ISO 2262:1984
(Main)General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes — Specification
General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes — Specification
Cancels and replaces the first edition (i.e. ISO 2262:1972). Applies to thimbles suitable for use with steel wire ropes complying with ISO 2408, having a maximum tensile grade of 1770 MPa, with diameters from 4 to 60 mm. Does not apply to thimbles for use with fibre ropes. Reeving thimbles and solid thimbles are not included.
Cosses d'usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec des câbles en acier — Spécifications
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 31-May-1984
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 105 - Steel wire ropes
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 105 - Steel wire ropes
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 04-Mar-2031
Relations
- Effective Date
- 23-Apr-2020
Overview
ISO 2262:1984 specifies the requirements for general purpose thimbles designed for use with steel wire ropes. This standard applies to thimbles compatible with steel wire ropes conforming to ISO 2408, having a maximum tensile grade of 1770 MPa and nominal diameters ranging from 4 to 60 mm. It replaces the first edition ISO 2262:1972 and excludes thimbles for fibre ropes, as well as reeving and solid thimbles.
This International Standard ensures that thimbles provide reliable protection to steel wire ropes by preventing wear and deformation where the rope forms loops or eyes. It defines material properties, dimensions, galvanizing requirements, workmanship, and mechanical testing procedures to guarantee performance and safety in lifting and rigging applications.
Key Topics
Scope and Application
Specifies thimbles for steel wire ropes with diameters 4–60 mm and tensile grade up to 1770 MPa. Not intended for fibre ropes or certain specialized thimbles.Material Requirements
Thimbles must be manufactured from steel conforming to ISO 630 or equivalent with tensile strength between 360 and 520 MPa and minimum elongation of 20% after fracture.Dimensions and Sizes
The standard provides detailed dimensional requirements mapped to rope diameters. Nominal thimble size corresponds to rope diameter, with dimensions such as width, height, and curvature specified to ensure proper fit and function.Galvanizing
Thimbles are required to be hot dip galvanized with a minimum zinc coating of 120 g/m² according to ISO 1461, ensuring corrosion resistance and extended durability.Workmanship and Quality
Thimbles must be free from defects including sharp edges or surface flaws that could damage the rope. Welding at the joint is prohibited, and a small gap at the joint is permitted after galvanizing.Mechanical Testing
Prototype tests involve applying axial loads of 32% of the minimum breaking load (MBL) to thimbles fitted on appropriate ropes, confirming structural integrity and deformation limits. Retesting protocols are defined if failures occur.Design Variants
Manufacturers may produce pointed or unpointed thimbles unless the purchaser specifies a preference.
Applications
ISO 2262:1984 thimbles are essential components in the construction, maritime, mining, and lifting industries where steel wire ropes are subject to heavy loading and abrasion. Typical applications include:
Lifting and hoisting equipment
Thimbles protect rope eyes in slings, improving safety during load handling.Marine rigging and mooring
Providing wear protection for ropes used in harsh marine environments.Cranes and winches
Enhancing the service life of ropes subjected to constant bending and tension.Industrial machinery
Used in pulley systems and cable assemblies requiring secure rope attachments.
By following ISO 2262 specifications, organizations ensure thimbles meet rigorous safety and quality benchmarks, thereby minimizing rope damage and operational risks.
Related Standards
ISO 2408 – Steel wire ropes for general purposes: Defines rope construction, tensile grades, and breaking loads compatible with ISO 2262 thimbles.
ISO 630 – Structural steels: Specifies material requirements applicable for thimble manufacturing.
ISO 1461 – Metallic coatings - Hot dip galvanized coatings: Details corrosion protection processes relevant for galvanized steel thimbles.
ISO 6892 – Metallic materials - Tensile testing: Defines test methods for assessing material tensile strength and elongation of thimbles.
Understanding and implementing ISO 2262 in conjunction with these related standards ensures comprehensive quality control in the manufacture and use of steel wire rope thimbles.
Keywords: ISO 2262, steel wire rope thimbles, lifting equipment, wire rope accessories, galvanized thimbles, tensile strength, mechanical testing, rope abrasion protection, industrial rigging standards, ISO 2408 compliance.
