ASTM B804-02(2007)
(Specification)Standard Specification for UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 Welded Pipe
Standard Specification for UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 Welded Pipe
ABSTRACT
This guide covers UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 welded pipe for general corrosion applications. The joints of the specimens shall be double or single welded and full penetration welded made. The welds shall be made either manually or automatically by an electric process involving the deposition of filler metal according to the class specified. The weld surface on either side of the weld shall be flush with the base plate. The contour of the reinforcement shall be reasonably smooth and free of irregularities. The deposited metal shall be fused uniformly into the plate surface. Transverse tension tests shall be made across the welded joint to assure that it must have the same minimum ultimate tensile strength as the specified minimum ultimate tensile strength of the plate. Transverse guided weld bend test shall be used to check cracks or other imperfections. The pipe shall be furnished with smooth ends, free of burrs and injurious defects and shall have a workmanlike finish.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 welded pipe for general corrosion applications. (Although no restrictions are placed on the sizes of pipe that may be furnished under this specification, commercial practice is commonly limited to sizes not less than 8 in. nominal diameter.)
1.2 Six classes of pipe are covered as follows:
1.2.1 Class 1 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes and shall be completely radiographed.
1.2.2 Class 2 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes. No radiography is required.
1.2.3 Class 3 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld may be made without the addition of filler metal. Welds are to be completely radiographed.
1.2.4 Class 4 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld may be made without the addition of filler metal. No radiography is required.
1.2.5 Class 5 pipe shall be single welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass exposed to the inside pipe surface may be made without the addition of filler metal. Welds are to be completely radiographed.
1.2.6 Class 6 pipe shall be single welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass exposed to the inside pipe surface may be made without the addition of filler metal. No radiography is required.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this standard: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:B804 −02(Reapproved 2007)
Standard Specification for
UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 Welded Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B804; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope dard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if
any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
1.1 This specification covers UNS N08367 and UNS
of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including
N08926 welded pipe for general corrosion applications. (Al-
those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet
though no restrictions are placed on the sizes of pipe that may
(MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the
be furnished under this specification, commercial practice is
manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health
commonly limited to sizes not less than 8 in. nominal diam-
practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limi-
eter.)
tations prior to use.
1.2 Six classes of pipe are covered as follows:
1.2.1 Class 1 pipe shall be double welded by processes
2. Referenced Documents
employing filler metal in all passes and shall be completely
2.1 ASTM Standards:
radiographed.
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
1.2.2 Class 2 pipe shall be double welded by processes
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
employing filler metal in all passes. No radiography is re-
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
quired.
of Steel Products
1.2.3 Class 3 pipe shall be double welded by processes
B625 Specification for UNS N08925, UNS N08031, UNS
employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld
N08932, UNS N08926, UNS N08354, and UNS R20033
may be made without the addition of filler metal. Welds are to
Plate, Sheet, and Strip
be completely radiographed.
B688 Specification for Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum-
1.2.4 Class 4 pipe shall be double welded by processes
Iron (UNS N08366 and UNS N08367) Plate, Sheet, and
employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld
Strip
may be made without the addition of filler metal. No radiog-
B880 Specification for General Requirements for Chemical
raphy is required.
Check Analysis Limits for Nickel, Nickel Alloys and
1.2.5 Class 5 pipe shall be single welded by processes
Cobalt Alloys
employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass
B899 Terminology Relating to Non-ferrous Metals and Al-
exposed to the inside pipe surface may be made without the
loys
addition of filler metal. Welds are to be completely radio-
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
graphed.
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
1.2.6 Class 6 pipe shall be single welded by processes
Determine Conformance with Specifications
employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass
E38 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Chromium
exposed to the inside pipe surface may be made without the
and Nickel-Chromium-Iron Alloys (Withdrawn 1989)
addition of filler metal. No radiography is required.
E354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Temperature,Electrical,Magnetic,andOtherSimilarIron,
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys
information only.
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
test methods portion, Section 13, of this standard: This stan- Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
1 2
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007. Published November 2007. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as B804 – 02. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/B0804-02R07. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
B804−02 (2007)
E1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel, resulting thickness of weld metal is equal to or greater than the
Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys minimum thickness of the adjacent base metal.
5.2.4 Weld defects shall be repaired by removal to sound
2.2 ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code:
metal and rewelding. Subsequent heat treatment and inspection
Section VIII, Division 1 Rules for Construction of Pressure
shall be as required on the original welds.
