ASTM D1895-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Apparent Density, Bulk Factor, and Pourability of Plastic Materials
Standard Test Methods for Apparent Density, Bulk Factor, and Pourability of Plastic Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These test methods provide useful indexes of performance of plastic materials such as powders and granules with respect to their handling in packaging and fabrication.
4.2 Apparent density is a measure of the fluffiness of a material.
4.3 Bulk factor is a measure of volume change that may be expected in fabrication.
4.4 Pourability characterizes the handling properties of a finely divided plastic material. It is a measure of the readiness with which such materials will flow through hoppers and feed tubes and deliver uniform weights of material.
SCOPE
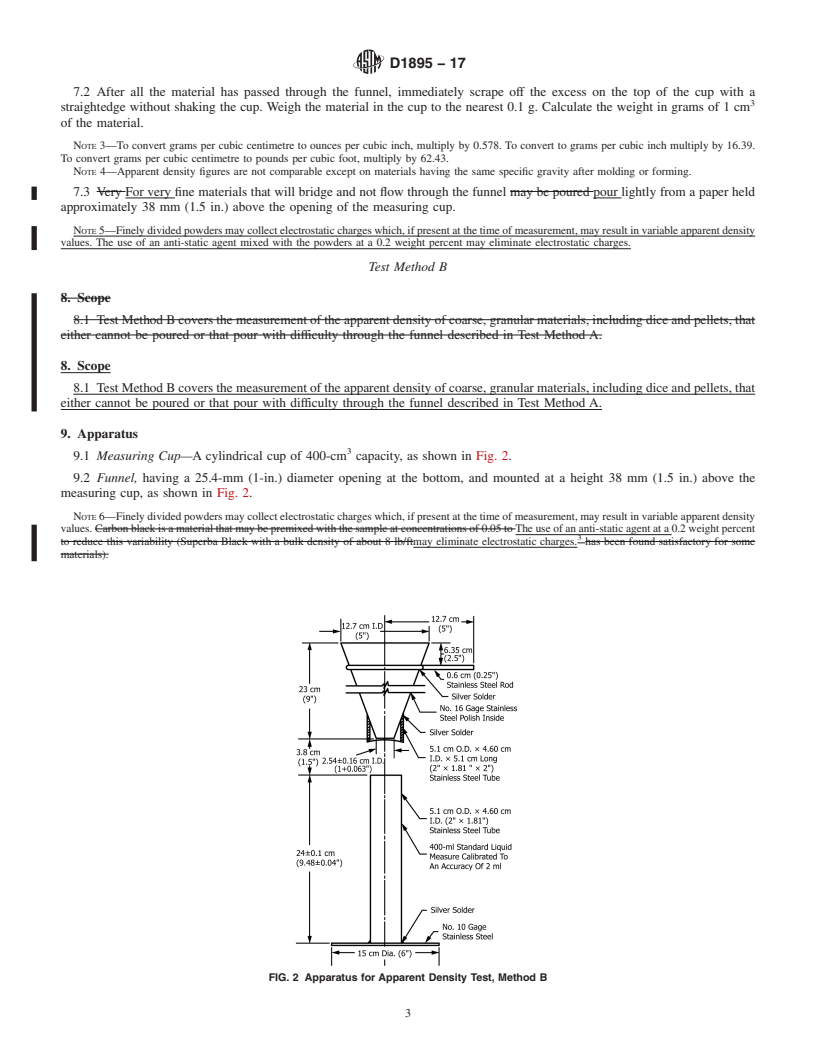
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of apparent density, bulk factor, and where applicable, the pourability of plastic materials such as molding powders. Different procedures are given for application to the various forms of these materials that are commonly encountered, from fine powders and granules to large flakes and cut fibers.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
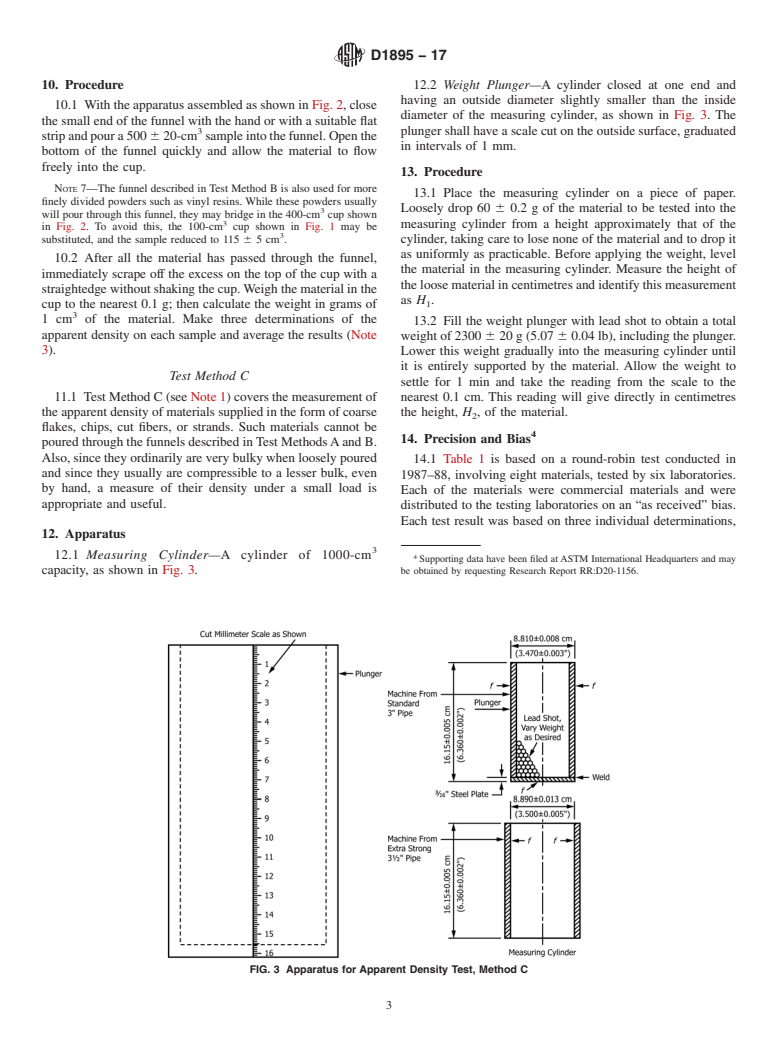
Note 1: Test Method A is equivalent to ISO Method R 60 as described in the appendix. Test Method C is identical with ISO Method R 61.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D1895 − 17
Standard Test Methods for
Apparent Density, Bulk Factor, and Pourability of Plastic
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1895; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope* 2.2 ISO Standards:
R60Determination of Apparent Density of Molding Mate-
1.1 These test methods cover the measurement of apparent
rials that Can be Poured from a Specified Funnel
density, bulk factor, and where applicable, the pourability of
R61Determination of Apparent Density of Molding Mate-
plastic materials such as molding powders. Different proce-
rial that Cannot be Poured from a Specified Funnel
dures are given for application to the various forms of these
materials that are commonly encountered, from fine powders
3. Terminology
and granules to large flakes and cut fibers.
3.1 Definitions:
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
3.1.1 apparent density—the weight per unit volume of a
material, including voids inherent in the material as tested.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1.1 The term bulk density is commonly used for mate-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
rials such as molding powder.
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter-
3.1.2 bulk factor—the ratio of the volume of any given
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
quantityofthelooseplasticmaterialtothevolumeofthesame
quantity of the material after molding or forming. The bulk
NOTE1—TestMethodAisequivalenttoISOMethodR60asdescribed
in the appendix. Test Method C is identical with ISO Method R61.
factor is also equal to the ratio of the density after molding or
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- forming to the apparent density of the material as received.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.3 pourability—a measure of the time required for a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
standard quantity of material to flow through a funnel of
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
specified dimensions.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 These test methods provide useful indexes of perfor-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: mance of plastic materials such as powders and granules with
D792Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela- respect to their handling in packaging and fabrication.
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
