ASTM F877-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Plastic Hot- and Cold-Water Distribution Systems
Standard Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Plastic Hot- and Cold-Water Distribution Systems
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers requirements, test methods, and methods of marking for crosslinked polyethylene plastic hot- and cold-water distribution systems components made in one standard dimension ratio and intended for 100 psi (0.69 MPa) water service up to and including a maximum working temperature of 180oF (82oC). Components are comprised of tubing and fittings. Requirements and test methods are included for materials, workmanship, dimensions and tolerances, hydrostatic sustained pressure strength, thermocycling resistance, fittings, and bend strength. Also included are tests related to system malfunctions. The components covered by this specification are intended for use in residential and commercial, hot and cold, potable water distribution systems as well as sealed central heating, including under-floor heating systems.
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values stated in parentheses are provided for information only.
Note 1—Suggested hydrostatic design stresses and hydrostatic pressure ratings for tubing and fittings are listed in Appendix X1. Design, assembly, and installation considerations are discussed in Appendix X2. An optional performance qualification and an in-plant quality control program are recommended in Appendix X3.
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 877 – 00 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX) Plastic Hot- and Cold-Water
Distribution Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 877; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
D 1598 Test Method for Time-to-Failure of Plastic Pipe
1.1 This specification covers requirements, test methods,
Under Constant Internal Pressure
and methods of marking for crosslinked polyethylene plastic
D 1599 Test Method for Short-Time Hydraulic Failure Pres-
hot- and cold-water distribution systems components made in
sure of Plastic Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
one standard dimension ratio and intended for 100 psi (0.69
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to
MPa) water service up to and including a maximum working
Plastics
temperature of 180°F (82°C). Components are comprised of
D 1898 Practice for Sampling of Plastics
tubing and fittings. Requirements and test methods are in-
D 2749 Symbols for Dimensions of Plastic Pipe Fittings
cluded for materials, workmanship, dimensions and tolerances,
D 2837 Test Method for Obtaining Hydrostatic Design
hydrostatic sustained pressure strength, thermocycling resis-
Basis for Thermoplastic Pipe Materials
tance, fittings, and bend strength. Also included are tests
D 3140 Practice for Flaring Polyolefin Pipe and Tubing
related to system malfunctions. The components covered by
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
this specification are intended for use in residential and
F 876 Specification for Crosslinked Polyethylene (PEX)
commercial, hot and cold, potable water distribution systems as
Tubing
well as sealed central heating, including under-floor heating
2.2 ANSI Standards:
systems.
B 36.10 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe
1.2 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes,
Z 17.1 Preferred Numbers
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These
2.3 AWWA Standard:
notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall
Manual M-11, Steel Pipe Design and Installation
not be considered as requirements of the specification.
2.4 Federal Standard:
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
Fed Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment (Civil Agencies)
as the standard. The values stated in parentheses are provided
2.5 Military Standard:
for information only.
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
NOTE 1—Suggested hydrostatic design stresses and hydrostatic pres-
2.6 NSF Standard:
sure ratings for tubing and fittings are listed in Appendix X1. Design,
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related
assembly, and installation considerations are discussed in Appendix X2.
Materials
An optional performance qualification and an in-plant quality control
program are recommended in Appendix X3.
3. Terminology
1.4 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
3.1 The terminology used in this specification is in accor-
test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
dance with Terminology F 412, Terminology D 1600, and
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
Symbols D 2749, unless otherwise specified. The abbreviation
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
for crosslinked polyethylene is PEX. Plastic tubing denotes a
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health
particular diameter schedule of plastic pipe in which outside
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
diameter of the tubing is equal to the nominal size plus ⁄8 in.
tions prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.04.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Available from American National Standards Institute, 11 West 42nd Street,
13th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Available from the American Water Works Association, 6666 W. Quincey Ave.,
Denver, CO 80235.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.61 on Water.
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
Current edition approved April 10, 2000. Published July 2000. Originally
Available from the National Sanitation Foundation, P.O. Box 1468, Ann Arbor,
published as F 877 – 84. Last previous edition F 877 – 99a.
MI 48106.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 877
Plastic pipe outside diameter schedule conforms to ANSI 4.3 Certification—PEX tubing and fittings, used for the
B 36.10. distribution of potable water, shall be products approved for
3.2 crosslinked polyethylene plastics—plastics prepared by that service by the regulatory bodies having such jurisdiction.
crosslinking (curing) polyethylene compounds. These products shall be tested for that service by a nationally
3.3 relation between standard dimension ratio, stress, and recognized and accredited testing laboratory and shall bear the
internal pressure—the following expressions, commonly certification mark of the testing agency.
known as the ISO equation, is used to relate standard dimen-
NOTE 2—Further information regarding testing and approval can be
sion ratio, stress, and internal pressure for tubing:
obtained from the National Sanitation Foundation or other accredited
laboratory.
