ASTM D4512-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Vibrated Apparent Packing Density of Fine Catalyst and Catalyst Carrier Particles and Powder
Standard Test Method for Vibrated Apparent Packing Density of Fine Catalyst and Catalyst Carrier Particles and Powder
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is for measuring the apparent packing density of catalyst or catalyst carrier powders that are smaller than 0.8 mm in diameter.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent packing density of fine catalyst and catalyst carrier powders smaller than 0.8 mm in diameter.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4512 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Vibrated Apparent Packing Density of Fine Catalyst and
1
Catalyst Carrier Particles and Powder
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4512; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the appar- 3.1 Definitions—See Terminology D3766.
entpackingdensityoffinecatalystandcatalystcarrierpowders
4. Significance and Use
smaller than 0.8 mm in diameter.
4.1 This test method is for measuring the apparent packing
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
density of catalyst or catalyst carrier powders that are smaller
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
than 0.8 mm in diameter.
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 5. Apparatus
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5.1 Graduated Glass or Plastic Cylinders,capacity100mL,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
feed and measuring, Class A or B per Specification E1272.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3
5.2 Vibrator, conventional hand-held, with hard rubber or
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
metal impactor.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- 5.3 Feed Funnel, plastic, glass, or metal as shown in Fig. 1.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
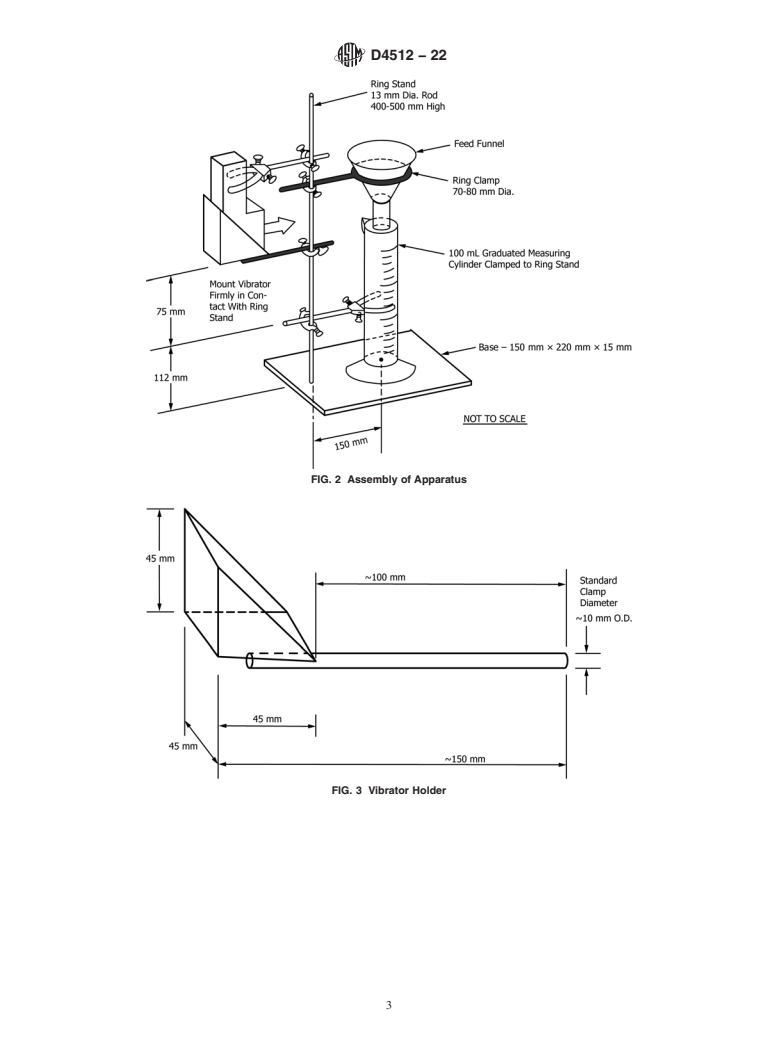
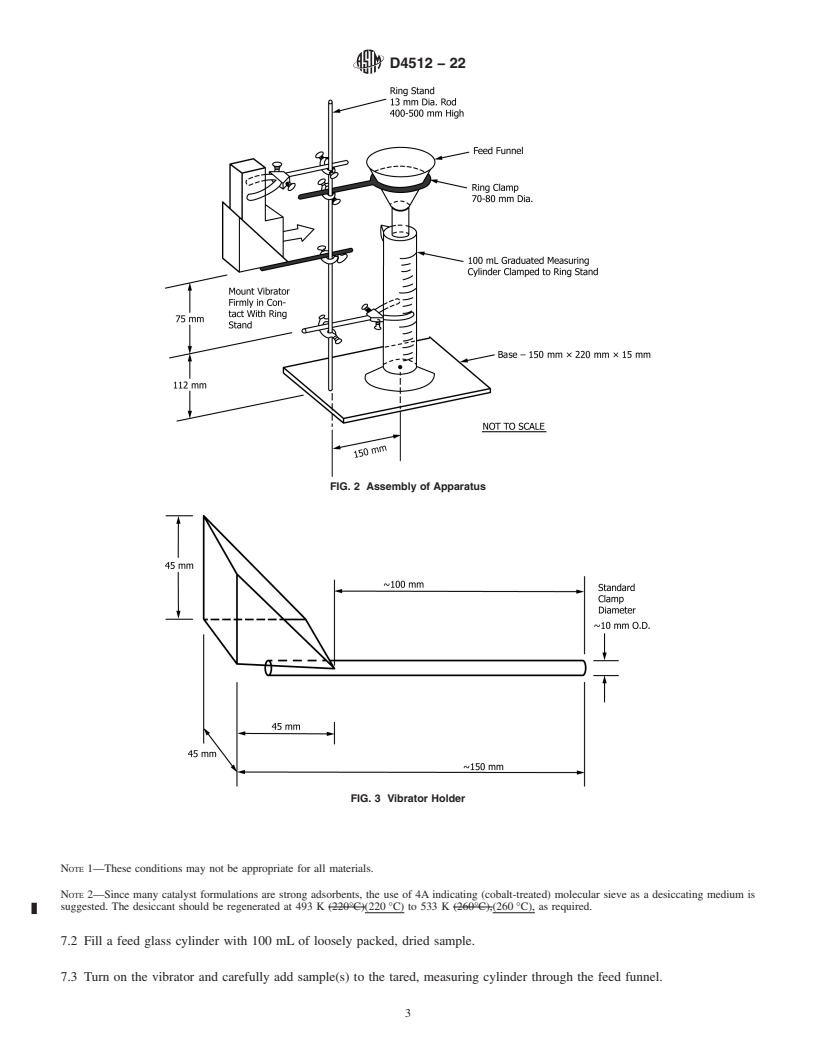
5.4 Ring Stand, vibrator holder and clamps as shown in
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
Figs. 2 and 3.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5.5 Desiccator, with a desiccant grade molecular sieve such
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
as 4A.
2. Referenced Documents
5.6 Balance, having sensitivity of 0.1 g.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.7 Drying Oven.
D3766 Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
E105 Guide for Probability Sampling of Materials
6. Sample
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,With
6.1 Test sample shall be obtained from larger composites by
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
riffling or splitting in accordance with subsection 5.12 of STP
Lot or Process
4
447A with the aim of obtaining a sample that represents the
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
particle size distribution of the larger composite. Guide E105
ASTM Test Methods
can provide guidance on constructing a sampling plan with the
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
representative sample size can be determined per Practice
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
E122.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylin-
7. Procedure
ders
7.1 Heat an adequate amount of sample(s) at 400 6 15 °C
for not less than 3 h. Normally, this treatment can take place in
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.02 on Physical-
3
Mechanical Properties. The sole source of supply of the vibrator known to the committee at this time
