ASTM D5874-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of the Impact Value (IV) of a Soil
Standard Test Method for Determination of the Impact Value (IV) of a Soil
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Impact Value (IV) of a soil either in the field or a test mold.
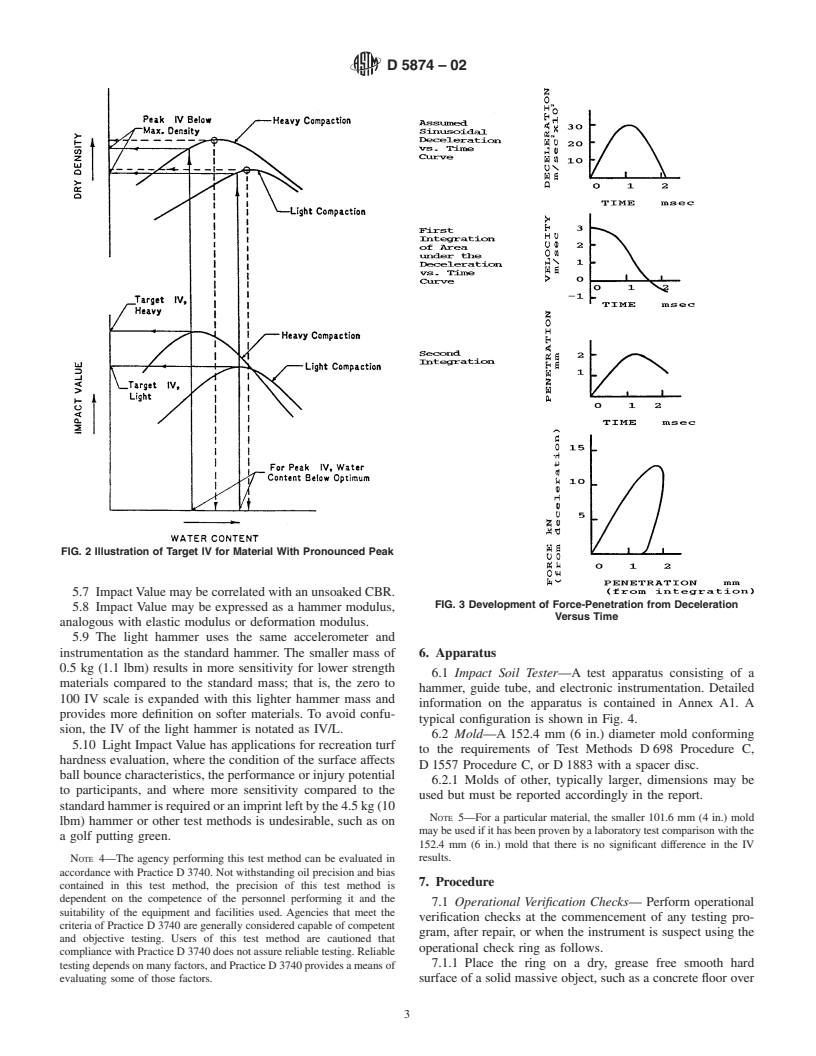
1.2 The standard test method, using a 4.5 kg (10 lbm) hammer, is suitable for, but not limited to, evaluating the strength of an unsaturated compacted fill, in particular pavement materials, soils, and soil-aggregates having maximum particle sizes less than 37.5 mm (1.5 in.).
1.3 By using a lighter 0.5 kg (1.1 lbm) hammer, this test method is applicable for evaluating lower strength soils such as fine grained cohesionless, highly organic, saturated, or highly plastic soils having a maximum particle size less than 9.5 mm (0.375 in.).
1.4 By performing laboratory test correlations for a particular soil using the 4.5 kg (10 lbm) hammer, IV may be correlated with an unsoaked California Bearing Ratio (CBR) or may be used to infer percentage compaction.
1.5 The values stated SI are to be regarded as the standard. The values stated in parentheses are given for information only.
