ASTM B625-99
(Specification)Standard Specification for UNS N08904, UNS N08925, UNS N08031, UNS N08932, UNS N08926, and UNS R20033 Plate, Sheet, and Strip
Standard Specification for UNS N08904, UNS N08925, UNS N08031, UNS N08932, UNS N08926, and UNS R20033 Plate, Sheet, and Strip
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers alloys UNS N08904, UNS N08925,* UNS N08031, UNS N08932, UNS N08926, and UNS R20033 plate, sheet, and strip in the annealed temper.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B 625 – 99
Standard Specification for
UNS N08904, UNS N08925, UNS N08031, UNS N08932,
UNS N08926, and UNS R20033 Plate, Sheet, and Strip
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 625; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers alloys UNS N08904, UNS 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
N08925,* UNS N08031, UNS N08932, UNS N08926, and 3.1.1 plate—material ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) and over in thick-
UNS R20033 plate, sheet, and strip in the annealed temper. ness and over 10 in. (254 mm) in width.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded 3.1.2 sheet—material under ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) in thickness
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for and 24 in. (609.6 mm) and over in width. Material under ⁄16in.
information only. (4.75 mm) in thickness and in all widths with No. 4 finish.
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to 3.1.3 strip—material under ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) in thickness
the test methods portion, Section 12, of this specification: This and under 24 in. (609.6 mm) in width.
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
4. Ordering Information
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health 4.1 Orders for material under this specification shall include
the following information:
practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limita-
tions prior to use. 4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
4.1.2 Alloy name or UNS number,
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.3 Form, plate, sheet or strip,
2.1 ASTM Standards: 4.1.4 Dimensions,
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials 4.1.5 Type edge required, for strip only (see 7.4.1),
E 10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materi- 4.1.6 Finish (Section 8)—For sheet with No. 4 finish,
als specify whether one or both sides are to be polished,
E 18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness and Rockwell 4.1.7 ASTM designation,
Superficial Hardness of Metallic Materials 4.1.8 Additions to the specification or special requirements,
E 29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to 4.1.9 Certification or test reports—State if certification or
Determine Conformance with Specifications test reports are required (Section 15), and
E 38 Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Chromium 4.1.10 Source inspection—State if inspection is required
and Nickel-Chromium-Iron Alloys (Section 13).
E 55 Practice for Sampling Wrought Nonferrous Metals and
5 5. Chemical Composition
Alloys for Determination of Chemical Composition
5.1 The material sampled, in accordance with 9.2, shall
E 140 Hardness Conversion Tables for Metals
E 353 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Stainless, conform to the composition limits specified in Table 1.
5.2 If a product analysis is subsequently made, the material
Heat-Resisting, Maraging, and Other Similar Chromium-
Nickel-Iron Alloys shall conform to the composition limits with the product
analysis variation specified in Table 2.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B-2 on 6. Mechanical Properties and Other Requirements
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
6.1 Tensile and Hardness Requirements— The material
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
shall conform to the mechanical property requirements speci-
Current edition approved May 10, 1999. Published June 1999. Originally
published as B 625 – 77. Last previous edition B 625 – 95.
fied in Table 3.
* New designation established in accordance with Practice E 527 and SAE
J1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Discontinued—See 1989 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.05.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B625–99
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition,%
Elements
UNS N08904 UNS N08925 UNS N08932 UNS N08031 UNS N08926 UNS R20033
Carbon, max 0.020 0.020 0.020 0.015 0.020 0.015
Manganese, max 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.0 2.00 2.0
Phosphorus, max 0.045 0.045 0.025 0.020 0.03 0.02
Sulfur, max 0.035 0.030 0.010 0.010 0.01 0.01
Silicon, max 1.00 0.50 0.40 0.3 0.5 0.50
Nickel 23.00–28.00 24.00–26.00 24.0–26.0 30.0–32.0 24.00–26.00 30.0–33.0
Chromium 19.00–23.00 19.00–21.00 24.0–26.0 26.0–28.0 19.00–21.00 31.0–35.0
Molybdenum 4.0–5.0 6.0–7.0 4.5–6.5 6.0–7.0 6.0–7.0 0.50–2.0
Copper 1.0–2.0 0.8–1.5 1.0–2.0 1.0–1.4 0.5–1.5 0.30–1.20
Nitrogen . 0.10–0.20 0.15–0.25 0.15–0.25 0.15–0.25 0.35–0.60
Iron balance balance balance balance balance balance
TABLE 2 Product Analysis Tolerances
8.1.1.3 No. 2B Finish—Bright, cold-rolled finish; produced
Tolerances Over the Max Limit or Under the Min Limit, % by giving a final light cold-rolled pass with polished rolls, to a
sheet which has been annealed and descaled.
