ISO 1874-2:1987
(Main)Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties
Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties
Plastiques — Matériaux polyamides (PA) pour moulage et extrusion — Partie 2: Préparation des éprouvettes et détermination des propriétés
General Information
- Status
- Withdrawn
- Publication Date
- 09-Dec-1987
- Withdrawal Date
- 09-Dec-1987
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 9 - Thermoplastic materials
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 61/SC 9/WG 8 - Polyamides
- Current Stage
- 9599 - Withdrawal of International Standard
- Start Date
- 07-Dec-1995
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Buy Documents
ISO 1874-2:1987 - Plastics -- Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials
ISO 1874-2:1987 - Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties Released:12/10/1987
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Smithers Quality Assessments
US management systems and product certification.

DIN CERTCO
DIN Group product certification.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 1874-2:1987 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties". This standard covers: Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties
Plastics — Polyamide (PA) moulding and extrusion materials — Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties
ISO 1874-2:1987 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 83.080.20 - Thermoplastic materials. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 1874-2:1987 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 1874-2:1995, ISO/R 1874:1971. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 1874-2:1987 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IS0
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
1874-2
First edition
1987- 12- 15
~~~
~
~
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOAHAR OPTAHMBAUMR il0 CTAHAAPTMBAUMM
Plastics - Polyamide (PA) homopolymers for
moulding and extrusion -
Part 2:
Preparation of test specimens and determination of
properties
Plastiques - Homopolymères polyamides (PA) pour moulage et extrusion -
Partie 2: Préparâtion des éprouvettes et détermination des caractéristiques
Refe :ne number
IS0 1874-2: 1987 (El
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through IS0 technical committees. Each member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the IS0 Council. They are approved in accordance with IS0 procedures requiring at
least 75 YO approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard IS0 1874-2 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 61,
Plastics.
Together with IS0 1874-1 : 1985 it cancels and replaces IS0 Recommendation
R 1874 : 1971, of which the two parts of IS0 1874 constitute a technical revision.
Users should note that all International Standards undergo revision from time to time
and that any reference made herein to any other International Standard implies its
latest edition, unless otherwise stated.
O International Organization for Standardization, 1987
Printed in Switzerland
~
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD IS0 1874-2 : 1987 (E)
Plastics - Polyamide (PA) homopolymers for
mouîding and extrusion -
Part 2:
Preparation of test specimens and determination of
properties
IS0 180, Plastics - Determination of hod impact strength of
1 Scope and field of application
rigid materials.
This part of IS0 1874 specifies methods for the preparation of
IS0 291, Plastics - Standard atmospheres for conditioning
test specimens and the determination of characteristic proper-
and testing.
ties of polyamide materials, including those properties used for
designation purposes as described in IS0 1874-1.
IS0 294, Plastics - Injection moulding test specimens of ther-
moplastic materials.
Fixed test conditions are essential to allow direct comparison of
results. Therefore, in specifications and agreements between IS0 307, Plastics - Polyamides - Determination of viscosity
interested parties, reference should be made to the methods number.
specified in this part of IS0 1874.
IS0 527, Plastics - Determination of tensile properties. 1 )
The properties of articles produced from polyamide materials
IS0 537, Plastics - Testing with the torsion pendulum.
by the nature of the moulding compound, the
are governed
design and gating of the mould and the state of the moulding
IS0 599, Plastics - Polyamide homopolymers - Determina-
resulting from processing and post-treatment conditions.
tion of matter extractable by boiling methanol.
Therefore, the results of tests carried out by the methods in this
part of IS0 1874 are valid only for the specified test specimens
IS0 899, Plastics - Determination of tensile creep.
and not for articles of other shapes or for specimens of other
IS0 960, Plastics - Polyamides - Determination of water
dimensions and/or that are produced under other conditions.
content. 1)
IS0 11 10, Plastics - Polyamides - Accelerated conditioning
2 References of test specimens. 1)
IS0 11û3, Plastics - Methods for determining the density and
IS0 75, Plastics and ebonite - Determination of temperature
relative density (specific gravity) of plastics excluding cellular
of deflection under load.
plastics.
