IEC 60825-1:2007
(Main)Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
IEC 60825-1 is applicable to safety of laser products emitting laser radiation in the wavelength range 180 nm to 1 mm. A laser product may consist of a single laser with or without a separate power supply or may incorporate one or more lasers in a complex optical, electrical, or mechanical system. Typically, laser products are used for demonstration of physical and optical phenomena, materials processing, data reading and storage, transmission and display of information, etc. Such systems have found use in industry, business, entertainment, research, education, medicine and consumer products. Laser products that are sold to other manufacturers for use as components of any system for subsequent sale are not subject to IEC 60825-1, since the final product will itself be subject to this standard. However, if the laser system within the laser product is operable when removed from the equipment, the requirements of this Part 1 apply to the removable unit. Any laser product is exempt from all further requirements of this Part 1 if classification by the manufacturer of that product according to Clauses 3, 8 and 9 shows that the emission level does not exceed the AEL (accessible emission limit) of Class 1 under all conditions of operation, maintenance, service and failure. In addition to the hazards resulting from laser radiation, laser equipment may also give rise to other hazards such as fire and electric shock. This Part 1 describes the minimum requirements. Compliance with this Part 1 may not be sufficient to achieve the required level of product safety. Laser products must conform to the applicable performance and testing requirements of the applicable product safety standards. Where a laser system forms a part of equipment which is subject to another IEC product safety standard (e.g. for medical equipment (IEC 60601-2-22), IT equipment (IEC 60950), audio and video equipment (IEC 60065), equipment for use in hazardous atmospheres (IEC 60079), or electric toys (IEC 62115)), this Part 1 will apply in accordance with the provisions of IEC Guide 104 ) for hazards resulting from laser radiation. If no product safety standard is applicable, then IEC 61010-1 applies. In previous editions, LEDs were included in the scope of IEC 60825-1, and they may be still included in other parts of the IEC 60825 series. However, with the development of lamp safety standards, optical radiation safety of LEDs in general can be more appropriately addressed by lamp safety standards. The removal of LEDs from the scope of this Part 1 does not preclude other standards from including LEDs whenever they refer to lasers. CIE S009 may be applied to determine the risk group class of an LED or product incorporating one or more LEDs. The MPE (maximum permissible exposure) values of this Part 1 were developed for laser radiation and do not apply to collateral radiation. However, if a concern exists that accessible collateral radiation might be hazardous, the laser MPE values may be applied to conservatively evaluate this potential hazard. The MPE values are not applicable to intentional human exposure to laser radiation for the purpose of medical or cosmetic/aesthetic treatment. The objectives of this part of IEC 60825 are the following: - to introduce a system of classification of lasers and laser products according to their degree of optical radiation hazard in order to aid hazard evaluation and to aid the determination of user control measures; - to establish requirements for the manufacturer to supply information so that proper precautions can be adopted; - to ensure, through labels and instructions, adequate warning to individuals of hazards associated with accessible radiation from laser products; - to reduce the possibility of injury by minimizing unnecessary accessible radiation and to give improved control of the laser radiation hazards through protective features. This second edition of IEC 60825-1 cancels and replaces the first edition published in 1993,
Sécurité des appareils à laser - Partie 1: Classification des matériels et exigences
La CEI 60825-1 s'applique à la sécurité des appareils à laser émettant un rayonnement laser dans la gamme des longueurs d'ondes de 180 nm à 1 mm. Un appareil à laser peut se composer d'un seul laser avec ou sans dispositif d'alimentation séparé, ou bien il peut comporter un ou plusieurs lasers dans un système complexe optique, électrique ou mécanique. Les appareils à laser sont généralement utilisés pour la démonstration des phénomènes physiques et optiques, le travail des matériaux, la lecture et le stockage des données, la transmission et la visualisation de l'information, etc. De tels systèmes sont utilisés dans l'industrie, le commerce, le spectacle, la recherche, l'enseignement, la médecine et les produits de consommation. Les appareils à laser qui sont vendus à d'autres fabricants pour être utilisés en tant que composants d'un matériel quelconque destiné à une vente ultérieure ne sont pas soumis à la CEI 60825-1, étant donné que l'appareil final sera lui-même soumis à cette norme. Cependant, si le système à laser dans l'appareil à laser est utilisable lorsqu'il est ôté de ce matériel, les exigences de cette Partie 1 s'appliquent à ce système amovible. Tout appareil à laser est exempt de toutes les exigences supplémentaires de la présente Partie 1, si la classification par le fabricant de cet appareil conformément aux Articles 3, 8 et 9 montre que le niveau d'émission ne dépasse pas les LEA (limite d'émission accessible) de la classe 1 dans toutes les conditions de fonctionnement, de maintenance, d'entretien et de défaillance. En complément des dangers associés au rayonnement laser, les matériels laser peuvent éventuellement présenter aussi d'autres dangers tels qu'un danger d'incendie ou un choc électrique. La présente Partie 1 décrit les exigences minimales. La conformité à cette Partie 1 peut ne pas être suffisante pour obtenir le niveau requis de sécurité de l'appareil. Il faut que les appareils à laser soient conformes aux exigences de performance et d'essais applicables des normes de sécurité de produits applicables. Lorsqu'un système à laser constitue une partie d'un matériel qui est soumis à une autre norme CEI de sécurité de produit (par exemple appareils médicaux (CEI 60601-2-22), matériels de traitement de l'information (CEI 60950), matériels audio et vidéo (CEI 60065), matériels pour utilisation en atmosphères dangereuses (CEI 60079), ou jouets électriques (CEI 62115)), la présente Partie 1 sera appliquée, conformément aux dispositions du Guide CEI 104 ), pour les dangers associés au rayonnement laser. Si aucune norme de sécurité de produit n'est applicable, la CEI 61010-1 s'applique. Dans les éditions précédentes, les DEL étaient comprises dans le domaine d'application de la CEI 60825-1, et elles peuvent être encore incluses dans les autres parties de la série CEI 60825. Cependant, avec le développement des normes de sécurité pour les lampes, la sécurité des rayonnements optiques des DEL en général peut être traitée de façon plus appropriée par les normes de sécurité pour les lampes. Le retrait des DEL du domaine d'application de la présente Partie 1 n'empêche pas que les autres normes traitent des DEL, à chaque fois qu'elles se rapportent aux lasers. La CIE S009 peut être appliquée pour déterminer la classe du groupe de risque d'une DEL ou d'un appareil comportant une ou plusieurs DEL. Les valeurs des EMP (expositions maximales permises) données dans cette Partie 1 ont été établies pour le rayonnement laser et ne s'appliquent pas au rayonnement connexe. Cependant, s'il demeure une inquiétude concernant le danger d'un rayonnement connexe, les valeurs des EMP pour les lasers peuvent être appliquées pour minimiser ce danger potentiel. Les valeurs des EMP ne sont pas applicables à l'exposition intentionnelle d'une personne au rayonnement laser dans le but d'un traitement médical ou cosmétique/esthétique. La présente partie de la CEI 60825 répond aux objectifs définis ci-dessous: - introduire un système de classi
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 29-Mar-2007
- Technical Committee
- TC 76 - Optical radiation safety and laser equipment
- Drafting Committee
- WG 8 - TC 76/WG 8
- Current Stage
- DELPUB - Deleted Publication
- Start Date
- 15-May-2014
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Revised
IEC 60825-1:2014 - Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements - Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
- Effective Date
- 05-Sep-2023
Overview
IEC 60825-1:2007, titled Safety of Laser Products - Part 1: Equipment Classification and Requirements, is an international standard developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It addresses the safety requirements for laser products emitting radiation within the wavelength range of 180 nm to 1 mm. This comprehensive standard applies to standalone lasers or integrated laser systems found in industrial, medical, research, educational, entertainment, and consumer applications.
