ISO 4603:1993
(Main)Textile glass — Woven fabrics — Determination of thickness
Textile glass — Woven fabrics — Determination of thickness
The principle of the method specified is based on measuring the thickness of conditioned test specimens under a known pressure by means of a suitable apparatus. Applies to textile-glass woven fabrics of single or folded yarns, rovings, textured yarns or combinations of these yarns having a thickness of 0,1 mm or more.
Verre textile — Tissus — Détermination de l'épaisseur
La présente Norme internationale prescrit une méthode pour la détermination de l'épaisseur d'un tissu de verre textile dont l'épaisseur est supérieure ou égale à 0,1 mm.1) La méthode est applicable aux tissus réalisés avec des fils simples ou retors (silionne ou verranne), des stratifils, des fils texturés, ou une combinaison de plusieurs de ces fils. Pour les tissus réalisés avec des fibres de verranne ou des fils texturés, y compris les tissus ne comprenant ces fils qu'en chaîne ou en trame, la méthode permet de déterminer aussi leur compressibilité.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 10-Nov-1993
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 13 - Composites and reinforcement fibres
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 13/WG 1 - Reinforcements and reinforcement products
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 11-Jun-2024
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Amended By
ISO 4603:1993/Amd 1:2010 - Textile glass — Woven fabrics — Determination of thickness — Amendment 1 - Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Parent
ISO 4603:1993/Amd 1:2010 - Textile glass — Woven fabrics — Determination of thickness — Amendment 1 - Effective Date
- 18-Dec-2008
Overview
ISO 4603:1993 is an international standard issued by ISO that specifies a method for determining the thickness of textile glass woven fabrics. This standard applies to fabrics made from single or folded yarns, rovings, textured yarns, or combinations thereof, with a minimum thickness of 0.1 mm. The method involves measuring the thickness of conditioned textile glass fabric specimens under a known pressure using a precise micrometer apparatus.
The purpose of ISO 4603:1993 is to provide a consistent, reliable test procedure for thickness measurement, which is essential for quality control, material specification, and ensuring compatibility in composite manufacturing and other technical applications involving textile glass woven fabrics.
Key Topics
Scope and Applicability
The standard applies to woven textile glass fabrics including those composed of staple-fibre, continuous-filament, and textured yarns. It is suitable for single or folded yarns and rovings with thicknesses of 0.1 mm or greater.Testing Principle
Thickness is determined by measuring the perpendicular distance between the fabric surfaces while applying a standardized pressure. The fabric must be conditioned to specified standard atmospheres before measurement.Apparatus Requirements
The measurement is performed using a dead-weight micrometer with ground and lapped circular measuring surfaces, ensuring flatness and parallelism with high precision. Both electronic and dial gauge micrometers are acceptable, provided they meet the required accuracy.Measurement Procedure
Specimens are measured at multiple points across the fabric width to obtain a representative average, with specific distances from roll edges and fabric selvedges. For certain fabric types, measurements at both low and high pressures determine compressibility.Data Interpretation
Results include the arithmetic mean thickness and, where applicable, compressibility percentage, calculated from the difference in thickness under varying pressures.Quality Control and Reporting
Confidence intervals for measured thickness must be within defined limits to ensure precision. The test report must specify the standard reference, fabric details, measurement conditions, and any deviations or incidents influencing results.
Applications
ISO 4603:1993 serves critical roles in industries utilizing textile glass woven fabrics, including:
Composite Manufacturing
Precise fabric thickness measurements ensure consistent laminate properties, performance, and quality control in advanced composites used in aerospace, automotive, and construction.Material Specification and Procurement
Suppliers and manufacturers use thickness data to conform to product specifications and verify fabric uniformity, aiding in quality assurance and supply chain management.Research and Development
The standard aids researchers in characterizing textile glass materials, assessing compressibility, and optimizing fabric processing parameters.Electrical and Electronic Components
For fabrics used in electrical insulation or electronic device applications, controlled thickness measurements support performance and reliability standards.
Related Standards
ISO 4603:1993 harmonizes with several related standards, enhancing testing accuracy and material conditioning:
- ISO 139:1973 – Textiles: Standard atmospheres for conditioning and testing.