4.2 Apparent density is a measure of the fluffiness of a
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
material.
D1505Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-
Gradient Technique
4.3 Bulk factor is a measure of volume change that may be
expected in fabrication.
1 4.4 Pourability characterizes the handling properties of a
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on
Plastics and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical
finely divided plastic material. It is a measure of the readiness
Methods.
with which such materials will flow through hoppers and feed
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2017. Published September 2017. Originally
ɛ1 tubes and deliver uniform weights of material.
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D1895–96(2010) .
DOI: 10.1520/D1895-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
the ASTM website. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1895 − 17
NOTE 3—To convert grams per cubic centimetre to ounces per cubic
APPARENT DENSITY
inch, multiply by 0.578. To convert to grams per cubic inch multiply by
Test Method A
16.39. To convert gram
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D1895 − 96 (Reapproved 2010) D1895 − 17
Standard Test Methods for
Apparent Density, Bulk Factor, and Pourability of Plastic
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1895; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Added research report information to Section 14 editorially in September 2010.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 1TheseThese test methods cover the measurement of apparent density, bulk factor, and where applicable, the pourability of
plastic materials such as molding powders. Different procedures are given for application to the various forms of these materials
that are commonly encountered, from fine powders and granules to large flakes and cut fibers.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—Test Method A is equivalent to ISO Method R 60 as described in the appendix. Test Method C is identical with ISO Method R 61.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density-Gradient Technique
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
R60 Determination of Apparent Density of Molding Materials that Can be Poured from a Specified Funnel
R61 Determination of Apparent Density of Molding Material that Cannot be Poured from a Specified Funnel
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 apparent density—the weight per unit volume of a material, including voids inherent in the material as tested.
3.1.1.1 The term bulk density is commonly used for materials such as molding powder.
3.1.2 bulk factor—the ratio of the volume of any given quantity of the loose plastic material to the volume of the same quantity
of the material after molding or forming. The bulk factor is also equal to the ratio of the density after molding or forming to the
apparent density of the material as received.
3.1.3 pourability—a measure of the time required for a standard quantity of material to flow through a funnel of specified
dimensions.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2010Sept. 1, 2017. Published January 2010September 2017. Originally approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 20032010
ɛ1
as D1895 – 96(2003).(2010) . DOI: 10.1520/D1895-17.
This edition includes the addition of an extensive ISO equivalency statement and keywords section. DOI: 10.1520/D1895-96R10E01.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1895 − 17
4. Significance and Use
4.1 These test methods provide useful indexes of performance of plastic materials such as powders and granules with respect
to their handling in packaging and fabrication.
4.2 Apparent density is a measure of the fluffiness of a material.
4.3 Bulk factor is a measure of volume change that may be expe
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.