1.6 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in Practice D 6026. The method used to specify how data are collected, calculated, or recorded in this standard is not directly related to the accuracy to which the data can be applied in design or other uses or both. How one applies the results obtained using this standard is beyond its scope.
1.7 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—The equipment and procedures contained in this test method are similar to those developed by B. Clegg in the 1970s at the University of Western Australia, Nedlands, Australia. Impact Value is also commonly known as Clegg Impact Value (CIV).
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5874–02
Standard Test Method for
1
Determination of the Impact Value (IV) of a Soil
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5874; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope * D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
2
Fluids
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the Impact
D 698 Test Method for Laboratory Compaction Character-
Value (IV) of a soil either in the field or a test mold.
3
istics of Soils Using Standard Effort (12 400 ft lbf/ft (600
1.2 The standard test method, using a 4.5 kg (10 lbm)
3 2
kNm/m ))
hammer, is suitable for, but not limited to, evaluating the
D 1556 Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the
strength of an unsaturated compacted fill, in particular pave-
2
Sand-Cone Method
ment materials, soils, and soil-aggregates having maximum
D 1557 Test Method for Laboratory Compaction Character-
particle sizes less than 37.5 mm (1.5 in.).
3
isticsofSoilsUsingModifiedEffort(56000ftlbf/ft (2700
1.3 By using a lighter 0.5 kg (1.1 lbm) hammer, this test
3
2
kNm/m ))
methodisapplicableforevaluatinglowerstrengthsoilssuchas
D 1883 Test Method for CBR (California Bearing Ratio) of
fine grained cohesionless, highly organic, saturated, or highly
2
Laboratory Compacted Soils
plastic soils having a maximum particle size less than 9.5 mm
D 2167 Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the
(0.375 in.).
2
Rubber-Balloon Method
1.4 By performing laboratory test correlations for a particu-
D 2216 Method for Laboratory Determination of Water
larsoilusingthe4.5kg(10lbm)hammer,IVmaybecorrelated
(Moisture) Content of Soil, Rock, and Soil-Aggregate
with an unsoaked California Bearing Ratio (CBR) or may be
2
Mixtures
used to infer percentage compaction.
D 2922 Test Methods for Density of Soil and Soil-
1.5 The values stated SI are to be regarded as the standard.
2
AggregatesinPlacebyNuclearMethods(ShallowDepth)
Thevaluesstatedinparenthesesaregivenforinformationonly.
D 2937 Test Method for Density of Soil in Place by the
1.6 All observed and calculated values shall conform to the
2
Drive-Cylinder Method
guidelines for significant digits and rounding established in
D 3017 Test Method for Water Content of Soil and Rock in
Practice D 6026. The method used to specify how data are
2
Place by Nuclear Methods (Shallow Depth)
collected,calculated,orrecordedinthisstandardisnotdirectly
D 3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
related to the accuracy to which the data can be applied in
Engaged in the Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock
design or other uses or both. How one applies the results
2
as Used in Engineering Design and Construction
obtained using this standard is beyond its scope.
D 4643 Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture)
1.7 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
2
Content of Soil by the Microwave Oven Method
tions, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
D 4959 Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture)
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
2
Content of Soil by Direct Heating Method
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
D 6026 Practice foUsing Significant Digits in Geotechnical
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
3
Data
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—The equipment and procedures contained in this test method 3. Terminology
are similar to those developed by B. Clegg in the 1970s at the University
3.1 Definitions—Except as listed below, all definitions are
ofWesternAustralia, Nedlands,Australia. ImpactValue is also commonly
in accordance with Terminology D 653.
known as Clegg Impact Value (CIV).
3.1.1 impact value (IV), n—the value expressed in units of
2. Referenced Documents tens of gravities (g) derived from the peak decelaration of a 4.5
kg (10 lbm) instrumented compaction hammer 50 mm (1.97
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in.) in diameter free falling 450 mm (18 in.).
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoiland
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.08 on Special and
Control Tests.
2
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2002. Published December 2002. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.08.
3
published as D 5874–95. Last previous edition D 5874–95. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.09.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ------------------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.