- ISO 291:1977 – Plastics: Standard atmospheres for conditioning and testing.
- ISO 2602:1980 – Statistical interpretation of test results – estimation of mean and confidence interval.
- ISO 5084:1977 – Textiles and knitted fabrics: Determination of thickness (for fabrics other than textile glass).
These referenced standards ensure environmental conditioning, statistical consistency, and complementary test methods.
Keywords: ISO 4603, textile glass fabrics, woven fabrics thickness, thickness measurement standard, textile glass testing, dead-weight micrometer, fabric compressibility, composite materials, textile quality control.
Buy Documents
ISO 4603:1993 - Textile glass -- Woven fabrics -- Determination of thickness
ISO 4603:1993 - Verre textile -- Tissus -- Détermination de l'épaisseur
ISO 4603:1993 - Verre textile -- Tissus -- Détermination de l'épaisseur
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Control Union Certifications
Global certification for agriculture and sustainability.

Bureau Veritas Bangladesh
Bureau Veritas certification services in Bangladesh.

ECOCERT France
Leader in organic and sustainability certification worldwide.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 4603:1993 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Textile glass — Woven fabrics — Determination of thickness". This standard covers: The principle of the method specified is based on measuring the thickness of conditioned test specimens under a known pressure by means of a suitable apparatus. Applies to textile-glass woven fabrics of single or folded yarns, rovings, textured yarns or combinations of these yarns having a thickness of 0,1 mm or more.
The principle of the method specified is based on measuring the thickness of conditioned test specimens under a known pressure by means of a suitable apparatus. Applies to textile-glass woven fabrics of single or folded yarns, rovings, textured yarns or combinations of these yarns having a thickness of 0,1 mm or more.
ISO 4603:1993 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 59.100.10 - Textile glass materials. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 4603:1993 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 4603:1993/Amd 1:2010, ISO 4603:1978; is excused to ISO 4603:1993/Amd 1:2010. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 4603:1993 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
ISO
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
Second edition
1993-11-15
Textile glass - Woven fabrics -
Determination of thickness
Dbtermina tion de Mpaisseur
Verre textile - Tissus -
Reference number
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work
of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Esch member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be
represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 4603 was prepared by Technical Committee
lSO/TC 61, Plastics, Sub-Committee SC 13, Composites and reinforce-
men t fibres.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition
(ISO 4603:1978), which has been technically revised.
8 ISO 1993
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or
by any means, electronie or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without per-
mission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 4603:1993(E)
Textile glass - Woven fabrics - Determination of
thickness
3 Definition
1 Scope
For the purposes of this International Standard, the
This International Standard specifies a method of de-
following definition applies.
termining the thickness of a textile-glass fabric having
a thickness of 0,l mm or more?
3.1 thickness of a textile-glass fabric: The per-
This method is applicable to woven fabrics of Single pendicular distance, in millimetres, between the sur-
or folded (plied) yarns (continuous-filament textile- faces of the fabric, measured at a specified pressure.
glass products or staple-fibre textile-glass products),
rovings, textured yarns or combinations of these
4 Principle
yarns.
Measurement of thickness of conditioned test speci-
For woven fabrics made from staple-fibre or textured
mens under a known pressure by means of a suitable
yarns, including those with such yarns in the weft or
apparatus.
this Standard also ena bles the
warp
only,
compressibility to be determined.
