ASTM D2692-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Air Wicking of Tire Fabrics, Tire Cord Fabrics, Tire Cord, and Yarns
Standard Test Method for Air Wicking of Tire Fabrics, Tire Cord Fabrics, Tire Cord, and Yarns
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is considered satisfactory for the acceptance testing of commercial shipments of tire fabrics since this test method has been used extensively in the trade for acceptance testing. This test method is also considered satisfactory for quality control.
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported test results when using this test method for acceptance testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias. As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are from a lot of material of the type in question. The test specimens should then be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The average results from the two laboratories may be compared using appropriate statistical analysis and an acceptable probability level chosen by the two parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consideration to the known bias.
This test method is applicable for testing the air permeability of any fabric that is embedded in a rubber compound, but is particularly useful when testing chafer fabrics to be used in a tubeless tire construction. In tubeless tires, chafer fabric yarns that are not wick proof represent potential channels for air to pass through, and thus, this test method provides a prediction of chafer permeability.
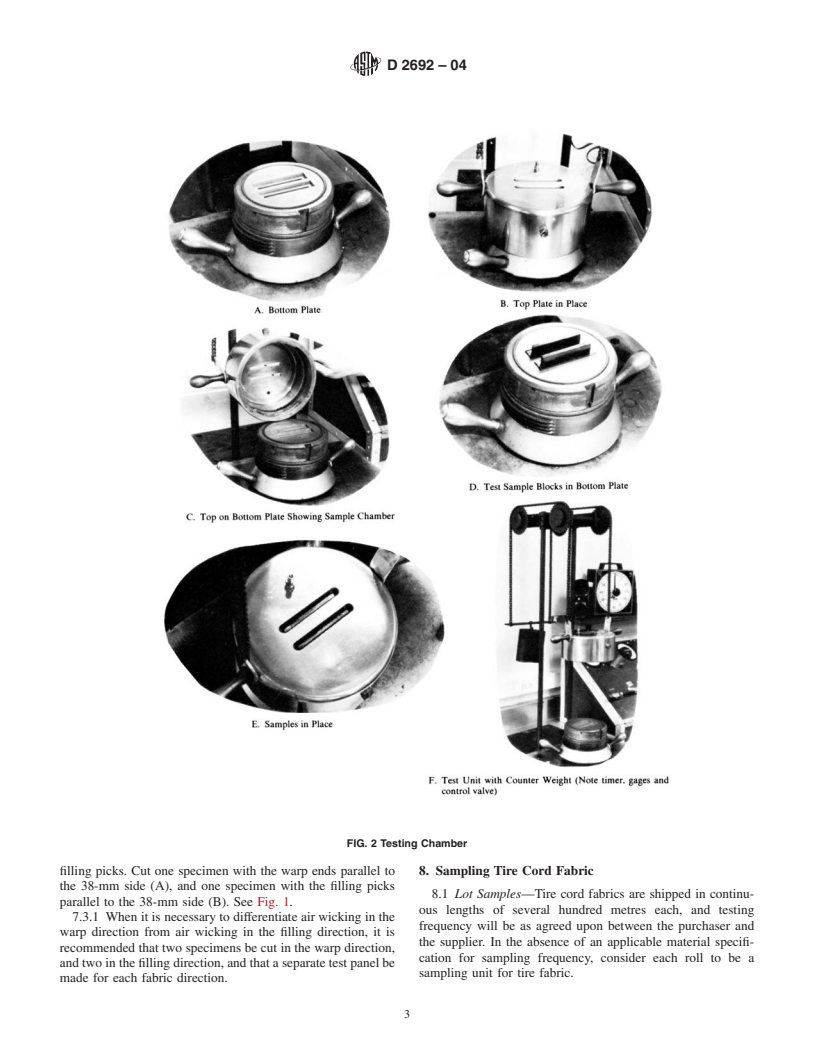
Evaluation of air wicking in other fabric and cord components in such products as tires, rubber brake diaphragms, and pneumatic hoses, is useful.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of longitudinal air permeability for tire fabrics, tire cord fabrics, tire cords, or yarns embedded in cured rubber compound. This test method is designed to demonstrate the effectiveness of fabric treatments intended to prevent air permeability. This test method is applicable to fabrics made from all types of fibers with all types of rubber compound.
1.2 This test method is written in SI units. The inch pound units which are provided are not necessarily exact equivalents of the SI units. Either system of units may be used in this test method.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See the Note in .
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D2692–04
Standard Test Method for
Air Wicking of Tire Fabrics, Tire Cord Fabrics, Tire Cord,
1
and Yarns
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2692; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1.1 Thefollowingtermsarerelevanttothisstandard:air
wicking, chafer fabric, test panel, in air wicking test, tire cord,
1.1 This test method covers the determination of longitudi-
tire cord fabric, tire fabric, vulcanization, wickproof, in tire
nalairpermeabilityfortirefabrics,tirecordfabrics,tirecords,
fabric, tire cord fabric, tire cord, or yarn.
or yarns embedded in cured rubber compound. This test
3.1.2 For definitions of other terms related to textiles, refer
method is designed to demonstrate the effectiveness of fabric
to Terminology D123.
treatments intended to prevent air permeability. This test
3.1.2.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
method is applicable to fabrics made from all types of fibers
skein and yarn.
with all types of rubber compound.
1.2 This test method is written in SI units. The inch pound
4. Summary of Test Method
units which are provided are not necessarily exact equivalents
4.1 Fabric specimens are embedded in a rubber compound
of the SI units. Either system of units may be used in this test
and air pressure is applied to freshly exposed yarn ends.
method.
Detergent solution is applied to the opposite end of the yarns
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
whichhavealsobeenfreshlyexposed.Airwickingisindicated
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
by continuous formation of air bubbles in the detergent
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
solution due to air passing along the axis of a yarn.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See the Note in
5. Significance and Use
11.1.
5.1 This test method is considered satisfactory for the
acceptance testing of commercial shipments of tire fabrics
2. Referenced Documents
2 sincethistestmethodhasbeenusedextensivelyinthetradefor
2.1 ASTM Standards:
acceptance testing. This test method is also considered satis-
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
factory for quality control.
D3182 Practice for Rubber—Materials, Equipment, and
5.1.1 In case of a dispute arising from differences in
Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Prepar-
reportedtestresultswhenusingthistestmethodforacceptance
ing Standard Vulcanized Sheets
testing of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the sup-
D6477 Terminology Relating to Tire Cord, Bead Wire,
plier should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is
Hose Reinforcing Wire, and Fabrics
a statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statis-
3. Terminology tical assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias.
As a minimum, the two parties should take a group of test
3.1 Definitions:
specimens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are
3.1.1 Fordefinitionsoftermsrelatingtotirecord,beadwire,
from a lot of material of the type in question. The test
hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D6477.
specimensshouldthenberandomlyassignedinequalnumbers
toeachlaboratoryfortesting.Theaverageresultsfromthetwo
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD13onTextiles
laboratories may be compared using appropriate statistical
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Tire Cord and Fabrics.
analysis and an acceptable probability level chosen by the two
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004. Published October 2004. Originallyap-
parties before the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its
proved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D2692–98.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
cause must be found and corrected or the purchaser and the
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
supplier must agree to interpret future test results with consid-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
eration to the known bias.
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2692–04
DIMENSIONS
a bcd e f g
Inches 3.0 1.5 3.5 0.5 0.25 0.75 2.25
Millimetres 76 38 89 12.6 6.4 19 57
NOTE 1—Lower case letters refer to dimensions. Capital letters refer to pieces prepared as outlined in 10.2.
FIG. 1 Test Panel
5.2 This test metho
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.