ASTM F3272-17
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selection, Care, and Use of Arc Protective Blankets
Standard Guide for Selection, Care, and Use of Arc Protective Blankets
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This guide provides positioning, installation, and anchoring techniques that may be used to arrange arc protective blankets to confine or divert the energies found from a fault that may include plasma arcing, pressure wave, and projectiles.
5.2 Arc protective blankets may be used in any electrical application to confine or divert energy away from a work zone for electrical or other workers who may be exposed to an electric arc in the event of an equipment or conductor failure.
5.3 Cables, splices, and any equipment components which have historical failures deemed to require additional protection or engineering controls which could benefit from added protection provided by an arc protective blanket.
5.4 This guide is designed for electrical engineers and qualified installers of arc protective blankets.
5.5 The practice is limited by the blanket protective value, the sturdiness of the installation, and the engineering assumptions of the hazard assessment.
5.6 These blankets do not typically provide dielectric protection.
5.7 They do not eliminate the need for arc-rated PPE but may reduce the level of the hazard in some installations.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides information for the selection, care, and use of arc protective blankets for personnel protection.
1.2 This guide covers positioning, and securing, arc protective blankets (tested to Test Method F2676) and channeling the thermal, ballistic, and concussive forces generated by an arc flash event using arc protective blankets.
1.3 This guide defines the use of the arc protective blanket to maximize its protective effectiveness to workers exposed to energized electrical equipment where complete de-energizing of the work zone cannot be achieved or for low-risk exposures with sufficient arc flash incident energy to warrant secondary protective means in the event of an arc flash.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. See IEEE/ASTM SI-10.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F3272 − 17
Standard Guide for
1
Selection, Care, and Use of Arc Protective Blankets
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F3272; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F2676 Test Method for Determining the Protective Perfor-
mance of an Arc Protective Blanket for Electric Arc
1.1 This guide provides information for the selection, care,
Hazards
and use of arc protective blankets for personnel protection.
2
2.2 IEEE/ASTM Standard:
1.2 This guide covers positioning, and securing, arc protec-
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 American National Standard for Metric
tive blankets (tested toTest Method F2676) and channeling the
Practice
thermal, ballistic, and concussive forces generated by an arc
3
2.3 NFPA Standard:
flash event using arc protective blankets.
NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
1.3 This guide defines the use of the arc protective blanket
4
2.4 CSA Standard:
to maximize its protective effectiveness to workers exposed to
CSA Z462 Workplace electrical safety
energized electrical equipment where complete de-energizing
5
2.5 OSHA Standards:
of the work zone cannot be achieved or for low-risk exposures
29 CFR 1910.269 Occupational Safety and Health Stan-
with sufficient arc flash incident energy to warrant secondary
dards: Special Industries
protective means in the event of an arc flash.
29 CFR 1926.950-969 Safety and Health Regulations for
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Construction
standard. See IEEE/ASTM SI-10.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3. Terminology
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Definitions:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 For definitions relating to the burning behavior of
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
textiles, see Terminology D4391 and for definitions relating to
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
electrical protective equipment for workers, see Terminology
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
F819.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.2 abnormal condition, n—abnormalities such as but not
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
limited to, oil or compound leaking from cable or joints,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
broken cable sheaths or joint sleeves, hot localized surface
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
temperatures of cables or joints, or joints that are swollen
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
beyond normal tolerance are presumed to lead to or be an
indication of an impending fault. Note: this term does not
2. Referenced Documents
appear in the standard.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.3 anchoring, v—method of physical attachment for se-
D4391 Terminology Relating to The Burning Behavior of
curing the blanket and all attached components (straps,
Textiles
stanchions,otherhardware,etc.)inplaceforthedurationofthe
F819 Terminology Relating to Electrical Protective Equip-
protection level for which the blanket is rated.
ment for Workers
3.1.4 blistered insulation, n—a condition in which electrical
insulation exhibits visible signs of thermal deformation usually
exhibited as a bubble on the insulation.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F18 on Electrical
Protective Equipment for Workers and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F18.65 on Wearing Apparel.
3
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2017. Published December 2017. DOI: Available from National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), 1 Batterymarch
10.1520/F3272-17. Park, Quincy, MA 02169-7471, http://www.nfpa.org.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from Canadian Standards Association (CSA), 178 Rexdale Blvd.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Toronto, ON M9W 1R3, Canada, http://www.csagroup.org.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), 200
the ASTM website. Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20210, http://www.osha.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F3272 − 17
3.1.5 conduit channel type construction, n—this is a com- 5.5 The practice is limited by the blanket protective value,
mon choice by many utilities because it is alr
...







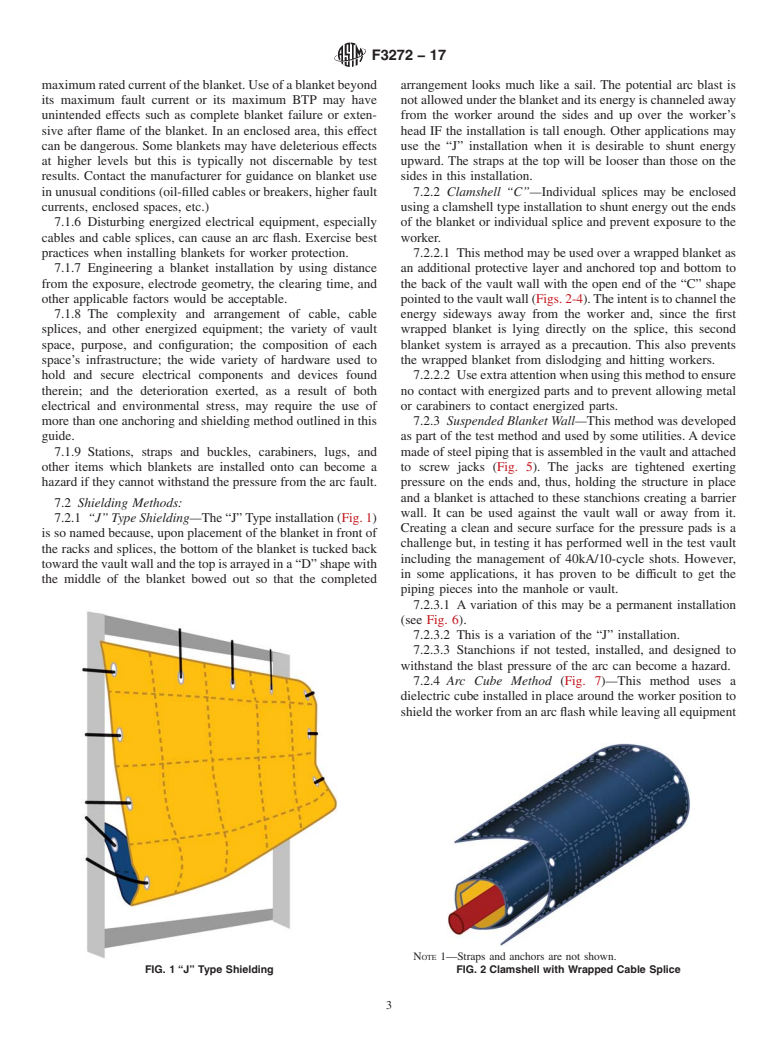
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.