Vessels
Section IX Qualification Standard for Welding and Brazing
5.3 HeatTreatment—Therecommendedheattreatmentshall
Procedures, Welders, Brazers, and Welding and Brazing
consist of heating to a minimum temperature of 2025°F for
Operators
UNS N08367 and 2012°F for UNS N08926 followed by
2.3 American Welding Society Standards:
quenching in water or rapidly cooling by other means.
AWSA5.11 Nickel and NickelAlloy Covered Welded Elec-
trodes
6. Chemical Composition
AWS A5.14 Nickel and Nickel Alloy Bare Welding Rods
6.1 The chemical composition of the pipe shall conform to
and Electrodes
the requirements in Table 1 of Specification B688 for UNS
N08367 and Table 1 of Specification B625 for UNS N08926.
3. Terminology
6.2 The alloy content of the deposited weld metal shall
3.1 Terms defined in Terminology B899 shall apply unless
conform to that required for the plate or the welding electrodes
otherwise defined in this standard.
as shown in Specification AWS A5.11 for ENiCrMo-3,
ENiCrMo-4, and ENiCrMo-10 orAWSA5.14 for ERNiCrMo-
4. Ordering Information
10, ERNiCrMo-3, and ERNiCrMo-4.
4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
6.3 If product analysis is made of the plate or weld metal by
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
the purchaser, the chemical composition thus determined shall
specification. Examples of such requirements include, but are
conform to the requirements specified in 6.1 and 6.2 subject to
not limited to, the following:
the permissible tolerances in Specification B880.
4.1.1 Quantity (feet or number of lengths),
4.1.2 Class (see 1.2),
7. Mechanical Properties and Other Requirements
4.1.3 Size (outside diameter and minimum wall thickness),
7.1 Mechanical Properties:
4.1.4 Length (specific or random),
7.1.1 The mechanical properties of the plate shall be in
4.1.5 ASTM specification number,
accordance with Table 1. Tension tests made by the plate
4.1.6 Authorization for repair of plate defects by welding
manufacturer shall qualify the plate material.
without prior approval if such is intended (see 9.4),
7.1.2 Transverse tension tests taken across the welded joint
4.1.7 Circumferential weld permissibility (see 8.3.2), and
shall have the same minimum ultimate tensile strength as the
4.1.8 Supplementary requirements.
specified minimum ultimate tensile strength of the plate.
5. Materials and Manufacture
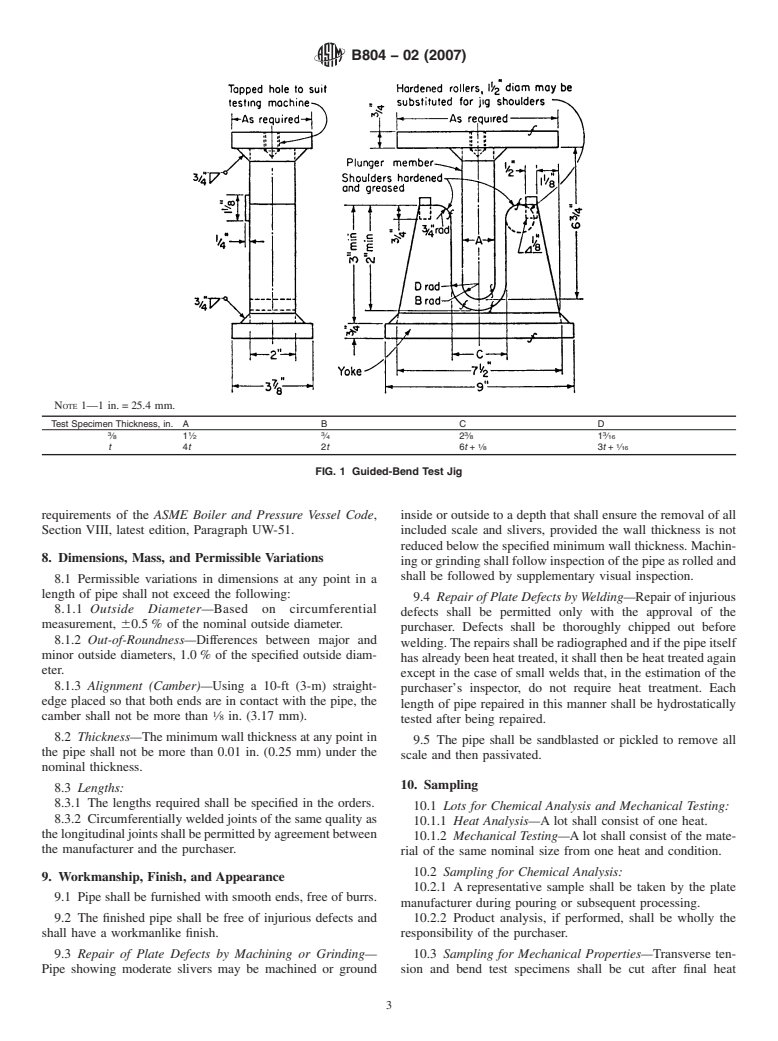
7.2 Transverse Guided Weld Bend Test Requirements—
5.1 Materials—The starting material shall conform to the Bends made in accordance with Fig. 1 shall be acceptable if no
requirements of Specification B688 for UNS N08367 and
cracks or other imperfections exceeding ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm) in any
Specification B625 for UNS N08926. directionarepresentintheweldmetalorbetweentheweldand
the pipe metal after bending. Cracks that originate along the
5.2 Manufacture:
edges of the specimen during testing, and that are less than ⁄4
5.2.1 The joints shall be double or single welded, full
in. (6.3 mm) measured in any direction, shall not be consid-
penetration welds made in accordance with ASME Boiler and
ered.
Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX.
5.2.2 The welds shall be made either manually or automati-
7.3 Pressure Test—Any pipe that shows leaks during the
cally by an electric process involving the deposition of filler pressure test conducted in accordance with 13.4 shall be
metal according to the class specified.
rejected, but any leaking areas may be cut out and the pipe
5.2.3 The weld surface on either side of the weld shall be
retested as above.
flush with the base plate or shall have a reasonably uniform
7.4 Radiographic Examination—For Classes 1, 3, and 5
crown, not to exceed ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm).Any weld reinforcement
pipe, radiographic examination shall be in accordance with the
may be removed at the manufacturer’s option or by agreement
between the manufacturer and purchaser. The contour of the
reinforcement shall be reasonably smooth and free of irregu- TABLE 1 Mechanical Property Requirements
larities. The deposited metal shall be fused uniformly into the
Elongation
Tensile Strength, min Yield Strength, min
in 2 in. or
plate surface. No concavity of contour is permitted unless the
Gage
50.8 mm,
ksi MPa ksi MPa
min, %
UNS # ⁄16 100 690 45 310 30
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
N08367
International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
> ⁄16 95 655 45 310 30
www.asme.org.
UNS 94 650 43 295 35
Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd., N08926
Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
B804−02 (2007)
NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
Test Specimen Thickness, in. A B C D
3 1 3 3 3
⁄8 1 ⁄2 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 1 ⁄16
1 1
t 4t 2t
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B804–96 Designation: B 804 – 02 (Reapproved 2007)
Standard Specification for
UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 Welded Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 804; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers UNS N08367 and UNS N08926 welded pipe for general corrosion applications. (Although no
restrictions are placed on the sizes of pipe that may be furnished under this specification, commercial practice is commonly limited
to sizes not less than 8 in. nominal diameter.)
1.2 Six classes of pipe are covered as follows:
1.2.1 Class 1 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes and shall be completely
radiographed.
1.2.2 Class 2 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes. No radiography is required.
1.2.3 Class 3 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld may be
made without the addition of filler metal. Welds are to be completely radiographed.
1.2.4 Class 4 pipe shall be double welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except the inside root weld may be
made without the addition of filler metal. No radiography is required.
1.2.5 Class 5 pipe shall be single welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass exposed to the
inside pipe surface may be made without the addition of filler metal. Welds are to be completely radiographed.
1.2.6 Class 6 pipe shall be single welded by processes employing filler metal in all passes except that the pass exposed to the
inside pipe surface may be made without the addition of filler metal. No radiography is required.
1.3 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformation
only.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this standard: This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standardtoestablishappropriatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
A 370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
B 625 Specification for UNS N08904, UNS N08925, UNS N08031, UNS N08932, UNS N08926, UNS N08354, and UNS
R20033 Plate, Sheet, and Strip
B 688 Specification for Chromium-Nickel-Molybdenum-Iron (UNS N08366 and UNS N08367) Plate, Sheet, and Strip
B 880 SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforChemicalCheckAnalysisLimitsforNickel,NickelAlloysandCobaltAlloys
B 899 Terminology Relating to Non-ferrous Metals and Alloys
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB-2onNonferrousMetalsandAlloysandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeB02.07onRefined
Nickel and Cobalt, and Alloys Containing Nickel or Cobalt or Both as Principal Constituents.
Current edition approved May 10, 1996. Published June 1996. Originally published as B804–89. Last previous edition B804–93.