The core objective of IEC 60825-1:2007 is to establish a classification system for laser products based on their potential optical radiation hazards. This classification assists manufacturers and users in evaluating risks, implementing appropriate safety measures, and ensuring correct hazard communication through labels and operating instructions. The standard also outlines manufacturer obligations concerning product information and safety features to minimize injury risks, such as laser-related eye injuries, fire, and electric shock.
Key Topics
Equipment Classification: Lasers are categorized by hazard levels (Class 1 to Class 4) depending on their accessible emission limits (AEL). Class 1 lasers are considered inherently safe under all conditions, whereas Class 4 lasers present high risk and require stringent control measures.
Accessible Emission Levels (AEL): The standard defines thresholds for radiation exposure, facilitating the classification and testing of laser products. Measurements consider factors such as viewing conditions and angular subtense for accurate evaluation.
Measurement and Testing: IEC 60825-1 provides specific methodologies for measuring laser radiation emission and determining compliance, including considerations for visible and invisible wavelengths and pulsed laser emissions.
Labels and Warning Signs: Clear labelling requirements ensure users are adequately warned of laser radiation hazards. Labels vary by laser class and include indications for invisible radiation, access panels, and output specifications.
Safety Features: Engineering controls such as protective housings, interlocks, key controls, beam stops, and viewing optics requirements are detailed to enhance user safety.
Additional Hazards: The standard recognizes that laser products may pose other risks beyond radiation-such as electric shock and fire-and mandates protective measures accordingly.
Interpretations and Amendments: Clarifications on application to pulse lasers and viewing conditions are provided through interpretation sheets, ensuring consistent implementation of the standard.
Applications
IEC 60825-1:2007 is critically applied in various sectors to safeguard users and operators from laser hazards:
Industrial Processing: Laser cutting, welding, and marking systems benefit from defined safety classifications and protective requirements to reduce workplace incidents.
Medical Devices: Lasers used in diagnostics, surgery, and therapeutic procedures adhere to IEC 60825-1 to meet safety profiles complementing medical standards like IEC 60601-2-22.
Research and Education: Laboratories employing lasers for experiments or demonstrations use the standard to maintain safe environments and comply with regulatory expectations.
Consumer Electronics: Products such as laser printers, optical drives, and entertainment devices incorporate safety features outlined by the standard to prevent accidental exposure.
Information Technology and Communication: Devices relying on laser data reading or transmission integrate the standard's safety requirements to ensure user protection.
Toys and Hazardous Atmospheres: IEC 60825-1 works alongside other IEC standards to address specific needs for laser-enabled toys and equipment used in potentially explosive atmospheres.
Related Standards
Compliance with IEC 60825-1:2007 complements other international safety standards, ensuring holistic product safety:
- IEC 60601-2-22: Specific safety for medical laser equipment.
- IEC 60950: Safety for information technology equipment.
- IEC 60065: Safety of audio, video, and similar electronic apparatus.
- IEC 60079: Equipment for use in explosive atmospheres.
- IEC 62115: Safety of electric toys.
- IEC 61010-1: Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use, applicable where no other safety standard exists.
- CIE S009: Provides risk group classification for LEDs, relevant as LEDs are generally outside IEC 60825-1’s scope but sometimes referenced.
Practical Value
Adhering to IEC 60825-1:2007 enables manufacturers and users to:
- Assess laser hazard levels accurately and consistently.
- Incorporate effective engineering and administrative controls.
- Label laser products appropriately to communicate risks clearly.
- Implement safe design principles to minimize optical radiation and collateral hazards.
- Facilitate regulatory approval and market access worldwide.
- Protect workers, consumers, and patients from laser-related injuries.
This standard is essential for anyone involved in the design, manufacturing, testing, and use of laser products, providing a globally recognized framework for laser safety.
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

NSF International
Global independent organization facilitating standards development and certification.

CIS Institut d.o.o.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) certification body. Notified Body NB-2890 for EU Regulation 2016/425 PPE.