2S/P 5 R 2 1
5. Classification
or
5.1 Tubing—This specification classifies PEX tubing by a
2S/P5~D /t!2 1
o
single standard dimension ratio that shall be SDR 9, and by a
maximum continuous use temperature that shall be 180°F
(82°C), and by nominal tubing diameters from ⁄8 in. through 2
where:
in.
S = stress in circumferential or hoop direction, psi (MPa),
P = internal pressure, psi (MPa), 5.2 Fittings—This specification classifies fittings, intended
t = minimum wall thickness, in.,
for use in systems with PEX tubing, by a maximum continuous
R = standard dimension ratio, SDR, and
use temperature that shall be 180°F (82°C) and by nominal
D = average outside diameter, in.
o sizes from ⁄8 in. through 2 in. on the basis of resistance to burst
3.4 standard dimension ratio (SDR)—a selected series of
pressure, hydrostatic sustained pressure, excessive temperature
numbers in which the average outside diameter to minimum
and pressure, and to failure by thermocycling.
wall thickness dimension ratios are constant for all sizes of
6. Requirements
tubing in each standard dimension ratio, and which are the
6.1 Workmanship—The tubing shall be homogeneous
ANSI Z 17.1 Preferred Number Series R 10 modified by +1. If
throughout and free of visible cracks, holes, foreign inclusions,
the wall thickness calculated by SDR for PEX tubing is less
or other defects. The pipe shall be as uniform as commercially
than 0.070 in. (1.78 mm), it shall be arbitrarily increased to
practicable in color, opacity, density, and other physical prop-
0.070 in. except for sizes ⁄4 in. and smaller.
erties.
3.5 standard material designation code—the crosslinked
6.2 Dimensions and Tolerances:
polyethylene tubing material designation code shall consist of
6.2.1 General:
the abbreviation PEX.
6.2.1.1 Tubing—The PEX tubing shall meet the require-
4. Materials
ments of Specification F 876. The tolerances for outside
4.1 General—This specification covers PEX tubing materi- diameters are also given in Table 1.
als as described in Specification F 876. 6.2.1.2 Out-of-Roundness—The maximum out-of-
4.2 Basic Materials Description—Crosslinked polyethylene roundness requirements, shown in Table 1 for tubing, apply to
tubing meeting the requirements of this specification are the average measured diameter after rounding with a rounding
primarily defined by two criteria namely, basic short-term tool recommended by the manufacturer.
properties and long-term hydrostatic strength, 4.2.1 and 4.2.2 6.2.2 Wall Thickness—Table 2 provides for wall thickness
respectively. tolerances. Calculated SDR 9 tubing wall thickness that fall
4.2.1 Basic Short-Term Properties—This specification cov- below 0.070 in. (1.78 mm) shall be arbitrarily increased to that
ers tubing materials meeting the requirements of Specification value except for sizes ⁄4 in. and smaller.
F 876. 6.2.3 Fittings (Basic Dimensions)—Fittings shall be com-
4.2.2 Long-Term Hydrostatic Pressure Strength—This patible with tubing made to the requirements of Table 1 and
specification covers PEX tubing which is further defined on the Table 2. Fittings shall be made from materials that are
basis of long-term hydrostatic strength tests (Appendix X1). generally regarded as corrosion resistant.
TABLE 1 Outside Diameters and Tolerances for PEX Tubing
A
Nominal Tubing Size Average Outside Diameter Tolerances for Average Diameter Out of Roundness
in. mm in. mm in. mm in. mm
⁄8 3 0.250 6.35 60.003 60.08 0.008 0.20
⁄4 7 0.375 9.52 60.003 60.08 0.008 0.20
⁄8 10 0.500 12.70 60.003 60.08 0.012 0.32
⁄2 13 0.625 15.88 60.004 60.10 0.016 0.40
⁄8 16 0.750 19.05 60.004 60.10 0.016 0.40
⁄4 19 0.875 22.22 60.004 60.10 0.016 0.40
1 25 1.125 28.58 60.005 60.12 0.020 0.48
1 ⁄4 32 1.375 34.92 60.005 60.12 0.020 0.48
1 ⁄2 38 1.625 41.28 60.006 60.16 0.024 0.60
2 51 2.125 53.98 60.006 60.16 0.030 0.76
A
The out-of-roundness specification applies only to tubing prior to coiling.
