ASTM D4206-96(2007)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sustained Burning of Liquid Mixtures Using the Small Scale Open-Cup Apparatus
Standard Test Method for Sustained Burning of Liquid Mixtures Using the Small Scale Open-Cup Apparatus
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Mixtures of flammable liquids and nonflammable liquids, such as an alcohol and water mixture, are classified by the U. S. Government by the definition of flammable liquid based on a closed-cup flash point method. Thus, mixtures may be classed as flammable even though they do not sustain burning. This test method determines the ability of a liquid mixture to sustain burning and, when used with a closed-cup flash point method, indicates the flammability characteristics of the mixture.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for determining the sustained burning characteristics of mixtures of flammable and nonflammable liquids and to mixtures containing liquids with widely different flash points.
This standard should be used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions and should not be used to describe or appraise the fire-hazard or fire-risk of materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However, results of the test may be used as elements of a fire-hazard assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes into account all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4206 − 96 (Reapproved2007)
Standard Test Method for
Sustained Burning of Liquid Mixtures Using the Small Scale
Open-Cup Apparatus
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4206; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
This test method may be used in conjunction with a flash point determination. If the flash point of
a mixture of flammable and nonflammable liquids or liquids of widely different flash points is below
the upper limit of a flammability classification (for example, 100°F specified by the U.S. Department
ofTransportation),thistestmaybeconductedtodeterminethesustainedburningcharacteristicsofthe
mixture.
This test method is a modification of the test for combustibility now incorporated as Schedule 2 of
the “Highly Flammable Liquids and Liquified Petroleum Gases Regulation, 1972” of the United
KingdomunderTheFactoriesAct,1961,whichisalsoissuedasBritishStandardBS-3900,PartA-11,
Small Scale Test for Combustibility. This sustained burning test was studied and proposed by the
ASTMCoordinatingCommitteeforFlashPointandRelatedProperties.Themajorpurposeofthistest
is similar to that of the British test—to provide a method for determining the sustained burning
characteristics by directly observing this property rather than by deducing them from the flash point.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 Thistestmethod describesaprocedurefordetermining
2.1 British Standards:
the sustained burning characteristics of mixtures of flammable
BS-3900Part A-11, Small Scale Test for Combustibility
and nonflammable liquids and to mixtures containing liquids
3. Summary of Test Method
with widely different flash points.
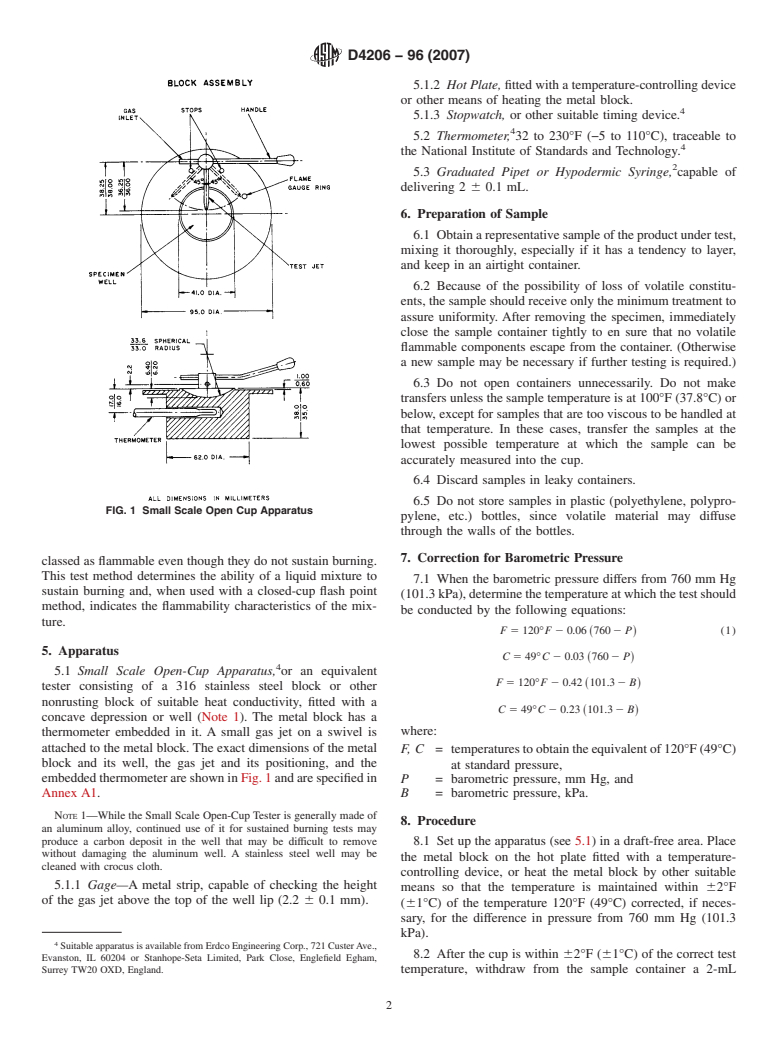
3.1 Ablockofaluminumalloy,orothernonrustingmetalof
1.2 This standard should be used to measure and describe
the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and suitable heat conductivity, with a concave depression (called
thewell)isheatedtotherequiredtemperatureof120°F(49°C).
