ISO 490:1993
(Main)Cinematography — Magnetic stripes and magnetic recording head gaps for sound record on 16 mm motion-picture film perforated along one edge (Type 1) — Positions and width dimensions
Cinematography — Magnetic stripes and magnetic recording head gaps for sound record on 16 mm motion-picture film perforated along one edge (Type 1) — Positions and width dimensions
Specifies location and width of magnetic striping, location and width of gaps of magnetic heads, film projection speed, and longitudinal picture-sound displacement.
Cinématographie — Pistes magnétiques et entrefers de têtes magnétiques d'enregistrement pour l'enregistrement du son sur film cinématographique 16 mm perforé sur un bord (Type 1) — Emplacement et largeurs
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 02-Jun-1993
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 36/WG 3 - Audio technology
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 04-Jun-2029
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 490:1993 is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that specifies the positions and width dimensions for magnetic stripes and magnetic recording head gaps used in sound recording on 16 mm motion-picture film perforated along one edge (Type 1). This standard is essential for maintaining uniformity and compatibility in cinematography equipment and film production, ensuring high-quality magnetic sound recording and playback.
The document addresses key parameters such as the location and width of magnetic striping, the dimensions of magnetic head gaps, film projection speed, and longitudinal picture-sound displacement. ISO 490:1993 replaces the earlier 1978 edition, incorporating technical revisions vital for modern film and sound processes.
Key Topics
Magnetic Striping Location and Width
The standard defines the exact positioning of the magnetic sound stripe on 16 mm film. The stripe is applied on the side toward the projector lamp for direct projection on reflection-type screens. A balance stripe may be added if the magnetic stripe increases film thickness beyond 0.005 mm to ensure even thickness across the film edges. The maximum acceptable thickness for magnetic and balance stripes is 0.020 mm.Magnetic Recording Head Gaps
Specifies the precise location and width of the magnetic recording head gaps, critical for accurate sound recording and playback. The effective head gaps must be at a right angle (90° ± 5') to the film's longitudinal axis to maintain sound quality.Film Projection Speed
Film projection speeds are detailed for different applications, including professional (cinematography and television) and non-professional use. The primary standards specify speeds of 24 frames/s for cinematography and television (50/60 Hz supplies), while secondary standards recognize slower speeds such as 18 frames/s for non-professional equipment.Longitudinal Picture-Sound Displacement
The magnetic sound recording on the film should precede the corresponding picture center by 28 ± 1 frames, ideally 28 ± 0.5 frames, to synchronize audio with visual content accurately.
Applications
ISO 490:1993 is critical for multiple fields within the motion picture and audiovisual industries:
Film Production and Post-Production
Ensures standardized application of magnetic sound stripes on 16 mm film stock, facilitating consistent sound recording quality and compatibility between different production and playback equipment.Film Projection and Exhibition
Defines projector head gap positioning and film speed to ensure fidelity in sound reproduction during film screenings.Broadcast and Television
Supports television standards involving magnetic sound recording on 16 mm film, especially adapting for 50 Hz and 60 Hz frequency supplies in different regions.Equipment Manufacturing
Provides technical specifications for manufacturers producing magnetic recording heads, projectors, and editing machines compliant with international norms.Archiving and Restoration
Helps archivists accurately preserve and restore audio tracks on historical 16 mm film reels by following internationally recognized positioning and dimension guidelines.
Related Standards
ISO 490:1993 references and complements several other ISO standards relevant to cinematography and film handling:
ISO 69:1990 – Cinematography - 16 mm motion-picture and magnetic film - Cutting and perforating dimensions. Defines film perforations crucial to proper striping and head alignment.
ISO 359:1983 – Cinematography - Projectable image area on 16 mm motion-picture prints - Dimensions and location. Specifies the picture frame area for synchronization.
ISO 1188:1984 – Cinematography - Recorded characteristic for magnetic sound on full-coat 16 mm motion-picture film - Specifications. Details sound recording parameters ensuring audio quality aligns with this standard’s guidelines.
ISO/TC 36 (Technical Committee on Cinematography) – The coordinating body responsible for the development and maintenance of this and related standards.