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB02onNonferrousMetalsandAlloysandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeB02.07onRefined
Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2007. Published November 2007. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as B 804 – 02.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
, Vol 01.03.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B 804 – 02 (2007)
E 38 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Chromium and Nickel-Chromium-Iron Alloys
E 354 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of High-Temperature, Electrical, Magnetic, and Other Similar Iron, Nickel, and
Cobalt Alloys
E 1019 TestMethodsforDeterminationofCarbon,Sulfur,Nitrogen,andOxygeninSteelandinIron,Nickel,andCobaltAlloys
E 1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel, Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
2.2 ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code:
Section VIII, Division 1 Rules for Construction of Pressure Vessels
Section IX Qualification Standard for Welding and Brazing Procedures, Welders, Brazers, and Welding and Brazing Operators
2.3 American Welding Society Standards:
AWS A5.11 Nickel and Nickel Alloy Covered Welded Electrodes
AWS A5.14 Nickel and Nickel Alloy Bare Welding Rods and Electrodes
3. Ordering Information
3.1Orders for material under this specification shall include the following information:
3.1.1Quantity (feet or number of lengths),
3.1.2Class (see Terminology
3.1 Terms defined in Terminology B 899 shall apply unless otherwise defined in this standard.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
specification. Examples of such requirements include, but are not limited to, the following:
4.1.1 Quantity (feet or number of lengths),
4.1.2 Class (see 1.2),
34.1.3 Size (outside diameter and minimum wall thickness),
34.1.4 Length (specific or random),
34.1.5 ASTM specification number,
34.1.6 Authorization for repair of plate defects by welding without prior approval if such is intended (see 8.49.4),
3.1.7Circumferential weld permissibility (see 7.3.2
4.1.7 Circumferential weld permissibility (see 8.3.2), and
3.1.8Supplementary requirements.
4.Materials and Manufacture
4.1
4.1.8 Supplementary requirements.
5. Materials and Manufacture
5.1 Materials—The starting material shall conform to the requirements of Specification B 688 for UNS N08367 and
Specification B 625 for UNS N08926.
4.2
5.2 Manufacture:
4.2.1The5.2.1 The joints shall be double or single welded, full penetration welds made in accordance with ASME Boiler and
Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX.
4.2.2The5.2.2 The welds shall be made either manually or automatically by an electric process involving the deposition of filler
metal according to the class specified.
4.2.3The5.2.3 The weld surface on either side of the weld shall be flush with the base plate or shall have a reasonably uniform
crown, not to exceed ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm). Any weld reinforcement may be removed at the manufacturer’s option or by agreement
between the manufacturer and purchaser. The contour of the reinforcement shall be reasonably smooth and free of irregularities.
The deposited metal shall be fused uniformly into the plate surface. No concavity of contour is permitted unless the resulting
thickness of weld metal is equal to or greater than the minimum thickness of the adjacent base metal.
45.2.4 Weld defects shall be repaired by removal to sound metal and rewelding. Subsequent heat treatment and inspection shall
be as required on the original welds.
Withdrawn.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.asme.org.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
B 804 – 02 (2007)
4.35.3 Heat Treatment—The recommended heat treatment shall consist of heating to a minimum temperature of 2025°F for
UNS N08367 and 2012°F for UNS N08926 followed by quenching in water or rapidly cooling by other means.
5.6. Chemical Composition
5.16.1 The chemical composition of the pipe shall conform to the requirements in Table 1 of Specification B 688 for UNS
N08367 and Table 1 of Specification B 625 for UNS N08926.
5.26.2 The alloy content of the deposited weld metal shall conform to that required for the plate or the welding electrodes as
shown in Specification AWS A5.11 for ENiCrMo-3, ENiCrMo-4, and ENiCrMo-10 or AWS A5.14 for ERNiCrMo-10,
ERNiCrMo-3, and ERNiCrMo-4.
5.3If6.3 If product analysis is made of the plate or weld metal by the purchaser, the chemical composition thus determined shall
conform to the requirements specified in 5.16.1 and 5.26.2 subject to the permissible tolerances in Table 1 of Specification
B688B 880 for UNS N08367 and specified in 5.1 and 5.2 subject to the permissible tolerances in Table 2 of Specification B625
for UNS N08926. .
6.7. Mechanical Properties and Other Requirements
6.17.1 Mechanical Properties:
6.1.1The7.1.1 The mechanical properties of the plate shall be in accordance with Table 1. Tension tests made by the plate
manufacturer shall qualify the plate material.
67.1.2 Transverse tension tests taken across the welded joint shall have the same minimum ultimate tensile strength as the
specified minimum ultimate tensile strength of the plate.