F 877
TABLE 2 Wall Thickness and Tolerances for PEX SDR 9 Plastic TABLE 4 Minimum Hydrostatic Sustained Pressure
A,B
Tubing Requirements for PEX SDR 9 Tubing and Fitting Assemblies
Minimum Wall Average Wall Nominal Tubing Size Pressure Required for Test,
Nominal Tubing Tolerance
A
Thickness Thickness, min psi (MPa)
in. mm in. mm in. mm in. mm in. mm 180°F (82.2°C)
A A
1 1
⁄8 3 0.047 1.19 +0.007 +0.18 0.049 1.24 ⁄8 3 355 (2.45)
A A
1 1
⁄4 7 0.062 1.57 +0.010 +0.25 0.064 1.63 ⁄4 7 305 (2.10)
A A
3 3
⁄8 10 0.070 1.78 +0.010 +0.25 0.072 1.83 ⁄8 10 250 (1.72)
A A
1 1
⁄2 13 0.070 1.78 +0.010 +0.25 0.072 1.83 ⁄2 13 195 (1.34)
5 5
⁄8 16 0.083 2.12 +0.010 +0.25 0.085 2.16 ⁄8 and 16 and 190 (1.31)
⁄4 19 0.097 2.47 +0.010 +0.25 0.099 2.51 larger larger
1 25 0.125 3.18 +0.013 +0.33 0.127 3.23
A
The fiber stress used to derive this test pressure is: 770 psi (5.31 MPa) at
1 ⁄4 32 0.153 3.88 +0.015 +0.38 0.155 3.94
180°F (82.2°C).
1 ⁄2 38 0.181 4.59 +0.019 +0.48 0.183 4.65
B
Test duration is 1000 h.
2 51 0.236 6.00 +0.024 +0.61 0.238 6.05
A 1
For tubing sizes of ⁄2 in. and below wall thickness minimums are not a function
of SDR.
sustained pressure strength requirements shown in Table 4
when tested in accordance with 7.4. The bend length and bend
6.3 Hydrostatic Burst:
angle is kept throughout the testing period by rigid secures
6.3.1 Tubing and fittings (tested as assemblies) shall meet
immediately outside the bend.
the minimum hydrostatic burst requirements shown in Table 3
6.7 Excessive Temperature—Pressure Capability:
when tested in accordance with 7.6.
6.7.1 General—In the event of a water heating system
6.3.2 Fittings assembled using the manufacturer’s instruc-
malfunction, PEX tubing shall have adequate strength to
tions shall meet the minimum hydrostatic burst requirement
accommodate short-term conditions, 48 h of 210°F (99°C), 150
shown in Table 3 when tested in accordance with 7.6.
psi (1034 kPa) until repairs can be made.
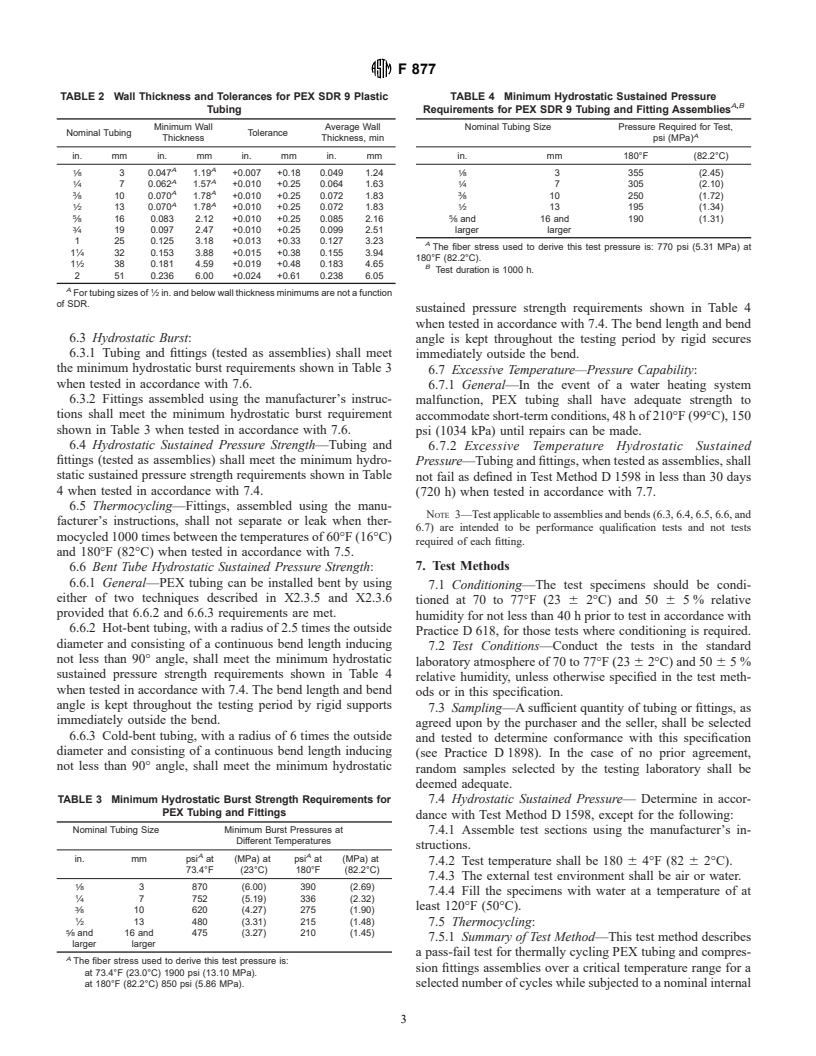
6.4 Hydrostatic Sustained Pressure Strength—Tubing and
6.7.2 Excessive Temperature Hydrostatic Sustained
fittings (tested as assemblies) shall meet the minimum hydro-
Pressure—Tubing and fittings, when tested as assemblies, shall
static sustained pressure strength requirements shown in Table
not fail as defined in Test Method D 1598 in less than 30 days
4 when tested in accordance with 7.4.
(720 h) when tested in accordance with 7.7.
6.5 Thermocycling—Fittings, assembled using the manu-
NOTE 3—Test applicable to assemblies and bends (6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6, and