By adhering to ISO 490:1993, industry professionals ensure consistency, interoperability, and high-quality sound reproduction in 16 mm motion-picture films, fostering global standardization in cinematic sound recording technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 490:1993 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Cinematography — Magnetic stripes and magnetic recording head gaps for sound record on 16 mm motion-picture film perforated along one edge (Type 1) — Positions and width dimensions". This standard covers: Specifies location and width of magnetic striping, location and width of gaps of magnetic heads, film projection speed, and longitudinal picture-sound displacement.
Specifies location and width of magnetic striping, location and width of gaps of magnetic heads, film projection speed, and longitudinal picture-sound displacement.
ISO 490:1993 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 37.060.20 - Motion picture films. Cartridges. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 490:1993 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 490:1978. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 490:1993 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL
ISO
STANDARD
Second edition
1993-06-0 1
- Magnetit stripes and
Cinematography
magnetic recording head gaps for Sound
record on 16 mm motion-picture film
perforated along one edge (Type 1) -
Positions and width dimensions
Cin6ma tographie - Pistes magnetiques et en trefers de tetes
mag& tiques d ‘enregis tremen t pour I’enregis tremen t du son sur film
cinematographique 16 mm perfor6 sur un bord (Type 7) - Emplacement
et largeurs
Reference number
ISO 490: 1993(E)
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work
of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Esch member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be
represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 490 was prepared by Technical Committee
lSO/TC 36, Cinematography.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (ISO 490:1978),
of which it constitutes a technical revision.
0 ISO 1993
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or
by any means, electronie or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without per-
mission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
Cinematography - Magnetit stripes and magnetic
recording head gaps for Sound record on 16 mm
motion-picture film perforated along one edge
- Positions and width dimensions
(Type 1)
ISO 4243:1979, Cinematography - Picture image
1 Scope
area and photographic Sound record on 16 mm
motion-picture release prints - Positions and dimen-
1.1 This International Standard specifies the location
sions.
and width of the magnetic striping on 16 mm
motion-picture film perforated along one edge
3 Location and width of magnetic
(Type 1) with picture, slit and perforated in accordance
striping
with ISO 69.
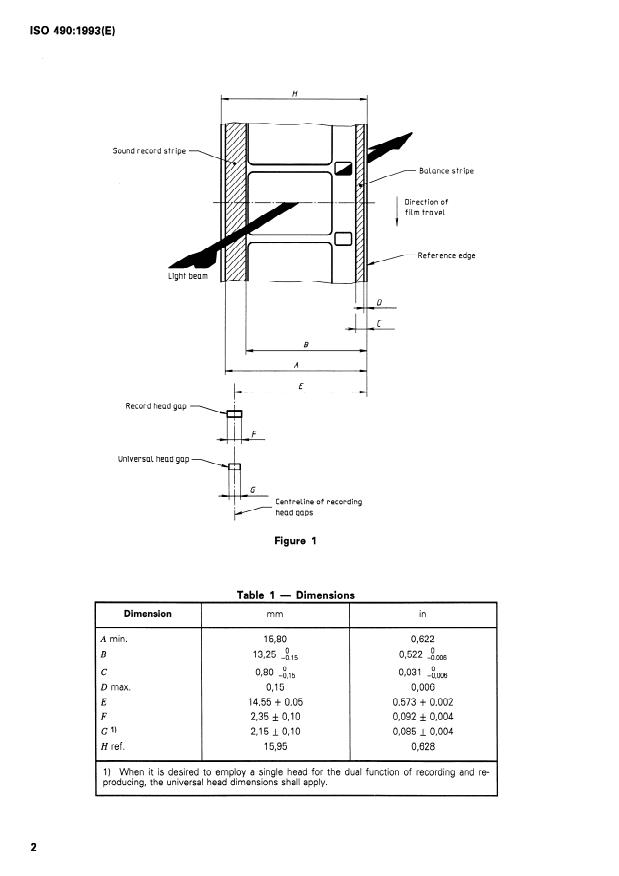
3.1 The location and width of the magnetic striping
1.2 This International Standard also specifies the lo-
shall be as shown in figure 1 and table 1.
cation and width of the magnetic recording head gaps
in Systems using a magnetic stripe on 16 mm
3.2 The magnetic striping shall be on the side of the
motion-picture film.
film toward the lamp of the projector arranged for di-
rect projection on a reflection-type Screen.
2 Normative references
3.3 If the magnetic Sound stripe increases the
thickness of the film by more than 0,005 mm, a bal-
The following Standards contain provisions which,
ante stripe shall be applied to equalize effectively the
through reference in this
...



Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...