ISO 1700:1988
(Main)Cinematography — 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film — Cutting and perforating dimensions
Cinematography — 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film — Cutting and perforating dimensions
This International Standard specifies the raw stock cutting and perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film.
Cinématographie — Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge — Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions de coupe et de perforation du film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 12-Oct-1988
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 36 - Cinematography
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 03-Jun-2028
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 1700:1988 specifies the cutting and perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film. The standard defines the dimensional tolerances and inspection context for safety-base film immediately after cutting and perforation. It is intended for manufacturers, lab technicians and equipment designers concerned with consistent film feed, image stability and interchangeability in cinematographic workflows.
Key Topics
- Scope and purpose: Establishes required cutting and perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S raw stock film. Applies to safety-base film as defined in ISO 543.
- Dimensions and tolerances: The standard provides a table of nominal dimensions and permissible tolerances that apply immediately after cutting and perforating. These are the reference values for production and quality control.
- Inspection conditions: Where dimensional precision is critical, the manufacturer should specify the atmospheric conditions (temperature and humidity) used during dimensional controls at the time of cutting and perforation.
- Annex guidance (informative):
- Perforation uniformity: Uniformity of pitch, margin and hole geometry across consecutive perforations is essential for image stability. Local variations between adjacent perforations have the greatest effect.
- Dimensional stability: Film can shrink or expand with temperature, humidity, or loss of solvents/plasticizers. Such changes are often uniform along a roll but must be considered in equipment design.
- Low-shrink film: The standard includes a definition for low-shrink film (maximum 0.2% shrinkage under specified conditioning and processing cycles).
- Humidity influence: High relative humidity tends to elongate film; this should be accounted for in handling and equipment design.
Applications
ISO 1700:1988 is valuable for:
- Film manufacturers producing 8 mm Type S raw stock who need to meet international dimensional standards.
- Quality control and inspection labs verifying cutting and perforating tolerances.
- Motion-picture equipment designers (cutters, perforators, transport mechanisms) requiring consistent feed and registration.
- Archivists and restoration professionals assessing dimensional stability and shrinkage characteristics.
Benefits include improved transport reliability, reduced image registration errors, and clearer procurement/specification language between suppliers and users.
Related Standards
- ISO 543 - Cinematography - Safety film: definitions, testing and marking (referenced by ISO 1700:1988).
For implementation, users should consult the dimensional tables and the informative annex in ISO 1700:1988, and coordinate with film manufacturers to confirm inspection atmosphere and product shrinkage characteristics.
ISO 1700:1988 - Cinematography -- 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film -- Cutting and perforating dimensions
ISO 1700:1988 - Cinématographie -- Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -- Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
ISO 1700:1988 - Cinématographie -- Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -- Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 1700:1988 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Cinematography — 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film — Cutting and perforating dimensions". This standard covers: This International Standard specifies the raw stock cutting and perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film.
This International Standard specifies the raw stock cutting and perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film.
ISO 1700:1988 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 37.060.20 - Motion picture films. Cartridges. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 1700:1988 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 1700:1981. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 1700:1988 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
ISO
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
T’hird edition
1988-10-15
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXP,YHAPOAHAFl OPrAHM3A~MFl I-IO CTAHJJAPTM3AL/MM
- 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw
Cinematography
- Cutting and perforating dimensions
stock film
Cinkma tographie - Film 8 IWII perfor6, type S, vierge - Dimensions de coupe et de
perfora tion
Reference number
ISO 1700 : 1988 (E)
ISO 1700 : 1988 El
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of
national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International
Standards is normally carried out through ISO technical committees. Esch member
body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been established has
the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, govern-
mental and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all
matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are circulated to
the member bodies for approval before their acceptance as International Standards by
the ISO Council. They are approved in accordance with ISO procedures requiring at
least 75 % approval by the member bodies voting.
International Standard ISO 1700 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 36,
Cinema tograph y.
This third edition cancels and replaces the second edition (ISO 1700 : 19811, of which it
constitutes a minor revision, the annex having been replaced.
Users should note that all International Standards undergo revision from time to time
and that any reference made herein to any other International Standard implies its
latest edition, unless otherwise stated.
