ISO 6392-2:1996
(Main)Earth-moving machinery — Lubrication fittings — Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles
Earth-moving machinery — Lubrication fittings — Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles
Describes the grease-gun nozzles to be used for the injection of grease into the lubrication points of earth-moving machinery in connection with the grease fittings.
Engins de terrassement — Raccords de graissage — Partie 2: Buses de pistolets à graisse
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 20-Nov-1996
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 23-Jun-2022
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 6392-2:1996 is an international standard developed by ISO Technical Committee ISO/TC 127, specifically the Subcommittee SC 3 on Operation and Maintenance of Earth-moving Machinery. This part of ISO 6392 focuses on grease-gun nozzles used for injecting grease into the lubrication points of earth-moving machinery. It complements Part 1 of ISO 6392, which specifies the corresponding grease fittings (nipples).
The standard ensures compatibility, safety, and efficiency by defining the dimensions, materials, finishes, and performance requirements for grease-gun nozzles. It covers two main nozzle types-the rubber nozzle-centre type and the steel nozzle-centre type-with a recommendation favoring the rubber nozzle-centre type due to better sealability and reduced grease leakage.
Key Topics
- Scope and Application: Specifies grease-gun nozzles used with lubrication fittings on earth-moving machinery referenced in ISO 6165.
- Nozzle Types:
- Rubber nozzle-centre type: Preferred for superior sealing and less grease leakage.
- Steel nozzle-centre type: Also specified but less recommended for earth-moving equipment.
- Mechanical Requirements:
- Must withstand a working pressure of 20 MPa and a destructive pressure of at least 80 MPa without leakage.
- Recommended use of grease-gun nozzles with relief valves, particularly in high-pressure applications such as track adjusters.
- Dimensional Specifications: Detailed dimensions for both nozzle types are illustrated with precise measurements to ensure interchangeability and ease of use.
- Material Standards:
- Rubber nozzle centre hardness between 75 to 95 IRHD.
- Steel parts must have a Rockwell hardness of at least 45 HRC.
- Zinc electroplating with chromate treatment to prevent corrosion (per ISO 2081).
- Operational Angles:
- Injection angle up to 10° maximum without grease leakage.
- Nozzle uncoupling angle up to 25° maximum for ease of removal.
- Installation Guidance: Provides recommended mounting positions for effective grease injection aligned with ISO 6165 machinery types.
Applications
ISO 6392-2:1996 is essential for manufacturers, maintenance personnel, and operators in the earth-moving and heavy equipment industries. Using standardized grease-gun nozzles ensures:
- Reliable and efficient lubrication, minimizing wear and tear.
- Compatibility with grease fittings to prevent grease leakage and equipment damage.
- Enhanced equipment longevity and performance by maintaining proper lubrication.
- Improved maintenance safety, especially in high-pressure grease injection applications.
- Simplified inventory and procurement through standardized nozzle specifications.
This standard supports effective lubrication processes for earth-moving equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and track-type tractors, aligning with maintenance best practices for durable and safe machine operation.
Related Standards
- ISO 6392-1: Earth-moving machinery - Lubrication fittings - Part 1: Nipple type – specifies the grease fittings compatible with the nozzles in Part 2.
- ISO 6165: Earth-moving machinery - Basic types - Vocabulary – defines the types of earth-moving equipment addressed by this standard.
- ISO 2081: Metallic and oxide coatings - Electroplated coatings of zinc with chromate treatment – referenced for nozzle body and cover finishes.
- ISO 48: Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic - Hardness determination – relevant for rubber nozzle centre specifications.
- ISO 674: Metallic materials - Hardness testing calibration – applies to steel component hardness testing.
Adherence to ISO 6392-2 ensures interoperability and quality in grease-gun nozzle production and usage within the earth-moving machinery sector. This standard is a key reference for lubrication system designers and maintenance engineers aiming for operational excellence in heavy equipment management.
Buy Documents
ISO 6392-2:1996 - Earth-moving machinery -- Lubrication fittings
ISO 6392-2:1996 - Engins de terrassement -- Raccords de graissage
ISO 6392-2:1996 - Engins de terrassement -- Raccords de graissage
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 6392-2:1996 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Earth-moving machinery — Lubrication fittings — Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles". This standard covers: Describes the grease-gun nozzles to be used for the injection of grease into the lubrication points of earth-moving machinery in connection with the grease fittings.
Describes the grease-gun nozzles to be used for the injection of grease into the lubrication points of earth-moving machinery in connection with the grease fittings.