flame under controlled conditions and should not be used to
describe or appraise the fire-hazard or fire-risk of materials, A standard source of flame, capable of being swung over the
centerofthewellandatagivendistancefromit,isattachedto
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. However,
results of the test may be used as elements of a fire-hazard the metal block.
assessment or a fire-risk assessment which takes into account
3.2 Two millilitres of the product under test are transferred
all of the factors which are pertinent to an assessment of the
to the well. After the product has reached the stated
fire hazard or fire risk of a particular end use.
temperature, the flame is passed over the well, held there for a
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
specified time, and then removed. The time of sustained
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
burning is then noted.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4. Significance and Use
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 Mixtures of flammable liquids and nonflammable
liquids, such as an alcohol and water mixture, are classified by
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
the U. S. Government by the definition of flammable liquid
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
based on a closed-cup flash point method. Thus, mixtures may
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
Current edition approved June 1, 2007. Published August 2007. Originally
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4206–96(2001).
DOI: 10.1520/D4206-96R07. Available from British Standards Institute (BSI), 389 Chiswick High Rd.,
McKelvie, A. N., “A Test for Ability to Support Combustion for Liquids LondonW44AL,U.K.,http://www.bsi-global.comorAmericanNationalStandards
Including Paints and Allied Products,” Journal of Oil Co. Chemical Assoc., 1972 , Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://
Vol 55, pp. 1086–1095. www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4206 − 96 (Reapproved2007)
be
D4206 − 96 (2007)
5.1.2 Hot Plate,fittedwithatemperature-controllingdevice
or other means of heating the metal block.
5.1.3 Stopwatch, or other suitable timing device.
5.2 Thermometer, 32 to 230°F (−5 to 110°C), traceable to
the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
5.3 Graduated Pipet or Hypodermic Syringe, capable of
delivering 2 6 0.1 mL.
6. Preparation of Sample
6.1 Obtainarepresentativesampleoftheproductundertest,
mixing it thoroughly, especially if it has a tendency to layer,
and keep in an airtight container.
6.2 Because of the possibility of loss of volatile constitu-
ents,thesampleshouldreceiveonlytheminimumtreatmentto
assure uniformity. After removing the specimen, immediately
close the sample container tightly to en sure that no volatile
flammable components escape from the container. (Otherwise
a new sample may be necessary if further testing is required.)
6.3 Do not open containers unnecessarily. Do not make
transfersunlessthesampletemperatureisat100°F(37.8°C)or
below, except for samples that are too viscous to be handled at
that temperature. In these cases, transfer the samples at the
lowest possible temperature at which the sample can be
accurately measured into the cup.
6.4 Discard samples in leaky containers.
6.5 Do not store samples in plastic (polyethylene, polypro-
FIG. 1 Small Scale Open Cup Apparatus
pylene, etc.) bottles, since volatile material may diffuse
through the walls of the bottles.
7. Correction for Barometric Pressure
classed as flammable even though they do not su
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.