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2022. Published August 2022. Originally is Wahl Clipper Corp., Sterling, IL. They recommend their Model 4120 used at low
ε1
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as D4512 – 03(2018) . speed to replace their Model 4180, which is discontinued. If you are aware of
DOI: 10.1520/D4512-22. alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
1
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on STP 447A, Manual on Test Sieving Methods, ASTM International, West
the ASTM website. Conshohocken, PA 19428.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4512 − 22
8. Calculation
8.1 Calculate the apparent packing density as follows:
APD 5 W/V (1)
where:
APD = apparent packing density, g/mL,
W = mass of samp
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D4512 − 03 (Reapproved 2018) D4512 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Vibrated Apparent Packing Density of Fine Catalyst and
1
Catalyst Carrier Particles and Powder
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4512; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Section 6.5 was updated editorially in May 2018.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent packing density of fine catalyst and catalyst carrier powders smaller
than 0.8 mm in diameter.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D3766 Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
E105 Guide for Probability Sampling of Materials
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a Lot or
Process
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E1272 Specification for Laboratory Glass Graduated Cylinders
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology D3766.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.02 on Physical-Mechanical
Properties.
Current edition approved May 1, 2018Aug. 1, 2022. Published June 2018August 2022. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 20132018 as
ε1
D4512–03(2013).D4512 – 03(2018) . DOI: 10.1520/D4512-03R18E01.10.1520/D4512-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4512 − 22
FIG. 1 Feed Funnel
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method is for measuring the apparent packing density of catalyst or catalyst carrier powders that are smaller than 0.8
mm in diameter.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Graduated Glass or Plastic Cylinders, capacity 100 mL, feed and measuring.measuring, Class A or B per Specification E1272.
3
5.2 Vibrator, conventional hand-held, with hard rubber or metal impactor.
5.3 Feed Funnel, plastic, glass, or metal as shown in Fig. 1.
5.4 Ring Stand, vibrator holder and clamps as shown in Figs. 2 and 3.
5.5 Desiccator, with a desiccant grade molecular sieve such as 4A.
5.6 Balance, having sensitivity of 0.1 g.
5.7 Drying Oven.
6. Sample
4
6.1 Test sample shall be obtained from larger composites by riffling or splitting in accordance with subsection 5.12 of STP 447A
with the aim of obtaining a sample that represents the particle size distribution of the larger composite. Guide E105 can provide
guidance on constructing a sampling plan with the representative sample size can be determined per Practice E122.
7. Procedure
7.1 Heat an adequate amount of sample(s) at 400 6 15°C15 °C for not less than 3 h. Normally, this treatment can take place in
air; however, in the case of materials that might react with air at elevated temperatures (such as, prereduced catalysts) the heat
treatment shall take place in an inert atmosphere. After heating, cool the test sample(s) in a desiccator or other suitable container
to eliminate the possibility of moisture adsorption prior to testing.
3
The sole source of supply of the vibrator known to
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.