UNS N08904
Elements
UNS N08925 UNS N08031 UNS N08926 UNS R20033
8.1.1.4 No. 4 Finish—General purpose, polished finish.
UNS N08932
Following initial grinding with coarser abrasives, sheets are
Carbon 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
generally finished last with abrasives approximately 120 to 150
Manganese 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04
mesh. Sheets can be produced with one or two sides polished.
Phosphorus 0.005 0.005 0.005 0.005
Sulfur 0.005 0.003 0.003 0.003 When polished on one side only, the other side may be rough
Silicon 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.05
ground in order to obtain the necessary flatness.
Chromium 0.20 0.30 0.25 0.30
8.1.1.5 Bright Annealed—Bright finish produced by cold
Nickel 0.20 0.30 0.25 0.30
Molybdenum 0.10 0.15 0.15 0.05
rolling to thickness, then annealing in a protective atmosphere.
Copper 0.10 0.04 0.04 0.10
8.1.2 Strip—The type of finish procurable on cold-rolled
Nitrogen . 0.01 0.01 0.03
strip shall be as follows:
8.1.2.1 No. 1 Finish—Cold rolled to specified thickness,
annealed, and pickled (see 8.2). Appearance of this finish is a
7. Dimensions and Permissible Variations
dull gray.
8.1.2.2 Bright Annealed—Bright finish produced by cold
7.1 Sheet—The material referred to as sheet shall conform
rolling to thickness, then annealing in a protective atmosphere.
to the variations in dimensions specified in Tables 4-9, inclu-
8.1.3 Plate—The types of finish procurable on plates shall
sive.
be as follows:
7.2 Cold-Rolled Strip—The material referred to as cold-
8.1.3.1 Hot Rolled, Annealed—Scale not removed.
rolled strip shall conform to the permissible variations in
8.1.3.2 Hot Rolled, Annealed, Descaled— Scale removed
dimensions specified in Tables 10-13, inclusive.
by a blast cleaning or pickling operation.
7.3 Plate—The material referred to as plate shall conform to
8.1.3.3 Cold Rolled, Annealed—Scale not removed.
the permissible variations in dimensions specified in Tables
8.1.3.4 Cold Rolled, Annealed, Descaled— Scale removed
14-19, inclusive.
by a blast cleaning or pickling operation.
7.4 Edges for Cold-Rolled Strip:
8.2 Sheet, Strip, and Plate—Material may be ground to
7.4.1 The various types of edges procurable shall be as
remove surface imperfections, provided such grinding does not
follows:
reduce the thickness or width at any point beyond the permis-
7.4.1.1 No. 1 Edge—Rolled edge, contour as specified.
sible variations in dimensions.
7.4.1.2 No. 3 Edge—An edge produced by slitting.
7.4.1.3 No. 5 Edge—Approximately square edge produced
9. Sampling
by rolling or filling, or both, after slitting.
9.1 Lots for Chemical Analysis and Mechanical Testing:
9.1.1 A lot for chemical analysis shall consist of one heat.
8. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
9.1.2 Plate—A lot of plate for testing and inspection pur-
8.1 The material shall be free of injurious imperfections and
poses shall consist of the products resulting from the rolling of
shall correspond to the designated finish as described below.
one heat of material in the same condition (temper) and
8.1.1 Sheet—The various types of finish procurable on sheet
specified thickness.
products shall be as follows:
9.1.3 Sheet and Strip—A lot of sheet or strip for testing and
8.1.1.1 No. 1 Finish—Hot rolled, annealed, and descaled;
inspection purposes shall consist of material from one heat in
produced by hot rolling to specified thicknesses followed by
the same form (sheet or strip), condition (temper), finish, and
annealing and descaling (see 8.2).
specified thickness but in no case more than 25 000 lb (11 340
8.1.1.2 No. 2D Finish—Dull, cold-rolled finish; produced
kg).