ISO 6392-2:1996 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 53.100 - Earth-moving machinery. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 6392-2:1996 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 6392:1980. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 6392-2:1996 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IS0 6392-2: 1996(E)
Foreword
IS0 (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national standards bodies (IS0 member bodies). The work of
preparing International Standards is normally carried out through IS0
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which
a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented
on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-
governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. IS0
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard IS0 6392-2 was prepared by Technical Committee
ISO/TC 127, Earth-moving machinery, Subcommittee SC 3, Operation and
maintenance.
This first edition of IS0 6392-2 together with IS0 6392-l cancels and
replaces IS0 6392:1980, which has been technically revised.
IS0 6392 consists of the following parts, under the general title Earfh-
moving machinery
- Lubrication fittings:
- Par? I: Nipple type
- Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles
Annexes A and B of this part of IS0 6392 are for information only.
0 IS0 1996
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced
or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and
microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 l CH-1211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD o IS0 IS0 6392-2: 1996(E)
Earth-moving machinery - Lubrication fittings -
Part 2:
Grease-gun nozzles
1 Scope
This part of IS0 6392 specifies grease-gun nozzles to be used for the injection of grease into the lubrication points
of earth-moving machinery by means of the grease fitting specified in part 1 of this International Standard.
The grease-gun nozzles covered by this part of IS0 6392 are used on the types of earth-moving machinery defined
in IS0 6165.
2 Normative reference
The following standard contains provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this part of
IS0 6392. At the time of publication, the edition indicated was valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties
to agreements based on this part of IS0 6392 are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most
recent edition of the standard indicated below. Members of IEC and IS0 maintain registers of currently valid
International Standards.
IS0 6165:- I) , Earth-moving machinery - Basic types - Vocabulary.
3 Nozzle type and mounting position
3.1 Nozzle type
Nozzle types are divided into two types: the rubber nozzle-centre type (see figure 2) and the steel nozzle-centre type
(see figure 3).
The rubber nozzle-centre type is recommended for the grease-gun nozzles to be used on earth-moving machinery.
For the grease injection into the grease fitting, the rubber nozzle-centre type is superior in sealability and grease
leakage is less compared to the steel nozzle-centre type.
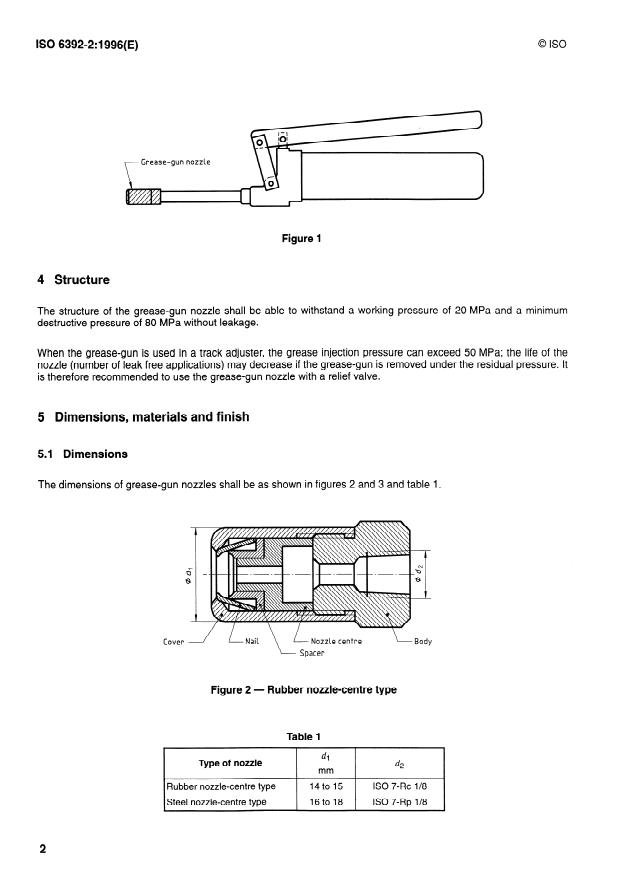
3.2 Mounting position
Figure 1 shows an example of the mounting position of the grease-gun nozzle. The specific type of grease gun is not
prescribed.
1) To be published. (Revision of IS0 6165:1987)
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
6392-2
Première édition
1996-11-15
Engins de terrassement - Raccords de
graissage -
Partie 2: .
Buses de pistolets à graisse
Earth-moving machinery - Lubrica tion fittings -
Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles
Numéro de référence
ISO 6392-2: 1996(F)
ISO 6392-2: 1996(F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. LIS0 colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des comi-
tés membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 6392-2 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 127, Engins de terrassement, sous-comité SC 3, Emploi et entre-
tien.
Conjointement à I’ISO 6392-1, cette première édition de I’ISO 6392-2
annule et remplace I’ISO 6392:1980, dont elles constituent une révision
technique.