Buy Documents
ISO 2262:1984 - General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes -- Specification
ISO 2262:1984 - Cosses d'usages courants destinées a etre utilisées avec des câbles en acier -- Spécifications
ISO 2262:1984 - Cosses d'usages courants destinées a etre utilisées avec des câbles en acier -- Spécifications
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 2262:1984 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes — Specification". This standard covers: Cancels and replaces the first edition (i.e. ISO 2262:1972). Applies to thimbles suitable for use with steel wire ropes complying with ISO 2408, having a maximum tensile grade of 1770 MPa, with diameters from 4 to 60 mm. Does not apply to thimbles for use with fibre ropes. Reeving thimbles and solid thimbles are not included.
Cancels and replaces the first edition (i.e. ISO 2262:1972). Applies to thimbles suitable for use with steel wire ropes complying with ISO 2408, having a maximum tensile grade of 1770 MPa, with diameters from 4 to 60 mm. Does not apply to thimbles for use with fibre ropes. Reeving thimbles and solid thimbles are not included.
ISO 2262:1984 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 53.020.30 - Accessories for lifting equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 2262:1984 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 2262:1972. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 2262:1984 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
International Standard
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATlON.ME)KAYHAPOAHAR OPTAHM3AUMR IlO CTAHAAPTlrl3ALWl~RGANlSATlON INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes -
Specification
Cosses d’usages courants destinbes 6 &re utilishes avec des &b/es en acier - Sphcifications
Second edition - 1984-07-15
Ref. No. IS0 22624984 (E)
UDC 667.72 : 621.885
G3
-
Descriptors : lifting equipment, wire rope, rope thimbles, specifications, tests, performance tests.
I
M
Price based on 3 pages
v,
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of developing International
Standards is carried out through IS0 technical committees. Every member body
interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been authorized has the
right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council.
International Standard IS0 2262 was developed by Technical Committee ISO/TC 111,
Round steel link chains, lifting hooks and accessories, and was circulated to the
member bodies in March 1983.
It has been approved by the member bodies of the following countries:
Australia India Romania
Austria South Africa, Rep. of
Italy
Belgium Japan Sweden
Canada Norway United Kingdom
Germany, F.R. Poland
following expressed disapproval of the document on
The member body of the country
technical gro unds :
Netherlands
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (i.e. IS0 2262-1972).
0 International Organization for Standardization, 1984
Printed in Switzerland
IS0 2262-1984 (E)
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes -
Specification
the following mechanical properties when tested in accordance
1 Scope and field of application
with IS0 6892:
This International Standard specifies the requirements for
-
tensile strength: 360 to 520 MPa (N/mm2);
general purpose thimbles suitable for use with steel wire ropes
complying with IS0 2408, having a maximum tensile grade of
-
elongation after fracture: 20 % min.
1 770 MPa(N/mm2), with diameters from 4 to 60 mm.
It does not apply to thimbles for use with fibre ropes.
6 Galvanizing
Reeving thimbles and solid thimbles are not included.
Unless otherwise specified, thimbles shall be galvanized with a
zinc coating of at least 120 g/m2 in accordance with IS0 1461.
2 References
IS0 630, Structural steels. 7 Workmanship and freedom from defects
Thimbles shall be neatly formed, and shall be free from any
Hot dip galvanized coatings on
IS0 1461, Metallic coatings -
flaw, defect, sharp edges or roughness, which might damage
fabrica ted ferrous products - Requiretnen ts.
the rope.
IS0 2408, Steel wire ropes for general purposes -
The joint formed at the point of the thimble shall not be welded.
Characteristics. 1)
A small gap at the joint may be allowed after galvanizing.
I SO 6892, Metallic materials - Tensile testing. 2)
The thimbles may either be pointed (see figure 1) or without
points (see figure 21, at the option of the manufacturer, unless
one or other type is specifically ordered by the purchaser.
3 Nominal size
The nominal size of a thimble is the nominal diameter of the
8 Prototype test
rope for which it has been primarily designed. The range of
sizes of thimbles covered by this International Standard is from
8.1 Object
4 to 60 mm.