International Organkation for Standardkation, 1988
Printed in Switzerland
INTERNATIONAL STANDARsD ISO 1700: 1988 (E)
Cinematography - 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw
stock film - Cutting and perforating dimensions
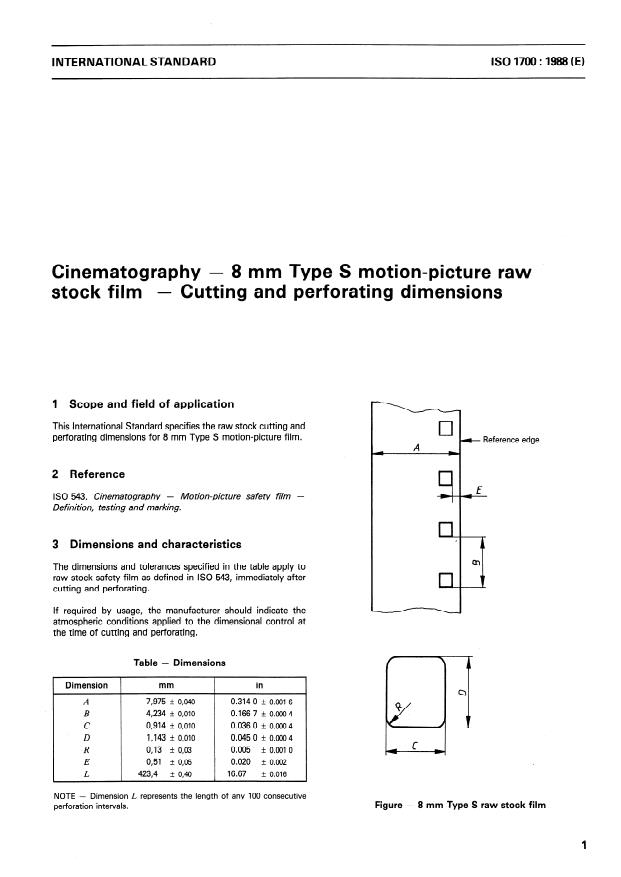
1 Scope and field of application
This International Standard specifies the raw stock cutting and
perforating dimensions for 8 mm Type S motion-picture film.
+ Reference edge
2 Reference
ISO 543, Cinematograph y - Motion-picture safety film -
Definition, tes ting and marking.
3 Dimensions and characteri
...
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Troisième édition
1988-10-15
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOfiHAR OPI-AHM3AuMR Il0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM
Cinématographie - Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -
Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
Cinematograph y - 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film - Cutting and perforating
dimensions
Numéro de référence
ISO 1700 : 1988 (F)
iso 1700 : 1988 (FI
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1700 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
Cette troisième édition annule et remplace la deuxième édition (ISO 1700 : 19811, dont
elle constitue une révision mineure, l’annexe ayant été changée.
L’attention des utilisateurs est attirée sur le fait que toutes les Normes internationales
sont de temps en temps soumises à révision et que toute référence faite à une autre
Norme internationale dans le présent document implique qu’il s’agit, sauf indication
contraire, de la dernière édition.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 l
Imprimé en Suisse
OS0 1700: 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -
Cinématographie -
Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
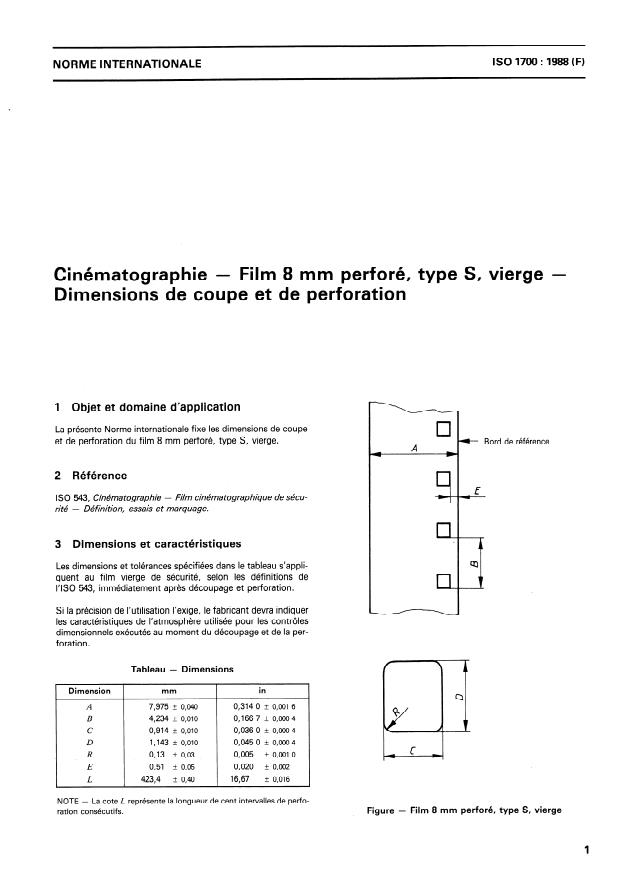
1 Objet et domaine d’application
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions de coupe
cl
et de perforation du film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge.