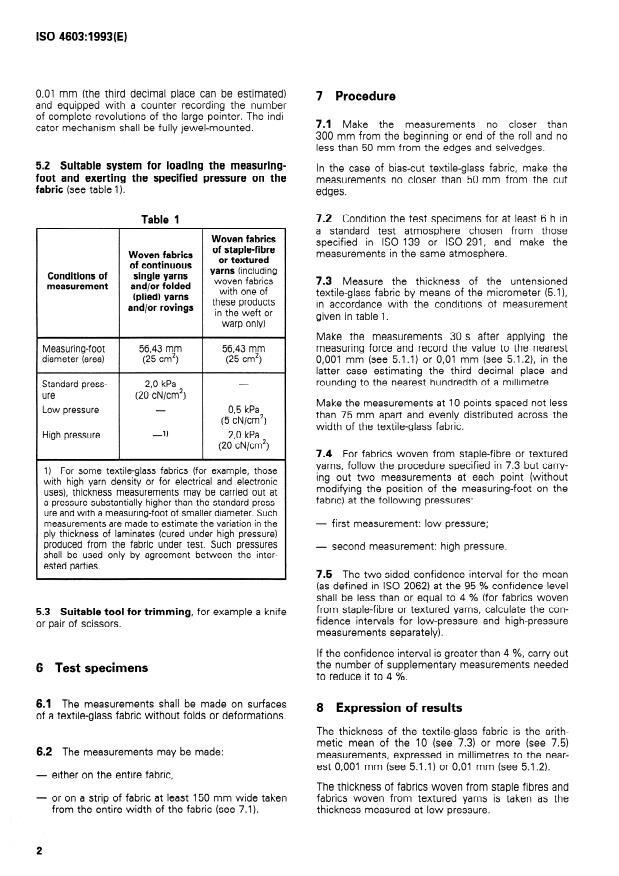
5 Apparatus
5.1 Dead-weight micrometer, with two ground and
lapped circular surfaces, flat to within 0,001 mm and
2 Normative references
parallel to within 0,003 mm. The faces shall move on
an axis perpendicular to themselves. The measuring
The following Standards contain provisions which,
spindle shall be vertical. The frame of the micrometer
through reference in this text, constitute provisions
shall be of such rigidity that a forte of 15 N applied to
of this International Standard. At the time of pub-
the housing, out of contact with the pressure-foot,
lication, the editions indicated were valid. All stan-
will produce a deflection of the frame not greater than
dards are subject to revision, and Parties to
0,Ol mm, as indicated on the micrometer read-out.
agreements based on this International Standard are
The calibration gauge used to check the instrument
encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying
shall be accurate to within + 0,001 mm.
the most recent editions of the Standards indicated
below. Members of IEC and ISO maintain registers
The types of micrometer described in 5.1 .l and 5.1.2
of currently valid International Standards.
may be used.
Standard atmospheres for
ISO 139:1973, Textiles -
5.1 .l Electronie micrometer.
conditioning and testing.
A suitable electronie micrometer with a digital read-
ISO 291:1977, Plastics - Standard atmospheres for out to 0,001 mm.
conditioning and testing.
5.1.2 Dial-gauge micrometer.
ISO 2602:1980, Statistical interpretation of test re-
The dial shall be at least 50 mm in diameter. lt shall
sults - Estimation of the mean - Confidence
in terval. be capable of being continuously read directly to
Determinatio,T of thickness of woven
1) Attention is drawn to the following International Standard: ISO 5084:1977, Textiles -
and knitted fabrics (other than textile floor coverings).
0,Ol mm (the third decimal place tan be estimated)
7 Procedure
and equipped with a counter recording the number
of complete revolutions of the large pointer. The indi-
7.1 Make the measurements no closer than
cator mechanism shall be fully jewel-mounted.
...
ISO
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1993-11-15
Verre textile - Tissus - Détermination
de l’épaisseur
Textile glass - Woven fabrics - Determination of thickness
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une féderation
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’elaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiee aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comite membre intéresse par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore etroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptes par les comites techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mites membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 4603 a ete élaboree par le comite technique
lSO/TC 61, Plastiques, sous-comité SC 13, Composites et fibres de ren-
forcemen t.
Cette deuxieme edition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 4603:1978), dont elle constitue une revision technique.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction reserves. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisee sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’editeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Verre textile - Tissus - Détermination de l’épaisseur
1 Domaine d’application 3 Définition
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale,
La présente Norme internationale prescrit une mé-
la définition suivante s’applique.
thode pour la determination de l’épaisseur d’un tissu
de verre textile dont l’épaisseur est supérieure ou
3.1 épaisseur d’un tissu de verre textile: Distance
égale à 0,l mm?
orthogonale entre les faces d’un tissu, mesurée sous
La methode est applicable aux tissus réalises avec une pression prescrite et exprimée en millimètres.
des fils simples ou retors (silionne ou verranne), des
stratifils, des fils textures, ou une combinaison de
4 Principe
plusieurs de ces fils.