Kiwa BDA Testing
Building and construction product certification.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
IEC 60825-1:2007 is a standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its full title is "Safety of laser products - Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements". This standard covers: IEC 60825-1 is applicable to safety of laser products emitting laser radiation in the wavelength range 180 nm to 1 mm. A laser product may consist of a single laser with or without a separate power supply or may incorporate one or more lasers in a complex optical, electrical, or mechanical system. Typically, laser products are used for demonstration of physical and optical phenomena, materials processing, data reading and storage, transmission and display of information, etc. Such systems have found use in industry, business, entertainment, research, education, medicine and consumer products. Laser products that are sold to other manufacturers for use as components of any system for subsequent sale are not subject to IEC 60825-1, since the final product will itself be subject to this standard. However, if the laser system within the laser product is operable when removed from the equipment, the requirements of this Part 1 apply to the removable unit. Any laser product is exempt from all further requirements of this Part 1 if classification by the manufacturer of that product according to Clauses 3, 8 and 9 shows that the emission level does not exceed the AEL (accessible emission limit) of Class 1 under all conditions of operation, maintenance, service and failure. In addition to the hazards resulting from laser radiation, laser equipment may also give rise to other hazards such as fire and electric shock. This Part 1 describes the minimum requirements. Compliance with this Part 1 may not be sufficient to achieve the required level of product safety. Laser products must conform to the applicable performance and testing requirements of the applicable product safety standards. Where a laser system forms a part of equipment which is subject to another IEC product safety standard (e.g. for medical equipment (IEC 60601-2-22), IT equipment (IEC 60950), audio and video equipment (IEC 60065), equipment for use in hazardous atmospheres (IEC 60079), or electric toys (IEC 62115)), this Part 1 will apply in accordance with the provisions of IEC Guide 104 ) for hazards resulting from laser radiation. If no product safety standard is applicable, then IEC 61010-1 applies. In previous editions, LEDs were included in the scope of IEC 60825-1, and they may be still included in other parts of the IEC 60825 series. However, with the development of lamp safety standards, optical radiation safety of LEDs in general can be more appropriately addressed by lamp safety standards. The removal of LEDs from the scope of this Part 1 does not preclude other standards from including LEDs whenever they refer to lasers. CIE S009 may be applied to determine the risk group class of an LED or product incorporating one or more LEDs. The MPE (maximum permissible exposure) values of this Part 1 were developed for laser radiation and do not apply to collateral radiation. However, if a concern exists that accessible collateral radiation might be hazardous, the laser MPE values may be applied to conservatively evaluate this potential hazard. The MPE values are not applicable to intentional human exposure to laser radiation for the purpose of medical or cosmetic/aesthetic treatment. The objectives of this part of IEC 60825 are the following: - to introduce a system of classification of lasers and laser products according to their degree of optical radiation hazard in order to aid hazard evaluation and to aid the determination of user control measures; - to establish requirements for the manufacturer to supply information so that proper precautions can be adopted; - to ensure, through labels and instructions, adequate warning to individuals of hazards associated with accessible radiation from laser products; - to reduce the possibility of injury by minimizing unnecessary accessible radiation and to give improved control of the laser radiation hazards through protective features. This second edition of IEC 60825-1 cancels and replaces the first edition published in 1993,
IEC 60825-1 is applicable to safety of laser products emitting laser radiation in the wavelength range 180 nm to 1 mm. A laser product may consist of a single laser with or without a separate power supply or may incorporate one or more lasers in a complex optical, electrical, or mechanical system. Typically, laser products are used for demonstration of physical and optical phenomena, materials processing, data reading and storage, transmission and display of information, etc. Such systems have found use in industry, business, entertainment, research, education, medicine and consumer products. Laser products that are sold to other manufacturers for use as components of any system for subsequent sale are not subject to IEC 60825-1, since the final product will itself be subject to this standard. However, if the laser system within the laser product is operable when removed from the equipment, the requirements of this Part 1 apply to the removable unit. Any laser product is exempt from all further requirements of this Part 1 if classification by the manufacturer of that product according to Clauses 3, 8 and 9 shows that the emission level does not exceed the AEL (accessible emission limit) of Class 1 under all conditions of operation, maintenance, service and failure. In addition to the hazards resulting from laser radiation, laser equipment may also give rise to other hazards such as fire and electric shock. This Part 1 describes the minimum requirements. Compliance with this Part 1 may not be sufficient to achieve the required level of product safety. Laser products must conform to the applicable performance and testing requirements of the applicable product safety standards. Where a laser system forms a part of equipment which is subject to another IEC product safety standard (e.g. for medical equipment (IEC 60601-2-22), IT equipment (IEC 60950), audio and video equipment (IEC 60065), equipment for use in hazardous atmospheres (IEC 60079), or electric toys (IEC 62115)), this Part 1 will apply in accordance with the provisions of IEC Guide 104 ) for hazards resulting from laser radiation. If no product safety standard is applicable, then IEC 61010-1 applies. In previous editions, LEDs were included in the scope of IEC 60825-1, and they may be still included in other parts of the IEC 60825 series. However, with the development of lamp safety standards, optical radiation safety of LEDs in general can be more appropriately addressed by lamp safety standards. The removal of LEDs from the scope of this Part 1 does not preclude other standards from including LEDs whenever they refer to lasers. CIE S009 may be applied to determine the risk group class of an LED or product incorporating one or more LEDs. The MPE (maximum permissible exposure) values of this Part 1 were developed for laser radiation and do not apply to collateral radiation. However, if a concern exists that accessible collateral radiation might be hazardous, the laser MPE values may be applied to conservatively evaluate this potential hazard. The MPE values are not applicable to intentional human exposure to laser radiation for the purpose of medical or cosmetic/aesthetic treatment. The objectives of this part of IEC 60825 are the following: - to introduce a system of classification of lasers and laser products according to their degree of optical radiation hazard in order to aid hazard evaluation and to aid the determination of user control measures; - to establish requirements for the manufacturer to supply information so that proper precautions can be adopted; - to ensure, through labels and instructions, adequate warning to individuals of hazards associated with accessible radiation from laser products; - to reduce the possibility of injury by minimizing unnecessary accessible radiation and to give improved control of the laser radiation hazards through protective features. This second edition of IEC 60825-1 cancels and replaces the first edition published in 1993,
IEC 60825-1:2007 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 13.110 - Safety of machinery; 31.260 - Optoelectronics. Laser equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
IEC 60825-1:2007 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to IEC TR 60825-9:1999, IEC 60825-1:2007/COR1:2008, IEC 60825-1:1993, IEC 60825-1:1993/AMD2:2001/COR1:2002, IEC 60825-1:2014, IEC 60825-1:1993/AMD1:1997, IEC 60825-1:1993/AMD2:2001, IEC 60825-1:2007/ISH1:2009, IEC 60825-1:2007/ISH2:2011. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
IEC 60825-1:2007 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
IEC 60825-1
Edition 2.0 2007-03
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
GROUP SAFETY PUBLICATION
PUBLICATION GROUPÉE DE SÉCURITÉ
Safety of laser products –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
Sécurité des appareils à laser –
Partie 1: Classification des matériels et exigences
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by
any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without permission in writing from either IEC or
IEC's member National Committee in the country of the requester.
If you have any questions about IEC copyright or have an enquiry about obtaining additional rights to this publication,
please contact the address below or your local IEC member National Committee for further information.
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf indication contraire, aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie
et les microfilms, sans l'accord écrit de la CEI ou du Comité national de la CEI du pays du demandeur.
Si vous avez des questions sur le copyright de la CEI ou si vous désirez obtenir des droits supplémentaires sur cette
publication, utilisez les coordonnées ci-après ou contactez le Comité national de la CEI de votre pays de résidence.
IEC Central Office
3, rue de Varembé
CH-1211 Geneva 20
Switzerland
Email: inmail@iec.ch
Web: www.iec.ch
About the IEC
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is the leading global organization that prepares and publishes
International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies.