The prototype test is intended to demonstrate that the thimble
specified by the manufacturer and having dimensions which
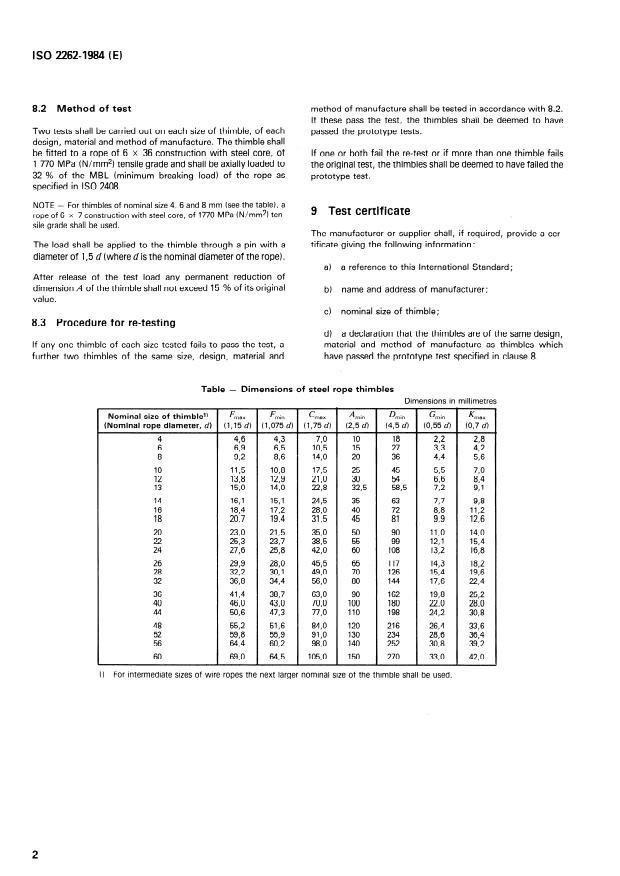
4 Dimensions
meet the requirements of this International Standard can with-
stand the maximum loading conditions likely to be imposed
The dimensions of thimbles shall comply with the appropriate
upon it unde
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEX&YHAPOfiHAR OPrAHM3AlJMR Il0 CTAH~APTM3AL&lM*ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec
des câbles en acier - Spécifications
General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes - Specifïcation
Deuxième édition - 1984-07-15
CDU 667.72 : 621.885
Réf. no : ISO 22624984 (F)
Descripteurs : appareil de levage, câble métallique, cosse, spécification,
essai, essai de fonctionnement.
Prix basé sur 3 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 2262 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 111,
Chaînes à maillons en acier rond, crochets de levage et accessoires, et a été soumise
aux comités membres en mars 1983.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’
Canada Pologne
Allemagne, R. F.
Inde Roumanie
Australie
Italie Royaume-Uni
Autriche Japon Suède
Belgique
Norvège
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’a désapprouvee pour des raisons techniques:
Pays- Bas
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 22624972).
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 2262-1984 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
.
Cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec
des câbles en acier - Spécifications
suivantes quand il est soumis aux essais conformément à
1 Objet et domaine d’application
I’ISO 6892 :
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les exigences des
- résistance à la traction: 360 à 520 MPa (N/mm*);
cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec des
câbles en acier conformes à I’ISO 2408, et ayant une résistance
-
allongement après rupture: 20 % min.
à la traction maximale de 1 770 MPa (N/mm*) et des diamètres
allant de 4 à 60 mm.
Elle n’est pas applicable aux cosses destinées à être utilisées
6 Galvanisation
avec des câbles en acier à âme en textile.
En l’absence d’autres spécifications, les cosses doivent être gal-
Les cosses pour faire passer les cordages et les cosses à haute
vanisées avec un revêtement de zinc d’au moins 120 g/m* con-
résistance ne sont pas incluses.
formément à I’ISO 1461.
2 Références
7 Exécution et absence des défauts
I SO 630, Aciers de construction métallique.
Les cosses doivent être faites avec soin et doivent être exemp-
tes de toute imperfection, de tout défaut, de bords pointus ou
ISO 1461, Revêtements métalliques - Revêtements de galva-
de toute rugosité qui pourraient endommager les câbles.
nisation à chaud sur produits finis en fer - Spécification.
