ASTM C1422/C1422M-20a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass
Standard Specification for Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for chemically strengthened glass products that are used in general building construction, transportation, solar, and other electronic applications, such as PC screens, notebooks, tablets, smart phones, and E-readers, as well as copy machine scanners, computer disks, and flat glass screens for television monitors. The technique covered in this specification usually involves conducting ion exchange of constituent alkali ions in a glass product by immersing it in a bath of molten salt containing larger alkali ions. Penetration of the larger ions into smaller host sites produces a layer of compression on the surface which strengthens the glass. Techniques such as ion implantation, dealkalization, etch-strengthening, and glaze coatings are specifically excluded from this specification.
1.2 Classification of chemically strengthened glass products is based on the laboratory measurements of surface compression and case depth (depth of compression) and not on the modulus of rupture (MOR). This specification does not purport to address end-use performance.
1.3 A test method for the measurement of case depth and surface compression is included in Section 8. Another test method for similar measurement using optically guided-wave equipment is included in Section 9.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system are not necessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used independently of the other, and values from the two systems shall not be combined.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1422/C1422M −20a
Standard Specification for
1
Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1422/C1422M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for chemi-
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
cally strengthened glass products that are used in general
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
building construction, transportation, solar, and other elec-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
tronic applications, such as PC screens, notebooks, tablets,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
smart phones, and E-readers, as well as copy machine
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
scanners, computer disks, and flat glass screens for television
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
monitors. The technique covered in this specification usually
involves conducting ion exchange of constituent alkali ions in
2. Referenced Documents
a glass product by immersing it in a bath of molten salt 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
containing larger alkali ions. Penetration of the larger ions into
C162Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
smaller host sites produces a layer of compression on the
C770Test Method for Measurement of Glass Stress—
surface which strengthens the glass. Techniques such as ion
Optical Coefficient
implantation, dealkalization, etch-strengthening, and glaze
C978Test Method for Photoelastic Determination of Re-
coatings are specifically excluded from this specification.
sidual Stress in a Transparent Glass Matrix Using a
1.2 Classificationofchemicallystrengthenedglassproducts Polarizing Microscope and Optical Retardation Compen-
is based on the laboratory measurements of surface compres- sation Procedures
sion and case depth (depth of compression) and not on the C1036Specification for Flat Glass
modulusofrupture(MOR).Thisspecificationdoesnotpurport C1279Test Method for Non-Destructive Photoelastic Mea-
to address end-use performance. surement of Edge and Surface Stresses in Annealed,
Heat-Strengthened, and Fully Tempered Flat Glass
1.3 A test method for the measurement of case depth and
C1648Guide for Choosing a Method for Determining the
surface compression is included in Section 8. Another test
Index of Refraction and Dispersion of Glass
method for similar measurement using optically guided-wave
E1967Test Method for the Automated Determination of
equipment is included in Section 9.
Refractive Index of Glass Samples Using the Oil Immer-
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
sion Method and a Phase Contrast Microscope
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
F218Test Method for Measuring Optical Retardation and
eachsystemarenotnecessarilyexactequivalents;therefore,to
Analyzing Stress in Glass
3
ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be
2.2 ANSI Standard:
used independently of the other, and values from the two
Z97.1-2015Safety Glazing Materials Used In Buildings -
systems shall not be combined.
Safety Performance Specifications And Methods Of Test
4
2.3 Federal Standard:
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
16 CFR 1201Consumer Product Safety Commission Safety
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Standard for Architectural Glazing Materials
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C14 on Glass Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.08 on Flat the ASTM website.
3
Glass. Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2020. Published September 2020. Originally 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
4
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 2020 as C1422/C1422M–20. AvailablefromU.S.ConsumerProductSafetyCommission(CPSC),4330East
DOI: 10.1520/C1422_C1422M-20A. West Hwy., Bethesda, MD 20814, http://www.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1422/C1422M − 20 C1422/C1422M − 20a
Standard Specification for
1
Chemically Strengthened Flat Glass
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1422/C1422M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for chemically strengthened glass products that are used in general building
construction, transportation, solar, and other electronic applications, such as PC screens, notebooks, tablets, smart phones, and
E-readers, as well as copy machine scanners, computer disks, and flat glass screens for television monitors. The technique covered
in this specification usually involves conducting ion exchange of constituent alkali ions in a glass product by immersing it in a bath
of molten salt containing larger alkali ions. Penetration of the larger ions into smaller host sites produces a layer of compression
on the surface which strengthens the glass. Techniques such as ion implantation, dealkalization, etch-strengthening, and glaze
coatings are specifically excluded from this specification.