About IEC publications
The technical content of IEC publications is kept under constant review by the IEC. Please make sure that you have the
latest edition, a corrigenda or an amendment might have been published.
ƒ Catalogue of IEC publications: www.iec.ch/searchpub
The IEC on-line Catalogue enables you to search by a variety of criteria (reference number, text, technical committee,…).
It also gives information on projects, withdrawn and replaced publications.
ƒ IEC Just Published: www.iec.ch/online_news/justpub
Stay up to date on all new IEC publications. Just Published details twice a month all new publications released. Available
on-line and also by email.
ƒ Electropedia: www.electropedia.org
The world's leading online dictionary of electronic and electrical terms containing more than 20 000 terms and definitions
in English and French, with equivalent terms in additional languages. Also known as the International Electrotechnical
Vocabulary online.
ƒ Customer Service Centre: www.iec.ch/webstore/custserv
If you wish to give us your feedback on this publication or need further assistance, please visit the Customer Service
Centre FAQ or contact us:
Email: csc@iec.ch
Tel.: +41 22 919 02 11
Fax: +41 22 919 03 00
A propos de la CEI
La Commission Electrotechnique Internationale (CEI) est la première organisation mondiale qui élabore et publie des
normes internationales pour tout ce qui a trait à l'électricité, à l'électronique et aux technologies apparentées.
A propos des publications CEI
Le contenu technique des publications de la CEI est constamment revu. Veuillez vous assurer que vous possédez
l’édition la plus récente, un corrigendum ou amendement peut avoir été publié.
ƒ Catalogue des publications de la CEI: www.iec.ch/searchpub/cur_fut-f.htm
Le Catalogue en-ligne de la CEI vous permet d’effectuer des recherches en utilisant différents critères (numéro de référence,
texte, comité d’études,…). Il donne aussi des informations sur les projets et les publications retirées ou remplacées.
ƒ Just Published CEI: www.iec.ch/online_news/justpub
Restez informé sur les nouvelles publications de la CEI. Just Published détaille deux fois par mois les nouvelles
publications parues. Disponible en-ligne et aussi par email.
ƒ Electropedia: www.electropedia.org
Le premier dictionnaire en ligne au monde de termes électroniques et électriques. Il contient plus de 20 000 termes et
définitions en anglais et en français, ainsi que les termes équivalents dans les langues additionnelles. Egalement appelé
Vocabulaire Electrotechnique International en ligne.
ƒ Service Clients: www.iec.ch/webstore/custserv/custserv_entry-f.htm
Si vous désirez nous donner des commentaires sur cette publication ou si vous avez des questions, visitez le FAQ du
Service clients ou contactez-nous:
Email: csc@iec.ch
Tél.: +41 22 919 02 11
Fax: +41 22 919 03 00
IEC 60825-1
Edition 2.0 2007-03
INTERNATIONAL
STANDARD
NORME
INTERNATIONALE
GROUP SAFETY PUBLICATION
PUBLICATION GROUPÉE DE SÉCURITÉ
Safety of laser products –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
Sécurité des appareils à laser –
Partie 1: Classification des matériels et exigences
INTERNATIONAL
ELECTROTECHNICAL
COMMISSION
COMMISSION
ELECTROTECHNIQUE
PRICE CODE
INTERNATIONALE
XD
CODE PRIX
ICS 13.110; 31.260 ISBN 2-8318-9085-3
– 1 –
Publication IEC 60825-1 (Second edition – 2007) I-SH 01
SAFETY OF LASER PRODUCTS –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
INTERPRETATION SHEET 1
This interpretation sheet has been prepared by committee 76: Optical radiation safety and
laser equipment.
The text of this interpretation sheet is based on the following documents:
ISH Report on voting
76/415/ISH 76/418/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this interpretation sheet can be found in the
report on voting indicated in the above table.
_____________
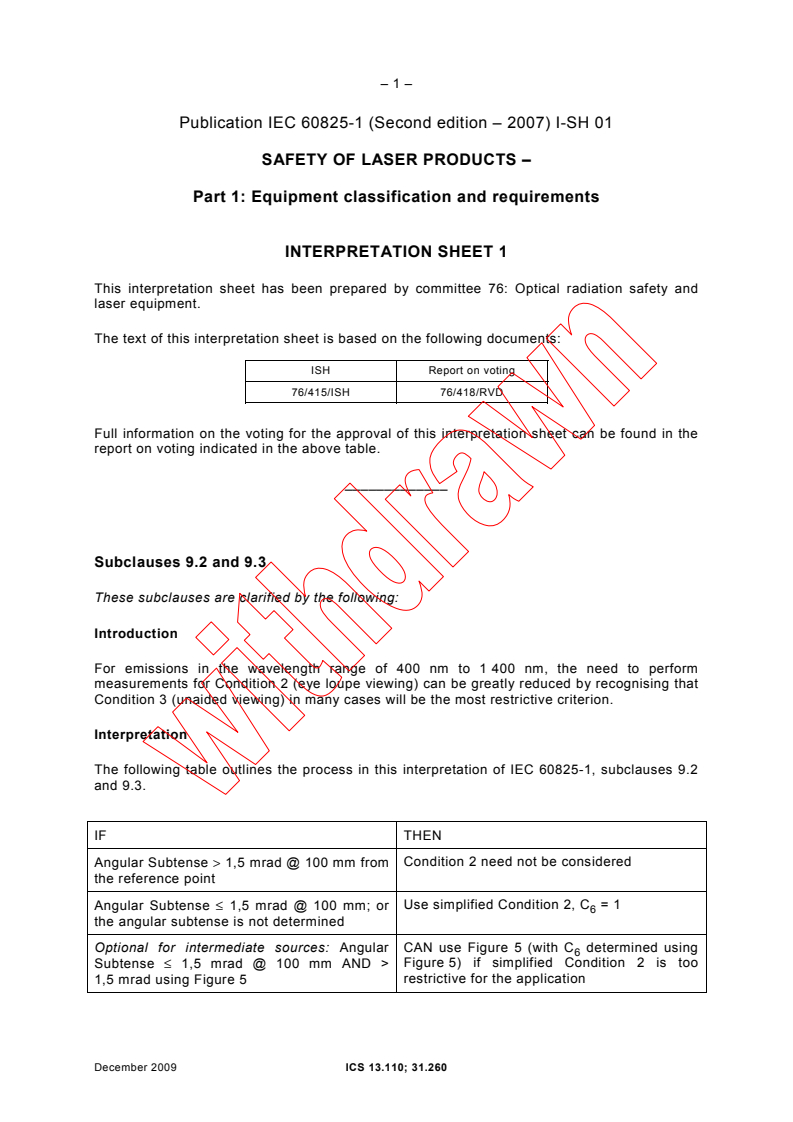
Subclauses 9.2 and 9.3
These subclauses are clarified by the following:
Introduction
For emissions in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 1 400 nm, the need to perform
measurements for Condition 2 (eye loupe viewing) can be greatly reduced by recognising that
Condition 3 (unaided viewing) in many cases will be the most restrictive criterion.
