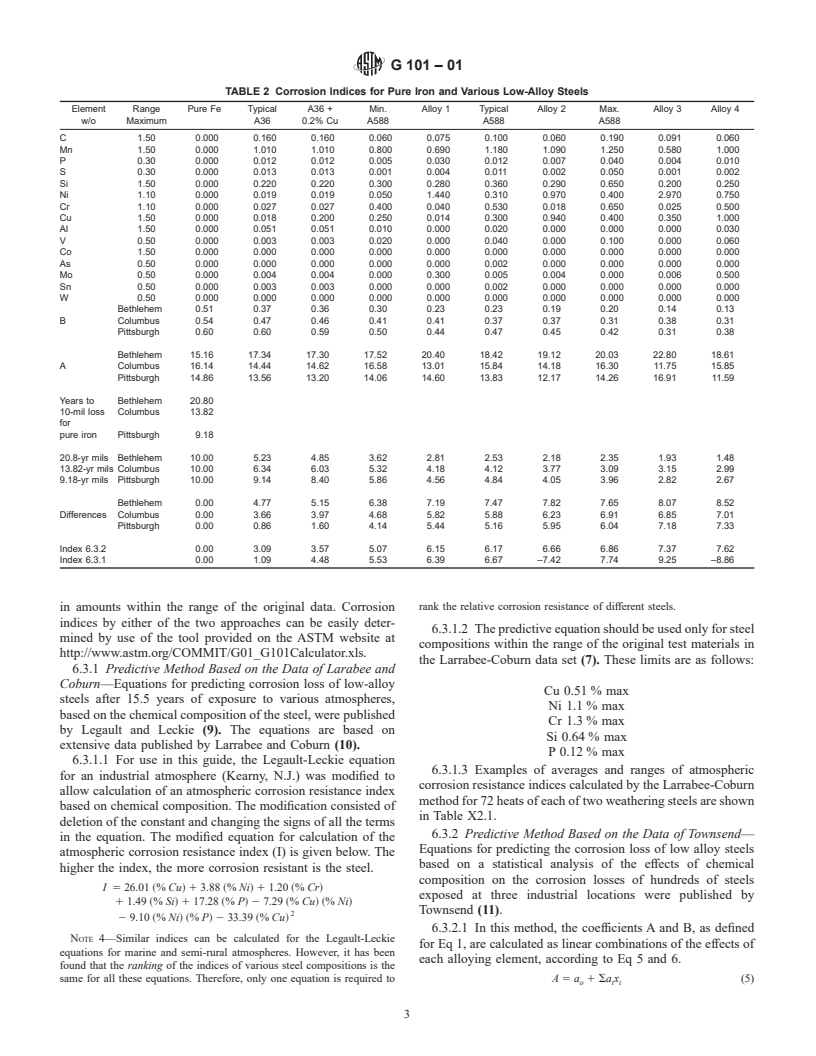
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G 101 – 01
Standard Guide for
Estimating the Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance of Low-
1
Alloy Steels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G 101; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope G 16 Guide for Applying Statistics to Analysis of Corrosion
4
Data
1.1 This guide presents two methods for estimating the
G 50 Practice for Conducting Atmospheric Corrosion Tests
atmospheric corrosion resistance of low-alloy weathering
4
on Metals
steels, such as those described in Specifications A 242/
A 242M, A 588/A 588M, A 606 Type 4, A 709/A 709M grades
3. Terminology
50W, HPS 70W, and 100W, A 852/A 852M, and A 871/
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
A 871M. One method gives an estimate of the long-term
3.1.1 low-alloy steels—Iron-carbon alloys containing
thickness loss of a steel at a specific site based on results of
greater than 1.0 % but less than 5.0 %, by mass, total alloying
short-term tests. The other gives an estimate of relative
elements.
corrosion resistance based on chemical composition.
NOTE 1—Most “low-alloy weathering steels” contain additions of both
2. Referenced Documents
chromium and copper, and may also contain additions of silicon, nickel,
phosphorus, or other alloying elements which enhance atmospheric
2.1 ASTM Standards:
corrosion resistance.
A 242/A 242M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy
2
Structural Steel
4. Summary of Guide
A 588/A 588M Specification for High-Strength Low-Alloy
4.1 In this guide, two general methods are presented for
Structural Steel with 50 Ksi (345 MPa) Minimum Yield
2 estimating the atmospheric corrosion resistance of low-alloy
Point to 4 in. (100 mm) Thick
weathering steels. These are not alternative methods; each
A 606 Specification for Steel, Sheet and Strip, High
method is intended for a specific purpose, as outlined in 5.2 and
Strength, Low-Alloy, Hot-Rolled and Cold Rolled, With
3 5.3.
Improved Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance
4.1.1 The first method utilizes linear regression analysis of
A 709/A 709M Specification for Carbon and High-Strength
short-term atmospheric corrosion data to enable prediction of
Low-Alloy Structural Steel Shapes, Plates, and Bars and
long-term performance by an extrapolation method.
Quenched-and-Tempered Alloy Structural Steel Plates for
4.1.2 The second method utilizes predictive equations based
Bridges
on the steel composition to calculate indices of atmospheric
A 852/A 852M Specification for Quenched and Tempered
corrosion resistance.
Low-Alloy Structural Steel Plate with 70 ksi (485 MPa)
2
Minimum Yield Strength to 4 in (100 mm) Thick
5. Significance and Use
A 871/A 871M Specification for High Strength Low-Alloy
5.1 In the past, ASTM specifications for low-alloy weath-
Structural Steel Plate With Atmospheric Corrosion Resis-
2 ering steels, such as Specifications A 242/A 242M, A 588/
tance
A 588M, A 606 Type 4, A 709/A 709M Grade 50W, HPS 70W,
G 1 Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Cor-
4 and 100W, A 852/A 852M, and A 871/A 871M stated that the
rosion Test Specimens
atmospheric corrosion resistance of these steels is “approxi-
mately two times that of carbon structural steel with copper.” A
1
footnote in the specifications stated that “two times carbon
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G01 on Corrosion of
Metals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.04on Atmospheric
structural steel with copper is equivalent to four times carbon
Corrosion.
structural steel without copper (Cu 0.02 maximum).” Because
Current edition approved May 10, 2001. Published May 2001. Originally
such statements relating the corrosion resistance of weathering
published as G 101 – 89. Last previous edition G 101 – 97.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.04.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G101–01
steels to that of other steels are imprecise and, more impor-
where:
5
tantly, lack significance to the user (1 and 2) , the present
C = corrosion loss,
guide was prepared to describe more meaningful methods of
t = time, and
estimating the atmospheric corrosion resistance of weathering A and B = constants. A is the corrosion loss at t = 1, and B
steels. is the slope of a log C versus log + plot.
5.2 The first method of this guide is intended for use in C may be expressed as mass loss per unit area, or as a
estimating the expected long-ter
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.