ASTM E2488-22
(Guide)Standard Guide for the Preparation and Evaluation of Liquid Baths Used for Temperature Calibration by Comparison
Standard Guide for the Preparation and Evaluation of Liquid Baths Used for Temperature Calibration by Comparison
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
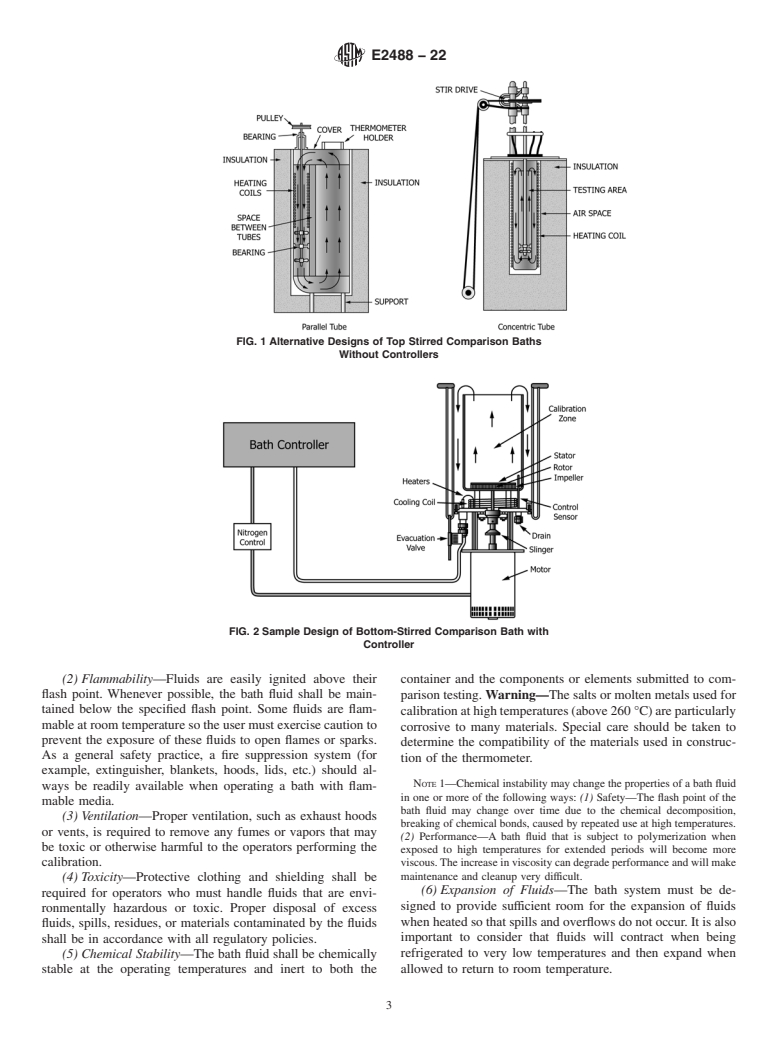
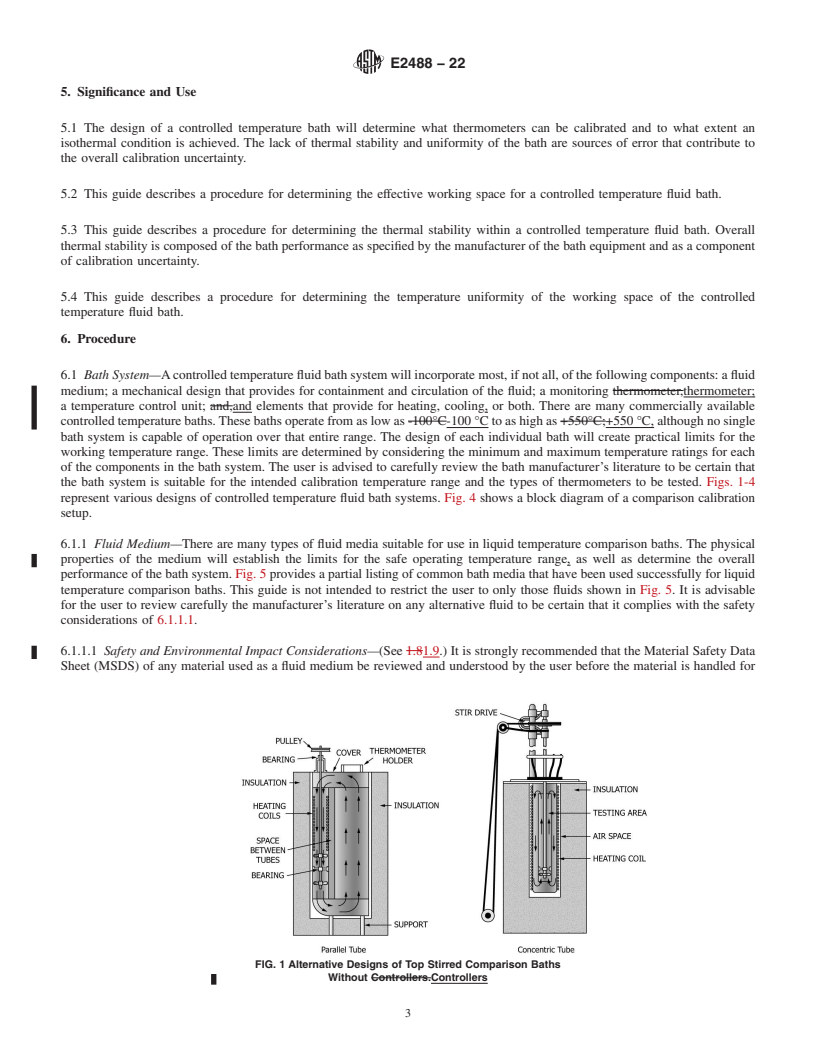
5.1 The design of a controlled temperature bath will determine what thermometers can be calibrated and to what extent an isothermal condition is achieved. The lack of thermal stability and uniformity of the bath are sources of error that contribute to the overall calibration uncertainty.
5.2 This guide describes a procedure for determining the effective working space for a controlled temperature fluid bath.
5.3 This guide describes a procedure for determining the thermal stability within a controlled temperature fluid bath. Overall thermal stability is composed of the bath performance as specified by the manufacturer of the bath equipment and as a component of calibration uncertainty.
5.4 This guide describes a procedure for determining the temperature uniformity of the working space of the controlled temperature fluid bath.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide is intended for use with controlled temperature comparison baths that contain test fluids and operate within the temperature range of –100 °C to 550 °C.
1.2 This guide describes the essential features of controlled temperature fluid baths used for the purpose of thermometer calibration by the comparison method.
1.3 This guide does not address the details on the design and construction of controlled-temperature fluid baths.
1.4 This guide describes a method to define the working space of a bath and evaluate the temperature variations within this space. Ideally, the working space will be as close as possible to isothermal.
1.5 This guide does not address fixed point baths, ice point baths, or vapor baths.
1.6 This guide does not address fluidized powder baths.
1.7 This guide does not address baths that are programmed to change temperature.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2488 − 22
Standard Guide for