Interpretation
The following table outlines the process in this interpretation of IEC 60825-1, subclauses 9.2
and 9.3.
IF THEN
Angular Subtense > 1,5 mrad @ 100 mm from Condition 2 need not be considered
the reference point
Use simplified Condition 2, C = 1
Angular Subtense ≤ 1,5 mrad @ 100 mm; or
the angular subtense is not determined
Optional for intermediate sources: Angular CAN use Figure 5 (with C determined using
Figure 5) if simplified Condition 2 is too
Subtense ≤ 1,5 mrad @ 100 mm AND >
restrictive for the application
1,5 mrad using Figure 5
December 2009 ICS 13.110; 31.260
– 2 –
Rationale
Based on independent studies (see for instance reference [1]), it is found that for extended
sources and for radiation in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 1 400 nm, Condition 3 will in
most cases be more restrictive than Condition 2 for extended sources (Figure 5). The main
reason for this is the magnification of the source obtained with Condition 2. Also, the aperture
stop of Condition 2 is limited to 3,5 mm since it simulates a case where there is a high level of
ambient lighting, while Condition 3 uses a 7 mm aperture stop, as it simulates a general
viewing condition including accidental exposure.
Row 1 in the table above:
If it can be shown that the apparent source is extended (α > 1,5 mrad) for unaided viewing at
100 mm distance from the reference point, Condition 2 does not have to be considered.
Row 2 in the table above:
If the source is not extended for unaided viewing (i.e. the angular subtense of the apparent
source is less than 1,5 mrad at 100 mm distance from the reference point), or if the angular
subtense of the apparent source is not determined (default simplified evaluation), Condition 2
needs to be considered, as it could be more restrictive than Condition 3.
Row 3 in the table above:
For the case that the optional application of Condition 2 for extended sources (Figure 5) is
considered, the following cases can be distinguished:
a) if the angular subtense of the apparent source is determined to be less than 1,5 mrad at
100 mm from the reference point, but appears extended (α >1,5 mrad) using Condition 2
for extended sources (Figure 5) (due to the magnification of the eye loupe), Condition 2 for
extended sources may be less restrictive than the simplified Condition 2 and can be
applied for the test. If Condition 2 for extended sources (per Figure 5) is used, the
corresponding angular subtense is also to be determined using this measurement setup. It
should be noted that in this case Condition 3 (where C =1) can be more restrictive than
Condition 2 for extended sources (Figure 5) and has to be considered.
b) if the angular subtense of the apparent source is determined to be less than 1,5 mrad at
100 mm from the reference point, and is also less than 1,5 mrad using Condition 2 for
extended sources (Figure 5), the simplified Condition 2 (Table 11) is applicable.
NOTE For the default (simplified) evaluation described in 9.3.2 of the standard, it is not necessary to determine
the angular subtense of the apparent source. The apparent source can be assumed to be a small source to simplify
the analysis, since this would be the most restrictive case. The simplified measurement conditions listed in Table
11 would apply (Row 2 in the table above).
References
[1] Influence of magnifiers on ocular exposure levels, G Vees, R Gilber and K Schulmeister,
ILSC Paper 503, ILSC 2009 Proceedings (Laser Institute of America)
___________
TC 76/Publication IEC 60825-1 (2007), second edition/I-SH 02
SAFETY OF LASER PRODUCTS –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
INTERPRETATION SHEET 2
This interpretation sheet has been prepared by technical committee 76: Optical radiation
safety and laser equipment.
The text of this interpretation sheet is based on the following documents:
ISH Report on voting
76/437/ISH 76/440/RVD
Full information on the voting for the approval of this interpretation sheet can be found in the
report on voting indicated in the above table.
___________
Subclause 8.3 f 3)
This subclause is clarified by the following:
Introduction
For pulse durations shorter than 1 ns, the application of the criterion given in 8.3 f 3) a) (the
-0,25
„N criterion“) produces overly-restrictive results when compared to the TOTP criterion 8.3
f 3) b).
NOTE This Interpretation Sheet also applies to MPE analyses (subclause A.3 c)).
Interpretation
In the wavelength range of 400 nm to 1 400 nm, the TOTP criterion (8.3 f 3) b)) can be
applied for the case of pulse trains with pulses of the same energy and duration.
–0,25
NOTE 1 If the “N criterion” is applied, it would have to be adopted as follows so that it results in equivalent
evaluations as the TOTP criterion:
Pulses with durations less than T are assigned pulse durations of T . If two or more pulses occur within a duration
i i
of T , these pulse groups are assigned a pulse duration of T . The reduction factor C is applied to the AEL that is
i i 5
applicable for T (i.e. C · AEL(T )). If one pulse occurs within T , the energy of that pulse is compared with the
i 5 i i
reduced AEL, i.e. with C · AEL(T )). If more than one pulse occurs within T , the sum of the energies of these
5 i i
pulses is compared with the reduced AEL.
NOTE 2 For the heading of 8.3 f 3) b)), instead of “for varying pulse widths or varying pulse durations” the
intended wording was “for varying pulse widths or varying pulse intervals“ as corrected in Corrigendum 1”.
Rationale
–0,25
For constant pulse durations and energies, the two criteria (the N and the TOTP criterion)
should be, as a general principle, equivalent for all pulse durations, as both reflect the same
January 2011 ICS 13.110; 31.260
thermal additivity of multiple pulse exposures and constant pulse trains are a special case of
non-constant pulse trains.
–0,25
For pulse durations longer than T , the TOTP and the N criteria, as given in IEC 60825-
i
1:2077, do produce mathematically identical evaluations. For pulse trains where individual
–0,25
pulse durations are shorter than 1 ns, because the N criterion is applied in IEC 60825-1
to the AEL for the single pulse (which for pulse durations less than 1 ns is smaller than the
–0,25
AEL for T of 18 µs or 50 µs), the N criterion and the TOTP criterion produce different
i
results. Since both rules are intended to reflect thermal additivity of pulses, the TOTP is the
–0,25
criterion equivalent with
more general criterion. Criteria that would make the current N
the TOTP criterion are outlined in NOTE 1 above.
This instruction will remain valid until a new version of IEC 60825-1 is published.