IS0 175, Plastics - Determination of the effects of liquid
IS0 1874-1, Plastics - Polyamide (PA) homopolymers for
chemicals, including water.
moulding and extrusion - Part 7: Designation.
IS0 178, Plastics - Determination of flexuralproperties of rigid
IS0 2039-1, Plastics - Determination of hardness - Part 1:
plastics.
Ball indentation method.
IS0 179, Plastics - Determination of Charpy impact strength
IS0 2039-2, Plastics - Determination of hardness - Part 2:
of rigid materials.
Rockwell hardness.
1) At present at the stage of draft.
IS0 1874-2 : 1987 (E)
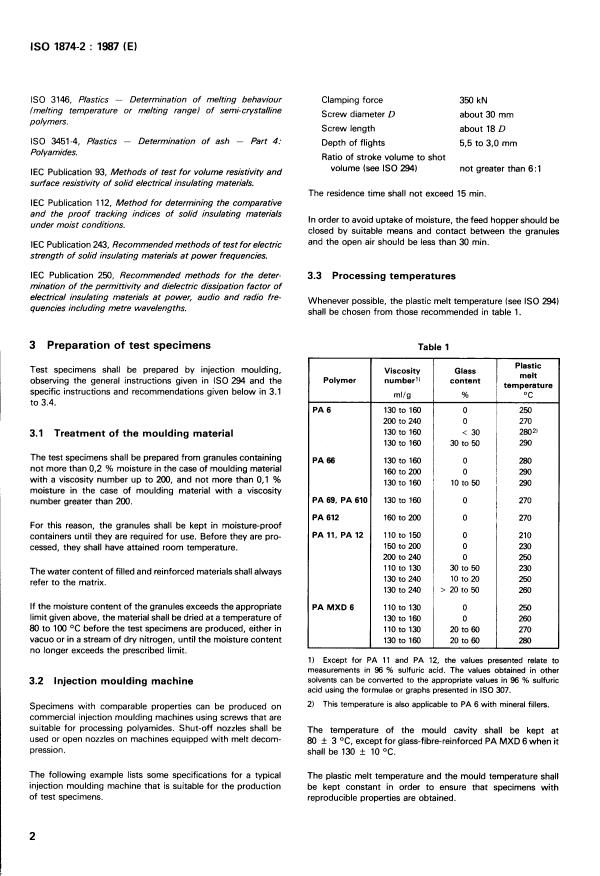
IS0 3146, Plastics - Determination of melting behaviour
Clamping force 350 kN
(melting temperature or melting range) of semi-crystalline
Screw diameter D
about 30 mm
polymers.
Screw length about 18 D
IS0 3451-4, Plastics - Determination of ash - Part 4:
Depth of flights 5,5 to 3,O mm
Polyamides.
Ratio of stroke volume to shot
volume (see IS0 294) not greater than 6:l
IEC Publication 93, Methods of test for volume resistivity and
surface resistivity of solid electrical insulating materials.
The residence time shall not exceed 15 min.
IEC Publication 112, Method for determining the comparative
and the proof tracking indices of solid insulating materials
In order to avoid uptake of moisture, the feed hopper should be
under moist conditions.
closed by suitable means and contact between the granules
and the open air should be less than 30 min.
IEC Publication 243, Recommended methods of test for electric
strength of solid insulating materials at power frequencies.
IEC Publication 250, Recommended methods for the deter-
3.3 Processing temperatures
mination of the permittivity and dielectric dissipation factor of
electrical insulating materials at power, audio and radio fre-
Whenever possible, the plastic melt temperature (see IS0 294)
quencies including metre wavelengths.
shall be chosen from those recommended in table 1.
3 Preparation of test specimens
Table 1
Plastic
Test specimens shall be prepared by injection moulding,
Viscosity Glass
melt
observing the general instructions given in IS0 294 and the Polymer number11 content
temperature
specific instructions and recommendations given below in 3.1
mllg % OC
to 3.4.