6.27.2 TransverseGuidedWeldBendTestRequirements—BendsmadeinaccordancewithFig.1shallbeacceptableifnocracks
or other imperfections exceeding ⁄8 in. (3.2 mm) in any direction are present in the weld metal or between the weld and the pipe
metal after bending. Cracks that originate along the edges of the specimen during testing, and that are less than ⁄4 in. (6.3 mm)
measured in any direction, shall not be considered.
6.3
7.3 Pressure Test—Any pipe that shows leaks during the pressure test conducted in accordance with 12.413.4 shall be rejected,
but any leaking areas may be cut out and the pipe retested as above.
6.4
7.4 Radiographic Examination—For Classes 1, 3, and 5 pipe, radiographic examination shall be in accordance with the
requirements of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section VIII, latest edition, Paragraph UW-51.
7.8. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
78.1 Permissible variations in dimensions at any point in a length of pipe shall not exceed the following:
7.1.18.1.1 Outside Diameter—Based on circumferential measurement, 60.5 % of the nominal outside diameter.
7.1.2
8.1.2 Out-of-Roundness—Differences between major and minor outside diameters, 1.0 % of the specified outside diameter.
7.1.3
8.1.3 Alignment (Camber)—Using a 10-ft (3-m) straightedge placed so that both ends are in contact with the pipe, the camber
shall not be more than ⁄8 in. (3.17 mm).
7.2
8.2 Thickness—The minimum wall thickness at any point in the pipe shall not be more than 0.01 in. (0.25 mm) under the
nominal thickness.
7.3
8.3 Lengths:
7.3.1The8.3.1 The lengths required shall be specified in the orders.
7.3.28.3.2 Circumferentially welded joints of the same quality as the longitudinal joints shall be permitted by agreement
between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
8.9. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
8.1Pipe9.1 Pipe shall be furnished with smooth ends, free of burrs.
TABLE 1 Mechanical Property Requirements
Elongation
Tensile Strength, min Yield Strength, min
in 2 in. or
Gage
50.8 mm,
ksi MPa ksi MPa
min, %
UNS # ⁄16 100 690 45 310 30
N08367
> ⁄16 95 655 45 310 30
UNS 94 650 43 295 35
N08926
B 804 – 02 (2007)
NOTE 1—1 in. = 25.4 mm.
Test Specimen Thickness, in. A B C D
3 1 3 3 3
⁄8 1 ⁄2 ⁄4 2 ⁄8 1 ⁄16
1 1
t 4t 2t 6t + ⁄8 3t + ⁄16
FIG. 1 Guided-Bend Test Jig
8.2The9.2 The finished pipe shall be free of injurious defects and shall have a workmanlike finish.
8.39.3 Repair of Plate Defects by Machining or Grinding—Pipe showing moderate slivers may be machined or ground inside
oroutsidetoadepththatshallensuretheremovalofallincludedscaleandslivers,providedthewallthicknessisnotreducedbelow
the specified minimum wall thickness. Machining or grinding shall follow inspection of the pipe as rolled and shall be followed
by supplementary visual inspection.
8.4
9.4 Repair of Plate Defects by Welding—Repair of injurious defects shall be permitted only with the approval of the purchaser.
Defects shall be thoroughly chipped out before welding. The repairs shall be radiographed and if the pipe itself has already been
heat treated, it shall then be heat treated again except in the case of small welds that, in the estimation of the purchaser’s inspector,
do not require heat treatment. Each length of pipe repaired in this manner shall be hydrostatically tested after being repaired.
8.5The9.5 The pipe shall be sandblasted or pickled to remove all scale and then passivated.
9.10. Sampling
9.1
10.1 Lots for Chemical Analysis and Mechanical Testing:
9.1.1
10.1.1 Heat Analysis—A lot shall consist of one heat.
9.1.2
10.1.2 Mechanical Testing—A lot shall consist of the material of the same nominal size from one heat and condition.
9.2
10.2 Sampling for Chemical Analysis:
9.2.1A10.2.1 A representative sample shall be taken by the plate manufacturer during pouring or subsequent processing.
910.2.2 Product analysis, if performed, shall be wholly the responsibility of the purchaser.
9.310.3 SamplingforMechanicalProperties—Transverse tension and bend test specimens shall be cut after final heat treatment
from the end of the finished pipe or from a test plate of the same material as the pipe that is attached to the end of the cylinder
and welded as a prolongation of the longitudinal pipe seam.
10.11. Number of Tests and Retests
10.111.1 Chemical Analysis—One test per lot.
10.2
11.2 Transverse Tension Test—One per lot.
B 804 – 02 (2007)
10.3
11.3 Transverse Guided Weld Bend Test—One face bend and one root bend per lot (Fig. 2).
10.4
11.4 Pressure Test—Each pipe sh
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.