January 2011 ICS 13.110; 31.260
– 2 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
CONTENTS
FOREWORD.5
1 Scope and object.7
2 Normative references .9
3 Terms and definitions .9
4 Engineering specifications.22
4.1 General remarks.22
4.2 Protective housing.22
4.3 Access panels and safety interlocks .22
4.4 Remote interlock connector .23
4.5 Manual reset .23
4.6 Key control.24
4.7 Laser radiation emission warning .24
4.8 Beam stop or attenuator .24
4.9 Controls .24
4.10 Viewing optics .24
4.11 Scanning safeguard.25
4.12 "Walk-in" access .25
4.13 Environmental conditions .25
4.14 Protection against other hazards .25
5 Labelling .26
5.1 General .26
5.2 Class 1 and Class 1M.28
5.3 Class 2 and Class 2M.29
5.4 Class 3R .30
5.5 Class 3B .30
5.6 Class 4.30
5.7 Aperture label.30
5.8 Radiation output and standards information.30
5.9 Labels for access panels .31
5.10 Warning for invisible laser radiation.32
5.11 Warning for visible laser radiation .32
6 Other informational requirements .32
6.1 Information for the user .32
6.2 Purchasing and servicing information .34
7 Additional requirements for specific laser products .34
7.1 Other parts of the standard series IEC 60825 .34
7.2 Medical laser products .35
7.3 Laser processing machines .35
7.4 Electric toys .35
7.5 Consumer electronic products .35
8 Classification.35
8.1 Introduction .35
8.2 Classification responsibilities.36
8.3 Classification rules .36
60825-1 © IEC:2007 – 3 –
9 Determination of the accessible emission level.40
9.1 Tests.40
9.2 Measurement of laser radiation .41
9.3 Measurement geometry.51
Annex A (informative) Maximum permissible exposure values.57
Annex B (informative) Examples of calculations .64
Annex C (informative) Description of the classes and potentially associated hazards.74
Annex D (informative) Biophysical considerations .80
Annex E (informative) MPEs and AELs expressed as radiance .90
Annex F (informative) Summary tables .94
Annex G (informative) Overview of associated parts of IEC 60825.97
Bibliography.99
Figure 1 – Warning label – Hazard symbol.27
Figure 2 – Explanatory label .28
Figure 3 – Measurement set-up to limit angle of acceptance by imaging the apparent
source onto the plane of the field stop .53
Figure 4 – Measurement set-up to limit angle of acceptance by placing a circular
aperture or a mask (serving as field stop) close to the apparent source .54
Figure 5 – Experimental set-up for the determination of the accessible emission
(above) and the angular subtense of the apparent source (below) for condition 2 when
an extended source is to be considered (i.e. not using the default, simplified
evaluation).55
Figure B.1 – Flowchart guide for the classification of laser products from supplied
output parameters.66
Figure B.2 – Flowchart guide for the classification of Class 1M and Class 2M laser
products .68
Figure B.3 – AEL for Class 1 ultra-violet laser products for selected emission durations
–9 3
from 10 s to 10 s .69
Figure B.4 – AEL for Class 1 ultra-violet laser products for emission durations
–9 3
from 10 s to 10 s at selected wavelengths .69
Figure B.5 – AEL for Class 1 visible and selected infra-red laser products (case C = 1) .70
Figure D.1 – Anatomy of the eye.80
Figure D.2 – Diagram of laser-induced damage in biological systems .82
Figure E.1 – Radiance as a function of wavelength .90
– 4 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
Table 1 – Requirements for safety interlocking .23
Table 2 – Additivity of effects on eye and skin of radiation of different spectral regions.37
Table 3 – Times below which pulse groups are summed .40
Table 4 – Accessible emission limits for Class 1 and Class 1M laser products
and C = 1 .44
Table 5 – Accessible emission limits for Class 1 laser products in the wavelength
range from 400 nm to 1 400 nm (retinal hazard region): extended sources .45
Table 6 – Accessible emission limits for Class 2 and Class 2M laser products .46
Table 7 – Accessible emission limits for Class 3R laser products and C = 1 .47
Table 8 – Accessible emission limits for Class 3R laser products in the wavelength
range from 400 nm to 1 400 nm (retinal hazard region): extended sources .48
Table 9 – Accessible emission limits for Class 3B laser products .49
Table 10 – Correction factors and breakpoints for use in AEL and MPE evaluations .50
Table 11 – Measurement aperture diameters and measurement distances for the
default (simplified) evaluation .52
Table 12 – Reference points .52
Table 13 – Limiting angle of acceptance γ .55
ph
Table A.1 – Maximum permissible exposure (MPE) for C = 1 at the cornea for
exposure to laser radiation.58
Table A.2 – Maximum permissible exposure (MPE) at the cornea for exposure to laser
radiation from extended sources in the wavelength range from 400 nm to 1 400 nm
(retinal hazard region) .59
Table A.3 – Maximum permissible exposure (MPE) of the skin to laser radiation.60
Table A.4 – Aperture diameters for measuring laser irradiance and radiant exposure .60
Table D.1 – Summary of pathological effects associated with excessive exposure to
light .84
Table D.2 – Explanation of measurement apertures applied to the MPEs.88
Table E.1 – Maximum radiance of a diffused source for Class 1.91
Table F.1 – Summary of the physical quantities used in this Part 1 .94
Table F.2 – Summary of manufacturer's requirements .95
Table G.1 – Overview of additional data in associated parts of IEC 60825 .98
60825-1 © IEC:2007 – 5 –
INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION
____________
SAFETY OF LASER PRODUCTS –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
FOREWORD
1) The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is a worldwide organization for standardization comprising
all national electrotechnical committees (IEC National Committees). The object of IEC is to promote
international co-operation on all questions concerning standardization in the electrical and electronic fields. To
this end and in addition to other activities, IEC publishes International Standards, Technical Specifications,
Technical Reports, Publicly Available Specifications (PAS) and Guides (hereafter referred to as “IEC
Publication(s)”). Their preparation is entrusted to technical committees; any IEC National Committee interested
in the subject dealt with may participate in this preparatory work. International, governmental and non-
governmental organizations liaising with the IEC also participate in this preparation. IEC collaborates closely
with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in accordance with conditions determined by
agreement between the two organizations.
2) The formal decisions or agreements of IEC on technical matters express, as nearly as possible, an international
consensus of opinion on the relevant subjects since each technical committee has representation from all
interested IEC National Committees.
3) IEC Publications have the form of recommendations for international use and are accepted by IEC National
Committees in that sense. While all reasonable efforts are made to ensure that the technical content of IEC
Publications is accurate, IEC cannot be held responsible for the way in which they are used or for any
misinterpretation by any end user.