PA 6
130 to 160 O 250
200 to 240 O 270
130 to 160 < 30 2802)
Treatment of the moulding material
3.1
130 to 160 30 to 50 290
The test specimens shall be prepared from granules containing
PA 66 130 to 160 O 280
not more than 0,2 % moisture in the case of moulding material
160 to 200 O 290
with a viscosity number up to 200, and not more than 0,l %
130 to 160 10 to 50
moisture in the case of moulding material with a viscosity
PA 69, PA 610 130 to 160 O 270
number greater than 200.
PA 612 160 to 200 O 270
For this reason, the granules shall be kept in moisture-proof
PA 11, PA 12 110 to 150 O 210
containers until they are required for use. Before they are pro-
150 to 200 O
cessed, they shall have attained room temperature. 230
200 to 240 O 250
110 to 130 30 to 50
The water content of filled and reinforced materials shall always
130 to 240 10 to 20 250
refer to the matrix.
130 to 240 > 20 to 50
If the moisture content of the granules exceeds the appropriate
P
...
IS0
NORME INTERNATIONALE
1874-2
Première édition
1987-12-1 5
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOAHAR OPrAHMJAiJMR il0 CTAHAAPTM3AiJMM
Plastiques - Homopolymères polyamides (PA) pour
moulage et extrusion -
Partie 2:
Préparation des éprouvettes et détermination des
caractéristiques
Plastics - Polyamide (PA) homopolymers for moulding and extrusion -
Part 2: Preparation of test specimens and determination of properties
Numéro de référence
IS0 1874-2 i 1987 (F)
Avant-propos
L‘ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I‘ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est normalement confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I‘ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I‘ISO qui requièrent l‘approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale IS0 1874-2 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 61,
Plastiques.
Conjointement avec I‘ISO 1874-1 : 1985, elles annulent et remplacent la Recommanda-
tion ISO/R 1874 : 1971, dont les deux parties de I’ISO 1874 constituent une révision
technique.
L’attention des utilisateurs est attirée sur le fait que toutes les Normes internationales
sont de temps en temps soumises à révision et que toute référence faite à une autre
Norme internationale dans le présent document implique qu’il s’agit, sauf indication
contraire, de la dernière édition.
O Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1987 0
Imprimé en Suisse
NORM E INTER NAT1 ON A LE IS0 1874-2 : 1987 (FI
Plastiques - Homopolymères polyamides (PA) pour
moulage et extrusion -
Partie 2:
Préparation des éprouvettes et détermination des
caractéristiques
1 Objet et domaine d'application IS0 180, Plastiques - Détermination de la résistance au choc
lzod des matières rigides.
La présente partie de I'ISO 1874 spécifie des méthodes pour la
IS0 291, Plastiques - Atmosphères normales de conditionne-
préparation des éprouvettes et la détermination des propriétés
ment et d'essai.
caractéristiques des matériaux polyamides, incluant les proprié-
tés utilisées aux fins de désignation comme indiqué dans
IS0 294, Matières plastiques - Moulage par injection des
I'ISO 1874-1.
éprouvettes en matières thermoplastiques.
Des conditions d'essai fixées sont essentielles pour permettre la
IS0 307, Plastiques - Polyamides - Détermination de l'indice
comparaison directe des résultats. En conséquence, dans les
de viscosité.
spécifications et agréments entre parties intéressées, la réfé-
rence aux méthodes spécifiées dans la présente partie de
IS0 527, Plastiques - Détermination des caractéristiques en
I'ISO 1874 devrait être faite.
traction. 1 )
Les propriétés des articles produits à partir de matériaux polya-
IS0 537, Plastiques - Essai au pendule de torsion.
mides sont gouvernées par la nature de la composition de mou-
IS0 599, Plastiques - Homopolymères polyamides - Détermi-
lage, la conception et l'alimentation du moule et l'état résultant
nation des matières extractibles par le méthanol bouillant.
de la transformation et des conditions de post-traitement. En
conséquence, les résultats des essais effectués selon les
IS0 899, Plastiques - Déterminations du fluage en traction.
méthodes spécifiées dans la présente partie de I'ISO 1874 sont
seulement valables pour les éprouvettes spécifiées et pas pour
IS0 960, Plastiques - Polyamides - Détermination de la
des articles d'autres formes ou pour des éprouvettes d'autres
teneur en eau. 1)
dimensions et/ou qui sont produites dans d'autres conditions.