by cold rolling to the specified thickness, annealing, and
descaling. The dull finish results from the descaling and
NOTE 1—Where material cannot be identified by heat, a lot shall consist
pickling operations. of not more than 500 lb (227 kg) of material in the same thickness and
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B625–99
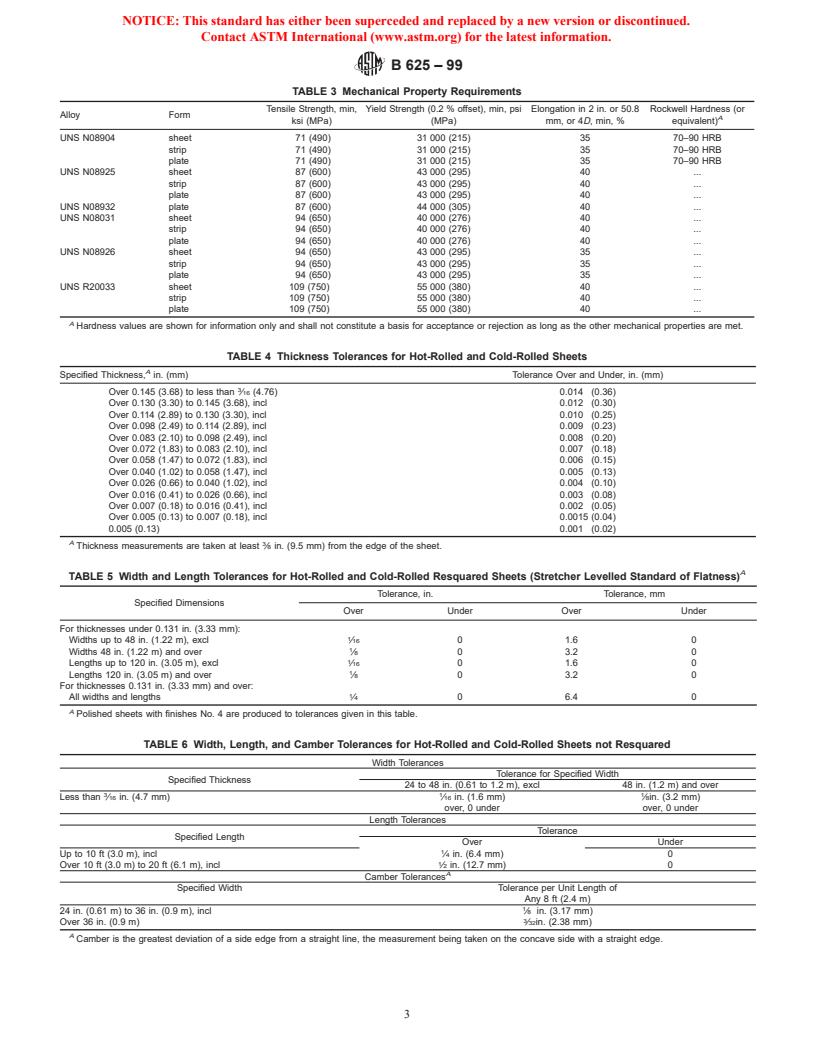
TABLE 3 Mechanical Property Requirements
Tensile Strength, min, Yield Strength (0.2 % offset), min, psi Elongation in 2 in. or 50.8 Rockwell Hardness (or
Alloy Form
A
ksi (MPa) (MPa) mm, or 4D, min, % equivalent)
UNS N08904 sheet 71 (490) 31 000 (215) 35 70–90 HRB
strip 71 (490) 31 000 (215) 35 70–90 HRB
plate 71 (490) 31 000 (215) 35 70–90 HRB
UNS N08925 sheet 87 (600) 43 000 (295) 40 .
strip 87 (600) 43 000 (295) 40 .
plate 87 (600) 43 000 (295) 40 .
UNS N08932 plate 87 (600) 44 000 (305) 40 .
UNS N08031 sheet 94 (650) 40 000 (276) 40 .
strip 94 (650) 40 000 (276) 40 .
plate 94 (650) 40 000 (276) 40 .
UNS N08926 sheet 94 (650) 43 000 (295) 35 .
strip 94 (650) 43 000 (295) 35 .
plate 94 (650) 43 000 (295) 35 .
UNS R20033 sheet 109 (750) 55 000 (380) 40 .
strip 109 (750) 55 000 (380) 40 .
plate 109 (750) 55 000 (380) 40 .
A
Hardness values are shown for information only and shall not constitute a basis for acceptance or rejection as long as the other mechanical properties are met.
TABLE 4 Thickness Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Sheets
A
Specified Thickness, in. (mm) Tolerance Over and Under, in. (mm)
Over 0.145 (3.68) to less than ⁄16 (4.76) 0.014 (0.36)
Over 0.130 (3.30) to 0.145 (3.68), incl 0.012 (0.30)
Over 0.114 (2.89) to 0.130 (3.30), incl 0.010 (0.25)
Over 0.098 (2.49) to 0.114 (2.89), incl 0.009 (0.23)
Over 0.083 (2.10) to 0.098 (2.49), incl 0.008 (0.20)
Over 0.072 (1.83) to 0.083 (2.10), incl 0.007 (0.18)
Over 0.058 (1.47) to 0.072 (1.83), incl 0.006 (0.15)
Over 0.040 (1.02) to 0.058 (1.47), incl 0.005 (0.13)
Over 0.026 (0.66) to 0.040 (1.02), incl 0.004 (0.10)
Over 0.016 (0.41) to 0.026 (0.66), incl 0.003 (0.08)
Over 0.007 (0.18) to 0.016 (0.41), incl 0.002 (0.05)
Over 0.005 (0.13) to 0.007 (0.18), incl 0.0015 (0.04)
0.005 (0.13) 0.001 (0.02)
A
Thickness measurements are taken at least ⁄8 in. (9.5 mm) from the edge of the sheet.