4) In order to promote international uniformity, IEC National Committees undertake to apply IEC Publications
transparently to the maximum extent possible in their national and regional publications. Any divergence
between any IEC Publication and the corresponding national or regional publication shall be clearly indicated in
the latter.
5) IEC provides no marking procedure to indicate its approval and cannot be rendered responsible for any
equipment declared to be in conformity with an IEC Publication.
6) All users should ensure that they have the latest edition of this publication.
7) No liability shall attach to IEC or its directors, employees, servants or agents including individual experts and
members of its technical committees and IEC National Committees for any personal injury, property damage or
other damage of any nature whatsoever, whether direct or indirect, or for costs (including legal fees) and
expenses arising out of the publication, use of, or reliance upon, this IEC Publication or any other IEC
Publications.
8) Attention is drawn to the Normative references cited in this publication. Use of the referenced publications is
indispensable for the correct application of this publication.
9) Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this IEC Publication may be the subject of
patent rights. IEC shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
International Standard IEC 60825-1 has been prepared by IEC technical committee 76:
Optical radiation safety and laser equipment.
This second edition of IEC 60825-1 cancels and replaces the first edition published in 1993,
its Amendment 1 (1997) and its Amendment 2 (2001). It constitutes a technical revision. The
user’s guide has been removed from this part of the IEC 60825 series and is now a separate
document (Part 14). Light emitting diodes (LEDs) have been removed from the scope of this
part of IEC 60825, but may still be included in other parts.
– 6 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
This part of IEC 60825 has the status of a Group Safety Publication, in accordance with
1)
, for aspects of laser radiation pertaining to human safety.
IEC Guide 104
The text of this standard is based on the following documents:
CDV Report on voting
76/338/CDV 76/357/RVC
Full information on the voting for the approval of this standard can be found in the report on
voting indicated in the above table.
This publication has been drafted in accordance with the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
The list of all parts of the IEC 60825 series, published under the title Safety of laser products,
can be found on the IEC website.
This part of IEC 60825 is also referred to as "Part 1" in this publication.
The committee has decided that the contents of this publication will remain unchanged until
the maintenance result date indicated on the IEC web site under "http://webstore.iec.ch" in
the data related to the specific publication. At this date, the publication will be
• reconfirmed;
• withdrawn;
• replaced by a revised edition, or
• amended.
The contents of the corrigendum of August 2008 have been included in this copy.
___________
)
IEC Guide 104:1997, The preparation of safety publications and the use of basic safety publications and group
safety publications
It gives guidance to IEC technical committees and to writers of specifications concerning the manner in which
safety publications should be drafted.
This guide does not constitute a normative reference and reference to it is given for information only.
60825-1 © IEC:2007 – 7 –
SAFETY OF LASER PRODUCTS –
Part 1: Equipment classification and requirements
1 Scope and object
IEC 60825-1 is applicable to safety of laser products emitting laser radiation in the
wavelength range 180 nm to 1 mm.
A laser product may consist of a single laser with or without a separate power supply or may
incorporate one or more lasers in a complex optical, electrical, or mechanical system.
Typically, laser products are used for demonstration of physical and optical phenomena,
materials processing, data reading and storage, transmission and display of information, etc.
Such systems have found use in industry, business, entertainment, research, education,
medicine and consumer products.
Laser products that are sold to other manufacturers for use as components of any system for
subsequent sale are not subject to IEC 60825-1, since the final product will itself be subject to
this standard. However, if the laser system within the laser product is operable when removed
from the equipment, the requirements of this Part 1 apply to the removable unit.
NOTE 1 Operable equipment does not require a tool to prepare for operation.
Any laser product is exempt from all further requirements of this Part 1 if classification by the
manufacturer of that product according to Clauses 3, 8 and 9 shows that the emission level
does not exceed the AEL (accessible emission limit) of Class 1 under all conditions of
operation, maintenance, service and failure.
NOTE 2 The above exemption is to ensure that inherently safe laser products are not unnecessarily subject to the
standard.
In addition to the hazards resulting from laser radiation, laser equipment may also give rise to
other hazards such as fire and electric shock.
NOTE 3 However, the classification and other requirements of this standard are intended to address only the
laser radiation hazards to the eyes and skin. Other hazards are not included within its scope.
This Part 1 describes the minimum requirements. Compliance with this Part 1 may not be
sufficient to achieve the required level of product safety. Laser products must conform to the
applicable performance and testing requirements of the applicable product safety standards.
NOTE 4 Other standards may contain additional requirements. Consideration should also be given to the intended
application and user group. For example, a class 3B or class 4 laser product may not be suitable for use as a
consumer product.
– 8 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
Where a laser system forms a part of equipment which is subject to another IEC product
safety standard (e.g. for medical equipment (IEC 60601-2-22), IT equipment (IEC 60950),
audio and video equipment (IEC 60065), equipment for use in hazardous atmospheres
(IEC 60079), or electric toys (IEC 62115)), this Part 1 will apply in accordance with the
)
provisions of IEC Guide 104 for hazards resulting from laser radiation. If no product safety
standard is applicable, then IEC 61010-1 applies.
In previous editions, LEDs were included in the scope of IEC 60825-1, and they may be still
included in other parts of the IEC 60825 series. However, with the development of lamp safety
standards, optical radiation safety of LEDs in general can be more appropriately addressed by
lamp safety standards. The removal of LEDs from the scope of this Part 1 does not preclude
other standards from including LEDs whenever they refer to lasers. CIE S009 may be applied
to determine the risk group class of an LED or product incorporating one or more LEDs.
The MPE (maximum permissible exposure) values of this Part 1 were developed for laser
radiation and do not apply to collateral radiation. However, if a concern exists that accessible
collateral radiation might be hazardous, the laser MPE values may be applied to
conservatively evaluate this potential hazard.
The MPE values are not applicable to intentional human exposure to laser radiation for the
purpose of medical or cosmetic/aesthetic treatment.
NOTE 5 Annexes A to H have been included for purposes of general guidance and to illustrate many typical
cases. However, the annexes are not regarded as definitive or exhaustive and reference should always be made to
the appropriate clause(s) in the normative part of this document.
The objectives of this part of IEC 60825 are the following:
• to introduce a system of classification of lasers and laser products according to their
degree of optical radiation hazard in order to aid hazard evaluation and to aid the
determination of user control measures;
• to establish requirements for the manufacturer to supply information so that proper
precautions can be adopted;
• to ensure, through labels and instructions, adequate warning to individuals of hazards
associated with accessible radiation from laser products;
• to reduce the possibility of injury by minimizing unnecessary accessible radiation and to
give improved control of the laser radiation hazards through protective features.
