ASTM F1473-97e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Notch Tensile Test to Measure the Resistance to Slow Crack Growth of Polyethylene Pipes and Resins
Standard Test Method for Notch Tensile Test to Measure the Resistance to Slow Crack Growth of Polyethylene Pipes and Resins
SCOPE
1.1 This test method determines the resistance of polyethylene materials to slow crack growth under conditions specified within.
1.2 The test is generally performed at 80oC and at 2.4 MPa, but may also be done at temperatures below 80oC and with other stresses low enough to preclude ductile failure and thereby eventually induce brittle type of failure. Generally, polyethylenes will ultimately fail in a brittle manner by slow crack growth at 80oC if the stress is below 2.4 MPa.
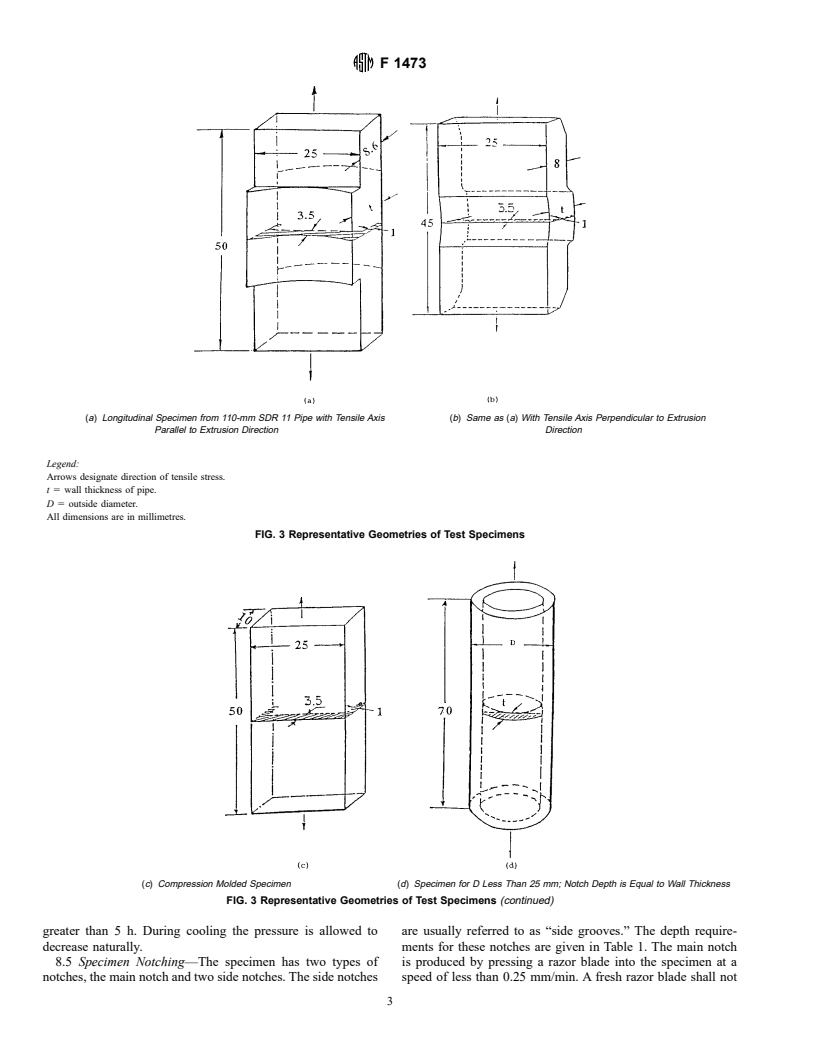
1.3 The test method is for specimens cut from compression molded plaques. See Appendix X1 for information relating to specimens from pipe.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: F 1473 – 97 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Notch Tensile Test to Measure the Resistance to Slow Crack
1
Growth of Polyethylene Pipes and Resins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1473; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Section 8.4 was corrected editorially in November 1998.
1. Scope 3.1.1 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F 412.
Abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D 1600,
1.1 This test method determines the resistance of polyeth-
unless otherwise indicated.
ylene materials to slow crack growth under conditions speci-
3.1.2 brittle failure—a pipe failure mode which exhibits no
fied within.
visible (to the naked eye) permanent material deformation
1.2 The test is generally performed at 80°C and at 2.4 MPa,
(stretching, elongation, or necking down) in the area of the
but may also be done at temperatures below 80°C and with
break (F 412).
other stresses low enough to preclude ductile failure and
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
thereby eventually induce brittle type of failure. Generally,
3.2.1 slow crack growth—the slow extension of the crack
polyethylenes will ultimately fail in a brittle manner by slow
with time.
crack growth at 80°C if the stress is below 2.4 MPa.
1.3 The test is for compression molded plaques and for pipe
4. Summary of Test Method
2
sizes 16 mm and greater.
4.1 A specimen is taken from a pipe with a specified
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
orientation relative to the extrusion direction or from compres-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sion molded plaques. It is precisely notched and then exposed
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
to a constant tensile stress at elevated temperatures in air. The
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
time for complete failure is recorded.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 This test method is useful to measure slow crack growth
2.1 ASTM Standards:
resistance of molded plaques of resins and extruded pipe at
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical
3 accelerated conditions such as 80°C, 2.4-MPa stress, and with
Insulating Materials for Testing
a sharp notch.
D 1248 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Molding and
3 5.2 The time to failure depends on the following test
Extrusion Materials
parameters: temperature; stress; notch depth; and specimen
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
3
geometry. Increasing temperature, stress, and notch depth
Plastics
decrease the time to failure. Thus, in reporting the time to
D 1928 Practice for Preparation of Compression-Molded
3
failure, all the conditions of the test must be specified.
Polyethylene Test Sheets and Test Specimens
D 3350 Specification for Polyethylene Plastics Pipe and
6. Apparatus
3
Fitting Materials
4 6.1 Lever Loading Machine, with a lever arm ratio of about
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
5:1. The tensile load may also be applied directly using dead
3. Terminology weights or any other method for producing a constant load. The
pull rods on the grips shall have universal action to preventing
3.1 Definitions:
bending. The grips shall be serrated to prevent slippage. The
load on the specimen shall be accurate to at least 60.5 %.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic
6.2 Furnace, heated by ordinary incandescent light bulbs
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test
covered with aluminum foil or any other suitable heating
Methods.
Current edition approved April 10, 1997. Published November 1997. Originally
element.
published as F 1473-94.
6.3 Temperature Controller, shall be able to control the
2
Lu, X., and Brown, N., “A Test for Slow Crack Growth Failure in Polyethylene
temperature within 60.5°C with respect to the set point.
Under a Constant Load,” Journal of Polymer Testing, Vol 11, pp. 309–319, 1992.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. 6.4 Temperature-Measuring Device, a thermometer or a
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F 1473
thermocouple which can measure the temperature with an
accuracy better than 0.5°C.
6.5 Timer, shall have an accuracy of at leas
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.