A
TABLE 5 Width and Length Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Resquared Sheets (Stretcher Levelled Standard of Flatness)
Tolerance, in. Tolerance, mm
Specified Dimensions
Over Under Over Under
For thicknesses under 0.131 in. (3.33 mm):
Widths up to 48 in. (1.22 m), excl ⁄16 0 1.6 0
Widths 48 in. (1.22 m) and over ⁄8 0 3.2 0
Lengths up to 120 in. (3.05 m), excl ⁄16 0 1.6 0
Lengths 120 in. (3.05 m) and over ⁄8 0 3.2 0
For thicknesses 0.131 in. (3.33 mm) and over:
All widths and lengths ⁄4 0 6.4 0
A
Polished sheets with finishes No. 4 are produced to tolerances given in this table.
TABLE 6 Width, Length, and Camber Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Sheets not Resquared
Width Tolerances
Tolerance for Specified Width
Specified Thickness
24 to 48 in. (0.61 to 1.2 m), excl 48 in. (1.2 m) and over
3 1 1
Less than ⁄16 in. (4.7 mm) ⁄16 in. (1.6 mm) ⁄8in. (3.2 mm)
over, 0 under over, 0 under
Length Tolerances
Tolerance
Specified Length
Over Under
Up to 10 ft (3.0 m), incl ⁄4 in. (6.4 mm) 0
Over 10 ft (3.0 m) to 20 ft (6.1 m), incl ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm) 0
A
Camber Tolerances
Specified Width Tolerance per Unit Length of
Any 8 ft (2.4 m)
24 in. (0.61 m) to 36 in. (0.9 m), incl ⁄8 in. (3.17 mm)
Over 36 in. (0.9 m) ⁄32in. (2.38 mm)
A
Camber is the greatest deviation of a side edge from a straight line, the measurement being taken on the concave side with a straight edge.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
B625–99
TABLE 7 Flatness Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Sheets
Sheets Not Specified to Stretcher Levelled Standard of Flatness (Exclusive of Dead Soft and Deep Drawing Sheets)
Flatness Tolerance (max deviation from a horizontal flat
Specified Thickness Width
surface)
0.062 in. (1.57 mm) and over To 60 in. (1.5 m), incl ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm)
Over 60 in. (1.5 m) to 72 in. (1.8 m), incl ⁄4 in. (19.0 mm)
Over 72 in. (1.8 m) 1 in. (25.4 mm)
Under 0.062 in. (1.57 mm) To 36 in. (0.9 m), incl ⁄2 in. (12.7 mm)
Over 36 in. (0.9 m) to 60 in. (1.5 m), incl ⁄4 in. (19.0 mm)
Over 60 in. (1.5 m) 1 in. (25.4 mm)
Sheets Specified to Stretcher-Levelled Standard of Flatness
Flatness Tolerance (max deviation
Specified Thickness Width Length
from a horizontal flat surface)
3 1
Under ⁄16 in. (4.75 mm) to 48 in. (1.22 m), incl to 96 in. (2.44 m), incl ⁄8 in. (3.17 mm)
3 1
Under ⁄16 in. (4.75 mm) to 48 in. (1.22 m), incl Over 96 in. (2.44 m) ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm)
3 1
Under ⁄16 in. (4.75 mm) Over 48 in. (1.22 m) to 96 in. (2.44 m), incl ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm)
3 1
Under ⁄16 in. (4.75 mm) Over 48 in. (1.22 m) Over 96 in. (2.44 m) ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm)
TABLE 8 Diameter Tolerances for Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Sheets Sheared Circles
Tolerance Over Specified Diameter (No Tolerance Under)
Specified Thickness Diameters Under 30 in. (0.762 m) Diameters 30 to 48 in (0.762 m to 1.219 Diameters Over 48 in. (1.219 m)
m)
1 3 1
0.0972 in. (2.47 mm) and thicker ⁄8 in. (3.17 mm) ⁄16 in. (4.76 mm) ⁄4 in. (6.35 mm)
3 5 7
0.0971 in. (2.47 mm) to 0.0568 in. (1.443 ⁄32 in. (2.38 mm) ⁄32 in. (3.97 mm) ⁄32 in. (5.56 mm)
mm), incl
1 1 3
0.0567 in. (1.440 mm) and thinner ⁄16in. (1.59 mm) ⁄8 in. (3.17 mm) ⁄16
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.