ASTM B833-20
(Specification)Standard Specification for Zinc and Zinc Alloy Wire for Thermal Spraying (Metallizing) for the Corrosion Protection of Steel
Standard Specification for Zinc and Zinc Alloy Wire for Thermal Spraying (Metallizing) for the Corrosion Protection of Steel
ABSTRACT
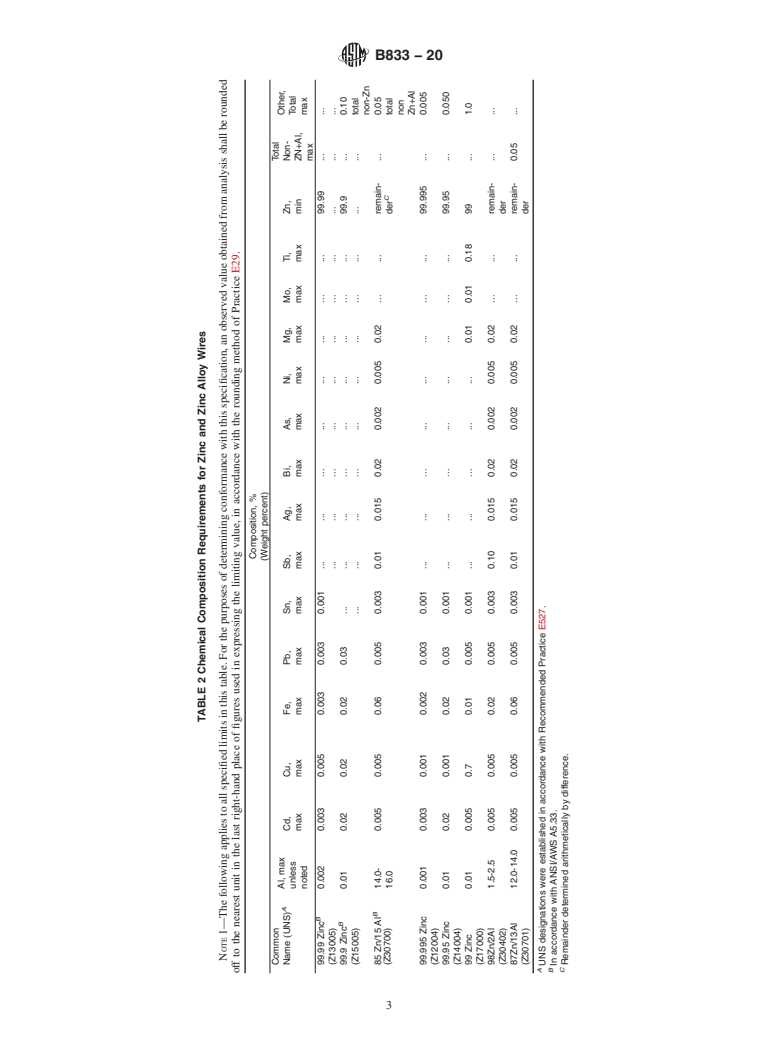
This specification covers zinc and zinc alloy wire used to deposit zinc coatings by thermal spraying (metallizing) for the corrosion protection of steel and iron. Zinc and zinc alloy wire provided under this specification is intended for use in oxy-fuel and electric arc thermal spraying equipment. The zinc used to manufacture the wire shall conform to the requirements for high grade zinc (Z15001) or special high grade zinc (Z13001). The wire shall conform to the chemical requirements for aluminum, cadmium, copper, iron, lead, tin, antimony, silver, bismuth, arsenic, nickel, magnesium, molybdenum, titanium, and zinc. The wire shall be clean and free of corrosion, adhering foreign material, scale, seams, nicks, burrs, bends or kinks which would interfere with the operation of thermal spraying equipment. The wire shall uncoil readily and shall be a continuous length per spool, coil, or drum. Splices or welds are permitted, provided that they do not interfere with the thermal spray equipment or coating process.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers zinc and zinc alloy wire used to deposit zinc coatings by thermal spraying (metallizing) for the corrosion protection of steel and iron. Zinc and zinc alloy wire provided under this specification is intended for use in oxy-fuel and electric arc thermal spraying equipment. Additional zinc alloy compositions used in thermal spraying primarily for electronic applications are found in Specification B943.
1.2 Zinc alloy wire compositions used in thermal spraying primarily for electronic applications are found in Specification B943.