Des éprouvettes sont conditionnées et leur épaisseur
Pour les tissus réalisés avec des fibres de verranne
est mesuree sous une pression connue, a l’aide d’un
ou des fils textures, y compris les tissus ne compre-
appareil approprie.
nant ces fils qu’en chaîne ou en trame, la methode
permet de déterminer aussi leur compressibilité.
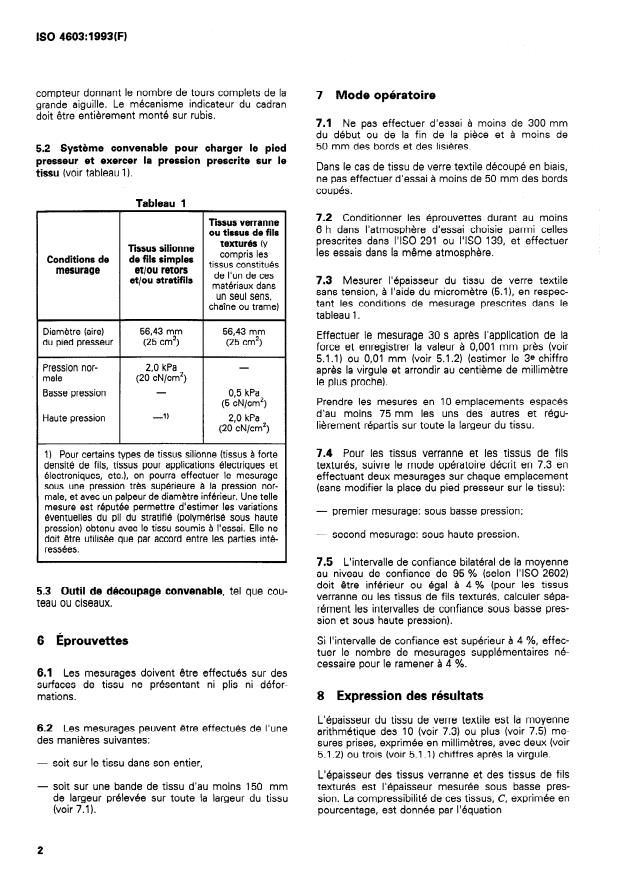
5 Appareillage
5.1 Micromètre, ayant deux surfaces circulaires po-
lies et superposées, planes a 0,001 mm près et pa-
2 Références normatives
ralleles à 0,003 mm prés. Les faces doivent se
déplacer selon un axe perpendiculaire a elles-mêmes.
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions
La tige de mesure doit être verticale. Le bâti du mi-
qui, par suite de la reference qui en est faite, consti-
crometre doit avoir une rigidité telle qu’une force de
tuent des dispositions valables pour la présente
15 N appliquée au carter, sans contact avec le pied
Norme internationale. Au moment de la publication,
presseur, produise une deformation du bâti au plus
les editions indiquées étaient en vigueur. Toute
égale à 0,Ol mm comme indique par le cadran. La
norme est sujette à revision et les parties prenantes
cale-etalon utilisée pour le contrôle de l’appareil doit
des accords fondes sur la présente Norme internatio-
être précise a + 0,001 mm.
nale sont invitees à rechercher la possibilité d’appli-
quer les éditions les plus recentes des normes
On peut utiliser les types de micrometres décrits en
indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CEI et de I’ISO
5.1.1 et 5.1.2.
possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en
vigueur a un moment donne.
5.1 .l Micromètre électronique.
ISO 139: 1973, Textiles - Atmosphères normales de
II s’agit d’un micromètre convenable, à affichage nu-
conditionnement et d’essai.
mérique, donnant les valeurs à 0,001 mm prés.
ISO 291 :1977, Plastiques - Atmosphères normales
5.1.2 Micromètre à cadran.
de conditionnement et d’essai.
Le cadran doit avoir un diametre d’au moins 50 mm.