L’ISO 6392 comprend les parties suivantes, présentées sous le titre
général Engins de terrassement - Raccords de graissage:
- Partie 1: Type à embout
.
Partie 2 . Buses de pistolets à graisse
Les annexes A et B de la présente partie de I’ISO 6392 sont données
uniquement à titre d’information.
0 ISO 1996
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé,
électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de
l’éditeur.
de normalisation
Organisation internationale
Case postale 56 l CH-l 211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE o ISO 160 6392-2: 1996(F)
Engins de terrassement - Raccords de graissage -
Partie 2:
Buses de pistolets à graisse
1 Domaine d’application
La présente partie de I’ISO 6392 fixe les exigences relatives aux buses de pistolets à graisse à utiliser pour
l’injection de graisse aux points de lubrification des engins de terrassement au moyen des raccords de graissage
prescrits dans I’ISO 6392-1.
Les buses de pistolet à graisse qui font l’objet de la présente partie de I’ISO 6392 sont utilisées sur les types
d’engins de terrassement définis dans I’ISO 6165.
2 Référence normative
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente partie de I’ISO 6392. Au moment de la publication, l’édition indiquée était en
vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente partie de
I’ISO 6392 sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition la plus récente de la norme indiquée ci-après.
Les membres de la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en vigueur à un moment
donné.
ISO 6165:- ‘), Engins de terrassement - Principaux types - Vocabulaire.
3 Types de buses et position de montage
3.1 Types de buses
Les types de buses sont au nombre de deux; l’un est le type à centre en caoutchouc (voir la figure 2) et l’autre est le
type à centre en acier (voir la figure 3).
II est recommandé d’utiliser les buses à centre en caoutchouc pour les pistolets à graisse destinés aux engins de
terrassement car, comparée à la buse à centre en acier, la buse à centre en caoutchouc est plus étanche et les
fuites de graisse sont moindres.
1) À publier. (Révision de I’ISO 6165:1987)
ISO
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
6392-2
Première édition
1996-11-15
Engins de terrassement - Raccords de
graissage -
Partie 2: .
Buses de pistolets à graisse
Earth-moving machinery - Lubrica tion fittings -
Part 2: Grease-gun nozzles
Numéro de référence
ISO 6392-2: 1996(F)
ISO 6392-2: 1996(F)
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. LIS0 colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des comi-
tés membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 6392-2 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 127, Engins de terrassement, sous-comité SC 3, Emploi et entre-
tien.
Conjointement à I’ISO 6392-1, cette première édition de I’ISO 6392-2
annule et remplace I’ISO 6392:1980, dont elles constituent une révision
technique.
L’ISO 6392 comprend les parties suivantes, présentées sous le titre
général Engins de terrassement - Raccords de graissage:
- Partie 1: Type à embout
.
Partie 2 . Buses de pistolets à graisse
Les annexes A et B de la présente partie de I’ISO 6392 sont données
uniquement à titre d’information.
0 ISO 1996
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé,
électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de
l’éditeur.
de normalisation
Organisation internationale
Case postale 56 l CH-l 211 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE o ISO 160 6392-2: 1996(F)
Engins de terrassement - Raccords de graissage -
Partie 2:
Buses de pistolets à graisse
1 Domaine d’application
La présente partie de I’ISO 6392 fixe les exigences relatives aux buses de pistolets à graisse à utiliser pour
l’injection de graisse aux points de lubrification des engins de terrassement au moyen des raccords de graissage
prescrits dans I’ISO 6392-1.
Les buses de pistolet à graisse qui font l’objet de la présente partie de I’ISO 6392 sont utilisées sur les types
d’engins de terrassement définis dans I’ISO 6165.
2 Référence normative
La norme suivante contient des dispositions qui, par suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente partie de I’ISO 6392. Au moment de la publication, l’édition indiquée était en
vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente partie de
I’ISO 6392 sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer l’édition la plus récente de la norme indiquée ci-après.
Les membres de la CEI et de I’ISO possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en vigueur à un moment
donné.
ISO 6165:- ‘), Engins de terrassement - Principaux types - Vocabulaire.
3 Types de buses et position de montage
3.1 Types de buses
Les types de buses sont au nombre de deux; l’un est le type à centre en caoutchouc (voir la figure 2) et l’autre est le
type à centre en acier (voir la figure 3).
II est recommandé d’utiliser les buses à centre en caoutchouc pour les pistolets à graisse destinés aux engins de
terrassement car, comparée à la buse à centre en acier, la buse à centre en caoutchouc est plus étanche et les
fuites de graisse sont moindres.
1) À publier. (Révision de I’ISO 6165:1987)
ISO
...











Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...