1.3 Zinc alloy wire compositions used as solders are found in Specification B907.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:B833 −20
Standard Specification for
Zinc and Zinc Alloy Wire for Thermal Spraying (Metallizing)
1
for the Corrosion Protection of Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B833; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
2
1. Scope* 2.2 ASTM Standards:
B6 Specification for Zinc
1.1 This specification covers zinc and zinc alloy wire used
B899 Terminology Relating to Non-ferrous Metals and Al-
to deposit zinc coatings by thermal spraying (metallizing) for
loys
the corrosion protection of steel and iron. Zinc and zinc alloy
B907 Specification for Zinc, Tin and Cadmium Base Alloys
wire provided under this specification is intended for use in
Used as Solders
oxy-fuel and electric arc thermal spraying equipment. Addi-
B943 Specification for Zinc and Tin Alloy Wire Used in
tional zinc alloy compositions used in thermal spraying pri-
Thermal Spraying for Electronic Applications
marily for electronic applications are found in Specification
B949 Specification for General Requirements for Zinc and
B943.
Zinc Alloy Products
1.2 Zinc alloy wire compositions used in thermal spraying
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
primarily for electronic applications are found in Specification
Determine Conformance with Specifications
B943.
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1.3 Zinc alloy wire compositions used as solders are found
in Specification B907. E536 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Zinc and Zinc
Alloys
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3
2.3 ANSI/AWS Standard:
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
ANSI/AWS A5.33 Specification for Solid and Ceramic
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Wires and Ceramic Rods for Thermal Spraying
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4
2.4 ISO Standards:
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar
ISO 3815-1 Zinc and zinc alloys — Part 1:Analysis of solid
with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
samples by optical emission spectrometry
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material
ISO 3815-2 Zinc and zinc alloys — Part 2: Analysis by
as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate
inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry
safety, health, and environmental practices, and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3. Terminology
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.1 Terms shall be defined in accordance with Terminology
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
B899.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
4. Ordering Information
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. 4.1 In order to make the application of this specification
complete, the purchaser shall supply the following information
2. Referenced Documents
to the seller in the purchase order or other governing docu-
ments:
2.1 The following ASTM documents of the issue in effect
on the date of material purchase form a part of this specifica-
tion to the extent referenced herein:
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee the ASTM website.
3
B02.04 on Zinc and Cadmium. Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd.,
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published April 2020. Originally Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
4
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as B833 – 13. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/B0833-20. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B833−20
4.1.1 Name, designation, and date of issue of this 7. Physical Properties and Mechanical Prop
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B833 − 13 B833 − 20
Standard Specification for
Zinc and Zinc Alloy Wire for Thermal Spraying (Metallizing)
1
for the Corrosion Protection of Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B833; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers zinc and zinc alloy wire used to deposit zinc coatings by thermal spraying (metallizing) for the
corrosion protection of steel and iron. Zinc and zinc alloy wire provided under this specification is intended for use in oxy-fuel
and electric arc thermal spraying equipment. Additional zinc alloy compositions used in thermal spraying primarily for electronic
applications are found in Specification B943.
1.2 Zinc alloy wire compositions used in thermal spraying primarily for electronic applications are found in Specification B943.
1.3 Zinc alloy wire compositions used as solders are found in Specification B907.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data
Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and
healthenvironmental practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following ASTM documents of the issue in effect on the date of material purchase form a part of this specification to
the extent referenced herein:
2
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B6 Specification for Zinc
B899 Terminology Relating to Non-ferrous Metals and Alloys
B907 Specification for Zinc, Tin and Cadmium Base Alloys Used as Solders
B943 Specification for Zinc and Tin Alloy Wire Used in Thermal Spraying for Electronic Applications
B949 Specification for General Requirements for Zinc and Zinc Alloy Products
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to Determine Conformance with Specifications
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
E536 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Zinc and Zinc Alloys
3
2.3 ANSI/AWS Standard:
ANSI/AWS A5.33 Specification for Solid and Ceramic Wires and Ceramic Rods for Thermal Spraying
4
2.4 ISO Standards:
ISO 3815-1 Zinc and zinc alloys — Part 1: Analysis of solid samples by optical emission spectrometry
ISO 3815-2 Zinc and zinc alloys — Part 2: Analysis by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B02.04 on Zinc
and Cadmium.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2013April 1, 2020. Published March 2013April 2020. Originally approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 20092013 as B833 –
06.13. DOI: 10.1520/B0833-13.10.1520/B0833-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Welding Society (AWS), 550 NW LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126, http://www.aws.org.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B833 − 20
3. Terminology
3.1 Terms shall be defined in accordance with Terminology B899.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 In order to make the application of this specification complete, the purchaser shall supply the
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.