___________
)
IEC Guide 104:1997, The preparation of safety publications and the use of basic safety publications and group
safety publications
60825-1 © IEC:2007 – 9 –
2 Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document.
For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition
of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
IEC 60050-845:1987, International Electrotechnical Vocabulary (IEV) – Chapter 845: Lighting
IEC 60601-2-22, Medical electrical equipment – Part 2: Particular requirements for the safety
of diagnostic and therapeutic laser equipment
IEC 61010-1, Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control, and
laboratory use – Part 1: General requirements
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the definitions of IEC 60050-845 as well as the following
apply.
NOTE For convenience here, the definitions have been arranged in English alphabetical order. Departures from
IEC 60050-845 are intentional and are indicated. In such cases, reference is made, between brackets, to the
definition of Part 845 of IEC 60050, with the mention “modified”.
3.1
access panel
part of the protective housing or enclosure which provides access to laser radiation when
removed or displaced
3.2
accessible emission
level of radiation determined at a position and with aperture stops (when the AEL is given in
-2
units of Watts or Joules) or limiting apertures (when the AEL is given in units of W⋅m or
-2
J⋅m ) as described in Clause 9
The accessible emission is determined where human access is considered, as specified in
Definition 3.37. The accessible emission is compared with the accessible emission limit
(Definition 3.3) in order to determine the class of the laser product. In the body of the
standard, whenever the term “emission level” is used, it is to be understood as accessible
emission.
NOTE When the beam diameter is larger than the aperture stop, the accessible emission when given in units of
Watts or Joules is less than the total emitted power or energy of the laser product. When the beam diameter is
-2 -2
smaller than the diameter of the limiting aperture, the accessible emission when given in units of W⋅m or J⋅m ,
i.e. as irradiance or radiant exposure averaged over the limiting aperture, is smaller than the actual irradiance or
radiant exposure of the beam. See also aperture stop (3.9) and limiting aperture (3.52).
3.3
accessible emission limit
AEL
the maximum accessible emission permitted within a particular class
NOTE Wherever the text refers to “emission level not exceeding the AEL” or similar wording, it is implicit that the
accessible emission is determined following the measurement criteria specified in Clause 9.
– 10 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
3.4
administrative control
safety measures of a non-engineering type such as: key supervision, safety training of
personnel, warning notices, count-down procedures, and range safety controls
3.5
alpha min
α
min
see angular subtense and minimum angular subtense (see 3.7 and 3.58)
3.6
angle of acceptance
plane angle within which a detector will respond to optical radiation, usually measured in
radians
This angle of acceptance may be controlled by apertures or optical elements in front of the
detector (see Figure 3 and 4). The angle of acceptance is also sometimes referred to as the
field of view.
Symbol: γ
3.7
angular subtense of the apparent source
α
angle subtended by an apparent source as viewed from a point in space, as shown in Figure 3
NOTE 1 The location and angular subtense of the apparent source depends on the viewing position in the beam
(see 3.11).
NOTE 2 The angular subtense of an apparent source is applicable in this Part 1 only in the wavelength range
from 400 nm to 1 400 nm, the retinal hazard region.
NOTE 3 The angular subtense of the source should not be confused with the divergence of the beam. The
angular subtense of the source can not be larger than the divergence of the beam but it is usually smaller than the
divergence of the beam.
3.8
aperture
any opening in the protective housing or other enclosure of a laser product through which
laser radiation is emitted, thereby allowing human access to such radiation
See also limiting aperture (3.52).
3.9
aperture stop
opening serving to define the area over which radiation is measured
3.10
apparent source
for a given evaluation location of the retinal hazard, the real or virtual object that forms the
smallest possible retinal image (considering the accommodation range of the human eye)
NOTE 1 The accommodation range of the eye is assumed to be variable from 100 mm to infinity. The location of
the apparent source for a given viewing position in the beam is that location to which the eye accommodates to
produce the most hazardous retinal irradiance condition.
NOTE 2 This definition is used to determine, for a given evaluation position, the location of the apparent origin of
laser radiation in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 1 400 nm. In the limit of vanishing divergence, i.e. in the case
of a well collimated beam, the location of the apparent source goes to infinity.
60825-1 © IEC:2007 – 11 –
3.11
beam
laser radiation that may be characterized by direction, divergence, diameter or scan speci-
fications
Scattered radiation from a non-specular reflection is not considered to be a beam.
3.12
beam attenuator
device which reduces the laser radiation to or below a specified level
3.13
beam diameter
beam width
the beam diameter d at a position in space is the diameter of the smallest circle which
u
contains u % of the total laser power (or energy)
For the purpose of this standard d is used.
NOTE 1 In the case of a Gaussian beam, d corresponds to the point where the irradiance (radiant exposure)
falls to 1/e of its central peak value.
NOTE 2 The second moment diameter definition (as defined in ISO 11146-1) is not used for beam profiles with
central high irradiance peaks and a low level background, such as produced by unstable resonators in the far field:
the power that passes through an aperture can be significantly underestimated when using the 2nd moment and
calculating the power with the assumption of a Gaussian beam profile.
3.14
beam divergence
far field plane angle of the cone defined by the beam diameter
If the beam diameters (see 3.13) at two points separated by a distance r are d and d ′ the
63 63
divergence is given by:
⎛ d' −d ⎞
63 63
ϕ = 2 arctan ⎜ ⎟
⎜ ⎟
2 r
⎝ ⎠
SI unit: radian
NOTE The second moment divergence definition (ISO 11146-1) is not used for beam profiles with central high
irradiance peaks and a low level background, such as produced by unstable resonators in the far field or beam
profiles that show diffraction patterns caused by apertures.
3.15
beam expander
combination of optical elements which will increase the diameter of a laser beam
3.16
beam path component
optical component which lies on a defined beam path (e.g. a beam steering mirror or a
focusing lens)
3.17
beam stop
device which terminates a laser beam path
3.18
Class 1 laser product
any laser product which during operation does not permit human access to accessible laser
radiation in excess of the accessible emission limits of Class 1 for applicable wavelengths and
emission durations (see 8.2 and 8.3 e))
– 12 – 60825-1 © IEC:2007
NOTE 1 See also the limitations of the classification scheme in Annex C.
NOTE 2 As tests for the determination of the classification of the product are limited to tests during operation, it
may be the case for embedded laser products that, depending on the product, radiation above the AEL of Class 1
can become accessible during maintenance when interlocks of access panels are overridden.
3.19
Class 1M laser product
any laser product in
...



Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...