IS0 1 110, Plastiques - Polyamides - Conditionnement accé-
léré des éprouvettes. 1
2 Références
IS0 1183, Plastiques - Méthodes pour déterminer la masse
volumique et la densité relative des plastiques à l'exclusion des
IS0 75, Matières plastiques et ébonite - Détermination de la
plastiques alvéolaires.
température de fléchissement sous charge.
IS0 175, Plastiques - Détermination de l'action des agents IS0 1874-1, Plastiques - Homopolymères polyamides IPA)
pour moulage et extrusion - Partie I: Désignation.
chimiques liquides, y compris l'eau.
IS0 178, Matières plastiques - Détermination des caractéristi- IS0 2039-1, Plastiques - Détermination de la dureté -
ques de flexion des matières plastiques rigides.
Partie 1: Méthode de pénétration à la bille.
IS0 179, Plastiques - Détermination de la résistance au choc
IS0 203-2, Plastiques - Détermination de la dureté -
Charpy des matières rigides.
Partie 2: Dureté Rockwell.
1) Actuellement au stade de projet.
IS0 1874-2 : 1987 (FI
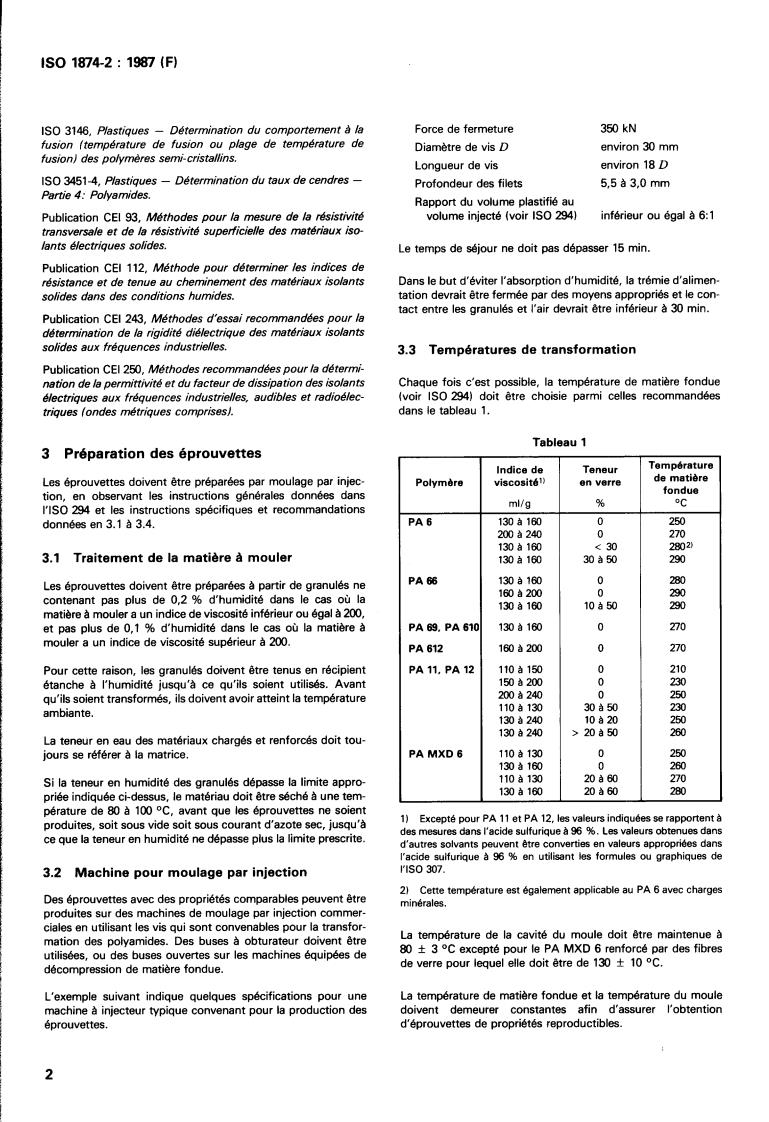
Force de fermeture 350 kN
IS0 3146, Plastiques - Détermination du comportement à la
fusion (température de fusion ou plage de température de
Diamètre de vis D environ 30 mm
fusion) des polymères semi-cristallins.