1.2 Classification of chemically strengthened glass products is based on the laboratory measurements of surface compression and
case depth (depth of compression) and not on the modulus of rupture (MOR). This specification does not purport to address end-use
performance.
1.3 A test method for the measurement of case depth and surface compression is included in Section 8. Another test method for
similar measurement using optically guided-wave equipment is included in Section 9.
1.4 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system mayare not benecessarily exact equivalents; therefore, to ensure conformance with the standard, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combiningother, and values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
standard.shall not be combined.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C162 Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
C770 Test Method for Measurement of Glass Stress—Optical Coefficient
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C14 on Glass and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.08 on Flat Glass.
Current edition approved April 15, 2020Aug. 1, 2020. Published April 2020September 2020. Originally approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 20152020
as C1422/C1422M – 15.C1422/C1422M – 20. DOI: 10.1520/C1422_C1422M-20.10.1520/C1422_C1422M-20A.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1422/C1422M − 20a
C978 Test Method for Photoelastic Determination of Residual Stress in a Transparent Glass Matrix Using a Polarizing
Microscope and Optical Retardation Compensation Procedures
C1036 Specification for Flat Glass
C1279 Test Method for Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-
Strengthened, and Fully Tempered Flat Glass
C1648 Guide for Choosing a Method for Determining the Index of Refraction and Dispersion of Glass
E1967 Test Method for the Automated Determination of Refractive Index of Glass Samples Using the Oil Immersion Method
and a Phase Contrast Microscope
F218 Test Method for Measuring Optical Retardation and Analyzing Stress in Glass
3
2.2
...








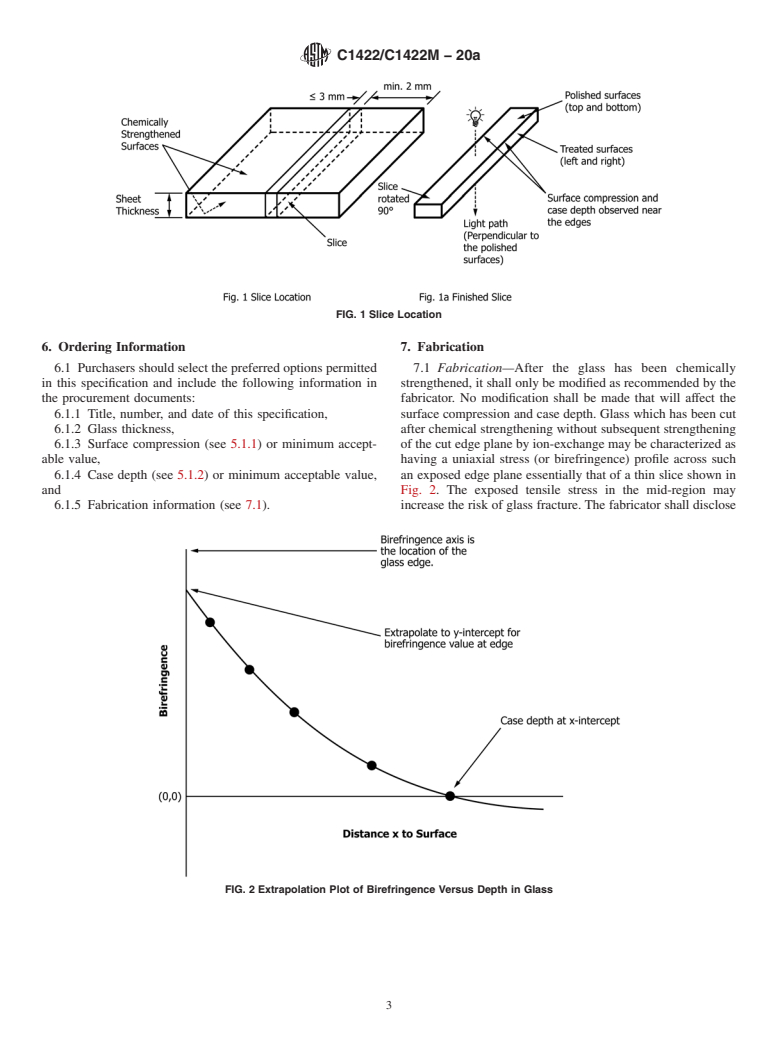


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.