ASTM D8352-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Relative Crystallinity of Zeolite Beta by X-Ray Diffraction
Standard Test Method for Determination of Relative Crystallinity of Zeolite Beta by X-Ray Diffraction
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Zeolite Beta is a siliceous zeolite that can be crystallized with SiO2/Al2O3 ratio greater than 20. Zeolite Beta, upon modification to the H-cation form in a post-crystallization step, has been used in catalytic NOx reduction, isomerization of waxes, alkylation of aromatics, hydrocarbon adsorption from exhaust gas emission, etc.
4.2 This X-ray procedure is designed to allow a reporting of the relative degree of crystallinity upon manufacture of zeolite Beta. The relative crystallinity of zeolite Beta number has proven useful in technology, research, and specifications.
4.3 The Integrated Peak Area Method (Procedure A) is preferred over the Peak Height Method (Procedure B) since it calculates XRD intensity as a sum from several peaks rather than utilizing just one peak. Drastic changes in intensity of individual peaks in the XRD pattern of zeolite Beta can result from changes in distribution of electron density within the unit cell of the zeolite Beta. The electron density distribution is dependent upon the following factors:
4.3.1 Extent of filling of pores with guest molecules and the nature of these guest molecules.
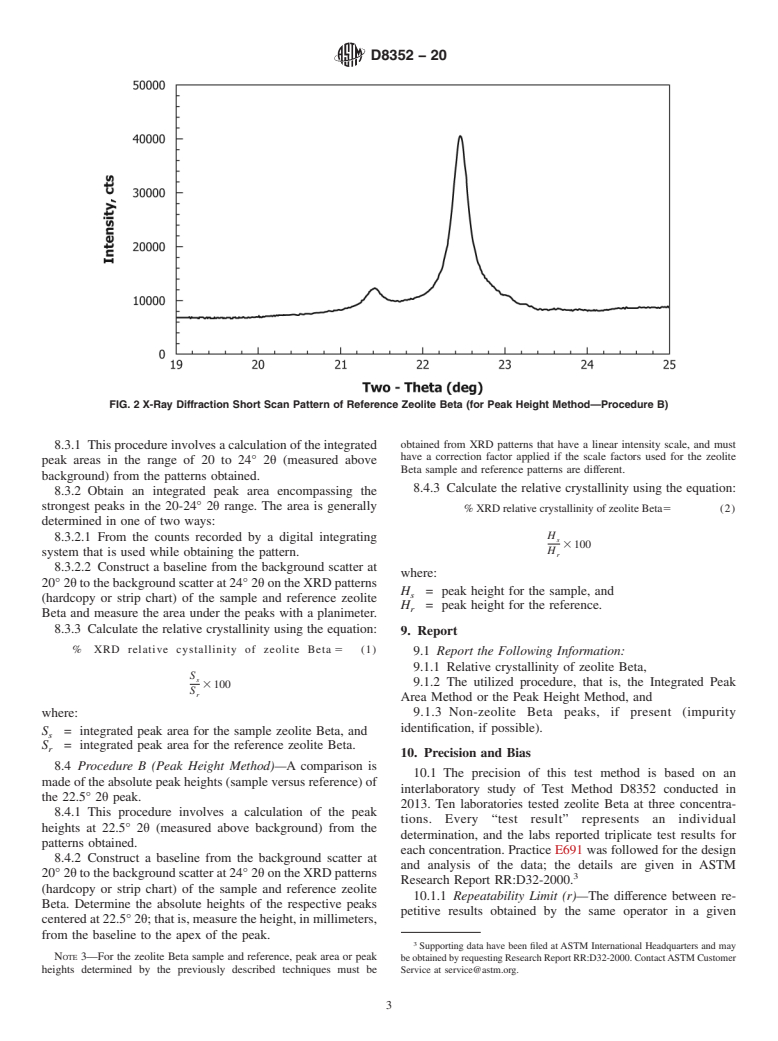
4.3.2 Type of cations and extent of their presence (these cations may also affect the absorption of X rays by the zeolite Beta sample).