- Bord de référence
A
2 Référence
Film cinématographique de sécu-
I SO 543, Cinématographie -
rité - Définition, essais et marquage.
3 Dimensions et caractéristiques
Les dimensions et tolérances spécifiées dans le tableau s’appli-
quent au film vierge de sé
...
ISO
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Troisième édition
1988-10-15
INTERNATIONAL ORGANIZATION FOR STANDARDIZATION
ORGANISATION INTERNATIONALE DE NORMALISATION
MEXAYHAPOfiHAR OPI-AHM3AuMR Il0 CTAH~APTM3A~MM
Cinématographie - Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -
Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
Cinematograph y - 8 mm Type S motion-picture raw stock film - Cutting and perforating
dimensions
Numéro de référence
ISO 1700 : 1988 (F)
iso 1700 : 1988 (FI
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération mondiale
d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de I’ISO). L’élaboration
des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux comités techniques de I’ISO.
Chaque comité membre intéressé par une étude a le droit de faire partie du comité
technique créé à cet effet. Les organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non
gouvernementales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO col-
labore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en ce qui
concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques sont soumis
aux comités membres pour approbation, avant leur acceptation comme Normes inter-
nationales par le Conseil de I’ISO. Les Normes internationales sont approuvées confor-
mément aux procédures de I’ISO qui requièrent l’approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1700 a été élaborée par le comité technique ISO/TC 36,
Cinématographie.
Cette troisième édition annule et remplace la deuxième édition (ISO 1700 : 19811, dont
elle constitue une révision mineure, l’annexe ayant été changée.
L’attention des utilisateurs est attirée sur le fait que toutes les Normes internationales
sont de temps en temps soumises à révision et que toute référence faite à une autre
Norme internationale dans le présent document implique qu’il s’agit, sauf indication
contraire, de la dernière édition.
@ Organisation internationale de normalisation, 1988 l
Imprimé en Suisse
OS0 1700: 1988 (F)
NORME INTERNATIONALE
Film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge -
Cinématographie -
Dimensions de coupe et de perforation
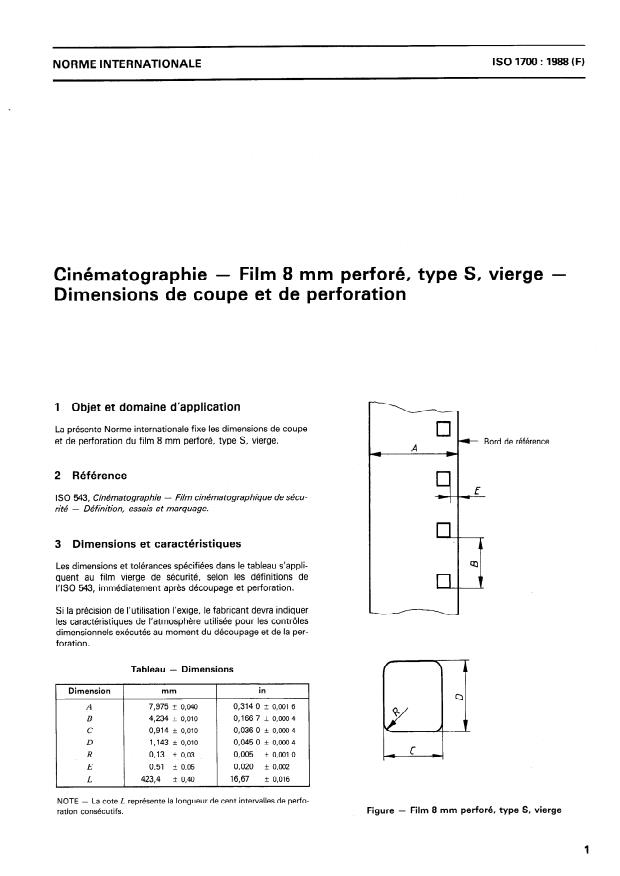
1 Objet et domaine d’application
La présente Norme internationale fixe les dimensions de coupe
cl
et de perforation du film 8 mm perforé, type S, vierge.
- Bord de référence
A
2 Référence
Film cinématographique de sécu-
I SO 543, Cinématographie -
rité - Définition, essais et marquage.
3 Dimensions et caractéristiques
Les dimensions et tolérances spécifiées dans le tableau s’appli-
quent au film vierge de sé
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...