ISO 2602:1980, Interprétation statistique de résultats II doit être gradue de façon continue afin de permettre
d’essais - Estimation de la moyenne - Intervalle de des lectures de 0,Ol mm (avec la possibilité d’estimer
confiance. le 3e chiffre après la virgule) et doit être équipé d’un
1) À noter la Norme internationale suivante traitant des textiles: ISO 5084:1977, Textiles - Détermination de l’épaisseur des
étoffes tissées et tricotées (autres que les revêtements de sol textiles).
compteur donnant le nombre de tours complets de la
7 Mode opé
...
ISO
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1993-11-15
Verre textile - Tissus - Détermination
de l’épaisseur
Textile glass - Woven fabrics - Determination of thickness
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une féderation
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’elaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiee aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comite membre intéresse par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore etroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptes par les comites techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mites membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 4603 a ete élaboree par le comite technique
lSO/TC 61, Plastiques, sous-comité SC 13, Composites et fibres de ren-
forcemen t.
Cette deuxieme edition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 4603:1978), dont elle constitue une revision technique.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction reserves. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisee sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’editeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-l 211 Geneve 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Verre textile - Tissus - Détermination de l’épaisseur
1 Domaine d’application 3 Définition
Pour les besoins de la présente Norme internationale,
La présente Norme internationale prescrit une mé-
la définition suivante s’applique.
thode pour la determination de l’épaisseur d’un tissu
de verre textile dont l’épaisseur est supérieure ou
3.1 épaisseur d’un tissu de verre textile: Distance
égale à 0,l mm?
orthogonale entre les faces d’un tissu, mesurée sous
La methode est applicable aux tissus réalises avec une pression prescrite et exprimée en millimètres.
des fils simples ou retors (silionne ou verranne), des
stratifils, des fils textures, ou une combinaison de
4 Principe
plusieurs de ces fils.
Des éprouvettes sont conditionnées et leur épaisseur
Pour les tissus réalisés avec des fibres de verranne
est mesuree sous une pression connue, a l’aide d’un
ou des fils textures, y compris les tissus ne compre-
appareil approprie.
nant ces fils qu’en chaîne ou en trame, la methode
permet de déterminer aussi leur compressibilité.
5 Appareillage
5.1 Micromètre, ayant deux surfaces circulaires po-
lies et superposées, planes a 0,001 mm près et pa-
2 Références normatives
ralleles à 0,003 mm prés. Les faces doivent se
déplacer selon un axe perpendiculaire a elles-mêmes.
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions
La tige de mesure doit être verticale. Le bâti du mi-
qui, par suite de la reference qui en est faite, consti-
crometre doit avoir une rigidité telle qu’une force de
tuent des dispositions valables pour la présente
15 N appliquée au carter, sans contact avec le pied
Norme internationale. Au moment de la publication,
presseur, produise une deformation du bâti au plus
les editions indiquées étaient en vigueur. Toute
égale à 0,Ol mm comme indique par le cadran. La
norme est sujette à revision et les parties prenantes
cale-etalon utilisée pour le contrôle de l’appareil doit
des accords fondes sur la présente Norme internatio-
être précise a + 0,001 mm.
nale sont invitees à rechercher la possibilité d’appli-
quer les éditions les plus recentes des normes
On peut utiliser les types de micrometres décrits en
indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CEI et de I’ISO
5.1.1 et 5.1.2.
possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en
vigueur a un moment donne.
5.1 .l Micromètre électronique.
ISO 139: 1973, Textiles - Atmosphères normales de
II s’agit d’un micromètre convenable, à affichage nu-
conditionnement et d’essai.
mérique, donnant les valeurs à 0,001 mm prés.
ISO 291 :1977, Plastiques - Atmosphères normales
5.1.2 Micromètre à cadran.
de conditionnement et d’essai.
Le cadran doit avoir un diametre d’au moins 50 mm.
ISO 2602:1980, Interprétation statistique de résultats II doit être gradue de façon continue afin de permettre
d’essais - Estimation de la moyenne - Intervalle de des lectures de 0,Ol mm (avec la possibilité d’estimer
confiance. le 3e chiffre après la virgule) et doit être équipé d’un
1) À noter la Norme internationale suivante traitant des textiles: ISO 5084:1977, Textiles - Détermination de l’épaisseur des
étoffes tissées et tricotées (autres que les revêtements de sol textiles).
compteur donnant le nombre de tours complets de la
7 Mode opé
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...