the Preparation and Evaluation of Liquid Baths Used for
1
Temperature Calibration by Comparison
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Many of the Standards and Test Methods under the jurisdiction of ASTM committee E20 on
Temperature Measurement make reference to the use of controlled temperature fluid baths for the
calibration of thermometers by the comparison method. In this method the thermometer under test is
measured while immersed in an isothermal medium whose temperature is simultaneously determined
by a calibrated reference thermometer. The uncertainty of all such comparison calibrations depends
upon how well the isothermal conditions can be maintained.The bath temperature must be stable over
time and uniform within the working space at the operating temperatures. This guide provides basic
information, options and instructions that will enable the user to prepare and evaluate controlled
temperature baths for calibrations.
1. Scope 1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
1.1 This guide is intended for use with controlled tempera-
standard.
ture comparison baths that contain test fluids and operate
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
within the temperature range of –100 °C to 550 °C.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2 This guide describes the essential features of controlled
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
temperature fluid baths used for the purpose of thermometer
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
calibration by the comparison method.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.3 Thisguidedoesnotaddressthedetailsonthedesignand
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
construction of controlled-temperature fluid baths.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
1.4 This guide describes a method to define the working
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
space of a bath and evaluate the temperature variations within
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
this space. Ideally, the working space will be as close as
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
possible to isothermal.