4.3.3 In this XRD method, the guest molecule H2O completes the filling of the pores. Other guest molecule types may also be present, including one of numerous amines, diamines, and quaternary ammonium cations that can function as a template for crystallization of the zeolite Beta structure.
4.3.4 Because of the factors mentioned in 4.3.1 – 4.3.3 that could vary the intensities of the XRD peaks in zeolite Beta, this XRD method will provide the best determination of relative crystallinity when the reference zeolite Beta and sample zeolite Beta have a similar history of preparation and composition.
4.4 If crystalline phases other than zeolite Beta are present in the sample, their diffraction peaks...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determination of the relative crystallinity of zeolite Beta containing samples using selected peaks from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the zeolite.
1.2 The test method provides a number that is the ratio of intensity of a portion of the XRD pattern of the sample zeolite Beta to intensity of the corresponding portion of the pattern of a reference zeolite Beta. The intensity ratio, expressed as a percentage, is then labeled percent XRD relative crystallinity of zeolite Beta. This type of comparison is commonly used in zeolite technology and is often referred to as percent crystallinity.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8352 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Relative Crystallinity of Zeolite Beta by
1
X-Ray Diffraction
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8352; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope zeolite Beta and the reference zeolite Beta are obtained under
thesameconditions.Fromthesepatterns,thereisachoicefrom
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for determination
two procedures for calculation of relative crystallinity of
of the relative crystallinity of zeolite Beta containing samples
zeolite Beta.
using selected peaks from the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern
of the zeolite.
3.2 Procedure A (Integrated Peak Area Method)—A com-
parison is made of the sums of intensities (sample versus
1.2 The test method provides a number that is the ratio of
reference) of the strong peaks, having maxima between about
intensity of a portion of the XRD pattern of the sample zeolite
3
20.0 and 24.0° 2θ.
Beta to intensity of the corresponding portion of the pattern of
a reference zeolite Beta. The intensity ratio, expressed as a
3.3 Procedure B (Peak Height Method)—A comparison is
percentage, is then labeled percent XRD relative crystallinity
made of the absolute peak heights (sample versus reference) of
of zeolite Beta. This type of comparison is commonly used in
the 22.5° 2θ peak.
zeolite technology and is often referred to as percent crystal-
linity.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 ZeoliteBetaisasiliceouszeolitethatcanbecrystallized
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with SiO /Al O ratio greater than 20. Zeolite Beta, upon
2 2 3
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
modification to the H-cation form in a post-crystallization step,
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
has been used in catalytic NOx reduction, isomerization of
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
waxes, alkylation of aromatics, hydrocarbon adsorption from
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
exhaust gas emission, etc.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.2 This X-ray procedure is designed to allow a reporting of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the relative degree of crystallinity upon manufacture of zeolite
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Beta. The relative crystallinity of zeolite Beta number has
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
proven useful in technology, research, and specifications.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.3 The Integrated Peak Area Method (Procedure A) is
2. Referenced Documents
preferred over the Peak Height Method (Procedure B) since it
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
calculates XRD intensity as a sum from several peaks rather
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
than utilizing just one peak. Drastic changes in intensity of
ASTM Test Methods
individual peaks in the XRD pattern of zeolite Beta can result
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
from changes in distribution of electron density within the unit
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
cell of the zeolite Beta. The electron density distribution is
dependent upon the following factors:
3. Summary of Test Method
4.3.1 Extent of filling of pores with guest molecules and the
3.1 This method applies to zeolite Beta samples with
nature of these guest molecules.
average crystallite size >150 nm. XRD patterns of the sample
4.3.2 Type of cations and extent of their presence (these
cations may also affect the absorption of X rays by the zeolite
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
Beta sample).
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.05 on Zeolites.
4.3.3 In this XRD method, the guest molecule H O com-
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2020. Published December 2020. DOI:
2
10.1520/D8352-20.
pletes the filling of the pores. Other guest molecule types may
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
also be present, including one of numerous amines, diamines,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and quaternary ammonium cations that can function as a
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. template for
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.