facturer’s instructions, shall not separate or leak when ther-
6.7) are intended to be performance qualification tests and not tests
mocycled 1000 times between the temperatures of 60°F (16°C)
required of each fitting.
and 180°F (82°C) when tested in accordance with 7.5.
7. Test Methods
6.6 Bent Tube Hydrostatic Sustained Pressure Strength:
6.6.1 General—PEX tubing can be installed bent by using
7.1 Conditioning—The test specimens should be condi-
either of two techniques described in X2.3.5 and X2.3.6
tioned at 70 to 77°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 6 5 % relative
provided that 6.6.2 and 6.6.3 requirements are met.
humidity for not less than 40 h prior to test in accordance with
6.6.2 Hot-bent tubing, with a radius of 2.5 times the outside
Practice D 618, for those tests where conditioning is required.
diameter and consisting of a continuous bend length inducing
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct the tests in the standard
not less than 90° angle, shall meet the minimum hydrostatic
laboratory atmosphere of 70 to 77°F (23 6 2°C) and 50 65%
sustained pressure strength requirements shown in Table 4
relative humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test meth-
when tested in accordance with 7.4. The bend length and bend
ods or in this specification.
angle is kept throughout the testing period by rigid supports
7.3 Sampling—A sufficient quantity of tubing or fittings, as
immediately outside the bend.
agreed upon by the purchaser and the seller, shall be selected
6.6.3 Cold-bent tubing, with a radius of 6 times the outside
and tested to determine conformance with this specification
diameter and consisting of a continuous bend length inducing
(see Practice D 1898). In the case of no prior agreement,
not less than 90° angle, shall meet the minimum hydrostatic
random samples selected by the testing laboratory shall be
deemed adequate.
TABLE 3 Minimum Hydrostatic Burst Strength Requirements for 7.4 Hydrostatic Sustained Pressure— Determine in accor-
PEX Tubing and Fittings
dance with Test Method D 1598, except for the following:
Nominal Tubing Size Minimum Burst Pressures at
7.4.1 Assemble test sections using the manufacturer’s in-
Different Temperatures
structions.
A A
in. mm psi at (MPa) at psi at (MPa) at
7.4.2 Test temperature shall be 180 6 4°F (82 6 2°C).
73.4°F (23°C) 180°F (82.2°C)
7.4.3 The external test environment shall be air or water.
⁄8 3 870 (6.00) 390 (2.69)
7.4.4 Fill the specimens with water at a temperature of at
⁄4 7 752 (5.19) 336 (2.32)
least 120°F (50°C).
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.