1.5 This guide does not address fixed point baths, ice point
2. Referenced Documents
baths, or vapor baths.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.6 This guide does not address fluidized powder baths.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E344 Terminology Relating to Thermometry and Hydrom-
1.7 This guide does not address baths that are programmed
etry
to change temperature.
E644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Ther-
mometers
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E20 on Temperature
Measurement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E20.07 on Funda-
2
mentals in Thermometry. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2022. Published December 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E2488 – 09 (2014). Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/E2488-22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2488 − 22
E839 Test Methods for Sheathed Thermocouples and 5.2 This guide describes a procedure for determining the
Sheathed Thermocouple Cable effective working space for a controlled temperature fluid bath.
2.2 Other Documents:
5.3 This guide describes a procedure for determining the
3
ITS-90 The International Temperature Scale of 1990
thermal stability within a controlled temperature fluid bath.
4
NIST Monograph 126 Platinum Resistance Thermometry
Overall thermal stability is composed of the bath performance
4
NIST Monograph 150 Liquid-in-Glass Thermometry
as specified by the manufacturer of the bath equipment and as
NIST SP250-22 Platinum Resistance Thermometer Calibra-
a component of calibration uncertainty.
4
tions
5.4
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2488 − 09 (Reapproved 2014) E2488 − 22
Standard Guide for
the Preparation and Evaluation of Liquid Baths Used for
1
Temperature Calibration by Comparison
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2488; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Many of the Standards and Test Methods under the jurisdiction of ASTM committee E20 on
Temperature Measurement make reference to the use of controlled temperature fluid baths for the
calibration of thermometers by the comparison method. In this method the thermometer under test is
measured while immersed in an isothermal medium whose temperature is simultaneously determined
by a calibrated reference thermometer. The uncertainty of all such comparison calibrations depends
upon how well the isothermal conditions can be maintained. The bath temperature must be stable over
time and uniform within the working space at the operating temperatures. This guide provides basic
information, options and instructions that will enable the user to prepare and evaluate controlled
temperature baths for calibrations.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide is intended for use with controlled temperature comparison baths that contain test fluids and operate within the
temperature range of –100°C–100 °C to 550°C.550 °C.
1.2 This guide describes the essential features of controlled temperature fluid baths used for the purpose of thermometer
calibration by the comparison method.
1.3 This guide does not address the details on the design and construction of controlled-temperature fluid baths.
1.4 This guide describes a method to define the working space of a bath and evaluate the temperature variations within this space.
Ideally, the working space will be as close as possible to isothermal.
1.5 This guide does not address fixed point baths, ice point baths, or vapor baths.
1.6 This guide does not address fluidized powder baths.
1.7 This guide does not address baths that are programmed to change temperature.
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E20 on Temperature Measurement and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E20.07 on Fundamentals
in Thermometry.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2014Nov. 15, 2022. Published December 2014December 2022. Originally approved in 2009. Last previous edition approved in 20092014
as E2488 – 09.E2488 – 09 (2014). DOI: 10.1520/E2488-09R14.10.1520/E2488-22.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2488 − 22
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.10 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
E344 Terminology Relating to Thermometry and Hydrometry
E644 Test Methods for Testing Industrial Resistance Thermometers
E839 Test Methods for Sheathed Thermocouples and Sheathed Thermocouple Cable
2.2 Other Documents:
3
ITS-90 The International Temperature Scale of 1990
4
NIST Monograph 126 Platinum Resistance Thermometry
4
NIST Monograph 150 Liquid-in-Glass Thermometry
4
NIST SP 250-22 Platinum Resistance Thermometer Calibrations
4
NIST SP 250-23 Liquid-in-Glass Thermometer Calibration Service
2.3 Military Standards:
5
MIL-STD-202G Test Methods for Electronic and Electrical Component Parts
3. Terminology
3.1 Standard terms used in this guide are defined in Terminology E344.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 bath gradient error, n—the error caused by temperature differences within the working space of the bath.
3.2.2 immersion
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.