environ 18 D
Longueur de vis
IS0 3451-4, Plastiques - Détermination du taux de cendres -
5,5 à 3.0 mm
Profondeur des filets
Partie 4: Polyamides.
Rapport du volume plastifié au
à 6:l
volume injecté (voir IS0 294) inférieur ou égal
Publication CE1 93, Méthodes pour la mesure de la ksistivité
transversale et de la résistivité superficielle des matériaux iso-
lants électriques solides.
Le temps de séjour ne doit pas dépasser 15 min.
Publication CE1 112, Méthode pour déterminer les indices de
Dans le but d'éviter l'absorption d'humidité, la trémie d'alimen-
résistance et de tenue au cheminement des matériaux isolants
tation devrait être fermée par des moyens appropriés et le con-
solides dans des conditions humides.
tact entre les granulés et l'air devrait être inférieur à 30 min.
Publication CE1 243, Méthodes d'essai recommandées pour la
détermination de la rigidité diélectrique des matériaux isolants
solides aux fréquences industrielles.
3.3 Températures de transformation
Publication CE1 250, Méthodes recommandées pour la détermi-
Chaque fois c'est possible, la température de matière fondue
nation de la permittivité et du facteur de dissipation des isolants
(voir IS0 294) doit être choisie parmi celles recommandées
électriques aux fréquences industrielles, audibles et radioélec-
dans le tableau 1.
triques fondes métriques comprises).
Tableau 1
3 Préparation des éprouvettes
Température
Indice de Teneur
de matière
Les éprouvettes doivent être préparées par moulage par injec- viscosité') en verre
Polymère
fondue
tion, en observant les instructions générales données dans
ml/g % OC
I'ISO 294 et les instructions spécifiques et recommandations
PA 6 130 à 160 O 250
données en 3.1 à 3.4.
200 a 240 O 270
130a 160 < 30 2802'
3.1 Traitement de la matière à mouler 30 à 50 290
130a 160
66 130 a 160 O 280
PA
Les éprouvettes doivent être préparées à partir de granulés ne
O 290
160 a 200
contenant pas plus de 0.2 % d'humidité dans le cas où la
130 a 160 10850 290
matière à mouler a un indice de viscosité inférieur ou égal à Mo,
PA 69, PA 61 130 a 160 O 270
et pas plus de 0.1 % d'humidité dans le cas où la matière à
mouler a un indice de viscosité supérieur à Mo.
PA 612 160 a 200 O 270
PA 11, PA 12 110 a 150 O
Pour cette raison, les granulés doivent être tenus en récipient
150 a 200 O 230
à l'humidité jusqu'à ce qu'ils soient utilisés. Avant
étanche
ma240 O 250
qu'ils soient transformés, ils doivent avoir atteint la température
30a50 230
110 a 130
ambiante.
130 a 240 10 a 20 250
130 a 240 > 20a50 260
La teneur en eau des matériaux chargés et renforcés doit tou-
PA MXD 6 110 a 130 O 250
jours se référer à la matrice.
130 a 160 O 260
110 a 130 20 a 60 270
Si la teneur en humidité des granulés dépasse la limite appro-
a 160 20 a 60 280
priée indiquée ci-dessus, le matériau doit être séché à une te
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...