Le joint formé au bout de la cosse ne doit pas être soudé. Un
ISO 2408, Câbles en acier pour usages courants - Caractéris-
petit espace au joint peut être permis après galvanisation.
tiques. l)
Les cosses peuvent comporter une partie pointue (voir figure 1)
ISO 6892, Matériaux métalliques - Essai de traction.*)
ou non (voir figure 2) au choix du fabricant, à moins que l’un ou
l’autre de ces types soit spécifié par l’acheteur.
3 Dimension nominale
8 Essai de prototype
La dimension nominale d’une cosse est le diamètre nominal du
câble pour lequel elle a été à l’origine concue. La gamme des
dimensions de cosses couvertes par la présente Norme interna-
8.1 Objet
tionale va de 4 à 60 mm.
L’essai de prototype est destiné à démontrer que la cosse spéci-
fiée par le fabricant, et ayant des dimensions qui satisfont aux
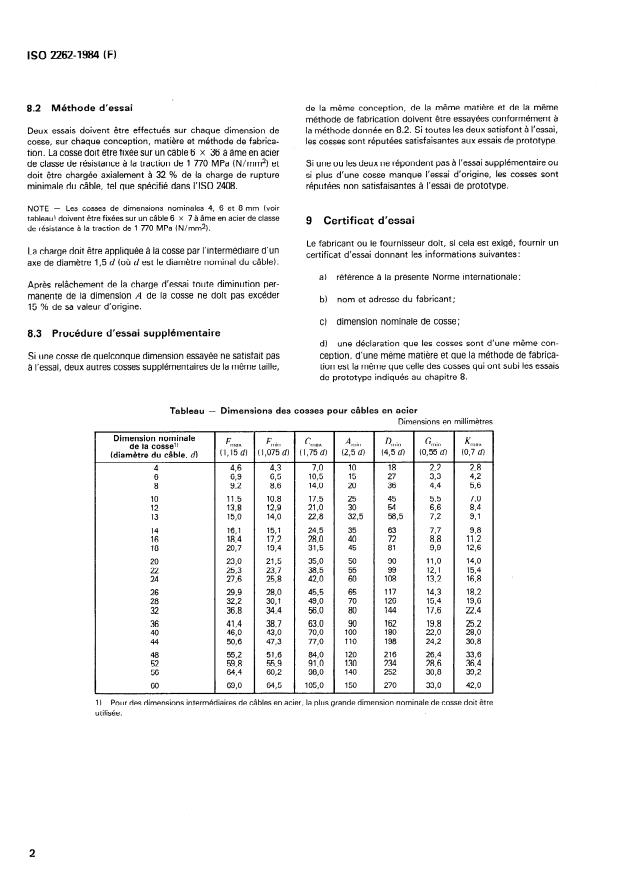
4 Dimensions
exigences de la présente Norme internationale, peut supporter
les conditions de charge maximale qui lui seront imposées vrai-
Les dimensions des cosses doivent correspondre aux valeurs
semblablement d
...
Norme internationale
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION.MEX&YHAPOfiHAR OPrAHM3AlJMR Il0 CTAH~APTM3AL&lM*ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
Cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec
des câbles en acier - Spécifications
General purpose thimbles for use with steel wire ropes - Specifïcation
Deuxième édition - 1984-07-15
CDU 667.72 : 621.885
Réf. no : ISO 22624984 (F)
Descripteurs : appareil de levage, câble métallique, cosse, spécification,
essai, essai de fonctionnement.
Prix basé sur 3 pages
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque
comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique
correspondant. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouverne-
mentales, en liaison avec I’ISO, participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO.
La Norme internationale ISO 2262 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 111,
Chaînes à maillons en acier rond, crochets de levage et accessoires, et a été soumise
aux comités membres en mars 1983.
Les comités membres des pays suivants l’ont approuvée:
Afrique du Sud, Rép. d’
Canada Pologne
Allemagne, R. F.
Inde Roumanie
Australie
Italie Royaume-Uni
Autriche Japon Suède
Belgique
Norvège
Le comité membre du pays suivant l’a désapprouvee pour des raisons techniques:
Pays- Bas
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition (ISO 22624972).
0 Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1984
Imprimé en Suisse
ISO 2262-1984 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
.
Cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec
des câbles en acier - Spécifications
suivantes quand il est soumis aux essais conformément à
1 Objet et domaine d’application
I’ISO 6892 :
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les exigences des
- résistance à la traction: 360 à 520 MPa (N/mm*);
cosses d’usages courants destinées à être utilisées avec des
câbles en acier conformes à I’ISO 2408, et ayant une résistance
-
allongement après rupture: 20 % min.
à la traction maximale de 1 770 MPa (N/mm*) et des diamètres
allant de 4 à 60 mm.
Elle n’est pas applicable aux cosses destinées à être utilisées
6 Galvanisation
avec des câbles en acier à âme en textile.
En l’absence d’autres spécifications, les cosses doivent être gal-
Les cosses pour faire passer les cordages et les cosses à haute
vanisées avec un revêtement de zinc d’au moins 120 g/m* con-
résistance ne sont pas incluses.
formément à I’ISO 1461.
2 Références
7 Exécution et absence des défauts
I SO 630, Aciers de construction métallique.
Les cosses doivent être faites avec soin et doivent être exemp-
tes de toute imperfection, de tout défaut, de bords pointus ou
ISO 1461, Revêtements métalliques - Revêtements de galva-
de toute rugosité qui pourraient endommager les câbles.
nisation à chaud sur produits finis en fer - Spécification.
Le joint formé au bout de la cosse ne doit pas être soudé. Un
ISO 2408, Câbles en acier pour usages courants - Caractéris-
petit espace au joint peut être permis après galvanisation.
tiques. l)
Les cosses peuvent comporter une partie pointue (voir figure 1)
ISO 6892, Matériaux métalliques - Essai de traction.*)
ou non (voir figure 2) au choix du fabricant, à moins que l’un ou
l’autre de ces types soit spécifié par l’acheteur.
3 Dimension nominale
8 Essai de prototype
La dimension nominale d’une cosse est le diamètre nominal du
câble pour lequel elle a été à l’origine concue. La gamme des
dimensions de cosses couvertes par la présente Norme interna-
8.1 Objet
tionale va de 4 à 60 mm.
L’essai de prototype est destiné à démontrer que la cosse spéci-
fiée par le fabricant, et ayant des dimensions qui satisfont aux
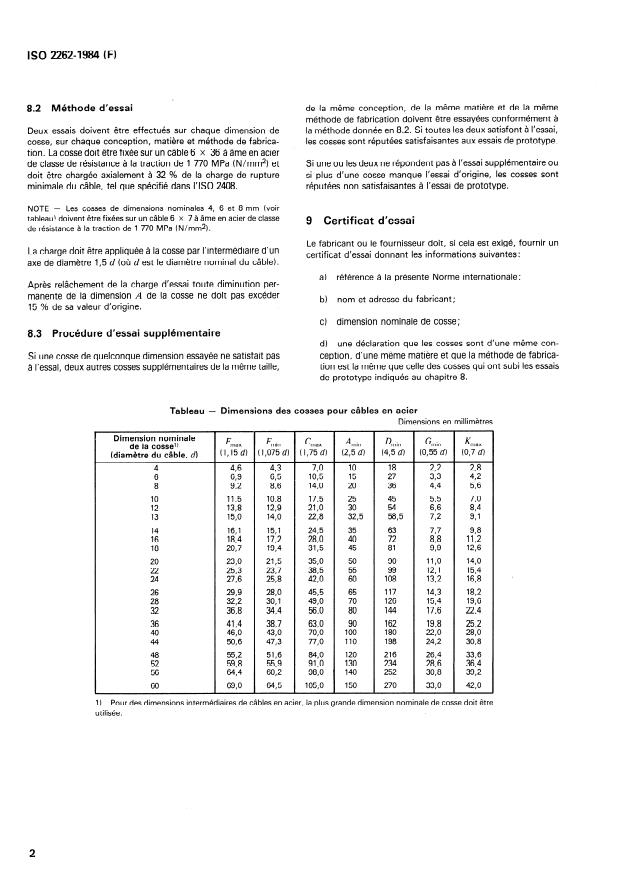
4 Dimensions
exigences de la présente Norme internationale, peut supporter
les conditions de charge maximale qui lui seront imposées vrai-
Les dimensions des cosses doivent correspondre aux valeurs
semblablement d
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...